Students get through the MP Board Class 11th Biology Important Questions Chapter 15 Plant Growth and Development which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
MP Board Class 11th Biology Important Chapter 15 Plant Growth and Development
Plant Growth and Development Class 11 Important Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
What is known as growth? Describe in brief different phases of growth.
Answer:
According to Miller, ‘Growth is the permanent change in the size, weight and volume in the cell and organs of the body’.
Phases of growth :
1. Ceil division phase: In this phase one cell divides to form many cells.
2. Cell enlargement phase: The newly formed cell increases in size and attains maturity. Large vacuoles develop within the cell.
3. Cell differentiation and morphogenesis: Here cells differentiate into tissue and formation of different organs begin.
Question 2.
What are plant hormones?
Answer:
Plant hormones are the organic chemical substances which regulate growth and other physiological functions in plants at a site away from its place of production and active in very minute quantity e.g., Auxin, Gibberellin.
![]()
Question 3.
What is Florigen?
Answer:
Florigen is a flowering hormone which is produced in presence of proper photoperiod by the phytochromes present in the plasma membrane of leaf cells. The hormone is then transported to the floral bud region where it induces flowering.
Question 4.
Write the name of hormone which accelerates the cell division.
Answer:
Cytokinin.
Question 5.
What is 2,4-D? Also elaborate it.
Answer:
It is an artificial growth hormone. 2,4-D stands for 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid.
Question 6.
Write the name of apparatus used for measuring plant growth.
Answer:
Auxanometer.
Question 7.
What are growth inhibitor hormones? Write two functions.
Answer:
Abscisic acid (ABA) and Ethylene are top two plant growth inhibitor hormones. For their function
Functions of abscisic acid :
1. It induces dormancy in buds and seeds as opposed to gibberellic acid which breaks dormancy.
2. It promotes senescence of leaves, appearance of abscission layer, leaf-fail and ageing which can be effectively reverted by application of cytokinins.
3. It inhibits lettuce seed germination but this can also be reversed by kinetin.
4. It inhibited gibberellin induced growth in various tests and is believed to be a powerful gibberellin antagonist.
Ethylene hormone was discovered by scientist Burg (1962) which is a gaseous hormone.
Main functions of ethylene :
- Triple response: Ethylene gas inhibits stem growth, helps in swelling of stem and destroys geotropism.
- Flowering: It decreases flowering but in pineapple it induces flowering.
- Sex modification: It increases number of female flower and decreases number of male flowers in plants.
- Ripening of fruits: It is used in ripening of fruits, therefore nowadays ethephone (schloroethyl phosphoric acid which produces ethylene gas) is used for ripening fruits at industrial level.
Question 8.
Elaborate I.A.A. and describe at least one function of it.
Answer:
I. A. A. is Indole Acetic Acid. It controls the growth of plants.
![]()
Question 9.
Write the name of hormones which initiate flowering.
Answer:
- Florigen,
- Vemalin.
Question 10.
Name the hormone that exists in gaseous state.
Answer:
Ethylene.
Question 11.
Why it is beneficial in some plants to cut the tip of newly formed branches?
Answer:
Cutting of branches, initiates growth of lateral buds which results into formation of more new branches and the plant becomes more dense.
Question 12.
Name two artificial plant hormones.
Answer:
- Naphthalene acetic acid (N. A. A.).
- 2,4, 5-Trichlorophenoxy acetic acid (2, 4, 5-T).
Plant Growth and Development Class 11 Important Questions Short Answer Type
Question 1.
What do you mean by growth-regulating substance? Name any three growth regulator substances.
Answer:
The chemical substances which regulates growth and development in organisms are called as growth regulating substances. Actually, these are the organic substances which are naturally produced in the plants to control the growth and other physiological functions at a site away from its place of production and are active in extremely minute quantities and called as hormones. Three plants hormones are :
- Auxin,
- Gibberellin,
- Cytokinin.
Question 2.
Give four functions of cytokinin hormone.
Answer:
Functions of cytokinin :
- Activates cell division.
- Helps in the expansion of green leaves.
- Accelerates protein synthesis.
- Inhibition of the breakdown of leaf pigments and nucleic acid. Chemically they are derivatives of adenine with furfuryl group at 6th position.
Question 3.
