Students get through the MP Board Class 11th Biology Important Questions Chapter 14 Respiration in Plants which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
MP Board Class 11th Biology Important Chapter 14 Respiration in Plants
Respiration in Plants Class 11 Important Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
What is glycolysis?
Answer:
Glycolysis is the process which occur in the cytoplasm in which one molecule of glucose is converted into two molecules of pyruvic acid.
C6H12O6 + 2 ATP + 4ADP + H3PO4 + 2NAD → 2CH3COCOOH + 2ADP + 4ATP + 2NADH2 + 2H2O
Question 2.
Where is glycolysis and Krebs cycle completed?
Answer:
Glycolysis: It is completed in the cytoplasm.
Krebs cycle: This process is completed in mitochondria.
![]()
Question 3.
How much energy is liberated by oxidation of 1 mole glucose?
Answer:
One mole glucose liberates 673 kcal or 38 ATP by aerobic oxidation and 21 kcal or 2 ATP by anaerobic process.
Question 4.
Why anaerobic respiration releases less energy than aerobic respiration?
Answer:
In anaerobic respiration, due to incomplete oxidation of food material some energy remains within it, whereas in aerobic respiration all energy liberates due to complete oxidation. Due to this, anaerobic respiration liberates less energy than aerobic respiration.
Question 5.
What is the initial and the end product of glycolysis and where does the complete process take place?
Answer:
The initial and the end product of glycolysis is glucose and pyruvic acid and the whole process takes place in the cell plasm.
Question 6.
Where does anaerobic respiration occurs in the cell?
Answer:
Anaerobic respiration occurs in the cytoplasm part of the cell.
Question 7.
What is anaerobic respiration?
Answer:
Type of respiration in which incomplete oxidation of food occurs in absence of oxygen is called as anaerobic respiration. Less energy is released during this respiration.
![]()
Question 8.
What is Aerobic respiration?
Answer:
Type of respiration in which complete oxidation of food occurs in the presence of oxygen is called as aerobic respiration. More energy is released during this process.
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6H2O + 6CO2 + 673 k.cal Energy [38 mol ATP].
![]()
Question 9.
Potted plant must not be kept in the room at night while sleeping. Why?
Answer:
During night photosynthesis do not occur thus plants can not use CO2 produced during respiration. Therefore, concentration of CO2 increases in the room, which may cause harm to the person sleeping in that room. Thus, potted plants are not kept in the room at night while sleeping.
Plant Growth and Development Class 11 Important Questions Short Answer Type
Question 1.
What is Respiratory Substrate? Name the substrate generally used. (NCERT)
Answer:
Such substances which undergoes decomposition inside the cells for production of energy are called as Respiratory substrate.
e.g. Food materials like carbohydrates, fats, proteins etc.
Substrate which is generally used as respiratory substrate is Glucose.
Question 2.
What is Oxidative phosphorylation? (NCERT)
Answer:
In all living beings ATP is generated during oxidative breakdown of complex food products. This process of synthesis of ATP molecules from ADP and inorganic phosphate by using the energy of food materials is called as oxidative phosphorylation.
Question 3.
What is the importance of energy released during breathing? (NCERT)
Answer:
During oxidation of food inside the cell, total energy produced by the respiratory substrate is not released at a time. It is stored in the form of ATP. Whenever body requires energy it decomposes to give energy. Thus, ATP is also called as energy currency. This energy is used for performing different life activities of the body.
Question 4.
Write differences between following : (NCERT)
(a) Respiration and Combustion.
(b) Glycolysis and Krebs cycle.
(c) Aerobic respiration and fermentation.
Answer:
(a) Differences between Respiration and Combustion used first, they decompose to produce glucose with the help of enzymes. When carbohydrates are not available, fat decomposes into fatty acid and glycerol. When both carbohydrates and fats are not available then protein decomposes to form glucose. Later glucose undergoes oxidation. Respiration is a catabolic process and the respiratory path is catabolic.
Fatty acid first converts into Acetyl Co-A, then enters into Krebs cycle. When fatty acid is to be synthesized in the living organisms Co-A is removed from the respiratory path. In this way respiratory path is used for synthesis (Anabolism) as well as decomposition (Catabolism) of fatty acid. Therefore respiratory pathway can be called as Amphibolic pathway.
