MP Board Class 10th Science Solutions Chapter 15 Our Environment
MP Board Class 10th Science Chapter 15 Intext Questions
Class 10th Science Chapter 15 Intext Questions Page No. 257
Question 1.
Why are some substances biodegradable and some non- biodegradable?
Answer:
Some substances can be broken down into simpler substances by the action of enzymes and other physical factors and are returned to the earth. Some substances cannot be degraded into simpler form and exists in nature for very long, deteriorating it and hence, are termed as non- biodegradable.
Question 2.
Give any two ways in which biodegradable substances would affect the environment.
Answer:
- These substances may cause pollution the environment.
- They may serve breeding ground for pathogens which may cause diseases
Question 3.
Give two ways in which non-biodegradable substances would affect me environment.
Answer:
- They do not degrade and pile up in the environment causing harm to the ecosystem.
- They may lead to bio-magnification in food chain disturbing the various trophic levels.
![]()
Class 10th Science Chapter 15 Intext Questions Page No. 261
Question 1.
What are the trophic levels? Give an example of a food chain and state the different trophic levels in it.
Answer:
Each step or level of a food chain is called Trophic levels.
Example for Food chain – Here grass is a producer because it prepares its own food. This grass is eaten by herbivores means secondary, small carnivores (Frog) are tertiary and higher carnivores are in the fourth level.
Question 2.
What is the role of decomposers in the ecosystem?
Answer:
Microorganisms, comprising bacteria and Fungi, break-down the dead remains and waste products of organisms. These microorganisms are the decomposers as they break-down the complex organic substances into simple inorganic substances that go into the soil and are used up once more by the plants.
Class 10th Science Chapter 15 Intext Questions Page No. 264
Question 1.
What is ozone and how does it affect any ecosystem?
Answer:
Ozone at the higher levels of the atmosphere is a product of UV radiations acting on O2 molecule. The higher energy UV radiations split apart some molecular Oa in free oxygen (O) atoms. These atoms then combine with the molecular O2 to form Ozone.
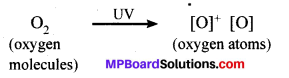
Ozone shields the surface of the earth from ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the Sun. This radiation is highly damaging to organisms for example, it is known to cause skin cancer in human beings.
![]()
Question 2.
How can you help in reducing the problem of waste disposal? Give any two methods.
Answer:
- We must minimise the usage of plastics,
- We can collect wastes and by this we can produce gas which is an alternate source of energy.
Class 10th Science Chapter 15 Ncert Textbook Exercises
Question 1.
Which of the following groups contain only biodegradable items?
(a) Grass, flowers and leather
(b) Grass, wood and plastic
(c) Fruit-peels, cake and lime-juice
(d) Cake, wood and grass
Answer:
(a), (c), (d)
Question 2.
Which of the following constitute a food-chain?
(a) Grass, wheat and mango
(b) Grass, goat and human
(c) Goat, cow and elephant
(d) Grass, fish and goat
Answer:
(b) Grass, goat and human
Question 3.
Which of the following are environment-friendly practices?
(a) Carrying cloth-bags to put purchases in while shopping
(b) Switching off unnecessary lights and fans
(c) Walking to school instead of getting your mother to drop you on her scooter
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 4.
What will happen if we kill all the organisms in one trophic level?
Answer:
If we kill all the organisms in one trophic level, the population size of organisms in lower level increases uncontrollably and the number of organisms in higher trophic level decreases due to non¬availability of food. This results in an imbalance in ecosystem.
Question 5.
Will the impact of removing all the organisms in a trophic level be different for different trophic levels? Can the organisms of any trophic level be removed without causing any damage to the ecosystem?
Answer:
- Removing producers: All the heterotrophs die.
- Removing herbivores: Carnivores would not get food.
- Removing carnivores: Herbivores would increase to unsustainable levels.
- Removing decomposers: Organic wastes, plant, and animal dead remains would pile up.
- The role of each and every species belonging to every trophic level is unique.
- No, the organisms of any trophic level cannot be removed without damaging the ecosystem.
Question 6.
What is the biological magnification? Will the levels of this magnification be different at different levels of the ecosystem?