Is any leafless plant can react with photoperiodism? Yes or No? Why? (NCERT)
Answer:
No, because flowering in some plants not only depend on light or dark period but it depends on duration of light. At the apical bud, floral but develops but it can not experience photoperiodism. Leaves can experience light or dark period. A hormone florigen is responsible for flowering. It travels from leaf to floral bud only when leaf is exposed to required period of light, Gibberellin and Anthesin hormones together induce flowering.
![]()
Question 4.
Give four functions of auxin.
Answer:
Functions of auxin :
- Helps to increase in height of plants.
- It induces root development.
- It induces production of parthenocarpic fruits.
- It prevents defoliation of leaves and induces flowering.
- Weed eradication.
Question 5.
Give importance of abscisic acid.
Answer:
Functions of abscisic acid :
1. It induces dormancy in buds and seeds as opposed to gibberellic acid which breaks dormancy.
2. It promotes senescence of leaves, appearance of abscission layer, leaf-fail and ageing which can be effectively reverted by application of cytokinins.
3. It inhibits lettuce seed germination but this can also be reversed by kinetin.
4. It inhibited gibberellin induced growth in various tests and is believed to be a powerful gibberellin antagonist.
Question 6.
Give four functions of gibberellin hormone.
Answer:
Functions of gibberellin :
- Parthenocarpic fruits may be produced by their application in tomato, pear, apple etc.
- Induces stem elongation by promoting growth of intemodes.
- Flower development in lettuce, barley etc.
- Seed germination by breaking their dormancy.
- Buds development.
Question 7.
Give four main functions of ethylene hormone.
Answer:
Ethylene hormone was discovered by scientist Burg (1962) which is a gaseous hormone.
Main functions of ethylene :
- Triple response: Ethylene gas inhibits stem growth, helps in swelling of stem and destroys geotropism.
- Flowering: It decreases flowering but in pineapple it induces flowering.
- Sex modification: It increases number of female flower and decreases number of male flowers in plants.
- Ripening of fruits: It is used in ripening of fruits, therefore nowadays ethephone (schloroethyl phosphoric acid which produces ethylene gas) is used for ripening fruits at industrial level.
Question 8.
Write short note on apical dominance?
Answer:
Apical dominance: In many plants where apical bud grows, axillary bud do not grow i.e., apical bud dominates growth of axillary bud. Actually apical bud produces a hormone which is transported to different parts of phloem and it inhibits growth of axillary bud. The hormone is auxin. On the other hand cytokinin induces growth of axillary bud.
Question 9.
What is phytochrome? Give its importance in plants.
Answer:
Phytochrome: It is well established that short day plant does not produce flower if the dark period is interrupted by a brief flash of light. It has been observed that the wavelength of 660 in the orange red colour is the most effective wavelength for inhibiting the process of flowering. Far red light on the contrary, does not break up a long night into two short nights. Besides, far red radiation of a wavelength of 740 has been found to reverse the effect of red light by Borthwick et al (1952) and Downs (1956) and is termed as red-far red reversible photoreaction.
If a brief flash of red light in the mid-night is followed by a brief flash of far red radiation, its inhibitory effect is counteracted and flowering takes place. If far red radiation is followed further in sequence by red light, flowering will again be inhibited, i.e., the radiation is last used in the sequence, will determine the response of the plant. This discovery ultimately resulted in the discovery of the pigment is called as phytochrome by Butter et al (1959), since light energy cannot be effected unless it is absorbed by a pigment.
The main characteristics of the pigment are :
- Proteinaceous in nature.
- Located in plasma membrane.
- Found in all green plants.
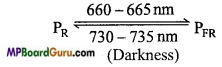
- Exists in two different forms :(a) Red light-absorbing forms designated as PR and
(b) Far-red light-absorbing forms designated as PFR. - Both of these forms are photochemically interconvertible.
- On absorbing red light (660-665 nm) PR form is converted into PFR form.
- On absorbing far-red light (730-735 nm) PFR form is converted into PR form.
- The PFR form of the pigment gradually changes into PR form in dark.
Spectrophotometric examination of the pigment by Briggs suggests that most of the phytochrome is found in inactive form. According to Hartman the biologically active form of phytochrome is some unknown derivative of PFR. He has suggested a different scheme of phytochrome action.
