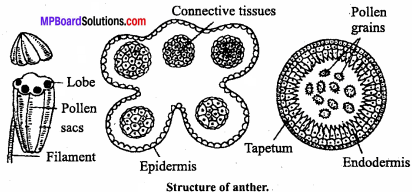
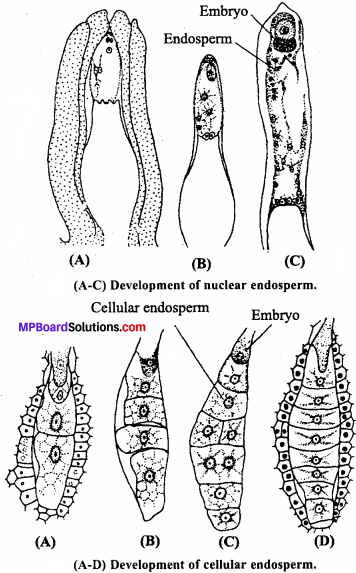
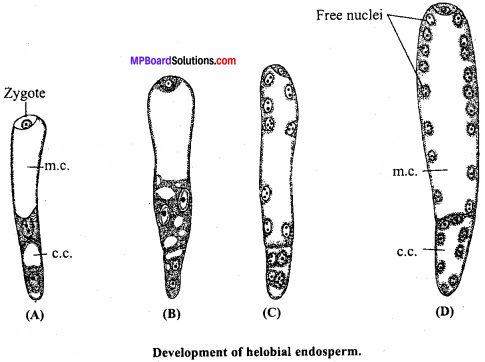
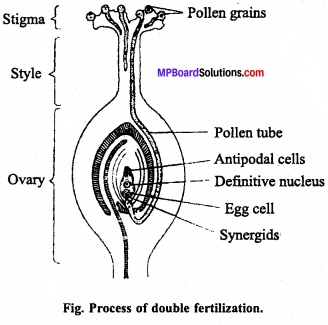
MP Board Class 12th Special Hindi सहायक वाचन Solutions Chapter 7 भारतीय गायिकाओं में बेजोड़ लता मंगेशकर (लेख, कुमार गंधर्व)
भारतीय गायिकाओं में बेजोड़ लता मंगेशकर अभ्यास प्रश्न
प्रश्न 1.
लता के गायन की विशेषताएँ लिखिए। (2016)
अथवा
भारतीय गायिकाओं में बेजोड़ लता मंगेशकर के गायन की विशेषताएँ लिखिए तथा बताइए कि लताजी की लोकप्रियता का मुख्य मर्म क्या है? (2009)
उत्तर:
लेखक का स्पष्ट मत है कि लता के जोड़ की गायिका हुई ही नहीं है। लता के कारण चित्रपट संगीत को और मनोरंजन की दुनिया को विलक्षण लोकप्रियता प्राप्त हुई है, यही नहीं लोगों का शास्त्रीय संगीत की ओर देखने का दृष्टिकोण भी बदला है। लता के गाने की मुख्य विशेषताएँ उसका ‘गानपन’ है। लता के गाने की एक और विशेषता है, उसके स्वरों की निर्मलता। लता के स्वरों में कोमलता और मुग्धता है। ऐसा अनुभव होता है कि लता का जीवन की ओर देखने का जो दृष्टिकोण है वही उसके गायन की निर्मलता में झलक रहा है। लता के गाने की एक और महत्त्वपूर्ण विशेषता है उसका ‘नादमय उच्चार’। उसके गीत के किन्हीं दो शब्दों का अन्तर स्वरों के आलाप द्वारा बड़ी सुन्दर रीति से भरा रहता है और ऐसा प्रतीत होता है कि वे दोनों शब्द विलीन होते-होते एक-दूसरे में मिल जाते हैं। यद्यपि गाने में यह बात पैदा करना बहुत कठिन है, परन्तु लता के साथ यह अत्यन्त सहज और स्वाभाविक ही बैठी है। वास्तव में,चित्रपट संगीत के क्षेत्र की लता साम्राज्ञी हैं।
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
“लता ने करुण रस के साथ उतना न्याय नहीं किया है। बजाए इसके, मुग्ध श्रृंगार की अभिव्यक्ति करने वाले गाने लता ने बड़ी उत्कटता से गाए हैं।” इस कथन से आप कहाँ तक सहमत हैं?
