Students get through the MP Board Class 11th Biology Important Questions Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
MP Board Class 11th Biology Important Questions Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination
Excretory Products and their Elimination Class 11 Important Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Define Glomerular filtrate rate (GFR). (NCERT)
Answer:
Quantity of glomerular filtrate or Nephric filtrate filtered per minute by the kidney of human is called as Glomerular filtrate rate (GFR).
Rate of filtration in a normal adult person is about 125ml per minute.
[Average volume of GF per day by the kidney is 190 litres.]
Question 2.
Write the name of excretory organs of following phylum animals :
(a) Protozoa,
(b) Coelenterates,
(c) Molluscs,
(d) Arthropods
(e) Annelida.
Answer:
(a) Protozoans : Plasma membrane, contractile vacuoles.
(b) Coelenterates: Diffusion by plasma membrane.
(c) Molluscs: Renal organs or kidney.
(d) Arthropodes : Malphighian tubules.
(e) Annelida : Nephridia for excretion.
![]()
Question 3.
Write the name of hormone which causes Addison’s disease.
Answer:
Mineralocorticosteriod hormone is responsible to increase the amount of water and sodium in urine. This disease is called Addison’s disease.
Question 4.
How does human skin and lungs function as an excretory organ?
Answer:
Human skin possesses sebaceous glands and sweat glands. These glands excrete some excretory substances with their secretion like sebum and sweat. Hence, skin is also called as excretory organ.
Lungs help for excretion by exhalation of CO2 from the body.
Question 5.
Why the excretion of uric acid in place of urea is more advantageous for birds and reptiles?
Answer:
Uric acid and their salts are relatively less harmful and water-insoluble, hence they are excreted in the form of solids and thus, water is not lost whereas, water is also lost in the excretion of urea. Thus, the excretion of uric acid in birds and reptiles is a mode of adaptation to prevent water loss.
Question 6.
In which part of body ammonia is converted into urea?
Answer:
Liver.
Question 7.
Explain the significance of ureotelism in ureotelic animals.
Or,
What is ureotelism? How it is advantageous over other excretions?
Answer:
Ureotelism is the urinary elimination of nitrogenous waste products mainly in the form of urea. Urea is relatively less harmful waste product in the nature. However urea is very soluble in water. Therefore, the ureotelic animals must be able to afford sufficient amount of water for excretion (in aquatic animals) concentrate urine (in Kangaroo and Rat) or retain considerable amount of urea in body fluids and blood (in Shark). Thus, this phenomenon is a type of adaptation in these animals.
Question 8.
What will be the ‘affect, if deamination process in the liver of human is stopped?
Answer:
If deamination process in the liver is stopped then conversion of ammonia into urea for its removal will stop. Excess amino acid reaches to the liver will fail to convert into carbohydrates by removal of amino group, as a result of which formation of pyruvic acid and ammonia will stop. Due to collection of toxic substances, other life activities will be affected.
Question 9.
Write the name of: (NCERT)
(a) One vertebrate in which excretion occurs through flame cells.
(b) Part of the kidney which lies embedded in between renal pyramids of medulla.
(c) Network of capillaries found surrounding Henle’s loop.
Answer:
(a) Planaria,
(b) Renal column of Bertini,
(c) Vasa recta.
![]()
Question 10.
What is Osmoregulation? (NCERT)
Answer:
The process by which osmotic pressure of the body fluids are maintained by addition or elimination of various substance like water, salt etc. is called as Osmoregulation.
Excretory Products and their Elimination Class 11 Important Questions Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Explain self regulation mechanism of Glomerular filtrate rate (GFR). (NCERT)
Answer:
Regulation of Glomerular filtrate rate (GFR) is done by ultrafiltration through glomerular capillaries, which is located at the joining of the afferent and efferent arterioles. Fall in glomerular filtrate rate induce glomerular capillaries to secrete renin, which activate renal blood circulation, thus again glomerular filtrate rate (GFR) become normal.
Question 2.
Describe Countercurrent mechanism in brief.
