MP Board Class 7th Science Solutions Chapter 16 Water: A Precious Resource
Activities
Activity – 1
Given here is the rainfall map of India (Fig.) It gives the average annual rainfall in different regions of our country?
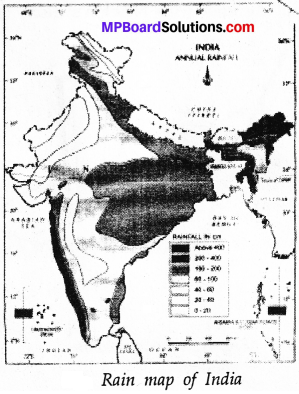
Question 1.
Are you blessed with sufficient rainfall?
Answer:
No.
Question 2.
Is there sufficient water available in your area throughout the year?
Answer:
Yes.
Question 3.
Can we attribute this to mismanagement of water resources?
Answer:
Yes.
Water: A Precious Resource Text Book Exercises
Question 1.
Mark T if the statement is true and F if it is false:
- The freshwater stored in the ground is much more than that present in the rivers and lakes of the world.
- Water shortage is a problem faced only by people living in rural areas.
- Water from rivers is the only source for irrigation in the fields.
- Rain is the ultimate source of water.
Answer:
- True
- False
- False
- True
![]()
Question 2.
Explain how groundwater is recharged?
Answer:
The ground water get recharged through the process of infiltration. The infiltration means seeping in water from rain, rivers and lakes into the empty spaces and crack deep below the ground.
Question 3.
There are ten tubewells in a lane of fifty houses. What could be the long term impact on the water table?
Answer:
The effect on the water table depends on the replenishment of the underground water. As only five families will share a tubewell, the water used for daily domestic purpose will not effect the water table as such. But if there is acute shortage of rains the water used by the families will not replenished and water table will fall down.
Question 4.
You have been asked to maintain a garden. How will you minimise the use of water?
Answer:
By collecting rain water. Also to minimise the wastage of water we will use the new technique of drip irrigation, which directly throws water at the base of plants.
![]()
Question 5.
Explain the factors responsible for the depletion of water table?
Answer:
Increasing population:
Increasing population creates demand for construction of houses, shops, offices, roads and pavements. This decreases the open areas like parks, and playgrounds. This, in turn, decreases the seepage of rainwater into the ground. What could be the consequence? Recall that a pukka floor does not allow water to seep in easily, while in a grass lawn water seeps through in no time.
Moreover a huge amount of water is required for construction work. Often groundwater is used for this purpose. So, on the one hand we are consuming more groundwater, and on the other we are allowing lesser water to seep into the ground. This results in depletion of water table. In fact, the water table in some parts of many cities has gone down to alarmingly low levels.
Increasing industries:
Water is used by all the industries. Almost everything that we use needs water somewhere in its production process. The number of industries is increasing continuously. Water used by most of the industries is drawn from the ground.
Agricultural activities:
A majority of farmers in India depend upon rains for irrigating their crops. Irrigation systems such as canals are there only in a few places. Even these systems may suffer from lack of water due to erratic rainfall. Therefore, farmers have to use groundwater for irrigation. Population pressure on agriculture forces increasing use of groundwater day by day. This results in depletion of water table.
Question 6.
Fill in the blanks with the appropriate answers:
- The water bearing layer of the earth is …………………………
- The process of water seepage into the ground is called ………………………
- The water bearing layer of the earth is ………………………
- The process of water seepage into the ground is called ………………………….
Answer:
- Well and handpumps
- Solid (ice), liquid (water), gas (water vapour)
- Aquifer
- Infiltration.
![]()
Question 7.
Which one of the following is not responsible for water shortage?
1. Rapid growth of industries
2. Increasing population
3. Heavy rainfall
4. Mismanagement of water resources.
Answer:
3. Heavy rainfall.
Question 8.
Choose the correct option. The total water –
1. In the lakes and rivers of the world remains constant.
2. Under the ground remains constant.
3. In the seas and oceans of the world remains constant.
4. Of the world remains constant.
Answer:
3. In the seas and oceans of the world remains constant.
Question 9.
Make a sketch showing groundwater and water table? Lab T it?
Answer:
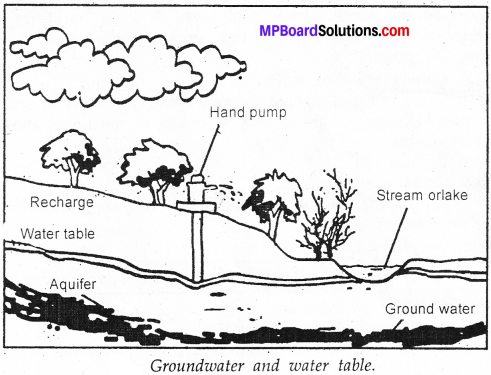
Extended Learning Activities and Projects
Question 1.