![]()
Question 10.
Why Abscisic acid is called as tension hormone? (NCERT)
Answer:
Abscisic acid is called as tension hormone due to following reasons :
- It prevents growth in plants.
- It induces leaf fall making the leaves weak.
- It prevents effect of gibberellin hormone.
- It prevents seed germination.
Question 11.
Short day plant and long-day plants show flowering together in one place. Explain it. (NCERT)
Answer:
1. Short-day plants: Need a short daylight period ranging between 8-10 hrs and a continuous dark period exceeding 12hours(14to \6his.),i.e., Xanthium, Soyabeans, Tobacco, Gossipium, Coffee etc. The salient features of such plants are given below :
- These plants require a relatively long period of darkness for flowering. It is generally longer than a certain critical length. If dark period is less, no flowering would result. If this period is interrupted even with a small exposure, the plants will not flower.
- No flowering occurs if a weak intensity of light is given to those plants.
- No flowering under alternating cycles of short dark and light period.
- They are also termed as long night plants because length and continuity of night determine the flowering.
2. Long day plants: These plants require a longer daylight (14 -16hrs) for flowering, e.g., Supuracea etc. They are characterised by the following :
- They require a photoperiod of more than a critical length. They require either a small period of darkness or no darkness for flowering.
- Flowering is full in continuous light.
- Darkness has inhibitory impact on these plants.
- They can be induced to flowering by short photoperiods but accompanied by shorter dark period.
Question 12.
Growth in flowering plants can not be described under one parameter. Why? (NCERT)
Answer:
Growth at cellular level in flowering plants is the result of growth in the proto¬plasm, which can not be measured. Thus growth in plants is measured by some other ways.
Some way of measurements are: Increase in fresh weight, dry weight, lengthwise area, volume and number of cells. At the root tip meristems produces more than 17,500 new cells by cell division per hour, whereas in watermelon at cell division stage growth is slow because cells increases in number without increasing in volume by multiplication, later growth become 3,50,000 times than previous time due to cell elongation. Increase in length of pollen tube per unit time can be measured easily. In dorsiventral leaves, growth in surface area of leaves is measured.
Thus, from above examples, it is clear that growth in plants can not be described under one parameter.
Plant Growth and Development Class 11 Important Questions Long Answer Type
Question 1.
What is growth? Describe various stages of cell growth.
Answer:
Growth: Growth is a vital process in which organism increase in its size, weight, volume and structure.
Stages of Growth :
1. Cell division: During this stage the cells divide and redivide by mitotic division for a definite period depending upon the organ of the plant in which growth is taking place.
2. Cell elongation phase: During this phase the newly formed cell increase in size due to their internal metabolic activities. In this phase cell wall materials and water increases 5 to 10 times of their original value
3. Cell differentiation phase: During its structural, qualitative and quantitative changes takes place and cells attain final definite shape, structure, function and properties.
Question 2.
What are photoperiodism and vernalization? Give their economic importance. (NCERT)
Answer:
1. Photoperiodism: The growth and development of large number of plants is dependent upon the duration of light availability called Photoperiodism. The reproductive growth and flowering is mainly controlled by light period and temperature. The flowering requires a certain day length, i.e., the relative length of day and night which is called as photoperiod.
Economic importance of photoperiodism :
- The knowledge regarding photoperiodism is important for hybridization.
- Characterization and structure of florigen is useful for industrial purposes.
- It is an excellent example of physiological preconditioning of plants.
- Induction to flowering may be used in horticulture.
- By this process plants which produces fruits once in a year, can produce fruits twice in a year.
2. Vernalization: It has been observed that if seeds of winter seasonal plants are kept at 0-5° C temperature for some days and then sown during spring season, flowering occurs in them like other spring seasonal plants. This phenomenon is called as vernalization.
If vernalized seeds are kept at high temperature for some time then vernalization effect is lost. This process is called as devernalization. It is believed that stimuli is received by apical meristem and vernalin hormone which is a gibberellin type hormone is secreted, which is transported to growth region.
In Siberia where soil remain cover by ice for 10 months, wheat is produced by this process in two months.
Economic importance of vernalization :
- By this process winter plants can be converted into spring plants.
- Crops can be protected from natural harm effects.