(b) differences between Glycolysis and Krebs cycle
| Glycolysis | Krebs cycle |
| 1. It is the first step of respiration process. | It is the second step of respiration process. |
| 2. It occurs in the cytoplasm part of the cell. | It occurs in the mitochondria part of the cell. |
| 3. It occurs in aerobic and anaerobic respiration both. | It occurs in the aerobic respiration only. |
| 4. It is linear pathway. | It is cyclic pathway. |
| 5. One molecule of glucose breaks into 2 molecules of pyruvic acid. | One molecule of Acetyl CoA breaks into CO2 and water. |
| 8 molecules of ATP are formed during this process. | 30 molecules of ATP are formed during this process |
(c) Differences between Aerobic respiration and Fermentation.
| Aerobic respiration | Fermentation |
| 1. Complete oxidation of carbohydrates occurs. | incomplete oxidation of carbohydrates occurs. |
| 2. It occurs in presence of oxygen. | It occurs in absence of oxygen. |
| 3. Quantity of CO2 produced is more. | Quantity of CO2 produced is less. |
| 4. It occurs inside the cell in the presence of specific enzymes. | It occurs outside the cell in the presence of zymase complex enzyme obtained from yeast. |
| 5. It is not a biological process. | it is a biological process. |
Question 5.
Respiration pathway is amphibolic. Discuss it. (NCERT)
Answer:
Generally glucose is used as respiratory substrate. If oligo or polysaccharides are used first, they decompose to produce glucose with the help of enzymes. When carbohydrates are not available, fat decomposes into fatty acid and glycerol. When both carbohydrates and fats are not available then protein decomposes to form glucose. Later glucos undergoes oxidation.
Respiration is a catabolic process and the respiratory path is catabolic. Fatty acid first converts into Acetyl Co-A, then enters into Krebs cycle. When fatty acid is to be synthesized in the living organisms Co-A is removed from the respiratory path. in this way respiratory path is used for synthesis (Anabolism) as well as decomposition (Catabolism) of fatty acid. Therefore respiratory pathway can be called as Amphibolic pathway.
![]()
Question 6.
Draw glycolysis through ray diagram.
Or
Explain glycolysis with the help of flow chart.
Answer:
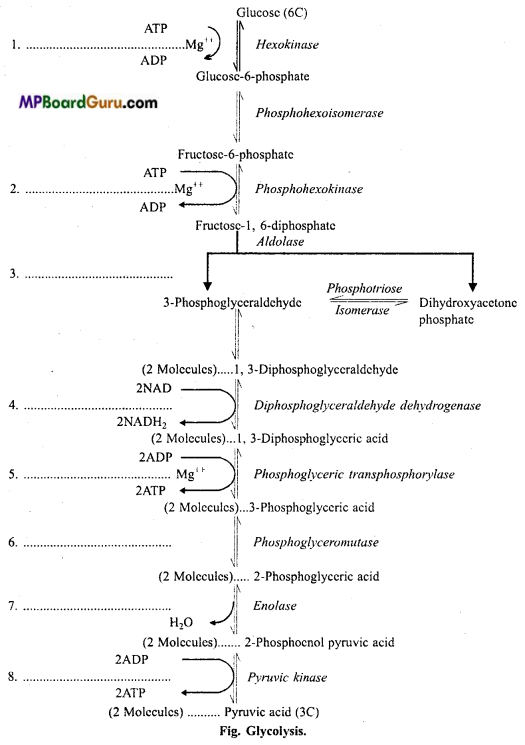
Question 7.
What are the main steps of aerobic respiration? Where does it occur?
Answer:
Aerobic respiration is completed in two steps :
- Glycolysis
- Krebs cycle.
1. Glycolysis: It occurs in the cytoplasm.

2. Krebs cycle : (TCA OR TRICARBOXYLIC ACID CYCLE)
Pyruvic acid produced by glycolysis undergoes aerobic oxidation in the matrix of mitochondria through the TCA cycle. This cycle serves as a common pathway for carbohydrates, fats and proteins. Before participating in TCA cycle pyruvic acid enters a mitochon¬drion. Here, it is decarboxylated and the remaining 2-carbon fragment is combined with a molecule of coenzyme A to form acetyl CoA. This reaction is an oxidation reduction process and produces H ions and electrons along with carbon dioxide. During the process NAD is reduced to NADH2.