Answer:
Mammal excretes hypertonic urine. Henle’s loop and Vasa recta plays an important role, for this Vasa recta are in the form of loops, surrounding Henle’s loop, hence blood flows in opposite direction in the two limbs of each Vasa recta, the blood flowing in the descending limb comes closer to the outgoing blood in the ascending limb, this is called Counter current system.
Na+ and Cl– are reabsorbed from the filtrate in ascending limb and subsequently released into the surrounding medullary tissue and retained by the vasa recta. This limb is impermeable to water. Thus, urine become progressively more hypotonic but the descending loop of Henle wall is permeable to water thus more water is reabsorbed by its wall and urine become hypertonic.
Question 3.
Generally terrestrial organisms excrete urea or uric acid not ammonia. Why? (NCERT)
Answer:
Sufficient water is not available for terrestrial animals for speedy elimination of ammonia. So, it is converted into urea in the liver or into uric acid.
Urea is less toxic than ammonia and requires less water for elimination from the body. Urea is excreted as urine, e.g., mammals, amphibians like frog, toad etc.
whereas in reptiles and birds ammonia is converted into uric acid, which is least toxic nitrogenous waste product and requires very little amount of water for elimination. In the cloaca of reptiles and birds, uric acid accumulates and further concentrated there and passes out the body as whitish semisolid crystal form. Actually, this is adaptation in terrestrial organisms due to their dry habitat.
Question 4.
Explain urination. (NCERT)
Answer:
Urination or Micturition: The process of excretion of urine out of the body from the urinary bladder when it gets filled is called as urination or micturition. A normal healthy man excrete 1 to 1 -5 litres of urine per day.
It is controlled by the nervous mechanism. When sufficient pressure is built up in the bladder, a spontaneous nervous activity is generated due to which smooth muscles of the bladder wall contract and the urethral sphincter are relaxed. As a result, urine comes out from the bladder through urethra.
Note: In adults, the sphincter opens only when it is convenient to urinate otherwise it remains closed even when the pressure inside the bladder is high. The act of urination may be both voluntary and involuntary, but voluntary control develops late.
![]()
Question 5.
Give importance of Liver, Lungs and Skin in excretion. (NCERT)
Answer:
1. Liver: Liver plays chief role in excretion. It converts the excessive amount of amino acids present in blood into ammonia and pyruvic acid in their oxidative deamination.
Pyruvic acid oxidizes to release energy while amino acids are converted into less harmful substance, the urea which is filtered from the blood by kidney. This urea is then released with urine.
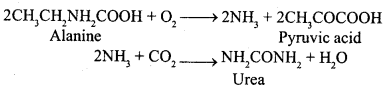
Urea
Liver also separates dead R.B.Cs. from the circulatory system and also converts its haemoglobin into useful bile salts.
Liver also converts the cholesterol, skatol and indole into less harmful substances and then mixes them in circulatory system. Kidney filters these substances from the blood.
2. Skin or integument: In aquatic animals where excretory organs are not developed, excretion takes place through general body surface (integument) by the process of diffusion. Mainly ammonia is excreted out into the surrounding water by this process. Higher animals like mammals including man possess two types of glands in their skin, sebaceous glands and sweat glands.
3. Lungs: Lungs help to eliminate the excretory waste products like carbon dioxide and some water in the form of vapour.
Question 6.
Give importance of Juxtra medullary tubules in function of kidney. (NCERT)
Answer:
30% Nephrons of the kidney has longer size of Henle’s loop. These nephrons are called as Juxtra medullary tubule. These tubules plays an important role in concentration mechanism of urine. When there is deficiency of water in the body vasopressin hormone is secreted, which induces reabsorption of water by the wall of the descending loop of Henle of extramedullary tubule. As a result of which more and more water is reabsorbed and hypertonic urine is produced. This mechanism of concentration of urine is called as counter current mechanism.
Question 7.
How the permeability of distal convoluted tubule and collecting tubule is controlled due to which the amount of water in the body is maintained?