- Flowering can be done in plants in short period of time.
- Crops can be produced in short period of time by this process.
![]()
Question 3.
In higher plants growth and differentiation is open. Explain it. (NCERT)
Answer:
In higher plants growth can be represented by a sigmoid curve (S-shaped curve).
There are three phases of this curve :
- Lag phase: When the rate of growth is very slow.
- Log phase: It is the phase of rapid growth.
- Steady phase: Growth slows down at this stage or reaches to an equilibrium as cell division stops.
When cell losses its division capacity, they proceed towards cell differentiation to produce different tissues to perform different functions. The growth of a cell, tissue, organ, organ system or an organism follow same pattern of growth, thus it is open, whereas development is flexible. Actually, development is the sum total of growth and differentiation.
Question 4.
Write short note on following :
(a) Arithmetic growth (NCERT)
(b) Geometrical growth
(c) Sigmoid growth rate
(d) Absolute and relative growth rate.
Answer:
(a) Arithmetic growth: After mitosis division one cell undergoes arithmetic growth by regular cell division, whereas the second cell differentiate and mature. It occurs in a constant rate.
(b) Geometrical growth: In geometrical growth both the cells produced by mitosis undergoes cell division. But due limited nutrient supply gradually growth rate become slow, at last it reaches to steady state.
(c) Sigmoid growth rate: If a graph drawn between increase in size of the organism versus time then ‘S’ shaped curve is obtained called as sigmoid curve. It has three phases :
- Lag phase: When the rate of growth is slow in initial stage.
- Log phase: When the rate of growth is fast or rapid.
- Steady phase: When rate of growth reaches to an equilibrium because rate of production of cells become equal to cell death.
(d) Absolute and relative growth rate: Measurement and comparison of complete development in unit time is called as Absolute growth rate, whereas measurement of growth per unit time by any other given way is called as relative growth rate.
Question 5.
Define Growth, Differentiation, Development, De-differentiation, Re-differentiation, Meristem and growth rate. (NCERT)
Answer:
- Growth: It is the irreversible or progressive increase in size, shape, volume and weight of an organism.
- Cell differentiation: After cell division and cell elongation a cell undergoes differentiation. The cell differentiates, change in shape, position and get modified, matured as permanent cells to perform specific function. This phenomenon is called as differentiation.
- Development: Development is the gradual growth of the living body in its life cycle.
- De-differentiation: Differentiated cells regain their cell division capacity in some specific condition. This phenomenon is called as De-differentiation.
- Re-differentiation: New cells formed by de-differentiated cells losses their cell division capacity again and become permanent tissue by differentiation to perform specific function. This is called as re differentiation.
- Meristems: Group of similar, immature plant cells, which can show regular cell division to form new cells are called as meristems.
- Growth rate: Increase in size, dry weight, volume or number of cells of the living organism per unit time is called as growth rate.
Question 6.
If you are asked to do following works which plant hormone can be used?
(a) To produce root in a twig of plant. (NCERT)
(b) To ripe fruit fast.
(c) To prevent falling of premature leaves.
(d) For growth of axillary bud.
(e) To promote flowering in rose.
(f) To close stomata soon.
Answer:
(a) Auxin,
(b) Ethylene,
(c) Gibberellin,
(d) Cytokinin,
(e) Gibberellin,
(f) Abscisic acid.
Question 7.
What will happen if: (NCERT)
(a) GA3 is provided to seedlings of rice.
(b) Dividing cells stops cell division.
(c) Keeping a decay fruit with unripen fruits.
(d) If you forget to add cytokinin in the culture medium of plant.
Answer:
(a) Rice plant will increase in height.
(b) Cells when loss capacity to divide, differentiate to form different tissues to perform specific function.
(c) If a decay fruit is kept with unripen fruits then all fruits will decay.
(d) If cytokinin is not added to culture medium of plant then it may affect formation of chlorophyll in the young leaves, growth of lateral branches, growth of adventitious branches. In absence of cytokinin abscission of leaves may occur.
Question 8.
What are synthetic growth hormone? What are their importance in agriculture?