Answer:
Some harmful chemicals enter our bodies through the food chain, one of the reasons is the use of several pesticides and other chemicals to protect our crops from disease and pests. These chemicals are either washed down into the soil or into the water bodies. From the soil, these are absorbed by the plants along with water and minerals and from the water bodies these are taken up by aquatic plants and animals.
This is one of the ways in which they enter the food chain. This phenomenon is known as biological magnification. This level of magnification be different at different levels of the ecosystem.
Example; Spraying of DDT will remain for a long time in the environment.
Question 7.
What are the problems caused by the non-biodegradable wastes that we generate?
Answer:
- Non-aesthetic look.
- Death of cattle by ingestion of plastic bags.
- The quality of soil is adversely affected.
- Biomagnification of harmful chemicals like DDT in birds disturb their calcium metabolism.
- Non – biodegradable wastes cause pollution of soil and water.
Question 8.
If all the waste we generate is biodegradable, will this have no impact on the environment?
Answer:
If all the waste we generate is biodegradable, there is a imbalance in nature. Because with the increase of wastes there is decrease in the number of decomposers. These wastes spread every where and microbes are more which causes many diseases to us.
Question 9.
Why is damage to the ozone layer a cause for concern? What steps are being taken to limit this damage?
Answer:
Damage to the ozone layer causes so many problems. At the higher levels of the atmosphere, ozone performs an essential function. It shields the surface of the earth from ultraviolet radiation from the sun. If ozone layer is damaged no organism can survive. The following are the steps being taken to limit this damage.
- We should minimize the use of vehicles.
- We should not encourage the burning of fossilic fuels.
- It is now mandatory for all the manufacturing companies to make CFC- free refrigerators throughout the world.
![]()
MP Board Class 10th Science Chapter 15 Additional Important Questions
MP Board Class 10th Science Chapter 15 Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
An environment consists of:
(a) Abiotic components
(b) Biotic components
(c) Both
(d) Not certain
Answer:
(c) Both
Question 2.
Waste could be:
(a) Abiotic components
(b) Biotic components
(c) Both
(d) Not certain
Answer:
(c) Both
Question 3.
Reduction of waste is important to:
(a) Make environmental balance proper.
(b) Make nearby beautiful
(c) waste can be transformed to useful products.
(d) Not clear
Answer:
(d) Not clear
Question 4.
Which one among following is non-biodegradable substance?
(a) Metal
(b) Wood
(c) Water
(d) Urea
Answer:
(a) Metal
Question 5.
Which among the following is a biodegradable waste?
(a) Wood
(b) Teflon pots
(c) Plastic cup
(d) Glass Cups
Answer:
(a) Wood
Question 6.
Most convenient ways of waste management is:
(a) 3 R : Reduce, reuse, recycle principle
(b) Production
(c) Use ban
(d) None
Answer:
(a) 3 R : Reduce, reuse, recycle principle
Question 7.
Which one is not a primary consumer?
(a) Grasshopper
(b) Deer
(c) Ant
(d) Leech
Answer:
(b) Deer
Question 8.
Humans are:
(a) Primary consumers
(b) Secondary consumers
(c) Top consumers
(d) All
Answer:
(d) All
Question 9.
Energy while going up in a trophic level is:
(a) Increased
(b) Decreased
(c) Remain same
(d) Can’t predict
Answer:
(b) Decreased
Question 10.
Pesticides are used to:
(a) Develop new varieties of crops.
(b) Kill unwanted plants.
(c) Kill insects and enrobes attacking crops.
(d) Save crops from birds.
Answer:
(c) Kill insects and enrobes attacking crops.
Question 11.
In a marine ecosystem producers are:
(a) Plants
(b) Sand
(c) Water
(d) Fishes
Answer:
(d) Fishes
Question 12.
Top consumer in a crop field is:
(a) Rat
(b) Hawk
(c) Snake
(d) (a) and (b)
Answer:
(b) Hawk
Question 13.
Effect of bio-magnification is maximum in:
(a) Primary consumers
(b) Secondary consumers
(c) Top consumers
(d) All of these
Answer:
(c) Top consumers
Question 14.
Which one of the following is artificial ecosystem?