Answer:
When the amount of water in our body is increased then nephrons absorb it from blood and dilute it. But when the amount of water in our body is decreased then nephrons or renal tubules absorb least amount of water and thus, the amount of urine is also decreased and urine becomes concentrated. Changes in the nature of urine resulting due to changes in the permeability of distal convoluted tubules and collecting tubules and their permeability is controlled by hormones.
The first hormone is aldosterone, that increases the process of reabsorption of Na+ from the filtrate of renal tubules and thus the amount of Na+ is also maintained. Second hormone is vasopressin which controls the dilution and concentration of urine. Hormone aldosterone is formed from the cortex of adrenal gland and the vasopressin hormone is secreted by posterior lobe of pituitary gland.
Question 8.
Draw a well labelled diagram of nephron of human.
Answer:
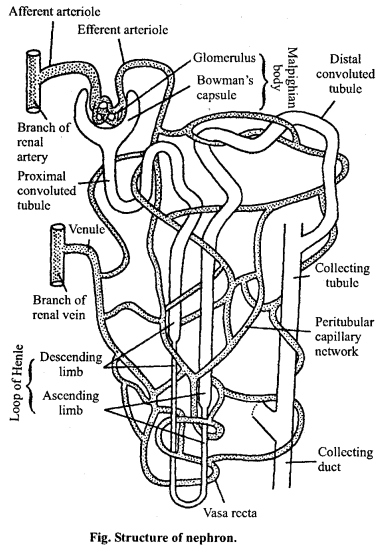
Question 9.
Describe any four functions of kidney.
Answer:
The chief function of kidney is to excrete the nitrogenous excretory substances out of the body. In addition to excretion kidney performs the following functions :
- Water balance: Kidneys play an important part in maintaining the concentration and osmotic pressure of blood by balancing the amount of water in the body. They remove excess amount of water out of the body.
- Salt balance: They also maintain the concentration of salts in blood.
- Acid-base balance: They maintain acid-base balance i.e., pH of the body fluid.
- Elimination of harmful substances: Kidneys eliminate harmful substances and extra water-soluble vitamins, extra drugs, toxic chemicals and pigments out of the body. They are excreted through urine.
Question 10.
Explain function of aldosterone.
Answer:
Aldosterone hormone is secreted by the adrenal gland. It regulates quantity of Na+ in the body. Reabsorption is regulated by a substance renin secreted by the kidney, which converts angiotensin benzene into angiotensin. Angiotensin induces adrenal cortex to secrete aldosterone.
![]()
Question 11.
What are nephrostomes? Explain its mechanism of working.
Answer:
These are funnel shaped structures. At the broad part hairs are found. Broader part open into coelome and narrow part open into renal vein. By the movement of hairs coelomic fluid enters into the renal vein. Nephrostome is found in the embryonic stage of frog, after this stage it degenerates.
Question 12.
What do you mean by Homeostasis and Diuresis?
Answer:
Homeostasis: Keeping environment of the body permanent and regulated is called as Homeostasis. Nephrons and kidney tubules help for permanent regulation. They reabsorbs water, minerals and other nutritive substances whereas removes out excretory substances.
Diuresis: Increase in quantity of secretion of urine is called as diuresis. The substance which increases quantity of urine are called as diuretic substances. Urea is a diuretic substance which increases quantity of urine. Glucose, coffee, tea etc. are also examples of diuretic substances.
Excretory Products and their Elimination Class 11 Important Questions Long Answer Type
Question 1.
Explain the structure of kidney in brief.
Or,
Describe the structure of human kidney.
Answer:
External structure of kidney : Kidneys are bean shaped structure which lie behind the peritoneum in the lumber region, one on either side of vertebral column. It has a length of about 10 cm breadth at about 5 cm and a thickness of about 4 cm. A kidney is concave-convex in outline. The concavity lies on the inner-medium side. It possesses a longitudinal opening known as hilum.