उत्तर:
लता द्वारा चित्रपट :
संगीत के क्षेत्र में गाये गये गीतों पर यदि दृष्टि डाली जाये तो एक पल को यह कथन उचित ही प्रतीत होता है कि “लता ने करुण रस के साथ उतना न्याय नहीं किया है। बजाए इसके, मुग्ध श्रृंगार की अभिव्यक्ति करने वाले गाने लता ने बड़ी उत्कटता से गाए हैं”,किन्तु हमें यह नहीं भूलना चाहिए कि चित्रपट-संगीत की दुनिया में यह अधिकार गायक अथवा गायिका के पास नहीं होता कि उसे किस प्रकार के गाने गाने को मिलें, अपितु संगीत दिग्दर्शक अपनी पसन्द से गायक-गायिकाओं को गाने गाने के लिए चुनकर देते हैं। अतः, इसे लता की व्यावसायिक मजबूरी अथवा सीमा से उत्पन्न स्थिति ही कहा जाये तो बेहतर होगा कि स्वर कोकिला को करुण रस को व्यक्त करने वाले गाने उतनी संख्या में नहीं मिल सके कि वह इस रस में भी अपने कौशल का प्रभावशाली प्रदर्शन कर पातीं, तथापि उन्हें जब-जब भी अवसर मिला उन्होंने करुण रस के साथ भी पूरा न्याय किया है।
उपर्युक्त चर्चा से स्पष्ट है कि गायकी के क्षेत्र में लता की विविधताएँ असीमित हैं और उनके कौशल का लोहा संगीत प्रेमी भली प्रकार मानते हैं। यह मात्र संयोग ही है कि जिन भी संगीत दिग्दर्शकों के साथ उन्होंने कार्य किया है,वे लता को करुण रस की अभिव्यक्ति वाले गाने पर्याप्त मात्रा में गाने को नहीं दे सके।
प्रश्न 3.
शास्त्रीय संगीत और चित्रपट संगीत में अन्तर बतलाइए। (2012)
उत्तर:
लेखक के अनुसार शास्त्रीय संगीत और चित्रपट संगीत के मध्य किसी भी प्रकार की तुलना करना बेमानी है। उसका कारण यह है कि शास्त्रीय संगीत और चित्रपट संगीत में तुलना हो ही नहीं सकती। जहाँ गंभीरता शास्त्रीय संगीत का स्थायी भाव है वहीं द्रुत लय और चपलता चित्रपट संगीत का मुख्य गुणधर्म है। चित्रपट संगीत का ताल प्राथमिक अवस्था का ताल होता है, जबकि शास्त्रीय संगीत में ताल अपने परिष्कृत रूप में पाया जाता है। चित्रपट संगीत में आधे तालों का उपयोग किया जाता है। उसकी लयकारी बिल्कुल भिन्न होती है, आसान होती है। यहाँ गीत और आघात को अधिक महत्त्व दिया जाता है तथा सुलभता और लोच को अग्र स्थान पर रखा जाता है। चित्रपट संगीत द्वारा लोगों की अभिजात्य संगीत से जान-पहचान होती है। वास्तव में,चित्रपट संगीत का तंत्र ही अलग है। यहाँ नवनिर्मित की बहुत गुंजाइश है।
प्रश्न 4.
“चित्रपट संगीत ने लोगों के कान बिगाड़ दिए हैं।” आप इस कथन से कहाँ तक सहमत हैं?
उत्तर:
यदि यह बात कही जाये तो कोई अतिशयोक्ति न होगी कि 70-80वें दशक तक का चित्रपट संगीत, शास्त्रीय संगीत की दृष्टि से भी उच्च कोटि का था, किन्तु उसके बाद के चित्रपट संगीत में हास का दौर प्रारम्भ हुआ जो आज तक जारी है। बीच-बीच में कुछेक फिल्मों के संगीत में अवश्य ही पुराने दौर के गीत-संगीत की झलक दिखाई पड़ी,किन्तु कमोबेश स्थिति बद-से-बदतर होती चली गयी। नये दौर के चित्रपट संगीत में न तो पहले जैसी कर्णप्रिय धुनें थीं और न ही संगीत दिग्दर्शकों की व्यक्तिगत सोच ही परिलक्षित होती थी। नित्य नये विकसित वाद्ययंत्रों उच्चकोटि की लाजवाब प्रौद्योगिकी के बाद भी आज के दौर का चित्रपट संगीत अपनी गहरी और लम्बी छाप नहीं छोड़ सका है।
वर्तमान में,चित्रपट संगीत का आलम यह है कि कोई गाना आज बनता, कल सुना जाता है और परसों तक लोग उसे भूल जाते हैं। इस दौर का संगीत कानफाडू वाद्य यन्त्रों की सहायता से श्रोता के शरीर को तो हो सकता उत्तेजित कर सका हो,किन्तु किसी भी अर्थों में वह सुनने वालों के मन-मस्तिष्क में नहीं उतर सका है। इस स्थिति का एक बड़ा दुष्परिणाम यह भी हुआ है कि आजकल का श्रोता इस कानफाड़ चित्रपट संगीत को सुन-सुनकर अच्छे संगीत की समझ खो चुका है।
उपर्युक्त चर्चा से स्पष्ट है कि चित्रपट संगीत ने लोगों के कान बिगाड़ दिए हैं और उन्हें शास्त्रीय संगीत नीरस और उबाऊ प्रतीत होने लगा है।
प्रश्न 5.