(a) Jungle
(b) Town
(c) A pond
(d) Mountain
Answer:
(b) Town
Question 15.
Cockroach is a:
(a) Producer
(b) Primary consumer
(c) Secondary consumer
(d) Decomposer
Answer:
(d) Decomposer
Question 16.
Energy source of an ecosystem is:
(a) Producers
(b) Sunlight
(c) Top consumer
(d) Atmospheric gases
Answer:
(b) Sunlight
Question 17.
Link between primary and secondary consumers are:
(a) Autotrophs
(b) Omnivorous
(c) Carnivorous
(d) Herbivorous
Answer:
(a) Autotrophs
Question 18.
What is CFC?
(a) A waste
(b) A coolant gas
(c) A bakery product
(d) An organization
Answer:
(b) A coolant gas
Question 19.
UNEP stands for:
(a) United Nations Environment Programme.
(b) United Nations Entertainment Programme.
(c) United Nations Excellence Programme.
(d) Unlimited Nations Excellence Programme.
Answer:
(a) United Nations Environment Programme.
Question 20.
How many atoms of oxygen compose an ozone molecule?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer:
(c) 3
![]()
MP Board Class 10th Science Chapter 15 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Which gas of our environment help in formation of energy which we get from various sources?
Answer:
Oxygen.
Question 2.
How non-biodegradable objects effect environment?
Answer:
They pollute the environment.
Question 3.
Name two substances you think as most non-biodegradable.
Answer:
Plastic and chemicals like pesticides.
Question 4.
Which organisms help in biodegradation of a substance?
Answer:
Decomposers.
Question 5.
Write three common waste produced by our daily use.
Answer:
Soap and detergent, consumed food materials used paper and plastic garbage.
Question 6.
Can a big tree be treated as an isolated small ecosystem?
Answer:
Yes.
Question 7.
Give examples of natural ecosystem.
Answer:
Forests, pond, river etc.
Question 8.
Give examples of artificial ecosystem.
Answer:
Aquariums, Garden, town etc.
Question 9.
Can a ecosystem survive without autotrophs?
Answer:
No.
Question 10.
At which category parasite come in an ecosystem?
Answer:
Decomposers.
Question 11.
At which level rabbit and mole come in trophic level?
Answer:
Rabbit – Primary level.
Mole – Primary and decomposer level.
Question 12.
How much percentage of sunlight is converted into chemical energy by all autotrophs?
Answer:
1 %.
Question 13.
What percentage of average organic matter is present at each step of trophic level?
Answer:
10%.
Question 14.
What kind of plants comes at primary consumers level?
Answer:
Carnivorous plants.
Question 15.
How many minimum food chains can be observed in a food web?
Answer:
2 – 3.
![]()
MP Board Class 10th Science Chapter 15 Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is ecosystem? What are components of ecosystem?
Answer:
An ecosystem includes all of the living things in a given area, interacting with each other and also with their non-living environments.
Components of ecosystem:
An ecosystem has two types of components – biotic component (plants, animals and organisms) and abiotic component (weather, earth, sun, soil, climate, atmosphere).
Question 2.
What is abiotic component?
Answer:
All the non-living things make the abiotic component of an ecosystem. Air, water and soil are the abiotic components.
Question 3.
What is the importance of abiotic component?
Answer:
Air provides oxygen (for respiration), carbon dioxide (for photosynthesis), water (for metabolic activities) and soil is the reservoir of various nutrients which are utilized by plants. Through plants; these nutrients reach other living beings.
Question 4.
What is a biotic component?
Answer:
Ail living beings make the biotic component of an ecosystem. Examples: Green plants, animals and other living beings. Bacteria and fungi are examples of biotic component.
Question 5.
What is a food chain?
Answer:
A food chain is a simple representation of transfer of energy from the sun to different biotic components of an ecosystem. Sun is the ultimate source of energy. Green plants convert solar energy into chemical energy during photosynthesis. When an animal takes food, this energy is supplied to the animal and the process goes on.
Question 6.
What is food web and trophic level?
Answer:
Food web: In an ecosystem, there can be many food chains which are interlinked at various levels. Thus, many food chains form a network which is called food web.