Acetyl CoA is also formed from the beta-oxidation of fatty acids. Acetyl CoA acts as a connecting link between glycolysis and Krebs cycle. After the conversion of pyruvic acid into Acetyl CoA, acetyl CoA enters into Krebs cycle.
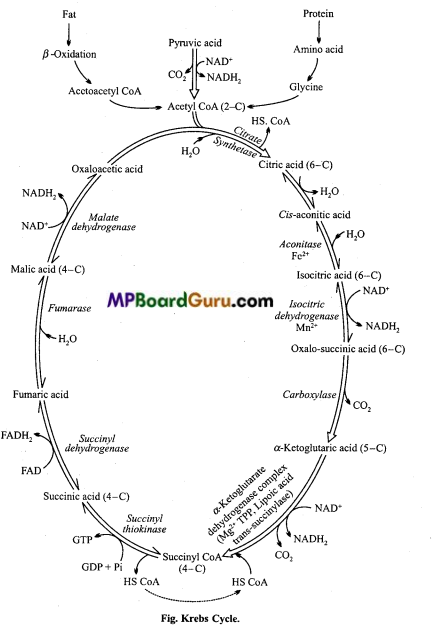
Steps of Krebs cycle are as follow :
1. Condensation: Acetyl CoA (2C compound) combines with oxaloacetic acid (4C compound) in the presence of condensing enzyme citrate synthetase to form citric acid (6C compound). It is the first product of Krebs cycle. CoA is released here.
Citrate synthetase
![]()
2. Dehydration: Citric acid in presence of aconitase enzyme is converted into cis- aconitic acid H20 is released here.
![]()
3. Hydration: Cis-aconitic acid is converted into isocitric acid with the addition of water in presence of enzyme aconitase.
![]()
4. Dehydration: Isocitric acid is oxidized into oxalosuccinic acid by reacting with NAD+ in presence of isocitrate dehydrogenase.

5. Decarboxylation: Oxalosuccinic acid converts into a-ketoglutaric acid by removal of one molecule of CO2 in presence of carboxylase enzyme.

![]()
6. Dehydrogenation and Decarboxylation: a-ketoglutaric acid reacts with NAD+ and CoA and get oxidized into succinyl CoA in presence of a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase enzyme. TPP, Lipoic acid and Mg++ are also required for this reaction.

7. Formation of GTP: Succinyl CoA on hydrolysis produces succinic acid and CoA in presence of succinyl thiokinase enzyme. During this process one molecule of GTP is formed from GDP by using energy released during the reaction.
![]()
8. Dehydrogenation: Succinic acid is oxidized into fumaric acid by reacting with FAD in presence of succinyl dehydrogenase enzyme. FADH2 is produced in the reaction.
Succinyl dehydrogenase

9. Hydration: Fumaric acid reacts with one molecule of water in presence of fumarase enzyme and forms malic acid.

10. Dehydrogenation: At last Malic acid is oxidized by reacting with NAD in presence of Malate dehydrogenase enzyme to form oxaloacetic acid.
![]()
Oxaloacetic acid thus produced combines with Acetyl CoA to form citric acid which again enter into the cycle thus the cycle is repeated.
![]()
Question 8.
Explain electron transport chain?
Answer:
Electron transport chain: As you know that, H ions and electrons removed from the respiratory substrate during oxidation do not directly react with oxygen. Instead they reduce acceptor molecules NAD and FAD to NADH2 and FADH2 respectively. These molecules then transfer their electron to a system of electron acceptors and transfer molecules. The proteins of the inner mitochondrial membrane act as electron transporting enzymes.
They are arranged in an ordered manner in the membrane and function in a specific sequence. This assembly of electron transport enzymes is known as mitochondrial respiratory chain or the electron transport chain. Specific enzymes of this chain receive electrons (and in a few cases protons also) from reduced prosthetic groups, NADH2 or FADH2 produced by glycolysis and the TCA cycle. The electrons are then transported successively from enzyme to enzyme, down a descending ‘stairway ’of energy-yielding reactions.
The electron transport chain includes several cytochromes, such as: Cyt-Q, Cyt-b, Cyt-C1, Cyt-c, Cyt-a and Cyt-a3.