Answer:
Synthetic growth hormone or growth regulator :
As hormone regulates growth in organisms therefore they are called as growth hormone. Following are few examples of growth regulators, their importance in agriculture are as follows:
1. Morpactins: It is a synthetic hormone and derivative of fluorine-carboxylic acids. It induces growth of axillary bud by inhibiting growth of stem, leaf lamina etc. It increases production of oranges.
2. Malic Hydrazide (MH): It is a synthetic hormone which inhibit growth of grass, shrubs and trees. It inhibits germination of potato and onion thus they can be kept for long period of time.
3. Cycocel (CCC): Chemically it is chloroethyl-trimethyl ammonium chloride. It is used to kill weeds.
4. Synthetic Auxin (IBA and N.A.A.): It prevents defoliation of fruits and leaves.
5. Alpha naphthalene acetic acid: It is a synthetic hormone used for inhibiting growth of buds in godown of potato. Therefore potatoes can be kept for long time.
6. 2, 4 Dichlorodiphenoxy acetic acid: It is used to kill weeds.
7. Ethaphone: Chemically it is 2-chloroethyl phosphoric acid. It is used for ripening fruits like banana, grapes, mango at industrial level.
![]()
Question 9.
What is flowering hormone? Describe various types of flowering hormones in plants.
Answer:
Flowering hormones: Flowering hormones are the hormones which induces flowering by the effect of temperature and light.
There are two types of flowering hormones :
- Vemalin,
- Florigen.
1.Vernalin: It induces flowering by regulating vernalization process. As a result of vernalization, i.e. when apical bud receives winter stimuli produces vernalin hormone which acts like gibberellin and induces flowering.
2. Florigen: Phytochrome pigments found in the green leaves after absorbing light rays produces florigen hormone which is transported to growing region, where it induces flowering process.
Question 10.
Describe various factors which affect growth.
Answer:
Factors affecting growth :
1. Food supply: It affects the rate of growth firstly because it provides growth material to the growing region and secondly because it provides potential energy to the growing region.
2. Water supply: It has a direct relationship with the rate of growth because it is necessary for all the metabolic activities of protoplasm and for increasing the turgidity of the cell for cell enlargement.
3. Oxygen supply: Oxygen increases growth as it helps in respiration to convert potential energy into kinetic energy required for the vital activities of protoplasm.
4. Temperature: It affects growth in a way that growth occur between 4-45°C, optimum activity takes place at 28-33°C.
5. Light: All the three aspects of light intensity, quality and periodicity affects growth. High intensity of light induce dwarfing of the plant and increases the loss of water. Weak light intensity reduces the rate of overall growth and also photosynthesis. Different colour (wavelength) also affects the growth of plants. In blue-violet colour light, intermodal growth is pronounced while green colour light reduces the expansion of leaves. The red colour favours elongation.
Infrared and ultraviolet are detrimental to growth. There is a remarkable effect of the duration of light on the growth of vegetative as well as reproductive structure.
6. Growth hormones: Now it is well established that the growth of plant is controlled by certain organic compounds present in very minute quantities. These compounds are called hormones, phytohormones or growth-promoting substances.
Plant Growth and Development Class 11 Important Questions Objective Type
1. Choose the correct answers:
Question 1.
Gibberellins was first extracted from :
(a) Gibberella fujikuroi
(b) Gelidium
(c) Gracelaria
(d) Aspergillus.
Answer:
(a) Gibberella fujikuroi
Question 2.
Storage sprouting of potato can be prevented by :
(a) IAA
(b) Malic hydrazide
(c) Cytokinins
(d) Gibberellins.
Answer:
(b) Malic hydrazide
![]()
Question 3.
The following is a naturally occurring growth inhibitor :
(a) IAA
(b) ABA
(c)NAA
(d) GA3.
Answer:
(b) ABA
Question 4.
The following hormone is concerned chiefly with cell division in plants :
(a) IAA
(b) Kinin (zeatin)
(c) GA3
(d) 2,4-D.
Answer:
(b) Kinin (zeatin)
Question 5.
Gibberellic acid has been successfully employed to induce flowering :
(a) In short-day plants under long-day conditions
(b) In long-day plant under short-day conditions
(c) For some plants
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) In long-day plant under short-day conditions
Question 6.
The leaves of Mimosa pudica drop down on touch because :
(a) The plant has nervous system
(b) The leaves are very tender
(c) The leaf tissues are injured
(d) The turgor of the leaf changes.
