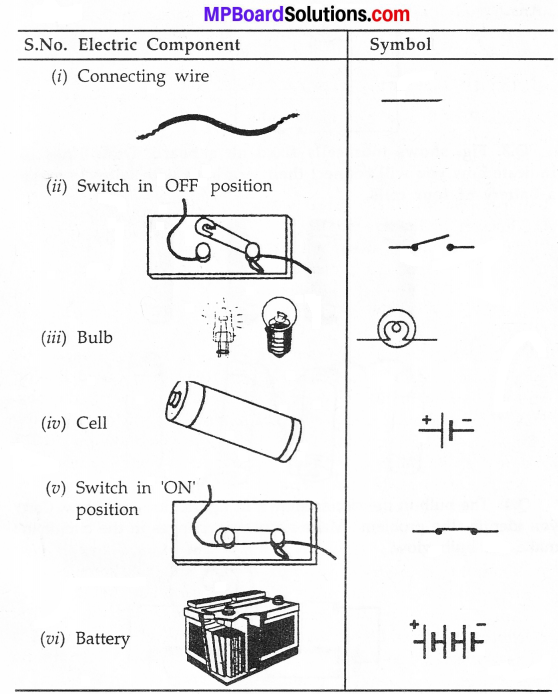
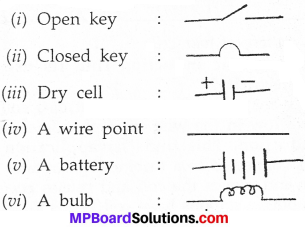
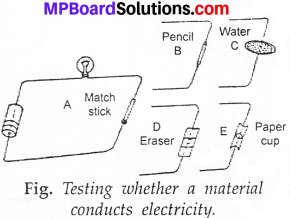
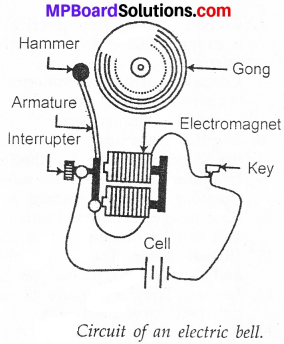
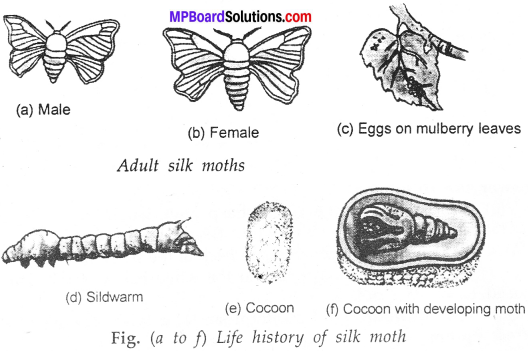
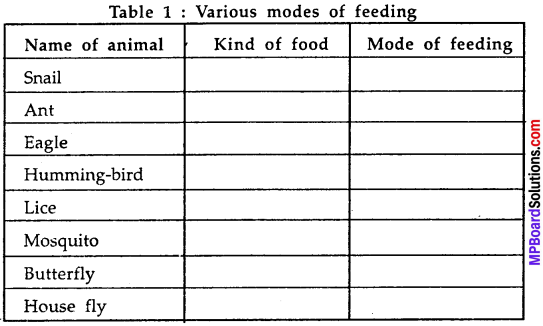
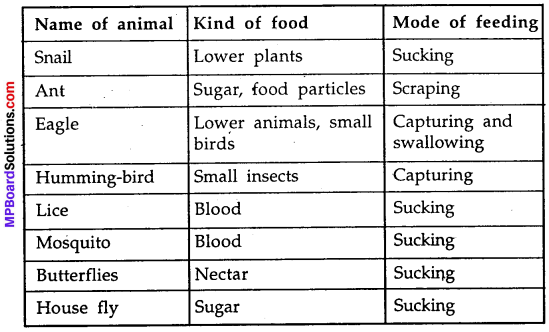
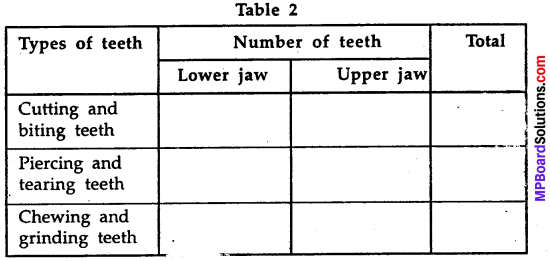
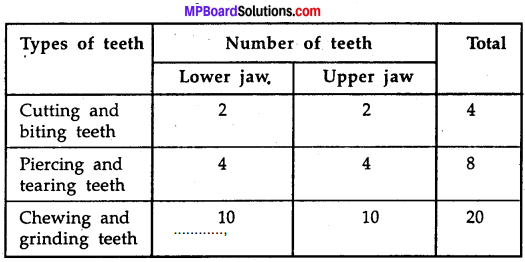
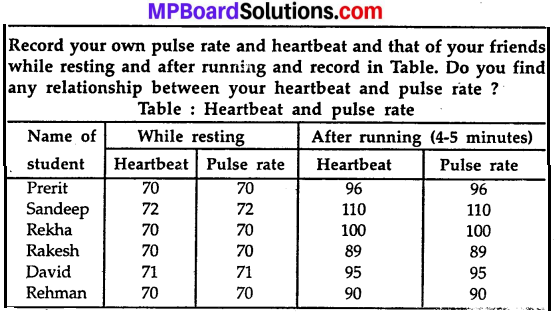
MP Board Class 7th Science Solutions Chapter 17 Forests: Our Lifeline
Forests: Our Lifeline Intex Questions
Question 1.