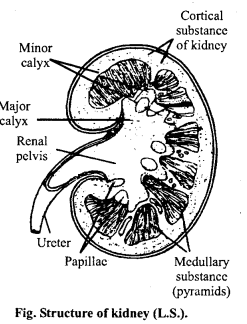
Internal structure: L.S. of kidney showing two parts : Outer cortex and Inner medulla. The cortex is dark red while the medulla is pale in colour. Renal medulla possesses 8-18 striated conical masses called medullary pyramids. The bases of the pyramids are towards the outer side while the apices end in papillae 1-3 such papillae enter a minor calyx. The minor calyx open into major calyx which in turn produce the renal pelvis.
Urine is produced by minute thread like tubular structures named nephrons or uriniferous tubules. They constitute the structural and functional units of the kidneys. The urine formed by the nephron is poured into collecting ducts. The collecting ducts open into larger ducts of bellini. The later open at the apices or papillae of medullary pyramids.
Question 2.
Explain the structure of nephron with suitable diagrams.
Or,
Describe the structure of nephron of human with diagramshort ?
Or,
Draw well labelled diagram of human nephron.
Answer:
Nephron or renal tubules are the chief functional units of the kidney, which are made up of following two parts :
1. Bowman’s capsule: The initial part of each tubule is formed of glomerulus and a two walled cup shaped structure called Bowman’s capsule. It possesses a globular tufts of capillaries called glomerulus. Glomerulus is formed by an afferent and an efferent arteriole. Glomerulus is situated in cortex of the kidneys.
2. Secretory part: The backward portion of Bowman’s capsule is called secretory portion. It is made up of following three parts :
- The coiled structure associated with Bowman’s capsule is called proximal convoluted tubule,
- The mid ‘U’ shaped portion of nephron is called Henle’s loop. It is found in renal medulla,
- The ascending limb of Henle’s loop passes into distal convoluted tubule. These tubules opens into larger ducts called collecting tubule or ducts.
For diagram:

Question 3.
What do you understand by Ammonotelism, Ureotelism and Uricotelism? Give example of each.
Answer:
Ammonotelic animals: Ammonotelic animals excreting the nitrogenous waste substances in the form of ammonia and the process of excretion is called Ammonotelism. For example Protozoans (e.g., Amoeba, Paramoecium), Sponges (Sycon), Coelenterates (e.g. Hydra), Annelids (e.g., Earthworm), Arthropods (e.g., Prawn), Molluscs (e.g., Sepia,Octopus) etc.
Ureotelic animals: Ureotelic animals excreting the nitrogenous waste products mainly in the form of urea. This process of excreting is called Ureotelism. For example Ascaris, Earthworm, Cartilagenous Fishes (Sharks), Amphibians (Frog, Toad), Aquatic reptiles (Turtles, Alligators.)
Uricotelic animals: Uricotelic animals are those which excrete thin nitrogenous waste product mainly as Uric acid. This process of excreting is called Uricotelism.
For example: Insects (Cockroach), Snake, Lizard, and birds etc.
![]()
Question 4.
Describe the process of urine formation.
Answer:
Urine is formed within kidney. Urine formation takes place in the following three stages:
- Ultrafiltration,
- Selective reabsorption,
- Secretion.
Ultrafiltration: In each glomerulus, the nitrogenous excretory products such as urea etc. come with the blood through afferent arteriole and pass out through the glomerulus to efferent arteriole. The diameter of afferent arterioles is larger than that of the efferent arterioles. Because of it some amount of blood is retained in the glomerulus, therefore, some blood collects into glomerulus as a result of which a pressure is created, called as glomerular filtration pressure (GFP). It is about +75 mm Hg. The osmotic pressure of plasma protein of part of plasma is filtered out.
It is known as glomerular filtrate. It is isotonic with blood. It has most of the water, urea, amino acids, glucose, vitamin C, proteins having molecular weight less than 70,000, inorganic ions and salts etc. R.B.C. W.B.C., high molecular weight compounds and some water which is retained by the osmotic pressure of plasma proteins do not filter out.