At the end of the chain the electrons and the accompanying protons (H+) are combined with O2 to form water. Oxygen is thus the terminal electron acceptor of the mitochon¬drial respiratory chain.
Three molecules of ATP are formed from ADP by using energy liberated during various steps of electron transport. ATP molecules are produced during given steps :
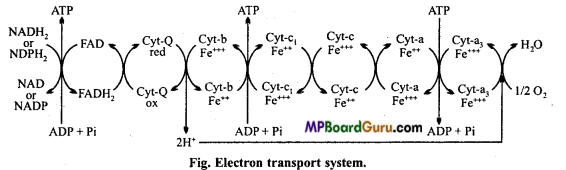
- When NADH2 is oxidized to NAD by reacting with FAD.
- When electron transfer from cytochrome-b to cytochrome-c1.
- When electron transfer from cytochrome-a to cytochrome-a3.
Now it is clear that oxidation of one molecule of reduced NADH2 or NADPH2 results in the formation of 3 molecules of ATP while oxidation of FADH2 leads to the formation of 2 molecules of ATP.
At each step of electron transport the electron acceptor has a higher electron affinity than the electron donor from which it receives the electron.
The energy from such electron transport is utilized in transporting protons (H+) from the matrix across the inner membrane to its outer side. This creates a higher proton concentration outside the inner membrane than in the matrix. The difference in proton concentration across the inner membrane is called proton gradient. Now it is clear that oxidation of one molecule or reduced NADH2 or NADPH2 results in the formation of 3 molecule of ATP while Oxidation of FADH2 leads to the formation of 1 molecules of ATP.
Question 9.
Draw Krebs cycle.
Or,
Explain Krebs cycle with flow chart.
Answer:
Question 10.
What is Respiratory quotient? What is R.Q. value of fat? (NCERT)
Answer:
Respiratory quotient: The ratio of volume of CO2 released to the volume of O2 absorbed during respiration is called respiratory ratio or R.Q. The value of R.Q. depends upon the chemical nature of respiratory substrate
\(\text { R.Q. }=\frac{\text { Volume of } \mathrm{CO}_{2} \text { released }}{\text { Volume of } \mathrm{O}_{2} \text { absorbed }}\)
The value of R.Q. varies with substrate. Thus, the measurement of R.Q. gives an idea of the nature of respiratory substrate being respired in a particular tissue. R.Q. is usually measured by Ganong’s respirometer.
Fatty substances: R.Q. of fatty substance is always less than unity (0-7). e.g., Germinating seeds of castor, mustard, linseed, til, etc.
C18H3O62 + 26O2 → 18CO2 + 18H2O
\(\mathrm{R.Q} .=\frac{18 \mathrm{CO}_{2}}{26 \mathrm{O}_{2}}=\frac{18}{26}=0 \cdot 7 \text { (less than unity). }\)
Plant Growth and Development Class 11 Important Questions Long Answer Type
Question 1.
Write differences between following : (NCERT)
(a) Aerobic and Anaerobic respiration.
(b) Glycolysis and Fermentation.
(c) Glycolysis and Citric acid cycle.
Answer:
(a) Differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration
| Aerobic Respiration | Anaerobic Respiration |
| 1. Aerobic respiration requires oxygen and takes place in cytoplasm and mitochondria. | It does not require oxygen and takes place in cytoplasm only. |
| 2. The substrate is completely oxidized. | The substrate is incompletely oxidized. |
| 3. End products are CO2 and H2O. | End products are ethyl alcohol and CO2. |
| 4. 38 ATP (673 kcal) energy is produced. | 2 ATP (21 kcal) energy is produced. |
| 5. Harmful substances are not formed. | Harmful substance ethyl alcohol is formed. |
(b) Differences between Glycolysis and Fermentation
| Glycolysis | Kerbs cycle |
| 1. This process occurs inside the cytoplasm of the cell. | It occurs outside the cell. |
| 2. It is a biochemical process. | 2. It is a biochemical process. |
| 3. Enzymes required for this process are found in the cytoplasm of the cell. | Zymase complex enzyme obtained from yeast cells help for this process. |
| 4. Energy is released in the form of ATP. | Energy is released in the form of heat. |
(c) Difference between Glycolysis and Citric acid cycle:
(a) Differences between Respiration and Combustion used first, they decompose to produce glucose with the help of enzymes. When carbohydrates are not available, fat decomposes into fatty acid and glycerol. When both carbohydrates and fats are not available then protein decomposes to form glucose. Later glucose undergoes oxidation. Respiration is a catabolic process and the respiratory path is catabolic.