Trophic level: Transfer of energy occurs through a food chain. Different levels in the food chain are called trophic level.
Question 7.
What are biodegradable substances?
Answer:
Substances which can be decomposed by microorganisms are called biodegradable substances. All the organic substances are biodegradable.
Question 8.
What are non-biodegradable substances?
Answer:
Substances which cannot be decomposed by microorganisms are non biodegradable. All inorganic substances are non-biodegradable. Many synthetic substances are also non biodegradable.
Question 9.
Give two differences between biodegradable and non bio-degradable.
Answer:
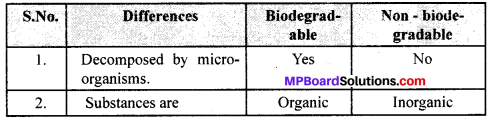
Question 10.
What is ozone layer? How it is protected from ultraviolet radiations?
Answer:
Ozone layer is also known as stratosphere. When ultraviolet radiations act on oxygen, the oxygen gets converted into ozone. Ozone layer works like a protective shield for living beings. The ozone layers guards from harmful ultraviolet rays of the sun.
![]()
MP Board Class 10th Science Chapter 15 Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is ecosystem? Explain in detail the components of ecosystem.
Answer:
An ecosystem includes all of living things in a given area, interacting with each other and also with their non living environments.
Components of ecosystem:
1. Biotic component (plants, animals and organisms) and abiotic components (weather, sun, soil, climate, atmosphere).
All living beings make the biotic component of an ecosystem. Examples: Green plants, animals and other living beings. Bacteria and fungi are examples of biotic component.
Green plants play the role of producers: Because they prepare the food by photosynthesis.
Animals and other living beings play the role of consumers; because they take food (directly or indirectly) from plants.
Bacteria and fungi play the role of decomposers; as they decompose dead remains of plants and animals so that raw materials of organisms can be channelized back to the environment.
2. Abiotic component: All the non-living things make the abiotic component of an ecosystem. Air, water and soil are the abiotic components.
Air provides oxygen (for respiration), carbon dioxide (for photosynthesis) and other gases for various needs of the living beings.
Water is essential for all living beings because all the metabolic activities happen in the presence of water.
Soil is the reservoir of various nutrients which .are utilized by plants. Through plants, these nutrients reach other living beings.
Question 2.
Explain in briefly about food chain.
Answer:
A food chain is a simple representation of transfer of energy from the sun to different biotic components of an ecosystem. Sun is the ultimate source of energy. Green plants convert solar energy into chemical energy during photosynthesis. When an animal takes food, this energy is supplied to the animal and the process goes on. A simple food chain can be shown as follows:
Producer → Primary consumer → Secondary consumer
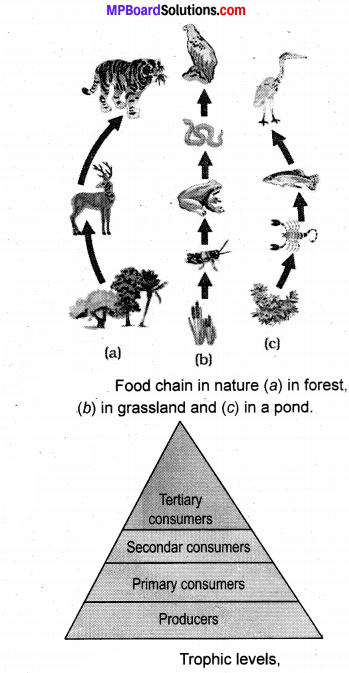
Real life cannot be as simple as a food chain shown above. In any ecosystem, there can be many food chains which are interlinked at various levels. Thus, many food chains form a network which is called food web.
Transfer of energy occurs through a food chain. Different levels in the food chain are called trophic level. Out of the energy consumed by an organism at a particular trophic level, 90% is utilized for its own need and rest 10% is left for the organism of the next trophic level. So. very little energy is tell for the organism which is at the tertiary level. Letus assume that a green plant makes 100% energy in the form of chemical energy, 90% of this energy would be utilized for its own purpose. This would leave just 10% energy for the primary consumer. Now, primary consumer shall also utilize 90% of energy which was consumed by it. This would leave just 1% energy for (10% of 100%) for the secondary consumer. By this logic, the tertiary consumer would get just 0.1% of energy which was originally made by the green plant. This is the reason, there can be just one or two organisms at the top of the food pyramid.