2. Selective reabsorption: In man nearly 170 litres of glomerular filtrate is filtered out but only 1 -5 litres of urine is formed in 24 hours. The filtrate is isotonic whereas urine is hypertonic, the filtrate is slightly alkaline and the urine is acidic. It shows that some substances are reabsorbed by the renal tubules from the glomerular filtrate. This is called as selective reabsorption.
The second step in the urine formation is the selective reabsorption in which major portion of water and some physiologically important solutes like glucose, amino acids and inorganic salts like sodium chloride and sodium bicarbonates are reabsorbed back into the blood in the peritubular capillaries and vasa rectae. This reabsorption process takes place in the proximal convoluted tubule.
The tubular reabsorption may be of active reabsorption or of passive reabsorption. Glucose and amino acids which are of considerable importance to the body are actively reabsorbed. The active absorption is very rapid and continues even when the concentrations of these substances fall much below that in the blood. Rest of the useful substances like sodium, potassium, phosphates, bicarbonates etc. are passively reabsorbed by the physical process of diffusion. Water is reabsorbed by osmosis. Sodium ions are reabsorbed both by the active and the passive transport mechanism.
Vasa recta maintain a higher osmotic pressure of the extracellular fluid. In the descending limb of the loop of Henle about 5% of the glomerular filtrate is reabsorbed.
Almost the total amount of glucose, most of the amino acids, about 70 percent of potassium ions and a large amount of calcium ions are reabsorbed actively in the proximal convoluted tubule. 25 percent of potassium ions and some amounts of chloride ions and some sodium ions are reabsorbed actively by the ascending limb of the loop of Henle. The ascending limb is impermeable to water hence no water is reabsorbed into the ascending limb. This makes the filtrate dilute than plasma.
The distal convoluted tubules actively reabsorbs sodium ions and in exchange excretes some potassium ions. Some chloride ions are also reabsorbed by the DCT.
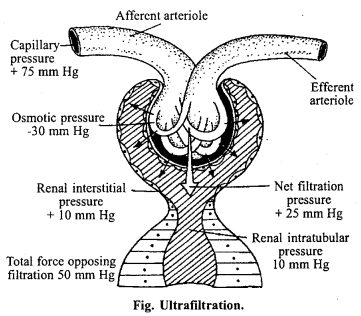
3. Secretion: The kidney tubules also excrete additional waste materials from the blood stream and put them into the filtrate. These excretory substances of blood are absorbed by the capillaries present in the wall of nephron. These absorbed excretory substances like urea, uric acid and ammonia etc. are diffused out from the capillaries of nephron and mixed with urine in nephron. This process of Bowman’s capsule is called as secretion.
![]()
Question 5.
Write short note on following :
(i) Green gland,
(ii) Nephridium.
Answer:
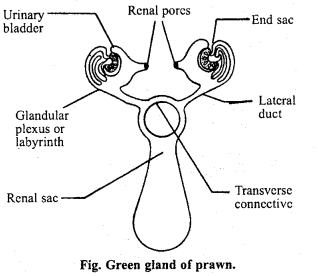
(i) Green glands: These are the principal excretory organs of Prawn. They are located in the second antennae. Each green gland consists of an end sac, a labyrinth and a bladder. Urine is first formed in the sac and passes through the fine tubules of labyrinth to the large sac-like bladder. A duct called ureter leads from the bladder to the base of antennae where it opens to the exterior. The end sac and the labyrinth probably excrete ammonia and uric acid respectively. The bladder also opens into thin-walled renal sac by a duct.
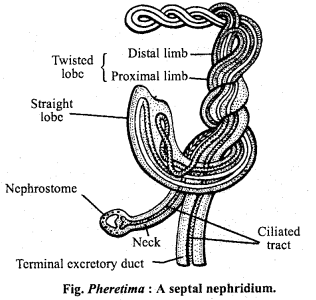
(ii) Nephridium: Annelids in general possess a excretory system consisting of long or short specialised tubules which are used for excretion and are called nephridia. Each nephridium consists of a ciliated funnel called nephrostome which opens into the body cavity or coelom. Nephrostome leads into a highly coiled tubule which finally opens outside the body through pores called nephridiopores present in the body wall. The nitrogenous wastes formed in the nephridia is propelled by ciliary movements and either thrown directly outside or into the alimentary canal.