Role play?
You are a water detective in your school? You have a term of six members? Survey the campus and make a note of the following:
- Total number of taps
- Number of taps leaking
- Amount of water wasted due to leakage
- Reasons of leakage
- Corrective measures taken.
Answer:
Do yourself.
![]()
Question 2.
Groundwater pumped out?
Try to find out if there are any hand pumps in your neighborhood. Go to the owner or the users of a few of these and find out the depth at which they struck water? If there are any differences/think of the probable reason? Write a brief report and discuss it in your class. If possible, visit a place water boring is going on to install a hand pump? Watch the process carefully and find out the depth of the water table at that place?
Answer:
Do yourself.
Question 3.
Catching rainwater – Traditional methods? Form groups of 4 to 5 students in the class and prepare a report on the various traditional ways of water harvesting. If possible, use the following web link: www.rainwaterharvesting.org.?
Answer:
Do yourself.
Question 4.
Conservation of water? Carry out a campaign to conserve water at home and in the school. Design posters to remind others of the importance of water resources?
Answer:
Do yourself.
Question 5.
Create a logo? Hold a competition to create a logo or a symbol depicting water scarcity?
Answer:
Do yourself.
Water: A Precious Resource Additional Important Questions
Objective Type Questions
Question 1.
Choose the correct alternative:
Question (a)
…………………………. is celebrated as the “world water day”?
(a) 22 March
(b) 20 March
(c) 22 April
(d) 20 April.
Answer:
(a) 22 March
Question (b)
Water is a Unique substance because?
(a) It is consumable
(b) It is colourless
(c) It exits in all three states
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(c) It exits in all three states
![]()
Question (c)
Year …………………….. was observed as the International Year of fresh water to make people aware of this dwindling natural resource?
(a) 2002
(b) 2003
(c) 2004
(d) 2005.
Answer:
(b) 2003
Question (d)
The earth’s surface is covered with water about?
(a) 70%
(b) 71%
(c) 72%
(d) 73%.
Answer:
(b) 71%
Question (e)
Main source of water on earth is –
(a) rain
(b) snow
(c) glaciers
(d) all the above.
Answer:
(a) rain
Question (f)
One of these is not a source of surface water –
(a) lake
(b) rain
(c) river
(d) spring.
Answer:
(d) spring.
![]()
Question (g)
This is level …………………. of ground water?
(a) sea level
(b) rain
(c) aquifer
(d) (b) and (c).
Answer:
(d) (b) and (c).
Question (h)
Water has maximum density at –
(a) 0°C
(b) 4°C
(c) 98.4°C
(d) 100°C.
Answer:
(b) 4°C
Question (i)
Water is –
(a) a mixture
(b) a compound
(c) an element
(d) none of these.
Answer:
(b) a compound
Question (j)
The purest form of natural water is –
(a) river
(b) sea
(c) rain
(d) spring.
Answer:
(c) rain
Question (k)
Common salt content of sea water is –
(a) 1.5%
(b) 2.5%
(c) 3.5%
(d) 10%.
Answer:
(b) 2.5%
![]()
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks:
- The amount of water recommended by the United Nations for drinking, cooking, washing and maintaining proper hygiene is a minimum of ……………………… liters per person per day.
- The water that is fit for use is ………………………..
- Solid form of …………………. water, and …………… , is present as ice caps at the poles of the earth.
- ……………………. water is present in lakes, oceans, rivers and even underground.
- The process of seeping of water into ground is called ………………………..
- Water in the aquifiers can be usually pumped out with the help of …………………………. or ………………………..
- Increase in population, industrial and agricultural activities are some common factors affecting ……………………….. table.
- The rain water can be used to recharge the …………………………
- Bhujpur in the Kutch area of ………………….. has a very erratic rainfall.
- ……………………… irrigation is a technique of watering plants.
Answer:
- 50
- Fresh water
- Snow, ice
- Liquid
- Infiltration
- Tubewells, handpumps
- Water
- Groundwater
- Gujarat
- Drip.
![]()
Question 3.
Which of the following statements are true (T) or false(F):
- Water is essential for all living beings.
- Water exists in three forms.
- There is an uneven distribution of water.
- Water shortage has become a matter of concern throughout the world.
- The gaseous form is the water vapour present in the air around us.
- Many villages do not have water supply system.
- The water – table does not varies from place to place.