What would happen if forests disappear?
Answer:
- If forests disappear, the amount of carbon dioxide in air will increase, resulting in the increase of earth’s temperature.
- In the absence of trees and plants, the animals will not get food and shelter.
- In the absence of trees, the soil will not hold water which will cause floods.
- Deforestation will ending our life and environment. Think, what, we can do to preserve our forests.
Forests: Our Lifeline Text Book Exercises
Question 1.
Explain how animals dwelling in the forest help it grow and regenerate?
Answer:
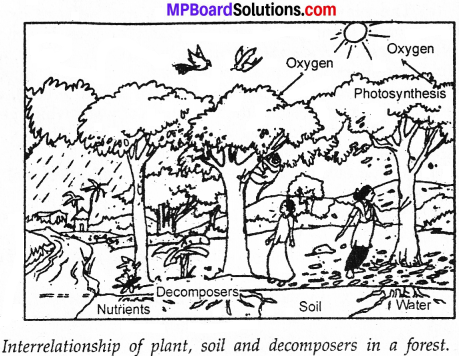
Animals help in growing and regenerating forests in many ways. Animals help in dispersing, seeds of certain plants. The decaying animal dung also provides nutrients to the seedling to plant. By this number of plants are growing which serve as a food for a number of herbivorous animals.
Herbivorous helps the carnivores to grow as they serve as food for them. So, the flora and fauna grows in the forests. Also, the animals work as the cleaning agents in the forest micro – organisms work on the death bodies of plants and animals and regenerate them.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain how forest prevent floods?
Answer:
If trees or widely we can say that forests are not present, rain will directly hit the ground and may cause the flood the area around it. Also, the heavy rain may damage the soil. Roots of trees and grasses basically bind the soil together, but in the absence of soil, they will be washed away or eroded.
The washed soil will get deposited in river and thus reduce the water carrying capacity of rivers. Which is the major causes of flood. Also, forests can absorb a lot of water. This also helps in preventing floods.
Question 3.
What are decomposers? Name any two of them. What do they do in the forest?
Answer:
The micro – organisms which convert the dead plants and animals to humus are known as decomposers. These micro – organisms play an important role in the forest. The any two decomposers are grubs and beetles. They clean the forests of the decaying dead bodies and replenishes the nutrient back to the forest soil.
Question 4.
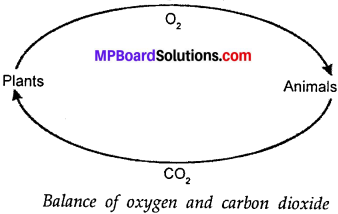
Explain the role of forest in maintaining the balance between oxygen and carbon – dioxide in the atmosphere?
Answer:
Plants release oxygen through the C02 photosynthesis. The Plants help to provide oxygen for animal respiration. They also maintain the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. That is why forests are called lungs.
Question 5.
Explain why there is no waste in a forest?
Answer:
The decomposers decompose the dead organisms. The decomposed matter is absorbed by plants as nutrients. Thus, there is no waste in a forest.
Question 6.
List five products we get from forests?
Answer:
We get following products from forests:
- Medicine
- Spice
- Wood
- Honey.
- Gum
Question 7.
Fill in the blanks:
- The insects, butterflies, honeybees and birds help flowering plants in ………………………..