Excretory Products and their Elimination Class 11 Important Questions Objective Type
1. Choose the correct answers:
Question 1.
The process of filtration takes place in :
(a) Renal capsules
(b) Henle’s loop
(c) Neck
(d) Papilla.
Answer:
(a) Renal capsules
Question 2.
The excretory organ of crustaceans is :
(a) Uriniferous tubules
(b) Green glands
(c) Cloacal glands
(d) Malpighian tubules.
Answer:
(b) Green glands
![]()
Question 3.
Contractile vacuole is responsible for :
(a) Osmoregulation and excretion
(b) Respiration
(c) Osmoregulation
(d) Excretion of excretory substances.
Answer:
(a) Osmoregulation and excretion
Question 4.
Vasopressin is associated with :
(a) Urine concentration
(b) Dilution of urine
(c) Digestion
(d) Heart beating.
Answer:
(a) Urine concentration
Question 5.
The excretory substance of human beings is :
(a) Amino acid
(b) Ammonia
(c) Urea
(d) Uric acid.
Answer:
(c) Urea
Question 6.
Concentration of urea is minimum in :
(a) Pulmonary vein
(b) Hepatic artery
(c) Portal vein
(d) Renal vein.
Answer:
(d) Renal vein.
Question 7.
Excretory products of human urine formed by protein metabolism are:
(a) Uracil, ammonia, urea
(b) Urea, uric acid, NaCl
(c) Urea, melanin, guanine
(d) Urea, uric acid, creatinine.
Answer:
(d) Urea, uric acid, creatinine.
Question 8.
Ammonia is converted into urea in :
(a) Kidneys
(b) Liver
(c) Intestine
(d) Spleen.
Answer:
(b) Liver
![]()
Question 9.
Proteolytic enzyme secreted by kidney is :
(a) Rennin
(b) Trypsin
(c) Erepsin
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) Rennin
Question 10.
The stage of urine formation in which blood is also excreted with urine is called:
(a) Creatinine
(b) Haematuria
(c) Anuria
(d) Ketonuria.
Answer:
(b) Haematuria
Question 11.
Aquatic snakes are generally :
(a) Aminotelic
(b) Aminophilic
(c) Ureotelic
(d) Uricotelic.
Answer:
(c) Ureotelic
Question 12.
The function of green gland is excretion. It is found in :
(a) Spider
(b) Insects
(c) Scorpion
(d) Crayfish.
Answer:
(d) Crayfish.
Question 13.
Ureotelism is found in :
(a) Mammals
(b) Aquatic insects
(c) Tadpole
(d) Birds.
Answer:
(a) Mammals
Question 14.
Excess urine formation and its removal is called :
(a) Serosis
(b) Diuresis
(c) Sclerosis
(d) Osteoporosis.
Answer:
(b) Diuresis
![]()
Question 15.
Fluid in Bowman’s, capsule is called :
(a) Water
(b) Urine
(c) Blood cells with Blood
(d) Blood plasma without Blood corpuscles.
Answer:
(d) Blood plasma without Blood corpuscles.
Question 16.
The structural and functional unit of kidney is :
(a) Neuron
(b) Nephron
(c) Respiratory cell
(d) Malpighian tubule.
Answer:
(b) Nephron
Question 17.
It is called the graveyard of R.B.Cs.:
(a) Kidney
(b) Gall bladder
(c) Spleen
(d) Liver.
Answer:
(c) Spleen
Question 18.
Haemodialysis is helpful for which diseased patient:
(a) Uremia
(b) Anaemia
(c) Diabetes
(d) Goitre.
Answer:
(a) Uremia
Question 19.
In the kidney of mammals Henle’s loop lies at the :
(a) Medulla
(b) Cortex
(c) Pelvis
(d) Ureter.