संगीत के क्षेत्र को विस्तीर्ण क्यों कहा गया है?
उत्तर:
लेखक ने संगीत के क्षेत्र को विस्तीर्ण कहा है, क्योंकि उसके अनुसार संगीत के क्षेत्र में अब तक अलक्षित, असंशोधित और अदृष्टिपूर्ण ऐसा बहुत बड़ा प्रान्त है जिसकी खोज अथवा जिस पर कार्य होना अभी बाकी है। वास्तव में,संगीत एक ऐसी विधा है, जिसमें असीम सम्भावनाएँ हैं, करने के लिए काफी कुछ है। प्रयोगधर्मियों के लिए संगीत जैसा विस्तीर्ण क्षेत्र कोई दूसरा नहीं है। संगीत के क्षेत्र में होने वाले नित नए प्रयोग और कार्य इसे और भी सम्भावनाओं वाला क्षेत्र बनाते हैं।
प्रश्न 6.
स्वर साम्राज्ञी लता मंगेशकर’ पर एक लघु निबन्ध लिखिए।
उत्तर:
वैसे तो भारतीय भूमि पर एक से बढ़कर एक कलाकारों,साहित्यकारों, वैज्ञानिकों और राजनेताओं ने जन्म लिया है, परन्तु इनमें से कुछेक ऐसे भी होते हैं, जो अपने कौशल के कारण जीवित किवदन्ती बन जाते हैं। ऐसी ही एक जीवित किवदन्ती हैं-स्वर साम्राज्ञी, स्वर कोकिला-लता मंगेशकर।
सुप्रसिद्ध गायक दीनानाथ मंगेशकर की सुपुत्री लताजी को यदि भारतीय चित्रपट संगीत का पर्याय कहा जाये तो कोई अतिशयोक्ति न होगी। उन्होंने अपने कोकिल कण्ठ के मीठे व कोमल स्वरों से आम जनमानस को आनन्दित करने का जो भागीरथ कार्य किया है उसकी जितनी भी प्रशंसा की जाये कम ही होगी।
यूँ तो लताजी के चित्रपट संगीत की दुनिया में कदम रखने से पूर्व और पश्चात् सैकड़ों गायिकाओं ने अपनी-अपनी आवाजों का जादू बिखेरा, किन्तु लताजी के गाये गीतों का नशा हर भारतीय के सिर चढ़कर बोला। सच कहा जाये तो भारतीय गायिकाओं में लता जी के जोड़ की दूसरी कोई गायिका हुई ही नहीं। लताजी के कारण चित्रपट संगीत और मनोरंजन की दुनिया को विलक्षण लोकप्रियता प्राप्त हुई है, यही नहीं लोगों का शास्त्रीय संगीत की ओर देखने का दृष्टिकोण भी पूरी तरह बदला है। उनकी अभिप्रेरणा से देश के कोने-कोने यहाँ तक कि विदेशों में भी बच्चे-बड़े स्वर में गाने गुनगुनाते रहे हैं। सुरों से सजे गाने सुनकर लताजी के श्रोता उनका अनुकरण करने का प्रयास करते रहे हैं।
लता मंगेशकर की लोकप्रियता का मुख्य मर्म उनके गायन में मौजूद ‘गानपन’ है। लताजी के स्वरों में कोमलता और मुग्धता है। उनके गले की हरकतें’ सामान्य से गाने को भी असाधारण रूप में परिवर्तित करने में सक्षम हैं। शास्त्रीय संगीत का गहरा ज्ञान लताजी को अपना सर्वश्रेष्ठ देने के योग्य बनाता है। उनके गाने की एक और विशेषता है, उनके स्वरों की निर्मलता। उनके गायन में एक अजब-सी मिठास है, जो श्रोता को बाँधे रखती है। लताजी की एक बड़ी विशेषता और है और वह है उनका ‘नादमय उच्चार’।
चित्रपट संगीत के क्षेत्र की लताजी निर्विवाद साम्राज्ञी हैं। उनकी लोकप्रियता के शिखर का स्थान अचल है। नयी पीढ़ी के संगीत को संस्कारित करने और सामान्य मनुष्य में संगीत विषयक अभिरुचि पैदा करने में उनका उल्लेखनीय योगदान रहा है। संगीत की लोकप्रियता, उसके प्रसार और अभिरुचि के विकास का श्रेय लताजी को जाता है। हम सभी वास्तव में बहुत सौभाग्यशाली हैं कि हम इस कालजयी कलाकार को देख-सुन पा रहे हैं।
प्रश्न 7.