This explains why the population of producers is always the largest in an ecosystem; followed by the population of herbivores and then that of carnivores. Moreover, herbivores needs to eat many plants in its lifetime to fulfill its energy need. Similarly, carnivores needs to eat many herbivores in its lifetime.
Question 3.
What is ozone layer depletion?
Answer:
Ozone layer is also known as stratosphere. When ultraviolet radiations act on oxygen, the oxygen gets converted into ozone.
Ozone layer works like a protective shield for living beings. The ozone layers guards from harmful ultraviolet radiations from the sun.
Effect of CFCs: Use of CFCs (Chlorofluorocarbon) has damaged the ozone layer. As a result, the ozone layer has become thinner at certain parts. In 1987, the UNEP (United Nations Environment Programme) succeeded in forging an agreement among different nations to freeze the CFC production at 1986 level. Later, an agreement was signed among different nations to phase out CFCs. It is important to note that CFC is used in refrigerators and aerosol sprays. India is also a signatory of that agreement and thanks to the efforts by the United Nations and different environmentalists, the CFC emission has been put under some control.
Problems of waste disposal: During our day to day activities, we produce lot of waste. While some of the waste is biodegradable, a large chunk is composed of non-biodegradable substances. Plastic waste is a serious concern because plastic is non-biodegradable. We need to respect our environment and find out ways to reduce the burden on our environment.
![]()
MP Board Class 10th Science Chapter 15 NCERT Textbook Activities
Class 10 Science Activity 15.1 Pages No. 256,257
- You might have seen an aquarium. Let us try to design one.
- What are the things that we need to keep in mind when we create an aquarium? The fish would need a free space for swimming (it could be a large jar), water, oxygen and food.
- We can provide oxygen through an oxygen through an oxygen pump (aerator) and fish food which is available in the market.
- If we add a few aquatic plants and animals it can become a self- sustaining SySieni.’ Can you think how this happens? An aquarium is an example of a human-made ecosy stem.
- Can we leave the aquarium as such after we set it up?
- Why does it have to be cleaned once in a while? Do we have to clean ponds or lakes in the same manner? Why or why not?
Observations:
- Pesticides are the chemicals sprayed to kill the pests infecting crop and harming them. These are very harmful to living organisms. These get biologically magnified in the food chains and in the bodies, once entered. Organic farming methods and other natural methods can be adopted to reduce dependence on chemicals.
Class 10 Science Activity 15.2 Page No. 257
- While creating an aquarium did you take care not to put an aquatic animal which would eat others? What would have happened otherwise?
- Make groups and discuss how each of the above groups of organisms are dependent on each other.
- Write the aquatic organisms in order of who eats whom and form a chain of at least three steps.

- Would you consider any one group of organisms to be of primary importance? Why or why not?
Observations:
- CFC’s are responsible for depletion of ozone layer.
- These chloroflouro carbons were banned in various countries and since, then ozone hole has decreased in size.
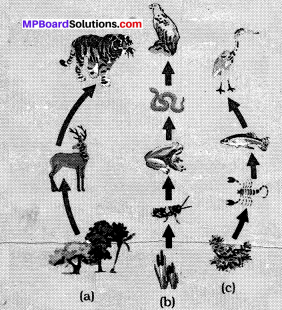
FIg. 15.1: Food chain ¡n nature (a) in forest, (b) in grassland and (c) in pond.
Class 10 Science Activity 15.3 Pages No. 244,245
- Newspaper reports about pesticide levels in ready made food items are often seen these days and some states have banned these products. Debate in groups the need for such bans.
- What do you think would be the source of pesticides in these food items? Could pesticides get into our bodies from this source through other food products too?
- Discuss what methods could be applied to reduce our intake of pesticides.
Observations:
- The materials that are non-biodegradable do not degrade easily. The hard materials that are not organic in nature take more time to decompose. The biodegradable materials turns soft and start decomposing and mixing in the soil. They completely change their form and structure.