Answer:
(d) The turgor of the leaf changes.
Question 7.
Vernalization is :
(a) Growth curve in response to light
(b) Recurrence of day and night
(c) Effect of day length on plant growth
(d) Acceleration of the ability of flower by low-temperature treatment.
Answer:
(d) Acceleration of the ability of flower by low-temperature treatment.
![]()
Question 8.
Effect of length of the day on flowering is called :
(a) Phototropism
(b) Photoperiodism
(c) Photorespiration
(d) Photo-oxidation.
Answer:
(b) Photoperiodism
Question 9.
In plants the hormone associated with cell division is :
(a) GA
(b) 2,4-D
(c) IAA
(d) Kinin.
Answer:
(d) Kinin.
Question 10.
Cytokinin:
(a) A hormone that stimulate cell division
(b) A process of cell division
(c) A form of cell movement ‘
(d) A substance that produces dormancy.
Answer:
(a) A hormone that stimulate cell division
Question 11.
Three main growth inducing hormones in plants are :
(a) Auxin, Gibberellin and Ethylene
(b) Gibberellin, Cytokinin and Abscisic acid
(c) Ethylene, Abscisic acid and cytokinin
(d) Auxin, Gibberellin and cytokinin.
Answer:
(d) Auxin, Gibberellin and cytokinin.
Question 12.
Cytokinesis induces:
(a) Cell division
(b) Cell elongation
(c) Stem elongation
(d) Parthenocarpy.
Answer:
(d) Parthenocarpy.
2. Fill in the blanks:
1. First auxin isolated from human urine is ……………………….. .
Answer:
IAA
2. ……………………….. is used in the ripening of fruits.
Answer:
Ethylene
3. ……………………….. hormone is reponsible for flowering.
Answer:
Florigen
4. ……………………….. hormone is used to increase length of genetically dwarf plants.
Answer:
Gibberellin
5. ……………………….. hormone increases abscissing and senescence.
Answer:
Abscisic acid
6. ……………………….. hormone is responsible for cell division.
Answer:
Cytokinin
7. Germination of seeds over parent plant is called ……………………….. .
Answer:
Vivipary
8. Bakani disease of rice is caused by a fungus known as ……………………….. .
Answer:
Gibberella fuji kuroi
9. Growth occurs per unit time period in the living organisms is called as ……………………….. .
Answer:
Growth rate
10. In ……………………….. growth after mitosis division only one daughter cell shows regular cell division.
Answer:
Arithmetic.
3. Match the following:
(A)
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Florigen | (a) IAA |
| 2. Abscission | (b) Protein |
| 3. Delay in senescence | (c) Cytokinin |
| 4. Aleuron layer | (d) ABA |
| 5. Auxin | (e) Flowering. |
Answer:
1. (e) Flowering.
2. (d) ABA
3. (c) Cytokinin
4. (b) Protein
5. (a) IAA.
![]()
(B)
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Dormin | (a) Auxin |
| 2. GA3 | (b) Abscisic acid |
| 3. Zeatin | (c) Gibberellin |
| 4. 2,4-D | (d) Cytokinin |
| 5. Termination of seed dormancy | (e) Gibberellin. |
Answer:
1. (b) Abscisic acid
2. (c) Gibberellin,
3. (d) Cytokinin
4. (a) Auxin
5. (e) Gibberellin.
4. Answer in one word:
1. Name the tissues responsible for growth in plants.
Answer:
Meristematic tissue
2. Write the name of various phases of growth.
Answer:
Cell division stage, Cell elongation stage, Cell maturation stage
3. Elaborate the term 2,4-D. Also write one function of it.
Answer:
2, 4 di phenoxy acetic acid, it is a growth hormone and used as weedicide
4. Elaborate the term IAA and write one function of it.
Answer:
Indole acetic acid, used in development of seedless fruits
5. Name the hormone which is found in gaseous state.
Answer:
Ethylene
6. Name the apparatus used for measurement of plant growth.
Answer:
Auxanometer
7. Name the growth regulator which help to stop germination of potato and onion.
Answer:
Malic hydrazide
8. Name any two synthetic Auxins.
Answer:
(a) I. B. A. (Indole buteric acid),
(b) N. A.A. (Naphthol acetic acid).