- Water drawn from under the ground gets replenished by seepage of rain water.
- Rainwater harvesting is not necessary.
- Rajasthan is a hot and dry place.
- Water allows sunlight to pass through it.
- Pure water has no taste.
Answer:
- True
- True
- True
- True
- True
- True
- False
- True
- False
- True
- True
- True.
Water: A Precious Resource Very short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is the most important property of water?
Answer:
The most important property of water is its ability to dissolve various substances. Hence, it is called a universal solvent.
Question 2.
What are the sources of water?
Answer:
The two main sources of natural water are surface water and underground water or subsoil water.
![]()
Question 3.
What are the different states of water?
Answer:
The different states of water are solid, liquid and gas.
Question 4.
What are the characteristics of pure water?
Answer:
The pure water is colourless, odourless, tasteless and transparent.
Question 5.
What do you mean by a resource?
Answer:
Materials that we get from the environment to meet our needs are called resources.
Question 6.
A part from water, what are the other natural resources?
Answer:
A part from water, air, forests, minerals and fossilfuels are natural resources.
Question 7.
What is the percentage of water that is available for human beings?
Answer:
Only a tiny fraction about 0.01% of total water is used by human beings.
![]()
Question 8.
List the sources of water for your daily use?
Answer:
Sources of water for our daily use are well, lakes, rivers and ponds.
Question 9.
Define saturated solution?
Answer:
A saturated solution of a solute at a given temperature is a solution which contains as much of the solute as it can dissolve at that temperature.
Question 10.
Define unsaturated solution?
Answer:
If a solution contains less of the solute than what it can dissolve at that temperature, then it is called all unsituated solution.
Question 11.
Name three forms of water?
Answer:
Three forms of water are solid, gaseous and liquid.
Question 12.
Which is universal solvent?
Answer:
Water.
![]()
Question 13.
What is the percentage of water (by weight) that an average elephant body has?
Answer:
An average elephant body has 80% water by weight.
Question 14.
If you have sample of tap water, well water and sea water, which do you think has the highest amount of salts?
Answer:
Sea water has highest amount of salts.
Question 15.
List the salts that can be obtained from the sea?
Answer:
- Common salt (NaCl)
- Sodium bromide (NaBr)
- Potassium iodide (Kl)
- Calcium salts.
Question 16.
Which sea has the highest salinity?
Answer:
Dead sea has the highest salinity.
Question 17.
Name two gaseous fuels which are prepared from water?
Answer:
Water gas and hydrogen gas.
Question 18.
Define water table?
Answer:
The depth at which water is found at a particular place is called water table.
Question 19.
What is Bawri?
Answer:
Bawri is a traditional way of collecting water.
Question 20.
What is potable water?
Answer:
The water which is fit for drinking is called potable water.
![]()
Question 21.
Define salinity of water?
Answer:
Water which has salts dissolved in it and is salty in taste is called salinity of water.
Question 22.
Define water cycle?
Answer:
The water from the earth reaches the atmosphere and from there it ultimately comes back to land, this is known as water cycle.
Question 23.
How does water cycle help in maintaining global climate?
Answer:
Liquid water on heating turns into water vapours. Water vapour on cooling again forms liquid water. This change of state of water over and over again makes the cycle in nature.
Question 24.
How are clouds formed?
Answer:
Water vapours being lighter and rise up in the atmosphere. At the upper layer of the atmosphere, where the temperature is lower. The vapours get condensed into tiny water droplets and clouds are formed.
![]()
Question 25.
Which unwanted material could be present in the water that you get from your local water supply?
Answer:
The unwanted materials in our water supply are dust particles, germs, bacteria and many other materials as impurities.
Question 26.
Define water harvesting?
Answer:
Most of the water that we get as rainfall just flows aways. This is a waste of precious natural resource. The rainwater can be used to recharge the groundwater. This is known as water harvesting or rainwater harvesting.
Question 27.
Define drip irrigation?
Answer:
Drip irrigation is a technique of watering plants by making use of narrow tubings which deliver water directly at the base of the plant.
Water: A Precious Resource Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Wrote a short note on source of water?
Answer:
Water is available to us through various sources. Rain water, lake Water, river water, sea water are some of the sources. Natural water from all these sources contain some impurities these are the dissolved minerals and salts. Apart from that, they contain some insoluble impurities too.
Question 2.
List the sources of water on the earth?
Answer:
There are two main sources of natural water:
- Underground water
- Surface water.
- Underground Water: There are mainly two types of underground water –
- (a) Well water
- (b) Spring water.
2. Surface water:
It is of three types:
- Rain water
- River and lake water
- Sea water.