Fatty acid first converts into Acetyl Co-A, then enters into Krebs cycle. When fatty acid is to be synthesized in the living organisms Co-A is removed from the respiratory path. In this way respiratory path is used for synthesis (Anabolism) as well as decomposition (Catabolism) of fatty acid. Therefore respiratory pathway can be called as Amphibolic pathway.
(b) differences between Glycolysis and Krebs cycle
| Glycolysis | Krebs cycle |
| 1. It is the first step of respiration process. | It is the second step of respiration process. |
| 2. It occurs in the cytoplasm part of the cell. | It occurs in the mitochondria part of the cell. |
| 3. It occurs in aerobic and anaerobic respiration both. | It occurs in the aerobic respiration only. |
| 4. It is linear pathway. | It is cyclic pathway. |
| 5. One molecule of glucose breaks into 2 molecules of pyruvic acid. | One molecule of Acetyl CoA breaks into CO2 and water. |
| 8 molecules of ATP are formed during this process. | 30 molecules of ATP are formed during this process |
(c) Differences between Aerobic respiration and Fermentation.
| Aerobic respiration | Fermentation |
| 1. Complete oxidation of carbohydrates occurs. | incomplete oxidation of carbohydrates occurs. |
| 2. It occurs in presence of oxygen. | It occurs in absence of oxygen. |
| 3. Quantity of CO2 produced is more. | Quantity of CO2 produced is less. |
| 4. It occurs inside the cell in the presence of specific enzymes. | It occurs outside the cell in the presence of zymase complex enzyme obtained from yeast. |
| 5. It is not a biological process. | it is a biological process. |
Question 2.
What is your imagination while calculating number of ATP molecules pro reduced during oxidation of one molecule of glucose? (NCERT)
Answer:
(A) In glycolysis cycle :
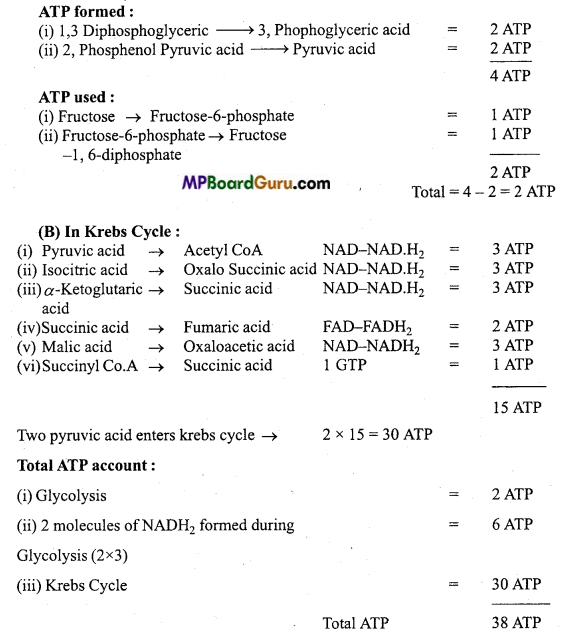
Thus, on complete oxidation of one molecule of glucose, 38 molecules of ATP are produced.
Above calculation is done on the basis of imagination of following points:
- Oxidation of glucose is systematic metabolic path in which from one substrate another intermediate compound is formed starting from glycolysis, Kerb’s cycle then through electron transport system.
- NADH2 produced during glycolysis enters into mitochondria and then into electron transport system to produce ATP by phosphorylation of ADP.
- Intermediate compounds does not help for formation of any other compound.
- Only glucose is used as substrate for respiration.
No any other compound can enter into intermediary path unless it converts into glucose.
![]()
Plant Growth and Development Class 11 Important Questions Objective Type
1. Choose the correct answers:
Question 1.
Glycolysis takes place in :
(a) Cytoplasm
(b) Chloroplast
(c) Ribosomes
(d) Mitochondria.
Answer:
(a) Cytoplasm
Question 2.
How many molecules of ATP are formed in Kreb’s cycle :
(a) 28
(b) 18
(c) 30
(d) 8.
Answer:
(c) 30
Question 3.