- The waste from plants – fruits and vegetables change the fastest.
Class 10 Science Activity 15.4 Page No. 248
- Find out from the library, internet or newspaper reports, Which chemicals are responsible for the depletion of the ozone layer.
- Find out if the regulations put in place to control the emission of these chemicals have succeeded in reducing the damage to the ozone layer. Has the size of the hole in the ozone layer changed in recent years?
Observations:
- CFCs, SO2 other pollutant gases are responsible for the depletion of ozone layer.
- Non-biodegradable materials take years to decompose. Plastics are generally non-biodegradable and not decompose. The materials like paper, jute etc. easily degrade and do not harm the environment.
Class 10 Science Activity 15.5 Page No. 249
- Collect waste material from your homes. This could include all the waste generated during a day, like kitchen waste (spoils food, vegetable peels, used tea leaves, milk packets and empty cartons), waste paper, empty medicine bottles/strips/ bubble packs, old and tom clothes and broken footwear.
- Bury this material in a pit in the school garden or it there is no space available, you can collect the material in an old bucket/flower pot and cover with at least 15cm of soil.
- Keep this material moist and observe at 15-day intervals,
- What are the materials which change their form and structure over time?
- Of these materials that are changed, which ones change the fastest.1?”
Observations:
- We cannot leave the aquarium as it is as waste is generated in it by fishes which need to be cleaned up frequently so that it does not become toxic and harm the living organisms. The water bodies should also be cleaned up properly to ensure better living conditions. The aquatic life is affected by such kind of pollutions.
Class 10 Science Activity 15.6 Pages No. 249-250
- Use the library or Internet to find out more about biodegradable and non-biodegradable substances.
- How long are various non-biodegradable substances expected to last in our environment?
- These days, new types of plastics which are said to be biodegradable are available. Find out more about such materials and whether they do or do not harm the environment.
Observations:
Phytoplankton → Zoo planktons → Small fishes → Large fishes Aquatic Food Chain
- Phytoplankton are the autotrophs present in the water body and are of prime importance.
- The removal of any one group from the food chain will disturb the whole aquatic ecosystem.
Class 10 Science Activity 15.7 Page No. 252
- Find out what happens to the waste generated at home. Is there a system in place to collect this waste?
- Find out how the local body (Panchayat, municipal corporation, resident welfare association) deals with the waste. Are there mechanisms in place to treat the biodegradable and non-biodegradable wastes separately?
- Calculate how much waste is generated at home in a day.
- How much of this waste is biodegradable?
- Suggest ways of dealing with this waste.
Observations:
- The waste generated at home are differentiated into biodegradable and non-biodegradable materials. They are placed separately in the bins and thereafter, processed.
Class 10 Science Activity 15.8 Page No. 253
- Find out how the sewage in your locality is treated. Are there mechanisms in place to ensure that local water bodies are not polluted by untreated sewage?
- Find out how the local industries in your locality treat their wastes. Are there mechanisms in place to ensure that the soil and water are not polluted by this waste?
Observations:
- The amount of waste generated in homes and in the class-rooms is very high. At the end of the day. number of dustbins are fully filled which are thrown away in dump yard which too have become problematic. The wastes should be reused and amount generated should be reduced.
Class 10 Science Activity 15.9 Page No. 253
- Search the Internet or library to find out what hazardous materials have to be dealt with while disposing of electronic items. How would these materials affect the environment?
- Find out how plastics are recycled. Does the recycling process have any impact on the environment?
Observations:
- ETP (Effluent treatment plant) or STP (Sewage treatment plant) are used to treats the waste generated before it enters the water body. All the harmful treatments are removed and level of the toxic materials are reduced.
Class 10 Science Activity 15.10 Page No. 253
- Search the Internet or library to find out what hazardous materials have to be dealt with while disposing of electronic items. How would these materials affect the environment?
- Find out how plastics are recycled. Does the recycling process have any impact on the environment?
Observations:
- Electronic items are very hazardous as they are non-biodegradable and increase the mars on the earth.
- Plastic are recycled after melting again and-reforming into new shapes and products. This process create lots of pollution by emitting dangerous fumes and harms the environment.