- A forest is a purifier of ……………………………. and …………………………
- Herbs form the ……………………………… layer in the forest.
- The decaying leaves and animal droppings in a forest enrich the ………………………….
Answer:
- Pollination
- Water, air
- Lowest
- Humus.
![]()
Question 8.
Why should we worry about the conditions and issues related to forests far from us?
Answer:
We should be worried about deforestation, as it would lead to floods, increase in earth’s temperature, depriving animals of their habitats and soil erosion.
Question 9.
Explain why there is a need of variety of animals and plants in a forest?
Answer:
Variety of animals are necessary for their survival and maintenance of food chain. For example, grass is eaten by insects, which in turn, are eaten by the frog. The frog is consumed by snakes and snakes is eaten by eagles.
Thus, it forms a food chain. There are so many food chains in the forest. All of these are linked. If any one food chain is disturbed, it affects other food chains. Also, animals convert the death plants and animals into humus and increase the fertility of soil.
Question 10.
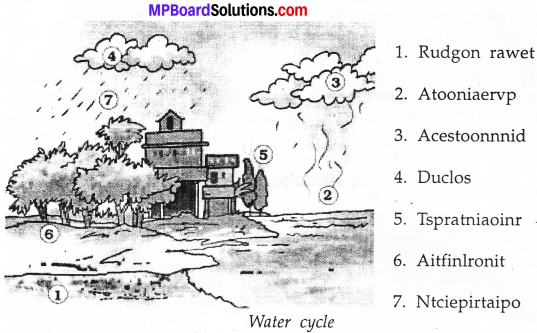
In figure, the artist has forgotten to put the labels and directions on the arrows. Mark the directions on the arrows and label the diagram using the following labels: clouds, rain, atmosphere, carbon dioxide, oxygen, plants, animals, soil roots, water table?
Answer:
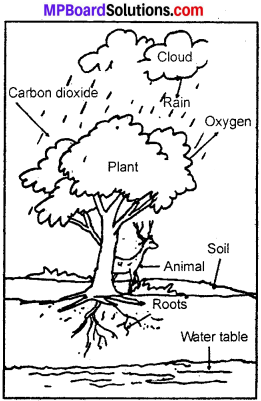
Question 11.
Which of the following is not a forest product?
1. Gum
2. Plywood
3. Sealing wax
4. Kerosene
Answer:
4. Kerosene.
Question 12.
Which of the following statements is not correct?
1. Forests protect the soil from erosion.
2. Plants and animals in a forest are not dependent on one another.
3. Forests influence the climate and water cycle.
4. Soil helps forests to grow and regenerate.
Answer:
2. Plants and animals in a forest are not dependent on one another.
Question 13.
Micro – organisms act upon the dead plants to produce?
1. Sand
2. Mushrooms
3. Humus
4. wood.
Answer:
3. humus.
![]()
Extended Learning – Activities and Projects
Question 1.
The Department of Environment is to decide whether some portion of a forest in your area could be cleared for a housing complex. Write a letter to the department explaining your point of view as a concerned citizen?
Answer:
Do yourself.
Question 2.
Visit a forest? Here is a list of points that would make your visit more fruitful?
- Make sure that you have permission to go into the forest.
- Make sure that you can find your way around. Get a map and go along with some one who is familiar with the area.
- Keep a record of the things you see and do. Observations make the visit interesting. Sketches and photographs are useful.
- You may record bird calls.
- Collect different kinds of seeds or hard fruits like nuts.
- Try to recognise various types of trees, shrubs, herbs, etc. Make lists of plants from different places in the forest and of different layers. You may not be able to name all the plants, but it is worth recording and seeing where they grow. Make a record of approximate heights of plants, crown shape, bark texture, leaf size, and flower colour.
- Learn to recognise the animal’s droppings.
- Interview the forest officials and the people of surrounding villages and other visitors.
- You must never collect birds eggs, and their nests should never be disturbed.
Answer:
Do yourself.
Forests: Our Lifeline Additional Important Questions
Objective Type Questions
Question 1.
Choose the correct alternative:
Question (a)
Plants give out during photosynthesis?
(a) carbon dioxide
(b) oxygen
(c) humus
(d) none of these.
Answer:
(b) oxygen
Question (b)
Interdependence of animals for food is called –
(a) food – order
(b) food – cycle
(c) food – chain
(d) none of these.