How many molecules of ATP are formed from the anaerobic respiration of one molecule of glucose :
(a) 8
(b) 16
(c) 2
(d) 14.
Answer:
(c) 2
Question 4.
What is ATP:
(a) Oxidative enzyme
(b) A hormone
(c) A protein
(d) Molecule of high energy phosphate bonds.
Answer:
(d) Molecule of high energy phosphate bonds.
![]()
Question 5.
ATP synthesis in mitochondria require :
(a) o2
(b) NADP
(c) FMN
(d) Pyruvic acid.
Answer:
(a) o2
Question 6.
Alcohol is formed in :
(a) Aerobic respiration
(b) Anaerobic respiration
(c) Photosynthesis
(d) Photorespiration.
Answer:
(b) Anaerobic respiration
Question 7.
Krebs cycle takes place in :
(a) Vesicles of E. R.
(b) Matrix of mitochondria
(c) Dictyosomes
(d) Lysosornes.
Answer:
(b) Matrix of mitochondria
Question 8.
Flowers and fruits maintain their flavour and taste when kept in refrigerators because:
(a) Deficiency of O2
(b) Respiration is inactive
(c) CO2 is collected
(d) H2O is converted into ice.
Answer:
(b) Respiration is inactive
![]()
Question 9.
End-product of glycolysis is :
(a) Oxalo acetic acid
(b) Acetic acid
(c) Pyruvic acid
(d) Malic acid.
Answer:
(c) Pyruvic acid
Question 10.
End-product of anaerobic respiration in our muscles is :
(a) Malic acid
(b) Lactic acid
(c) Citric acid
(d) Alcohol.
Answer:
(b) Lactic acid
Question 11.
End product of Krebs cycle is :
(a) CO2 and H2O
(b) H2O and Citric acid
(c) H2O and OAA
(d) HO2 and NADPH2.
Answer:
(a) CO2 and H2O
Question 12.
Another name of TCA cycle is :
(a) Krebs cycle
(b) Calvin’s cycle
(c) EMP
(d) Hatch and Slack cycle.
Answer:
(a) Krebs cycle
Question 13.
EMP Energy pack of a living cell is :
(a) Cytochrome
(b) ADP
(c) ATP
(d) Chlorophyll.
Answer:
(c) ATP
Question 14.
Addition of phosphate molecule to ADP to form ATP is called as :
(a) Protein synthesis
(b) Photosynthesis
(c) Phosphorylation
(d) Pinocytosis.
Answer:
(c) Phosphorylation
![]()
Question 15.
In which process oxidative phosphorylation occurs :
(a) Protein synthesis
(b) Nitrogen fixation
(c) Respiration
(d) Transpiration.
Answer:
(c) Respiration
Question 16.
Photorespiration is characteristic feature of which type of plant:
(a) C3
(b) C4
(c) CAM
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) C3
Question 17.
How much quantity of energy is released during aerobic respiration of one molecule of glucose:
(a) 637 k. cal
(b) 640 k. cal
(c) 673 k. cal
(d) 693 k. cal.
Answer:
(c) 673 k. cal
Question 18.
Link between glycolysis and Krebs cycle is :
(a) Citric acid
(b) Malic acid
(c) Fumaric acid
(d) Acetyl Co-A.
Answer:
(d) Acetyl Co-A.
![]()
Question 19.
What is essential for both photosynthesis and respiration :
(a) Chlorophyll
(b) CO2
(c) Water
(d) Cytochrome.
Answer:
(d) Cytochrome.
Question 20.
How much quantity of energy is released on hydrolysis of ATP into ADP :
(a) 120 cal
(b) 1200 cal
(c) 12000 cal
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) 12000 cal
Question 21.
R.Q. of germinating castor seed is :
(a) One
(b) Less than one
(c) More than one
(d) Zero.
Answer:
(b) Less than one
Question 22.
Cytochrome contains:
(a) Mg
(b) Fe
(c) Mn
(d) Cu.
Answer:
(b) Fe
Question 23.
How many molecules of ATP are formed during glycolysis :
(a) 0
(b) 2
(c) 4
(d) 8.
Answer:
(d) 8.
![]()
Question 24.
Photorespiration is related to :
(a) Glyoxysome
(b) Lysosome
(c) Mesosome
(d) Ribosome.
Answer:
(a) Glyoxysome
Question 25.