Answer:
(a) Medulla
![]()
Question 20.
Human kidney is :
(a) Pronephron
(b) Mesonephron
(c) Metanephron
(d) Opisthonephron.
Answer:
(c) Metanephron
2. Fill in the blanks:
(A)
1. The excretory orgen of prawn is …………………….. .
Answer:
Green glands,
2. Aquatic animals excrete nitrogenous excretory substances as …………………….. .
Answer:
Ammonia,
3. The substances that increases urine formation are called …………………….. .
Answer:
Diuretics,
4. The artificial removal of excretory substances from the body is called …………………….. .
Answer:
Haemodialysis,
5. …………………….. is responsible for the concentration of urea.
Answer:
Henle’s loop,
6. The yellow colour of the urine is due to the presence of …………………….. .
Answer:
Bilirubin,
7. The formation of the urea takes place in …………………….. .
Answer:
Liver,
8. The functional unit of kidneys are …………………….. .
Answer:
Nephron.
(B)
1. Ascending loop of Henle is …………………….. to water, whereas descending loop of Henle is …………………….. to it.
Answer:
Impermeable, permeable,
2. In the distal convoluated tubule of nephron of the kidney reabsorption of water occurs due to …………………….. hormone.
Answer:
Anti diuretic hormone (ADH),
3. In the glomerular filtrate in addition to …………………….. all other substances of blood plasma are found.
Answer:
Nitrogenous wastes,
4. A normal healthy adult human excrete …………………….. urea per day.
Answer:
25-30gm.
![]()
3. Match the following:
(A)
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Malpighian tubules | (a) Vasopressin |
| 2. Nephridia | (b) Bird |
| 3. Water absorption | (c) Glomerulus |
| 4. Ultrafiltration | (d) Cockroach |
| 5. Uric acid | (e) Earthworm. |
Answer:
1. (d) Cockroach
2. (e) Earthworm.
3. (a) Vasopressin
4. (c) Glomerulus
5. (b) Bird.
(B)
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Bilirubin | (a) Urecotelic |
| 2. Birds and snake | (b) Green gland |
| 3. Urine | (c) Kidney |
| 4. Prawn | (d) Bile juice |
| 5. Henle’s loop | (e) Urea. |
Answer:
1. (d) Bile juice
2. (a) Urecotelic
3. (e) Urea.
4. (b) Green gland
5. (c) Kidney.
(C)
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Ammonotelism | (a) Bird |
| 2. Bowman’s capsule | (b) Reabsorption of water |
| 3. Urination | (c) Bony fishes |
| 4. Excretion of uric acid | (d) Urinary bladder |
| 5. ADH | (e) Nephron. |
Answer:
1. (c) Bony fishes
2. (e) Nephron.
3. (d) Urinary bladder
4, (a) Bird,
5. (b) Reabsorption of water.
4. Answer in one word :
1. Name the pigment found in urine.
Answer:
Urochrome,
2. Name the substance which regulates the excretion of sodium and potassium in urine and place where it is formed.
Answer:
Aldosterone, Adrenal cortex,
3. Name the factor which regulates the volume of urine.
Answer:
Vasopressin hormone,
4. Name the excretory organ of Hydra.
Answer:
Plasma membrane,
5. Name the hormone which regulates the secretion of urine in nephron.
Answer:
Vasopressin,
6. Name the excretory substance of Man.
Answer:
Urea, CO2,
7. What is loop of Henle?
Answer:
U shape tube of nephron,
8. Name the artery which carries blood towards the kidney.
Answer:
Renal artery,
9. Where is urea formed?
Answer:
Liver.
![]()
5. Write true or false:
1. Micturition occurs by reflex action.
Answer:
True,
2. ADH helps for excretion of urine by making it hypotonic.
Answer:
False,
3. Henle’s loop plays important role in making urine concentrated.
Answer:
True,
4. In the Bowman’s capsule protein less liquid is filtered out from the blood plasma.
Answer:
False,
5. In the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) active reabsorption of glucose occurs.
Answer:
True.