![]()
Question 3.
Write a short rote an river water?
Answer:
The river water is mainly due to rain or due to melting of snow on the mountains. The river water usually carries some suspended impurities and some soluble impurities. The soluble impurities are the dissolved salts and minerals. Apart from that they may carry certain micro – organisms and organic matter due to contamination.
Question 4.
Write a short note on sea water?
Answer:
Sea water is the largest source of natural water. But it is not fit either for drinking or for irrigation directly. This is because it contains a large number of dissolved salts of chlorides, bromides, iodides, sulphates and carbonates. The sea water is a rich source for common salt. It is recovered from sea water by evaporation and then is purified to remove the other impurities present.
Question 5.
Write a short note an underground water?
Answer:
Water present underneath the earth is tapped as it is an excellent source of pure drinking water. We usually dig wells. Depending on the geographical conditions of the place, the depth in which water is available is estimated. Well water contains some dissolved impurities.
Again the nature of the impurities depends on the geographical conditions. We also get water from springs under the earth. Such springs usually contain some dissolved mineral salts. However the spring water does not contain suspended impurities as it comes from deep under the earth.
Question 6.
Write a short note on rain water?
Answer:
It is the purest form of natural water available to us. Though the first few droplets of rain bring along with them some dust particles and micro-organisms, the later drops are free from impurities.
![]()
Question 7.
What are the properties of water?
Answer:
Properties of Water:
- Pure water is colourless, odourless and tasteless.
- Pure water freezes at 0 degree Celsius and boils at 100 degree celsius.
- The density of water is 1 g/cc. It means that 1 cc of water at 1 degree Celsius weighs 1 gram.
Question 8.
What are the different ways by which water vapour is put into the atmosphere?
Answer:
The different ways by which water vapours put into atmosphere are as follows:
- Factories and thermal stations produce a lot of steam and put is into the atmosphere.
- Water in ponds, rivers and lakes, ocean gets evaporated due to atmospheric heat.
- Plants throughout water vapours during respiration.
Question 9.
What makes the sea water so saline?
Answer:
Rivers flowing from different places bring water containing dissolved salts and minerals into the sea. Sea water is continuously evaporated by the heat of the sun. This evaporated water forms clouds and again fall on the earth as rain. This rain water again dissolves salts into it and goes into the sea. Thus the amount of salts in sea water goes on increasing.
![]()
Question 10.
How will you show that saline water is not fit for agriculture?
Answer:
Take two healthy plants of same type. Water both the plants separately one with ffesh water and other with saline water. Continue to water similarly for seven days and observe. The plant which was watered with saline water wilts. This shows that saline water is not fit for plants or agriculture.
Water: A Precious Resource Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Draw a diagram to show water cycle?
Answer:
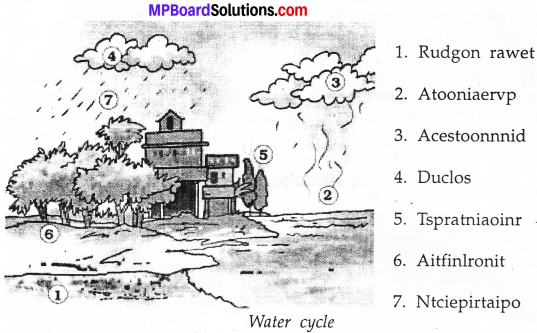
Question 2.
What are the causes of water scarcity?
Answer:
Causes of Water Scarcity:
- Overpopulation
- Over – irrigation for agriculture
- Water pollution
- Climatic change and variability
- Indiscriminate cutting of forest
- Increase in demand for water
- Misuse of water
- Poor water resource management
- Disputes between the states for sharing water
- Destruction of natural water reservoirs.
![]()
Question 3.
What are the methods to prevent water scarcity? Ans. Methods to prevent water scarcity:
- Control population by adopting small family norms
- Prevent misuse and wastage of water
- Prevent water pollution
- Replace large flush tanks with smaller ones.
- Build dams, bunds and tanks to store rainwater.
- Replace large flush tanks with smaller ones.
- Recharge underground water
- Recycle waste water for gardening
- Follow drip irrigation or low water sprinklers for agriculture.
Question 4.
What are the effect of water scarcity on the life of people?
Answer:
Effect of water scarcity on the life of the people:
- Long walk to fetch water.
- Have to pay high price for buying water.
- Low scope for generating employment.
- Uncertainty over availability of water for agriculture.
- Area will remain backward and neglected.
- Increase incidents of crime.
- More incidence of diseases due to poor sanitary conditions.
- Fall in the productivity of animals.