Answer:
(c) food – chain
![]()
Question (c)
Small trees and grass and shrubs from the –
Answer:
(a) Canopy
(b) Under stories
(c) Lowest canopy
(d) All of these
Answer:
(b) Under stories
Question (d)
Deforestation leads to
(a) Soil erosion
(b) Floods
(c) Both of these
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Both of these
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks:
- The branch part of a tree above the stem is known as the ……………………… of the tree.
- The micro – organisms which convert the dead plants and animals to humus are known as …………………………
- The plants help to provide ………………………….. for animal respiration.
- The plants maintain the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the …………………………
- The covered ground with decaying material acts like a ……………………………
- The root system helps water to seep down in the ……………………………
- Forests protect the soil from ………………………..
- Forests are the lifeline for the forest dwelling …………………………….
Answer:
- Crown
- Decomposers
- Oxygen
- Atmosphere
- Sponge
- Ground
- Erosion
- Communities.
![]()
Question 3.
Which of the following statements are true (T) or false (F):
- Forests cause rain on the earth.
- In a forests, the herbs form the lowest layer of the vegetation.
- The various components of the forest are not interdependent on one another.
- The forests keeps on growing and changing, and can regenerate.
- Soils helps forests to grow and regenerate.
- Forests influence climate, water – cycle and air quality.
- Forests is a renewable natural resources.
Answer:
- True
- Ture
- False
- True
- True
- True
- True.
Forests: Our Lifeline Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What do you mean by forest?
Answer:
Forest is a place hosting a number of animals and plants.
Question 2.
Name any two trees in forest?
Answer:
Sheesham, Neem.
Question 3.
Write any three things we get from forests?
Answer:
Gum, medicine and wood.
Question 4.
Which plants constitute canopy in forests?
Answer:
Tall and giant trees.
![]()
Question 5.
What is the basic unit of any food chain?
Answer:
Plants.
Question 6.
Write one food chain in forest?
Answer:
Grass → Insects → Frog → Snake → Eagle
Question 7.
How is forest environment?
Answer:
Forest environment is peaceful and a cool breeze is blowing.
Question 8.
Name some animals that live deep inside forest?
Answer:
Bison, Jackals, Boar, Elephants.
Question 9.
What is humus?
Answer:
Humus is a dark coloured substance which is formed from the dead bodies of plants and animals.
Question 10.
What happens if an animal dies in the forest?
Answer:
The dead animals become food for vultures, jackals, insects and crows.
Question 11.
How does forest help in preventing floods?
Answer:
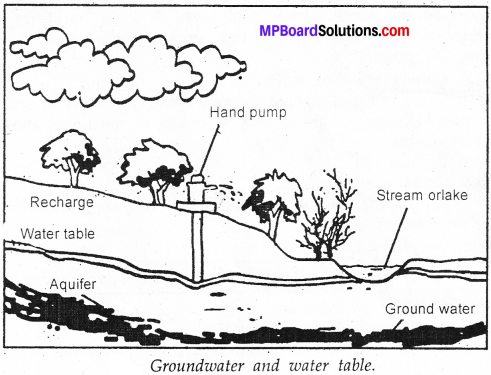
Forests absorb the rain .water in the soil and prevent the floods.
![]()
Question 12.
What is seed dispersal?
Answer:
The method by which plants scatter their seeds to reduce competition between off springs.
Question 13.
Define soil erosion?
Answer:
The weaving away of the soil by wind or water.
Question 14.
What do you mean by canopy?
Answer:
The branches of the tall trees look like a roof over the other plants in the forest is called canopy.
Question 15.
Define crown?
Answer:
Branch part of a tree above the stem is known as the crown.
Question 16.
What is deforestation?
Answer:
Cutting and destroying the forest is called deforestation.
Question 17.
What are the effects of deforestation?
Answer:
Floods, rising temperature, scarcity of flood and wood and disturbed flood chains are the results of deforestation.
![]()
Question 18.
What do you mean by afforestation?
Answer:
Planting more trees is called afforestation.
Question 19.
What would happen if it rains heavily in your town?
Answer:
There will be water logging or even flood. Everything will be in a mesh. No food, no water. No place, no stay.
Forests: Our Lifeline Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Define soil erosion?
Answer:
Removal of fertile top layers of earth (soil) is called soil erosion. The soil erosion can be brought about by various agents like – water, wind, glaciers and ocean waves. Erosion occurs in both wet and arid regions. The various human activities like falling of trees, over – cropping and improper tilling accelerate soil erosion. The soil erosion can lead to floods.
Question 2.
What are the major factors that lead to soil erosion? Name them?
Answer:
The major factors that lead to soil erosion are the following:
- Overgrazing by livestock
- Deforestation
- Over cultivation
- Poor irrigation facilities
- Water logging
- Shifting cultivation.