Electron transport system is found in which part of the mitochondria :
(a) Outer membrane
(b) Inner cristae
(c) Inner membrane
(d) Inner membrane sac.
Answer:
(c) Inner membrane
Question 26.
Meaning of photophosphorylation is :
(a) Formation of ATP from ADP
(b) Formation of NADP
(c) Formation of ADP from ATP
(d) Formation of PGA.
Answer:
(a) Formation of ATP from ADP
Question 27.
In glycolysis process which substance converts into end product:
(a) Protein into glucose
(b) Glucose into fructose
(c) Starch into glucose
(d) Glucose into pyruvic acid.
Answer:
(d) Glucose into pyruvic acid.
![]()
Question 28.
Power house of the cell is :
(a) Golgi complex
(b) Ribosome
(c) Mitochondria
(d) Lysosome.
Answer:
(c) Mitochondria
Question 29.
Enzymes involved in glycolysis are found in the :
(a) Mitochondria
(b) Cytoplasm
(c) Mitochondria and cytoplasm
(d) Vacuole.
Answer:
(b) Cytoplasm
Question 30.
Which of the following can respire without oxygen :
(a) Root
(b) Seed
(c) Stem
(d) Leaf.
Answer:
(b) Seed
2. Fill in the blanks:
1. C6H12O6 + ………….. → 6CO + 6H2O + ………….. ATP.
Answer:
6O2, 38,
2. R.Q. of organic acid is always ………….. .
Answer:
More than one,
3. C6H12O6 ![]() ………….. + 2CO2.
………….. + 2CO2.
Answer:
2C, H5OH,
4. Respiratory quotient is measured by ………….. .
Answer:
Respirometer,
5. Krebs cycle occurs in the ………….. part of the cell.
Answer:
Mitochondria,
6. Energy coin of the cell is ………….. .
Answer:
ATP,
7. In ………….. respiration incomplete oxidation of food occurs.
Answer:
Anaerobic,
8. End product of glycolysis is ………….. .
Answer:
Pyruvic acid,
9. Fermentation is done by ………….. enzyme of yeast cell.
Answer:
Zymase,
10. ………….. is a link between glycolysis and Kerbs cycle.
Answer:
Acetyl CoA,
11. ………….. is oxidised during respiration process.
Answer:
Glucose,
12. The arrangement of electron transport enzymes through which electron transfer from one electron acceptor to other is called as ………….. .
Answer:
Electron transport system.
3. Match the following:
(A)
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Glycolysis | (a) Electron transport system |
| 2. Krebs cycle | (b) Cytoplasm |
| 3. Photorespiration | (c) Mitochondria |
| 4. ADP + Pi → ATP | (d) C3 plants |
| 5. Cytochrome | (e) Phosphorylation. |
Answer:
1. (b) Cytoplasm
2. (c) Mitochondria
3. (d) C3 plants
4. (e) Phosphorylation.
5. (a) Electron transport system.
![]()
(B)
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Carbohydrates | (a) R.Q, – less than one |
| 2. Protein | (b) R.Q.- Unity (1) |
| 3. Organic acid | (c) R.Q. – 0 |
| 4. Fat | (d) R.Q. – 0.7 |
| 5. Succulent plants | (e) R.Q. – more than one. |
Answer:
1. (b) R.Q.- Unity (1)
2. (a) R.Q, – less than one
3. (e) R.Q. – more than one.
4. (d) R.Q. – 0.7
5. (c) R.Q. – 0
4. Answer in one word:
1. What is net gain of energy from oxidation of one mole of glucose?
Answer:
673 Kcal in aerobic respiration and 21 kcal in anaerobic respiration,
2. Where does anaerobic respiration occur in cell?
Answer:
Cytoplasm,
3. Name the organelle structure where electron transport chain occurs?
Answer:
Inner membrane of mitochondria,
4. Where does glycolysis takes place?
Answer:
Cytoplasm,
5. What is ATP?
Answer:
Energy-rich compound which binds phosphate,
6. Which process is responsible for alcohol formation?
Answer:
Anaerobic respiration,
7. Where does Krebs cycle takes place?
Answer:
In the matrix of mitochondria,
8. How many molecules of ATP are formed during glycolysis?
Answer:
8 ATP,
9. In which form energy is released during respiration?
Answer:
ATP.