पाठ में विभिन्न प्रदेशों के विविध लोकगीतों की चर्चा की गई है। आप भी अपनी क्षेत्रीय बोली का कोई लोकगीत लिखिए तथा उसका मातृभाषा में अनुवाद कीजिए।
उत्तर:
विद्यार्थी स्वयं लिखें।
![]()
भारतीय गायिकाओं में बेजोड़ लता मंगेशकर अति लघु उत्तरीय प्रश्न
प्रश्न 1.
लता मंगेशकर के पिताजी का नाम क्या था? वह क्या थे?
उत्तर:
लता मंगेशकर के पिताजी का नाम दीनानाथ मंगेशकर था। वह अपने जमाने के सुप्रसिद्ध गायक थे।
प्रश्न 2.
शास्त्रीय गायकी से आप क्या समझते हैं?
उत्तर:
शास्त्रीय गायकी गायन की एक ऐसी विधा है जिसमें गायन को कुछ निर्धारित नियमों के अन्दर ही गाया बजाया जाता है। ख्याल, ध्रुपद, धमार आदि शास्त्रीय गायकी के अन्तर्गत ही आते हैं।
भारतीय गायिकाओं में बेजोड़ लता मंगेशकर पाठ का सारांश
‘कुमार गंधर्व’ द्वारा लिखित प्रस्तुत लेख, भारतीय गायिकाओं में बेजोड़ लता मंगेशकर’ में स्वर साम्राज्ञी, लता मंगेशकर’ की प्रशंसा बहुत ही सुन्दर एवं विश्लेषणात्मक ढंग से की गई है।
लेखक के अनुसार भारत-भूमि पर अब तक सैकड़ों प्रतिभाशाली एवं सुरीले कण्ठ वाली गायिकाएँ पैदा हुई हैं, जिन्होंने अपने गायन से जन-जन को आनन्दित एवं प्रभावित किया है, किन्तु इन सब में से लता मंगेशकर का स्थान निर्विवादित रूप से सर्वोच्च है। लताजी का गायन व्यक्ति के तन से होता हुआ मन तक पहुँचता है और अन्तस को एक पारलौकिक अनुभूति प्रदान करता है। सुप्रसिद्ध गायक दीनानाथ मंगेशकर की सुपुत्री लता मंगेशकर की आवाज जितनी कोमल है, उतनी ही उसमें मिठास भी है। लताजी का गायन सुप्रसिद्ध चित्रपट-गायिका नूरजहाँ से भी कहीं बेहतर और मर्म को छू लेने वाला है।
लेखक के अनुसार लताजी के कारण चित्रपट संगीत और मनोरंजन की दुनिया को विलक्षण लोकप्रियता प्राप्त हुई है, साथ ही, लोगों का शास्त्रीय संगीत की ओर देखने का दृष्टिकोण भी एकदम बदला है। ये लताजी के कण्ठ का ही जादू है जो साधारण प्रकार के लोगों को भी संगीत के सुर-ताल और लय की सक्ष्मता समझ में आने लगी है। वास्तव में संगीत की लोकप्रियता, उसके प्रसार और अभिरुचि के विकास का श्रेय लताजी को ही देना पड़ेगा।
लताजी की लोकप्रियता का मुख्य मर्म उनका ‘गानपन’ है। उनके गाने की एक और विशेषता है, उसके स्वरों की निर्मलता। लताजी के स्वरों में कोमलता और मुग्धता है। साथ ही, लताजी के गाने में ‘नादमय उच्चार’ का भी अपना महत्त्व है।
लेखक के अनुसार शास्त्रीय संगीत और चित्रपट संगीत की तुलना बेमानी है। जहाँ गंभीरता शास्त्रीय संगीत का स्थायी भाव है वहीं द्रुतलय और चपलता चित्रपट संगीत का मुख्य गुणधर्म है। यह ठीक है कि चित्रपट संगीत से जुड़े व्यक्ति के लिए शास्त्रीय संगीत का ज्ञान होना परमावश्यक है और वह ज्ञान लताजी के पास नि:संशय भरपूर है। लताजी चित्रपट संगीत के क्षेत्र की सर्वमान्य साम्राज्ञी हैं। उनकी लोकप्रियता दुनिया के कोने-कोने में है। लताजी जैसा कलाकार शताब्दियों में एकाध ही पैदा होता है। यह हमारा सौभाग्य है कि हम शताब्दियों के इस कलाकार को यूँ जीता-जागता, घूमता-फिरता देख पा रहे हैं।