Question 3.
Write about the dependence of animals on plants?
Answer:
Dependence of Animals on Plants:
- Plants produce food by the process of photosynthesis and animals depend directly or indirectly on them for food.
- Plants produce oxygen during photosynthesis and animals use this oxygen for respiration.
- Plants act as habitat for the animals dwelling on trees.
![]()
Question 4.
Write about the dependence of plants on animals?
Answer:
Dependence of Plants on Animals:
- Animals produce carbon dioxide during respiration which is released in the atmosphere. Plants use this oxygen for preparing food.
- A number of insects, birds and bats help in pollination.
- Some animals help in dispersal of fruits and seeds.
Question 5.
How forests help in bringing rain?
Answer:
Trees absorbs water from the soil through their roots. They then release the excess of water through the process of transpiration in the form of water vapours. These water vapours form clouds and clouds bring rain.
Question 6.
How are forests useful to us?
Answer:
The forests are very useful to us for the following reasons:
- They conserve soil and water.
- They are helpful in causing rains.
- They give us food and fruit.
- They are the natural habitats of animals.
- They help in the maintenance of ecological balance.
![]()
Question 7.
Write a short note on deforestation?
Answer:
Deforestation is another important cause which brings about soil erosion. Deforestation leads to depletion of water vapour in the atmosphere so which in turn adversely affects the formation of rain bearing clouds and consequently the rainfall. In the absence of adequate rainfall, the soil dries up and its nutrient value is affected.
The decrease in rainfall affects the growth of plants and trees, thus leads to the formation of deserts. When there is no plant cover over the earth, it becomes naked. When rain falls over this naked earth, the water does not percolate down the earth and washes away. Similarly, strong winds also take away the top soil, thus causing soil erosion.
Question 8.
In which layer of the soil would you find humus? What is its importance to the soil?
Answer:
Humus is found in the top of layer of soil. The presence of humus ensures that the nutrients of the dead plants and animals are released into the soil. From there, these nutrients are again absorbed by the roots of the living plants.
Forests: Our Lifeline Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
How we can conserved the forests?
Answer:
- Unplanned and indiscriminate deforestation must be stopped.
- Forest should not be over – exploited.
- Use of wood as fuel should be discouraged.
- Plant new fast growing trees.
- Protect forest from fires, insects and diseases.
- Protect national parks, wildlife sanctuaries or biosphere reserves.
- Follow the guidelines of international organizations like W.W.F. and UNESCO for forest conservation.
![]()
Question 2.
Write the uses of forests?
Answer:
Forests are useful to us for the following reasons:
- Forests provide timber for building and furniture.
- Forests keep the environment cool and increase the chances of rainfall.
- The roots of the trees hold the soil firmly thereby checking soil erosion.
- Forests provide habitat to a variety of wild plants and animals.
- The plants of forests use CO2 and release oxygen in photosynthesis, thereby maintaining balance of gases in atmosphere.
- Forests provide animal products such as honey, lac, wax, etc.
- Forests provide plant products such as fruits, nuts, gums, resins, fibres, medicines, essential oil (like sandal wood), etc.
- They are involved in the absorption of water which percolates in the soil, thereby becoming a part of the groundwater.
Question 3.
What will happen if forests disappear?
Answer:
- Soil erosion will increase which will affect soil fertility and productivity.
- Air pollution will increase which will ultimately threaten thirty existence of life on the Earth.
- Unpredictable changes will take place in weather and climate.
- Reduction in rainfall.
- Reduction in recharging of existing water resources
- Wildlife may also disappear along with forest.
- Shortage of forest products.
- Disturbance in ecological balance.
- Increase in temperature
- Global warming may reach in flooding of low lying area.
Question 4.
Draw a figure to show the difference between canopy and under stories?
Answer:
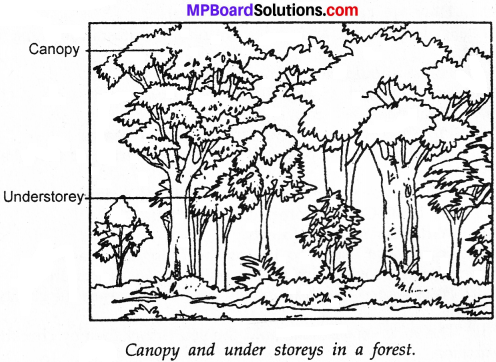
Question 5.
Draw a figure to show in the dependence of plant, soil and decomposers in a forest?
Answer: