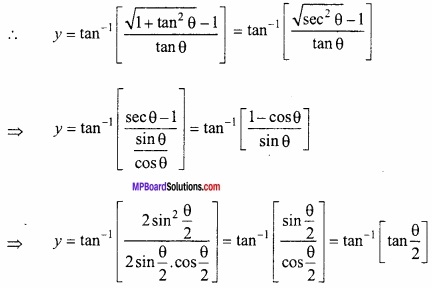
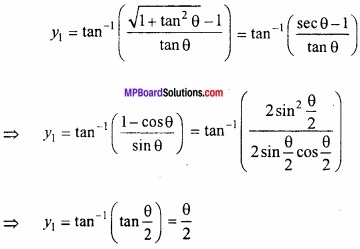
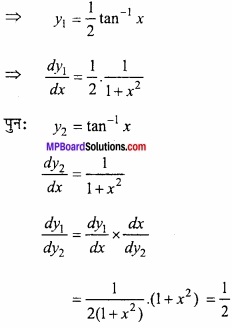
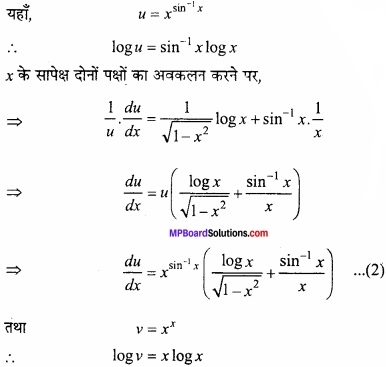
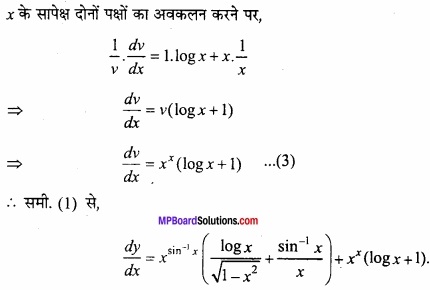
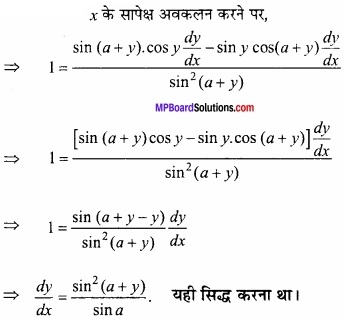
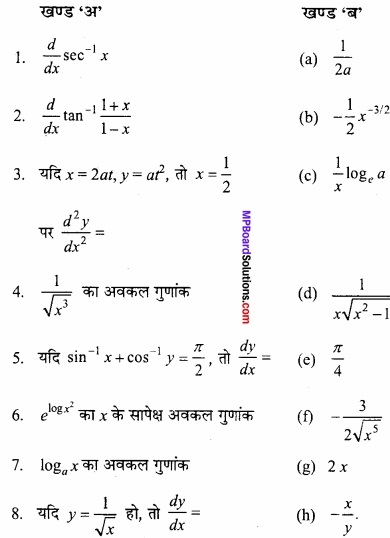
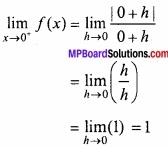
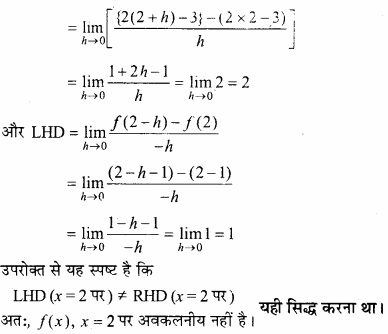
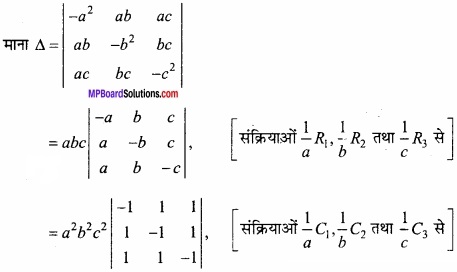
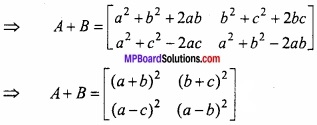
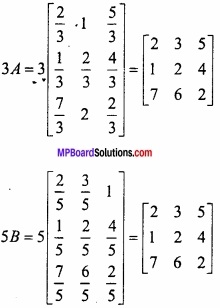
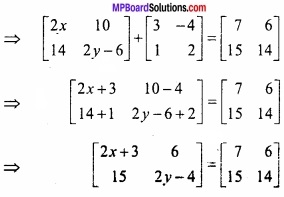
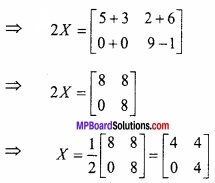
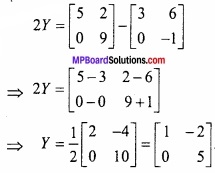
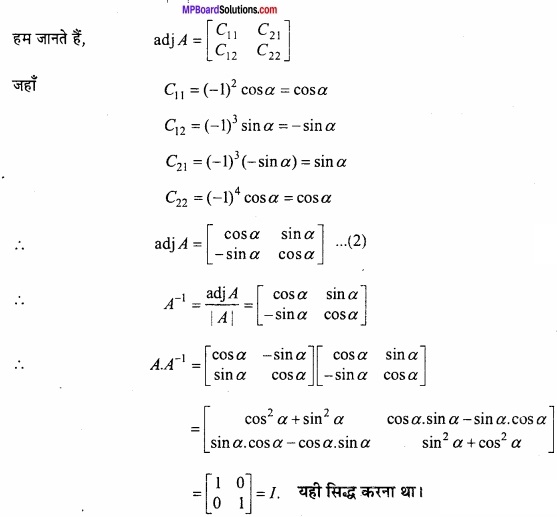
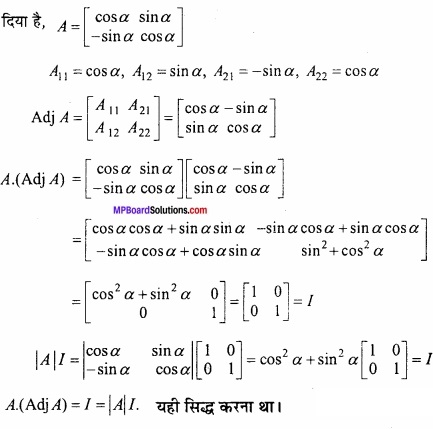
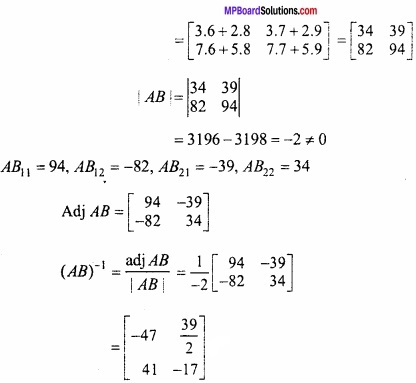
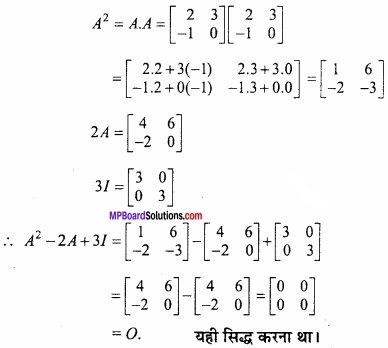
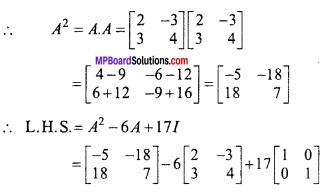
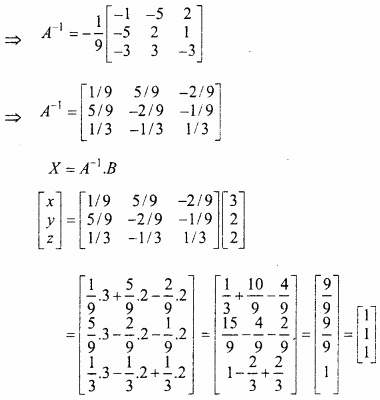
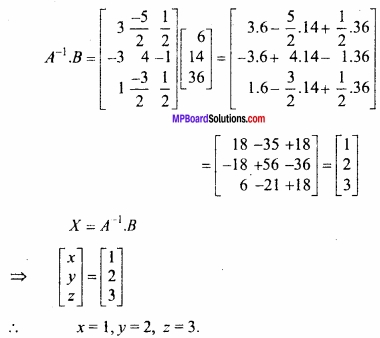
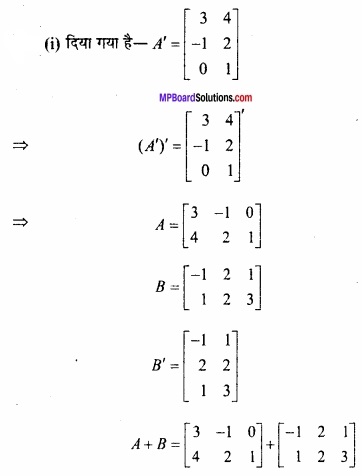
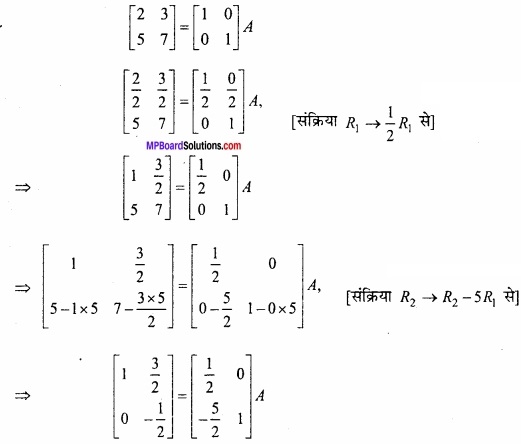
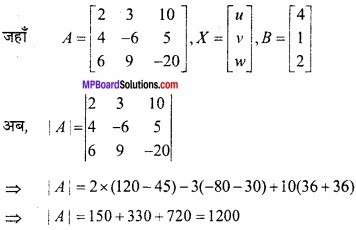
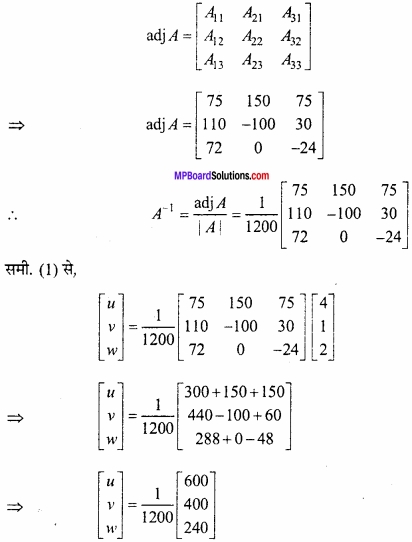
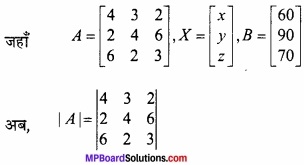
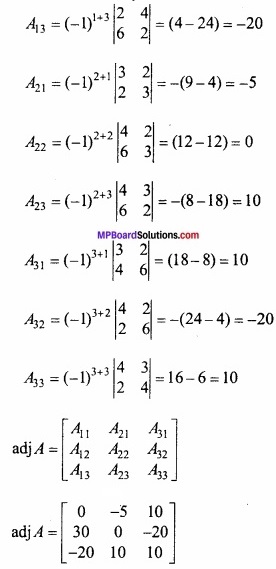
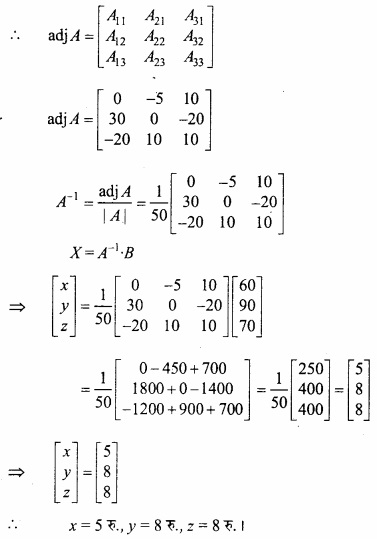
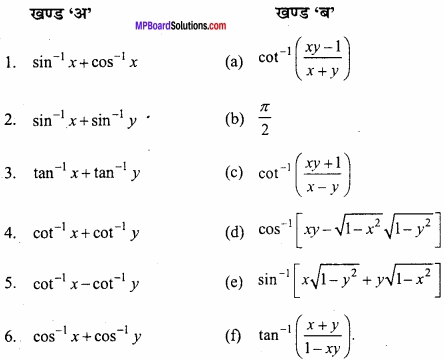
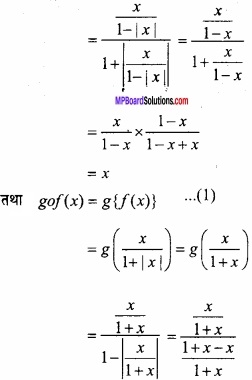
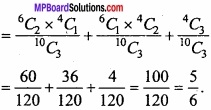
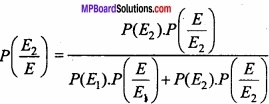
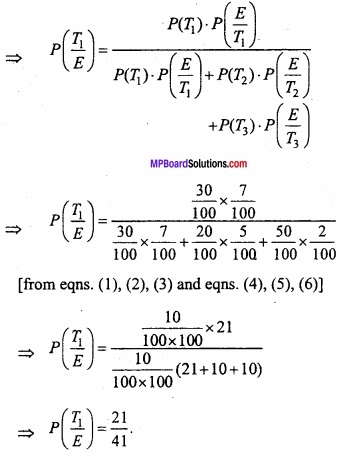
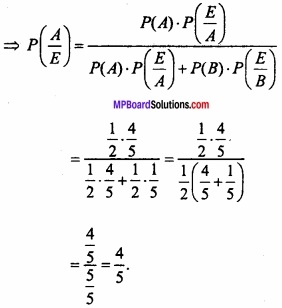
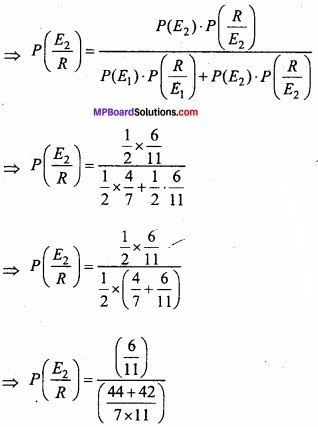
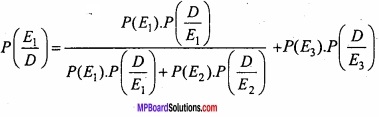
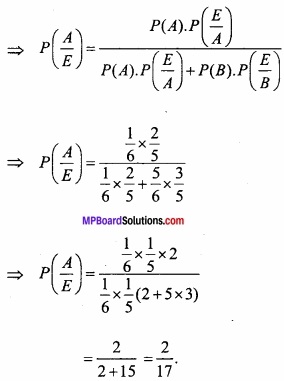
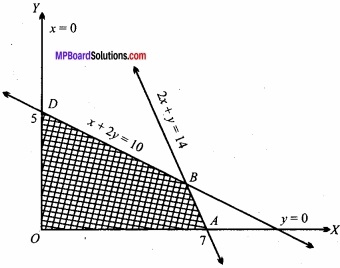
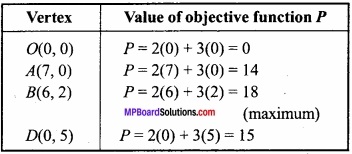
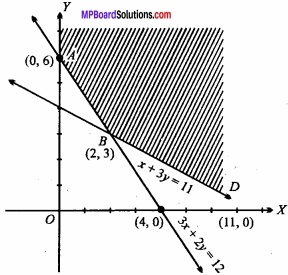
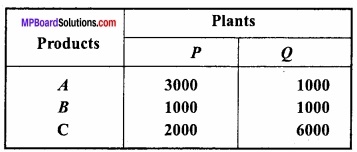
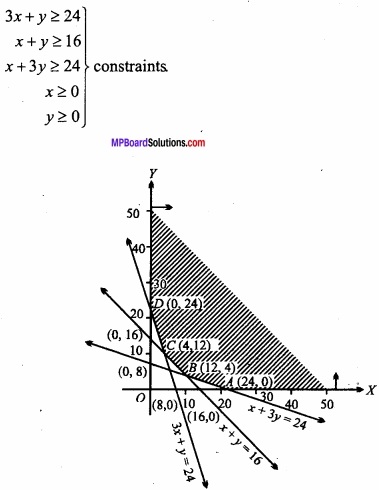
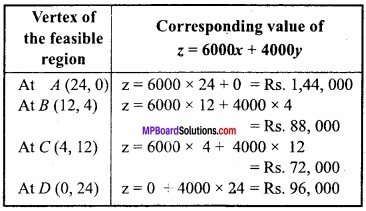
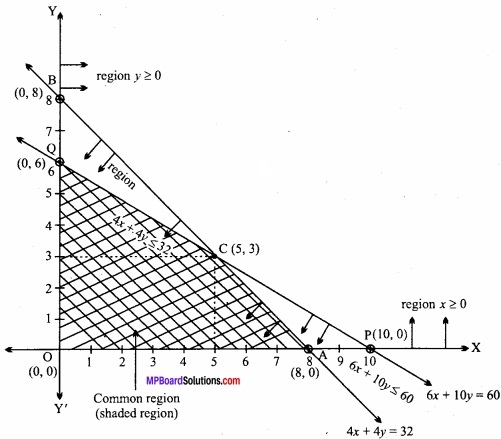
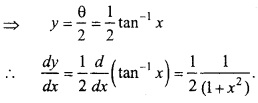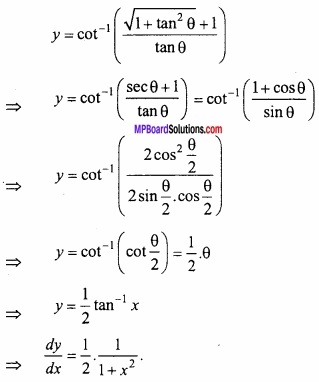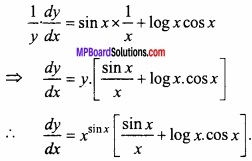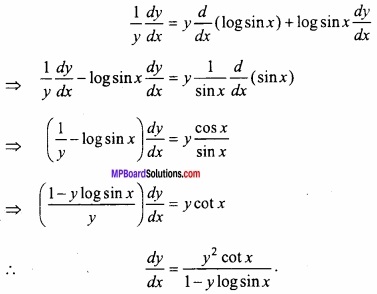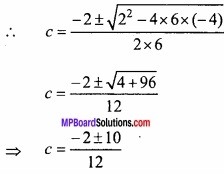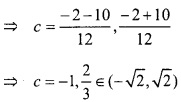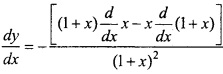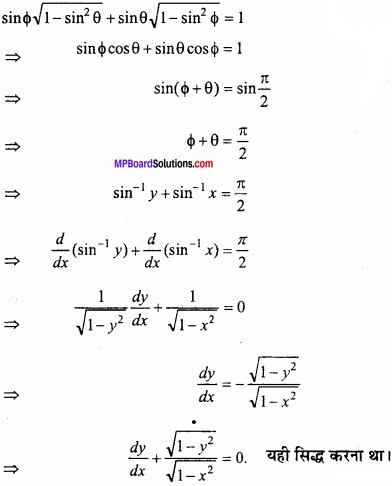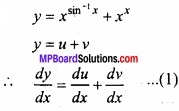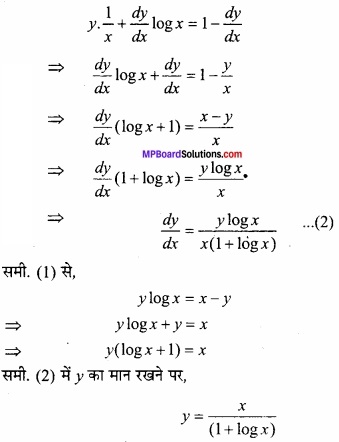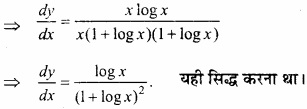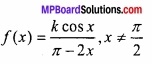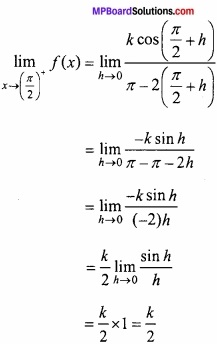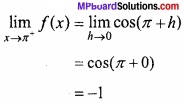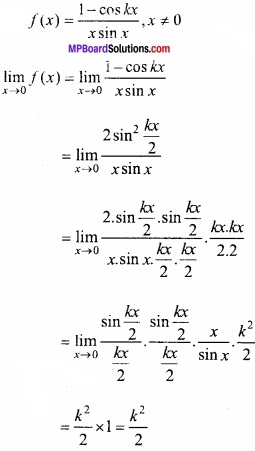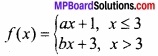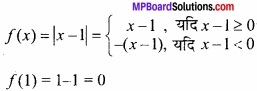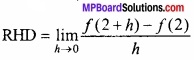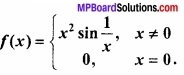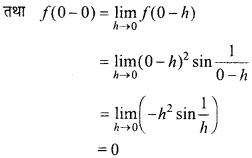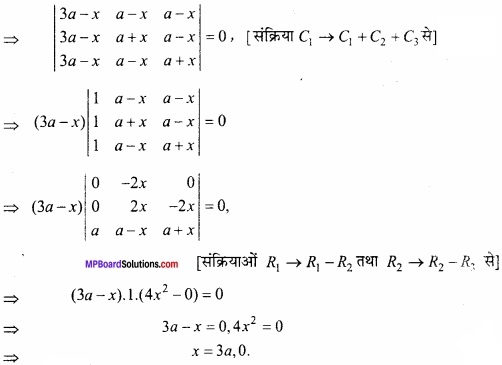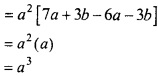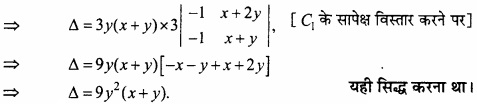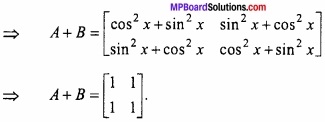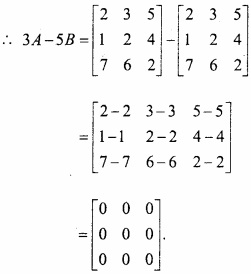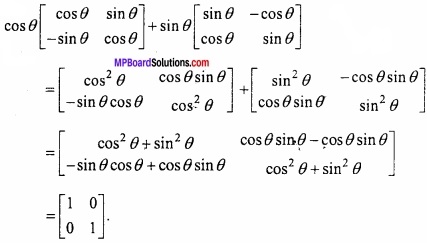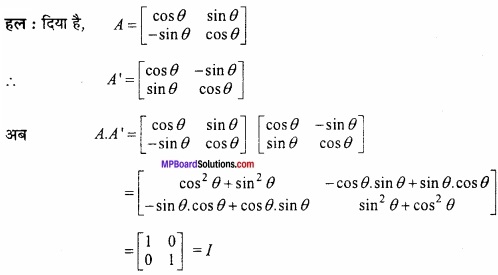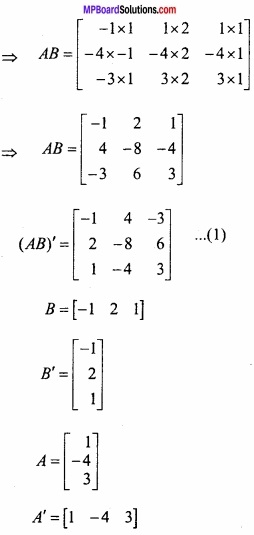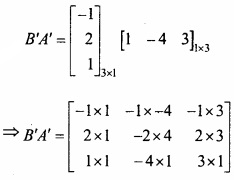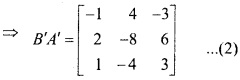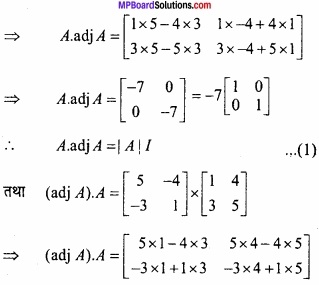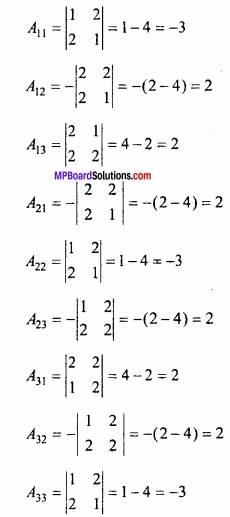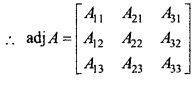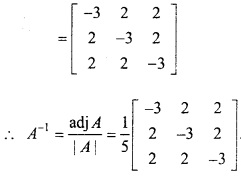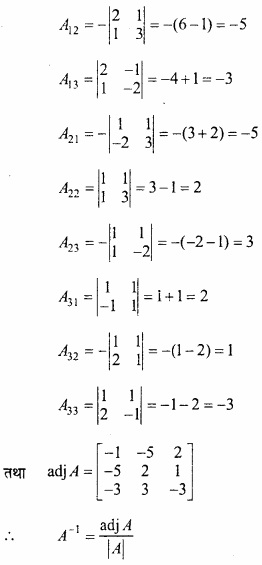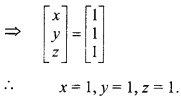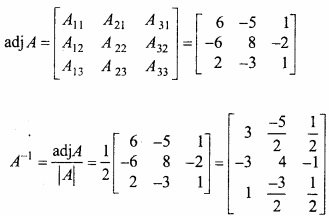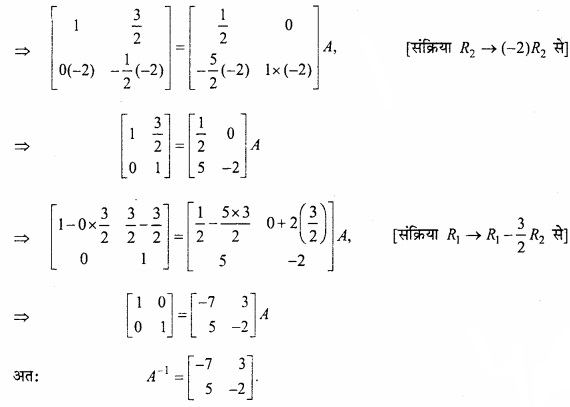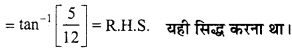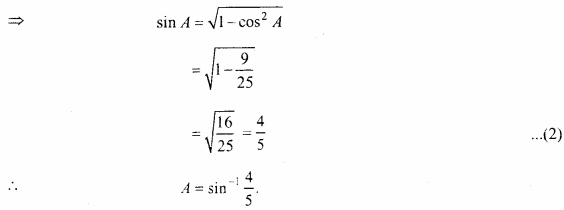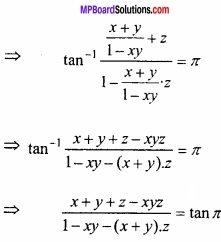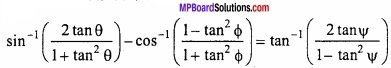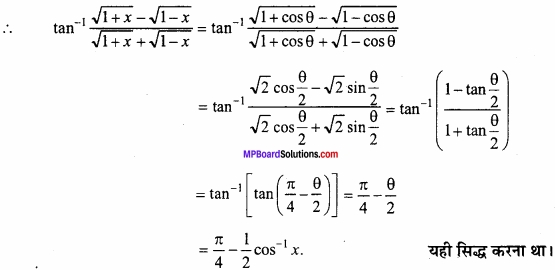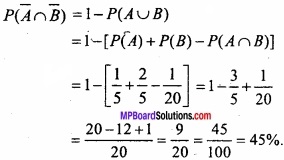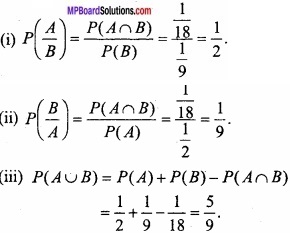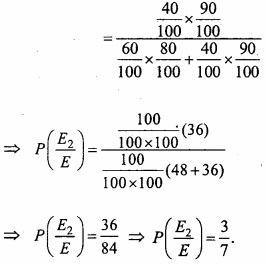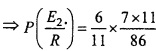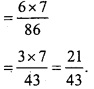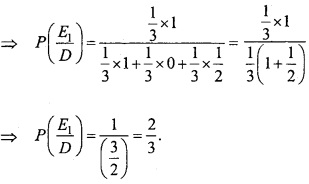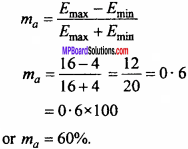MP Board Class 12th Maths Important Questions Chapter 6 अवकलज के अनुप्रयोग
अवकलज के अनुप्रयोग Important Questions
अवकलज के अनुप्रयोग वस्तुनिष्ठ प्रश्न
प्रश्न 1.
सही विकल्प चुनकर लिखिए –
प्रश्न 1.
एक वृत्त की त्रिज्या r = 6 cm पर r के सापेक्ष क्षेत्रफल में परिवर्तन की दर है –
(a) 10π
(b) 12π
(c) 8π
(d) 11π
उत्तर:
(b) 12π
प्रश्न 2.
किसी बिन्दु पर y = x + 1, वक्र y2 = 4x की स्पर्श रेखा है –
(a) (1, 2)
(b) (2, 1)
(c) (1, -2)
(d) (- 1, 2)
उत्तर:
(a) (1, 2)
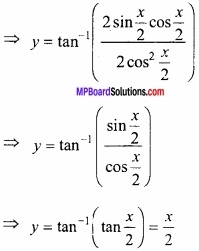
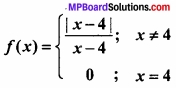
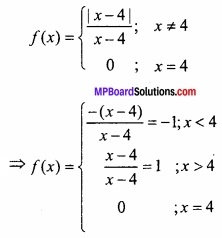
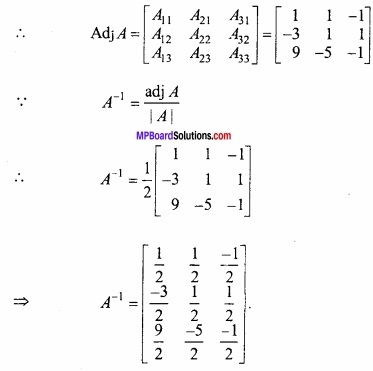
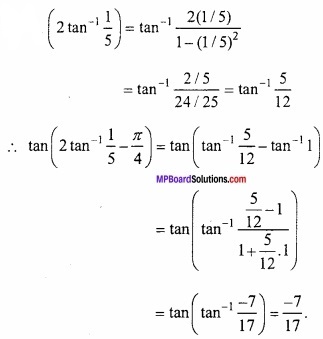
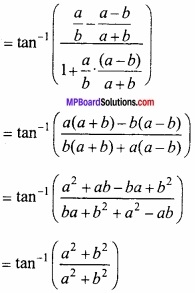
![]()
प्रश्न 3.
x मीटर भुजा वाले घन की भुजा में 2% की वृद्धि के कारण से घन के आयतन में सन्निकट परिवर्तन ज्ञात कीजिए।
(a) 0.03 x3
(b) 0.02 x3
(c) 0.06 x3
(d) 0.09 x3
उत्तर:
(c) 0.06 x3
प्रश्न 4.
वक्र x2 = 2y पर (0, 5) से न्यूनतम दूरी पर स्थित बिन्दु है –
(a) (2\(\sqrt{2}\), 4)
(b) (2\(\sqrt{2}\), 0)
(c) (0, 0)
(d) (2, 2)
उत्तर:
(a) (2\(\sqrt{2}\), 4)
प्रश्न 5.
f (x) = x4 – x2 – 2x+6 का न्यूनतम मान होगा –
(a) 6
(b) 4
(c) 8
(d) इनमें से कोई नहीं।
उत्तर:
(b) 4
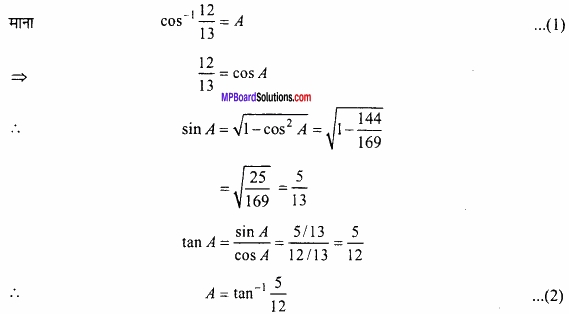
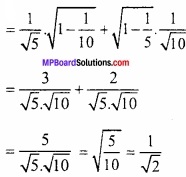
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति कीजिए –
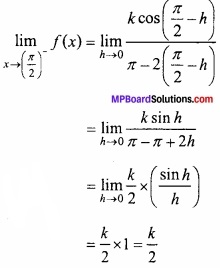
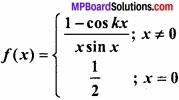
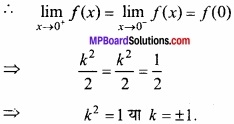
- 0 ≤ x ≤ π के लिए फलन f (x) = cosx ………………….. फलन होगा।
- एक वृत्तीय प्लेट की त्रिज्या 0.2 सेमी/सेकण्ड की दर से बढ़ रही है। जब r = 10 सेमी हो, तो क्षेत्रफल के परिवर्तन की दर ………………….. है।
- फलन y = x(5 – x), x = ………………. पर उच्चिष्ठ है।
- 2x + 3y का न्यूनतम मान, जब xy = 6, है ……………………… है।
- sin x + cos x का उच्चिष्ठ मान ……………….. है।
- रेखा y = mx + 1 वक्र y2 = 4x की स्पर्श रेखा है, तो m का मान …………………………….
- वक्र y = x2 के बिन्दु (1, 1) पर स्पर्श रेखा की प्रवणता ………………………. है।
- अवकलों के प्रयोग द्वारा 10.6 का सन्निकटतम मान ………………………. है।
उत्तर:
- ह्रासमान
- 4π cm2/ sec
- \(\frac{5}{2}\)
- 12
- \(\sqrt{2}\)
- 1
- 2
- 0.8
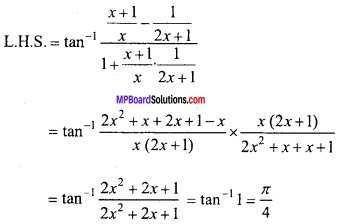
![]()
प्रश्न 3.
निम्न कथनों में सत्य/असत्य बताइए –
- फलन f (x) = ex – e-x, x के सभी वास्तविक मानों के लिए वर्धमान फलन \(\frac{1}{2}\) x2 है।
- यदि किसी समद्विबाहु त्रिभुज की समान भुजाओं की लम्बाई x हो, तो उसका महत्तम क्षेत्रफल \(\frac{1}{2}\) x2 होगा।
- फलन f (x) = 3x2 – 4x अंतराल (- ∞, \(\frac{2}{3}\) ) में वर्द्धमान है।
- फलन f (x) = x – cot x सदैव ह्रासमान है।
- वक्र y = ex के बिन्दु (0, 1) पर अभिलम्ब का समीकरण x + y = 1 है।
उत्तर:
- सत्य
- सत्य
- असत्य
- असत्य
- सत्य।
प्रश्न 4.
एक शब्द/वाक्य में उत्तर दीजिए –
- \(\sqrt{49.5}\) का सन्निकट मान ज्ञात कीजिए।
- परवलय y2 = 4ax के बिन्दु (x’, y’) पर स्पर्श रेखा का समीकरण ज्ञात कीजिए।
- वक्र y = x2 + 1 के बिन्दु (1, 2) पर स्पर्श रेखा की प्रवणता ज्ञात कीजिए।
- फलन sin x + cos x का उच्चिष्ठ मान ज्ञात कीजिए।
- एक बर्फ का गोला चर त्रिज्या रखता है, उसके आयतन में परिवर्तन क्या होगा, जब उसकी त्रिज्या 1 मीटर हो।
- किसी वर्ग की एक भुजा में 0.2 सेमी/सेकण्ड की दर से वृद्धि होती है। वर्ग के परिमाप की दर ज्ञात कीजिए।
उत्तर:
- 7.0357
- yy’ = 2a (x + x’)
- 3, 3
- \(\sqrt{2}\)
- 4π घन मीटर/सेकण्ड
- 0.8 सेमी/सेकण्ड।
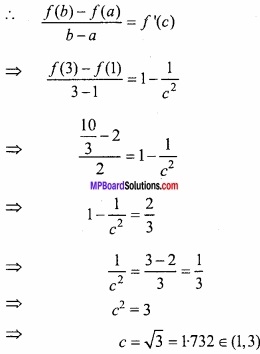
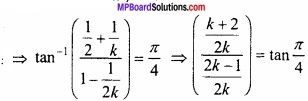
![]()
अवकलज के अनुप्रयोग दीर्घ उत्तरीय प्रश्न – I
प्रश्न 1.
एक वृत्त की त्रिज्या 2 सेमी/सेकण्ड की एकसमान दर से बढ़ रही है। क्षेत्रफल में वृद्धि किस दर से होगी जबकि त्रिज्या 10 सेमी हो?
हल:
दिया है:
\(\frac{dr}{dt}\) = 2 सेमी/सेकण्ड
माना कि वृत्त का क्षेत्रफल A वर्ग सेमी है।
तब [ \(\frac{dA}{dt}\) ]r=10 = ?
∵ वृत्त का क्षेत्रफल A = πr2
∴ \(\frac{dA}{dt}\) = π(2r). \(\frac{dr}{dt}\) = π(2r).(2)
⇒ \(\frac{dA}{dt}\) = 4πr
∴ [ \(\frac{dA}{dt}\) ]r=10 = 4π(10)
= 40π वर्ग सेमी/सेकण्ड
अर्थात् क्षेत्रफल 40π वर्ग सेमी/सेकण्ड की दर से बढ़ रहा है।
![]()
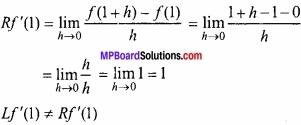
प्रश्न 2.
एक हवा के बुलबुले की त्रिज्या 1/2 से.मी. प्रति सेकण्ड की दर से बढ़ रही है। जब बुलबुले की त्रिज्या 1 से.मी. है तब किस दर से बुलबुले का आयतन बढ़ रहा है?
हल:
बुलबुले की त्रिज्या r हो, तो
∴ आयतन V = \(\frac{4}{3}\) πr3
प्रश्न 3.
एक गुब्बारे की त्रिज्या 10 सेमी/सेकण्ड की दर से बढ़ रही है, जब गुब्बारे की त्रिज्या 15 सेमी है तब किस दर पर गुब्बारे की सतही क्षेत्रफल बढ़ रहा है?
हल:
माना गुब्बारे की त्रिज्या । है। यदि समय । पर उसकी सतही क्षेत्रफल A हो, तो
A = 4πr 2
समय t के साथ गुब्बारे के त्रिज्या में वृद्धि दर \(\frac{dr}{dt}\) = 10 सेमी/सेकण्ड
समय t के साथ गुब्बारे की क्षेत्रफल में वृद्धि के दर = \(\frac{dA}{dt}\)
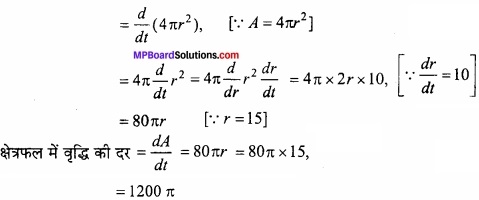
अतः जब गुब्बारे की त्रिज्या 15 सेमी है, तब उसका क्षेत्रफल = 1200π वर्ग सेमी/सेकण्ड की दर से बढ़ रहा है।
प्रश्न 4.
वे अन्तराल ज्ञात कीजिये जिनमें फलन f (x) = 2x3 – 15x2 + 36x + 1 वर्धमान या ह्रासमान है।
हल:
f (x) = 2x3 – 15x2 + 36x + 1
⇒ f'(x) = 6x2 – 30x + 36
= 6(x2 – 5x + 6)
= 6(x – 2)(x – 3)
फलन f (x) के वर्धमान होने के लिए,
f'(x) > 0 = (x – 2 )(x – 3) > 0
⇒ या तो x – 2 > 0 तथा x – 3 > 0
⇒ x > 2 तथा x > 3
⇒ x > 3 स्पष्ट है फलन, अन्तराल (3, ∞) में वर्धमान होगा।
पुनः (x – 2)(x – 3) > 0
या तो x – 2 < 0 तथा x – 3 < 0
⇒ x < 2 तथा x < 3
⇒ x < 2
स्पष्ट है फलन, अन्तराल (-∞, 2) में वर्धमान होगा।
अतः दिया गया फलन, अन्तराल (-∞, 2)∪(3, ∞) में वर्धमान होगा।
पुनः f (x) के एक ह्रासमान फलन होने के लिए,
f'(x) < 0
⇒ (x – 2)(x – 3) < 0
या तो x – 2 < 0 तथा x – 3 > 0
⇒ x < 2 तथा x > 3, जो असम्भव है।
या x – 2 > 0 तथा x – 3 < 0 ⇒ x > 2 तथा x < 3
⇒ 2 < x < 3
अत: फलन f (x) एक ह्रासमान फलन है, जबकि 2 < x < 3.
अर्थात् फलन f (x) अन्तराल (2, 3) में ह्रासमान होगा।
![]()
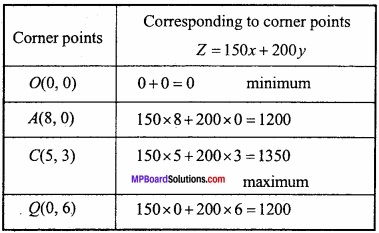
प्रश्न 5.
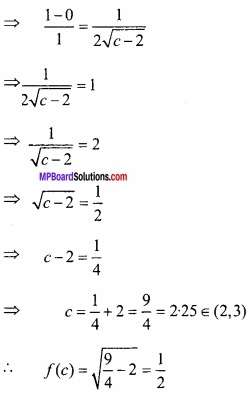
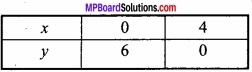
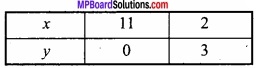
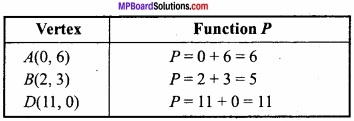
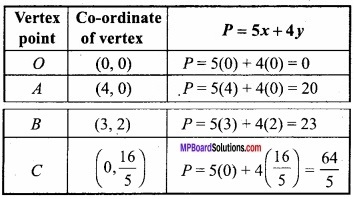
(A) यदि x + y = 8 हो, तो xy का महत्तम मान ज्ञात कीजिए।
हल:
माना
P = xy
⇒ x + y = 8
⇒ y = 8 – x
∴ P = x(8 – x) = 8x – x2
⇒ \(\frac{dP}{dx}\) = 8 – 2x
⇒ \(\frac { d^{ 2 }P }{ dx^{ 2 } } \) = -2
महत्तम और न्यूनतम मान के लिए,
8 – 2x = 0
⇒ x = 4
अब x = 4 पर \(\frac { d^{ 2 }P }{ dx^{ 2 } } \) = -2, जो ऋणात्मक है।
∴ x = 4 पर P का मान महत्तम है।
जब x = 4 तब y = 4
P का महत्तम मान = xy, जब x = 4, y = 4
= 4 × 4 = 16.
(B) यदि x + y = 10 हो, तो xy का महत्तम मान ज्ञात कीजिए।
हल:
प्रश्न क्र. 5 (A) की भाँति हल करें।
![]()
प्रश्न 6.
यदि वृत्त की त्रिज्या 3 सेमी/सेकण्ड की दर से बढ़ रही है। जब वृत्त की त्रिज्या 10 सेमी है, तब किस दर से वृत्त का क्षेत्रफल बढ़ रहा है?
हल:
माना कि वृत्त की त्रिज्या है।
यदि समय t पर उसका क्षेत्रफल A हो, तो –
A = πr2
समय t के साथ वृत्त की त्रिज्या में वृद्धि की दर = \(\frac{dr}{dt}\) = 3 सेमी/सेकण्ड।
समय t के साथ वृत्त के क्षेत्रफल में वृद्धि की दर = \(\frac{dA}{dt}\)
= \(\frac { d }{ dx } \) (πr2)
= \(\frac { d }{ dr } \) (πr2). \(\frac { dr }{ dt } \)
= π.2r.3 [∵ \(\frac { dr }{ dt } \) = 3]
= 6πr
अतः वृत्त के क्षेत्रफल में अभीष्ट वृद्धि की दर = \(\frac{dA}{dt}\) = 6πr
= 6π × 10,
= 60π [r = 10 पर]
अतः r = 10 सेमी पर वृत्त का क्षेत्रफल 607 वर्ग सेमी/सेकण्ड की दर से बढ़ रहा है।
प्रश्न 7.
एक घन का आयतन 9 सेमी/सेकण्ड की दर से बढ़ रहा है। यदि इसके कोर की लंबाई 10 सेमी है, तो इसके पृष्ठ का क्षेत्रफल किस दर से बढ़ रहा है? (NCERT)
हल:
माना घन का आयतन V है तथा घन की कोर की लंबाई a सेमी है।
घन का आयतन V = a3
∴ \(\frac{dV}{dt}\) = \(\frac{d}{dt}\)a3
दिया है:
\(\frac{dV}{dt}\) = 9 सेमी3/सेकण्ड
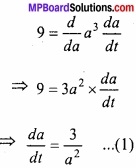
माना घन का पृष्ठ S है।
S = 6a2

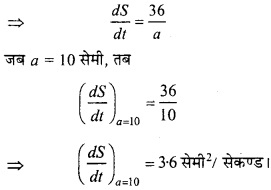
प्रश्न 8.
(A) एक आदमी जिसकी ऊँचाई 180 सेमी है, एक बिजली के खम्भे से 1.2 मीटर प्रति सेकण्ड की दर से दूर हट रहा है। यदि बिजली के खम्भे की ऊँचाई 4.5 मीटर है, तो वह दर ज्ञात कीजिए जिस पर उसकी छाया बढ़ रही है।
हल:
AB = बिजली का खम्भा, PQ = आदमी, QC = x = छाया की लम्बाई, माना BQ = y
\(\frac{dy}{dx}\) = 1.2 = वह दर जिससे आदमी दूर हट रहा है।
\(\frac{dx}{dt}\) = वह दर जिससे छाया बढ़ रही है।
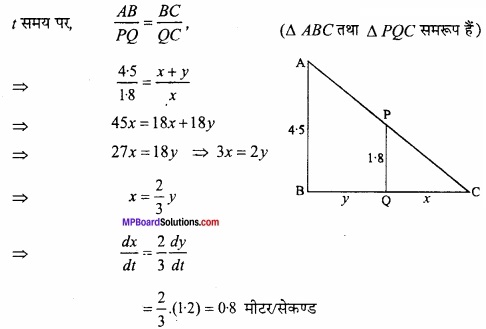
0.8 मीटर/सेकण्ड 0.8 मीटर/सेकण्ड छाया बढ़ने की दर होगी।
(B) 2 मीटर ऊँचाई का आदमी 6 मीटर ऊँचे बिजली के खंभे से दूर 5 किमी/घण्टा की समान चाल से चलता है। उसकी छाया की लंबाई की वृद्धि दर ज्ञात कीजिये। (NCERT)
हल: प्रश्न 8 (A) की भाँति हल करें।
[उत्तर: \(\frac{5}{2}\) किमी/घण्टा।]
![]()
प्रश्न 9.
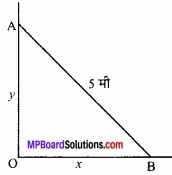
एक सीढ़ी जो 5 मीटर लम्बी है, एक दीवार से झुकी है। सीढ़ी का निचला सिरा दीवार से दूर धरातल के सहारे 2 मीटर/सेकण्ड की दर से खींचा जाता है। जब सीढ़ी का निचला सिरा दीवार से 4 मीटर दूर है, तब किस दर से दीवार पर इसकी ऊँचाई घट रही है? (NCERT)
हल:
माना, किसी समय सीढ़ी का निचला सिरा दीवार से x मीटर की दूरी पर है तथा इस समय दीवार की ऊँचाई ” मीटर है। तब चित्रानुसार,
x2 + y2 = 25 …………………. (1)
t के सापेक्ष अवकलन करने पर,
2x \(\frac{dx}{dt}\) + 2y\(\frac{dy}{dt}\) = 0
⇒ x\(\frac{dx}{dt}\) + y\(\frac{dy}{dt}\) = 0 …………………….. (2)
सीढ़ी के निचले सिरे की दीवार से दूर खींचे जाने की दर,
\(\frac{dx}{dt}\) = 2 मीटर/सेकण्ड।
∴ x.2 + y\(\frac{dy}{dt}\) = 0
⇒ y\(\frac{dy}{dt}\) = -2x
⇒ \(\frac{dy}{dt}\) = \(\frac{-2x}{y}\)
जब x = 4 मीटर, तब समी. (1) से,
16 + y2 = 25
⇒ y2 = 25 – 16 = 9
⇒ y = 3 मीटर
∴ समी. (3) से,
\(\frac{dy}{dt}\) = –\(\frac { 2\times 4 }{ 3 } \) = –\(\frac{8}{3}\)
अतः दीवार पर सीढ़ी की ऊँचाई 8/3 मीटर/सेकण्ड की दर से घट रही है।
प्रश्न 10.
वे अन्तराल ज्ञात कीजिए जिनमें फलन, f (x) = 5x2 + 7x – 13 वर्धमान या ह्रासमान है।
हल:
दिया है:
f (x) = 5x2 + 7x – 13
∴ f'(x) = 10x + 7
फलन f(x) के वर्धमान होने के लिए,
f'(x) > 0
⇒ 10x + 7 > 0
⇒ x > \(\frac{-7}{10}\)
∴ फलन. f (x), अन्तराल ( \(\frac{-7}{10}\), ∞) में एक वर्धमान फलन है।
पुनः फलन f (x) के ह्रासमान होने के लिए,
f'(x) < 0
⇒ 10x + 7 < 0
⇒ x < \(\frac{-7}{10}\)
∴ फलन. f (x), अन्तराल (- ∞, \(\frac{-7}{10}\) ) में एक वर्धमान फलन है।
![]()
प्रश्न 11.
वे अन्तराल ज्ञात कीजिए, जिनमें फलन f (x) = 2x3 – 24x + 5 वर्धमान या हासमान है।
हल:
दिया गया फलन है:
f (x) = 2x3 – 24x + 5
x के सापेक्ष अवकलन करने पर,
f'(x) = 6x2 – 24
⇒ f'(x) = 6(x2 – 4)
⇒ f'(x) = 6(x + 2)(x – 2)
(A) फलन f (x) के वर्धमान होने के लिए शर्त,
f'(x) > 0
6(x + 2)(x – 2) > 0 ⇒ 6(x + 2)(x – 2) < 0
∴ f (x), x ∈ (-2,-2) में वर्धमान है।
(B) फलन f (x) के ह्रासमान होने के लिए शर्त,
f'(x) < 0 ⇒ 6(x + 2)(x – 2) < 0 ∴ f (x), x ∈ (-2, 2) में ह्रासमान है।
प्रश्न 12.
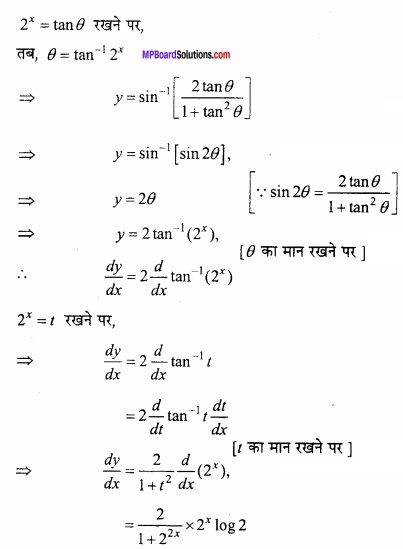
सिद्ध कीजिए x के सभी वास्तविक मानों के लिए फलन f (x) = x – cos x वर्धमान फलन है। हल: दिया गया फलन है: f (x) = X – cos x f'(x) = 1- (- sin x) ⇒ f'(x) = 1 + sin x हम जानते हैं x के सभी वास्तविक मानों के लिए, -1 ≤ sin x ≤ 1 – 1 + 1 ≤ 1 + sin x ≤ 1 + 1 0 ≤ 1 + sin x ≤ 2
अत:
x के सभी वास्तविक मानों के लिए 1 + sin x धनात्मक है स्पष्टतः f'(x) भी धनात्मक होगा। अर्थात् f'(x) > 0. यही सिद्ध करना था।
![]()
प्रश्न 13.
a का वह न्यूनतम मान ज्ञात कीजिए जिसके लिए अंतराल [1, 2] में f (x) = x2 + ax + 1 से प्रदत्त फलन निरंतर वर्धमान है। (NCERT)
हल:
दिया है:
f (x) = x2 + ax + 1
∴ f'(x) = 2x + a
अब, 1 < x < 2
⇒ 2 < 2x < 4
⇒ 2 + a < 2x + a < 4 + a
⇒ 2 + a < f'(x) < 4 + a f (x) के निरंतर वर्धमान होने के लिए हम जानते हैं कि f'(x) > 0
अर्थात् 2 + a > 0 ⇒ a > -2
अत: a का न्यूनतम मान -2 है।
प्रश्न 14.
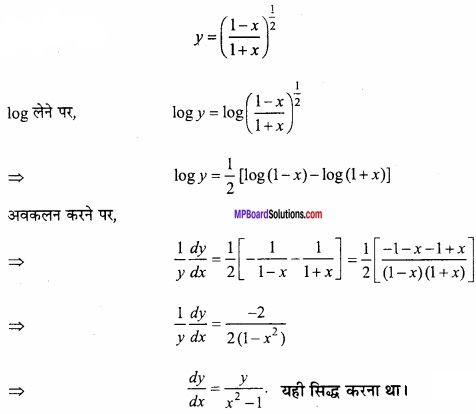
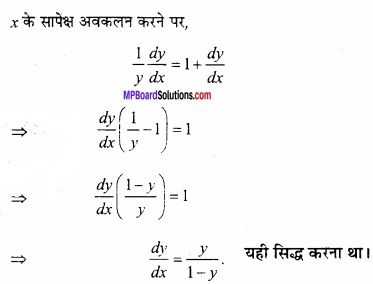
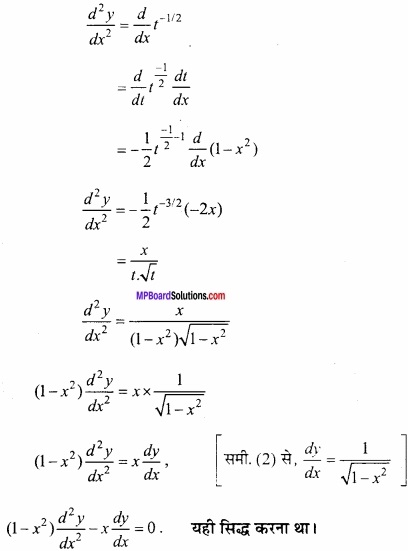
मान लीजिए [-1, 1] से असंयुक्त एक अन्तराल I हो, तो सिद्ध कीजिए कि f (x) = x + \(\frac{1}{x}\) से प्रदत्त फलन निरंतर वर्धमान है। (NCERT)
हल:
f (x) = x + \(\frac{1}{x}\)
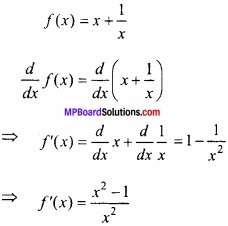
अन्तराल [-1, 1] असंयुक्त है
यदि x < -1 तब f'(x) > 0
यदि x > 1 तब f'(x) > 0
अतः अन्तराल I में f (x) निरंतर वर्धमान है। यही सिद्ध करना था।
![]()
प्रश्न 15.
वे अन्तराल ज्ञात कीजिये जिनमें निम्न फलन वर्धमान या ह्रासमान है –
f (x) = x4 – \(\frac { x^{ 3 } }{ 3 } \)
हल:
f (x) = x4 – \(\frac { x^{ 3 } }{ 3 } \)
⇒ f'(x) = 4x3 – \(\frac { 3.x^{ 2 } }{ 3 } \)
⇒ f'(x) = x2 (4x – 1)
f'(x) = 0 लेने पर,
x2 (4x – 1) = 0
⇒ x = 0 या x = \(\frac{1}{4}\)

अत: 0 तथा \(\frac{1}{4}\), X अक्ष को तीन असंयुक्त अंतराल में बाँटते है –
(-∞, 0), (0, \(\frac{1}{4}\) ), ( \(\frac{1}{4}\), ∞)
अन्तराल (-∞, 0) मे –
f'(x) = x2 (4x – 1), [∵ x2 = +ve]
[तथा 4x – 1 = 0 ]
⇒ f'(x) < 0
अन्तराल (-∞, 0) मे –
f'(x) = x2 (4x – 1), [∵ x2 = +ve]
[तथा 4x – 1 = 0 ]
⇒ f'(x) < 0
∴ अन्तराल (-∞, 0) मे f (x) हसमान है।
अन्तराल (0, \(\frac{1}{4}\) ) मे –
f'(x) = x2 (4x – 1), [∵ x2 = +ve]
[तथा 4x – 1 = 0 ]
⇒ f'(x) > 0
∴ अन्तराल ( \(\frac{1}{4}\), ∞) मे f (x) वर्धमान है।
प्रश्न 16.
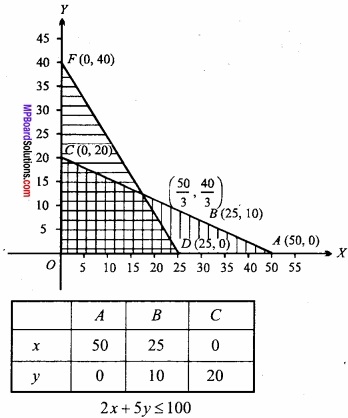
एक आयत का परिमाप 100 सेमी है। अधिकतम क्षेत्रफल के लिए आयत की भुजाएँ ज्ञात कीजिए।
हल:
माना कि आयत की लम्बाई x और चौड़ाई y है। तब,
आयत का परिमाप = 2(x + y)
⇒ 2x + 2y = 100
⇒ x + y = 50
माना आयत का क्षेत्रफल A है। तब
A = xy = x (50 – x) = 50x – x2, [समी. (1) से]
∴ \(\frac{dA}{dx}\) = 50 – 2x
और \(\frac { d^{ 2 }A }{ dx^{ 2 } } \) = -2
A अधिकतम अथवा न्यूनतम होगा जब
\(\frac{dA}{dx}\) = 0
⇒ 50 – 2x = 0 या x = 25
x के प्रत्येक मान के लिए \(\frac { d^{ 2 }A }{ dx^{ 2 } } \) ऋण है।
∴ x = 25 पर आयत का क्षेत्रफल अधिकतम है।
समी. (1) से,
y = 50 – x = 50 – 25 = 25
अत: आयत की प्रत्येक भुजा 25 सेमी हुई।
![]()
प्रश्न 17.
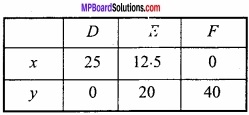
एक आयत का क्षेत्रफल 25 वर्ग सेमी है, इसकी लम्बाई और चौड़ाई ज्ञात कीजिए जबकि इसका परिमाप न्यूनतम हो।
हल:
माना आयत की लम्बाई x व चौड़ाई y इकाई है।
दिया है: आयत का क्षेत्रफल A = 25 वर्ग इकाई
xy = 25 …………………… (1)
आयत का परिमाप
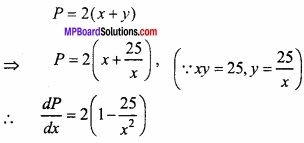
उच्चिष्ठ या निम्निष्ठ के लिये \(\frac{dP}{dx}\) = 0
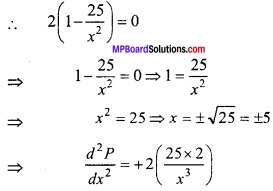
जो x = 5 के लिये + ve है।
∴ न्यूनतम परिमाप के लिये x = 5 सेमी।
y = \(\frac{25}{x}\) = \(\frac{25}{5}\) = 5 सेमी।
![]()
प्रश्न 18.
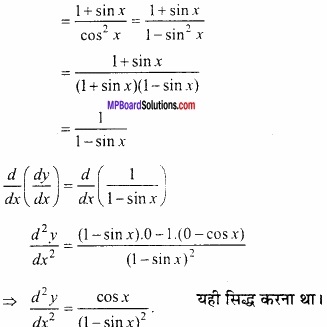
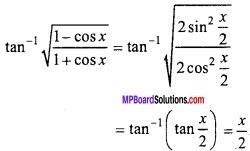
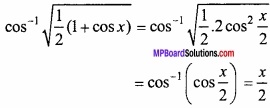
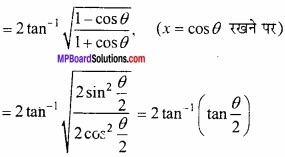
सिद्ध कीजिए कि sin x + cos x का उच्चिष्ठ मान \(\sqrt{2}\) है।
हल:
माना f (x) = sin x + cos x ………………. (1)
∴ f'(x) = cos x – sin x ………………… (2)
तथा f”(x) = – sinx – cox ……………….. (3)
उच्चिष्ठ या निम्निष्ठ मान के लिए,
f”(x) = 0
∴ cos x – sin x = 0
⇒ sin x = cos x
⇒ tan x = 1
∴ x = \(\frac { \pi }{ 4 } \), \(\frac { 3\pi }{ 4 } \), \(\frac { 5\pi }{ 4 } \)
अब समी. (3) में x = \(\frac { \pi }{ 4 } \) रखने पर,
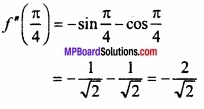
चूंकि f”( \(\frac { \pi }{ 4 } \) )ऋणात्मक है। अत: x = \(\frac { \pi }{ 4 } \) पर दिया गया फलन उच्चिष्ठ है। इसी प्रकार दिया गया फलन x = \(\frac { 3\pi }{ 4 } \), \(\frac { 5\pi }{ 4 } \) ………………. पर भी उच्चिष्ठ होगा।
समी. (1) में x = \(\frac { \pi }{ 4 } \) रखने पर,
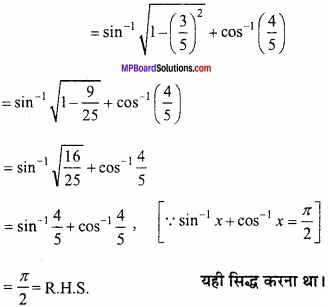
उच्चिष्ठ मान f ( \(\frac { \pi }{ 4 } \) ) = sin \(\frac { \pi }{ 4 } \) + cos \(\frac { \pi }{ 4 } \)
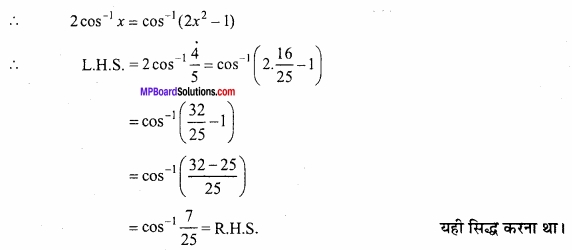
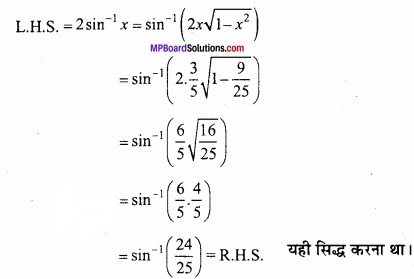
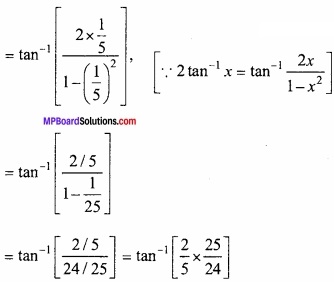
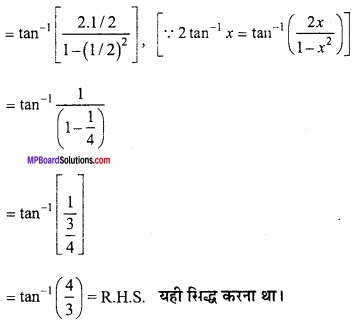
= \(\frac { 1 }{ \sqrt { 2 } } \) + \(\frac { 1 }{ \sqrt { 2 } } \) = \(\frac { 2 }{ \sqrt { 2 } } \) = \(\sqrt{2}\) यही सिद्ध करना था।
प्रश्न 19.
दो धनात्मक संख्याएँ इस प्रकार ज्ञात कीजिए कि x + y = 60 तथा xy3 उच्चिष्ठ हो। (NCERT)
हल:
दिया हुआ है:
x + y = 60
माना u = xy3
समी. (1) से x का मान समी. (2) में रखने पर,
image 16
∴ u के उच्चिष्ठ व निम्निष्ठ मान के लिए \(\frac{du}{dy}\) = 0
∴ 180y2 – 4y3 = 0
⇒ 4y2 (45 – y) = 0
⇒ y = 0, y = 45
⇒ y = 45 (∵ y ≠ 0)
अब y = 45 पर \(\frac { d^{ 2 }u }{ dy^{ 2 } } \) का मान
= 360 × 45 – 12 × 45 × 45
= 12 × 45(30 – 45), (∵y ≠ 0)
जो सप्तस्ततः ऋणात्मक है।
अतिएव y = 45 पर, u उच्चिष्ठ है।
∴ समी. (1) से,
x + 45 = 60
⇒ x = 60 – 45 = 15
अतः अभीष्ट 15 और है 45 है।
![]()
प्रश्न 20.
वक्र y = x3 – x + 1 की स्पर्श रेखा की प्रवणता उस बिन्दु पर ज्ञात कीजिए जिसकाx निर्देशांक 2 है। (NCERT)
हल:
दिये गये वक्र का समीकरण है –
y = x3 – x + 1
\(\frac{dy}{dx}\) = \(\frac{d}{dx}\) (x3 – x + 1)
= \(\frac{d}{dx}\) x3 – \(\frac{d}{dx}\) x + \(\frac{d}{dx}\) 1
⇒ \(\frac{dy}{dx}\) = 3x2 – 1 + 0
⇒ \(\frac{dy}{dx}\) = 3x2 – 1
x = 2 पर स्पर्श रेखा की प्रवणता
( \(\frac{dy}{dx}\) )x=2 = 3(2)2 – 1
= 3 × 4 – 1 = 11
प्रश्न 21.
वक्र y = \(\frac { x-1 }{ x-2 } \), x ≠ 2 के x = 10 परस्पर्श रेखा की प्रवणता ज्ञात कीजिए। (NCERT)
हल:
दिये गये वक्र का समीकरण है –
y = \(\frac { x-1 }{ x-2 } \)
\(\frac{dy}{dx}\) = \(\frac{d}{dx}\) = ( \(\frac { x-1 }{ x-2 } \) )
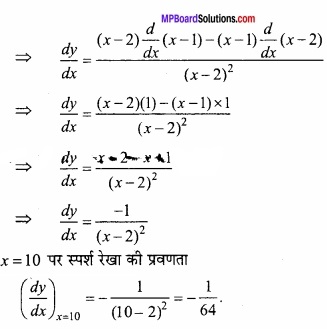
प्रश्न 22.
वक्र y = x3 – 3x2 – 9x + 7 पर उन बिन्दुओं को ज्ञात कीजिए जिन पर स्पर्श रेखा X अक्ष के समान्तर है। (NCERT)
हल:
दिये गये वक्र का समीकरण है –
y = x3 – 3x2 – 9x + 7
image 18
स्पर्श रेखा X – अक्ष के समान्तर है।
∴ \(\frac{dy}{dx}\) = 0
3(x – 3)(x + 1) = 0
⇒ x = 3, -1
जब x = 3 तब y = (3)3 – 3(3)2 – 9 × 3 + 7
y = 27 – 27 – 27 + 7
y = – 20
जब x = -1 तब y = (-1)3 – 3(-1)2 – 9(-1) + 7
y = – 1 – 3 + 9 + 7
y = 12
बिन्दुओं (3, -20) और (-1, 12) पर स्पर्श रेखाएँ x – अक्ष के समान्तर होगी।
![]()
प्रश्न 23.
परवलय y2 = 4ax के बिन्दु (at2, 2at) पर स्पर्श रेखा का समीकरण ज्ञात कीजिए। (NCERT)
हल:
परवलय का समीकरण है –
y2 = 4ax
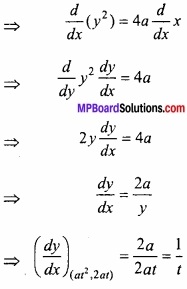
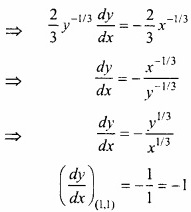
(x1y1) स्पर्श रेखा का समीकरण है –
y – y1 = \(\frac{dy}{dx}\) (x – x2)
जँहा x1 = at2, y1 = 2at, \(\frac{dy}{dx}\) = \(\frac{1}{t}\)
y – 2at = \(\frac{1}{t}\)(x – at2)
⇒ yt – 2at2 = x – at2
⇒ x – ty + at2 = 0.
प्रश्न 24.
वक्र x2/3 + y2/3 = 2 के बिन्दु (1, 1) पर स्पर्श रेखा का समीकरण ज्ञात कीजिए। (NCERT)
हल:
वक्र का समीकरण है –
x2/3 + y2/3 = 2
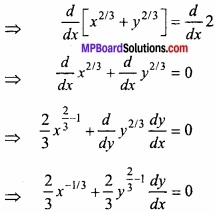
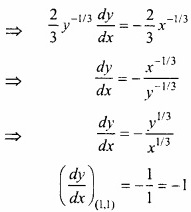
(x1y1) पर स्पर्श रेखा का समीकरण है
y – y1 = ( \(\frac{dy}{dx}\) ) (x1y1) (x – x1)
यहाँ x1 = 1, y1 = 1, \(\frac{dy}{dx}\) = -1
y – 1 = -(x – 1)
⇒ y – 1 = -x + 1
⇒ x + y – 2 = 0.
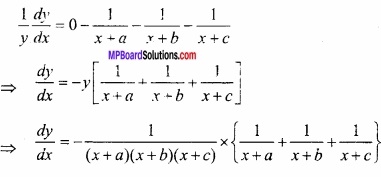
प्रश्न 25.
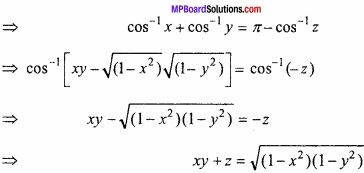
वक्र 2y + x2 = 3 के बिन्दु (1, 1) पर अभिलम्ब का समीकरण ज्ञात कीजिए। (NCERT)
हल:
दिये गये वक्र का समीकरण है:
2y + x2 = 3
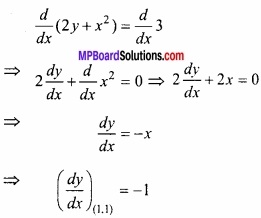
(x1, y1) पर अभिलम्ब का समीकरण होगा –
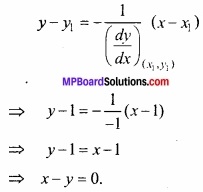
![]()
प्रश्न 26.
(A) वक्र x = cost, y = sint के t = = पर अभिलम्ब का समीकरण ज्ञात कीजिए। (NCERT)
हल:
I वक्र का समीकरण है –
x = cos t
\(\frac{dx}{dt}\) = \(\frac{d}{dt}\)cos t
⇒ \(\frac{dx}{dt}\) = – sin t
II वक्र का समीकरण है –
y = sin t
\(\frac{dy}{dt}\) = \(\frac{d}{dt}\) sin t
⇒ \(\frac{dy}{dt}\) = cos t

(x1, y1) पर अभिलम्ब का समीकरण है –
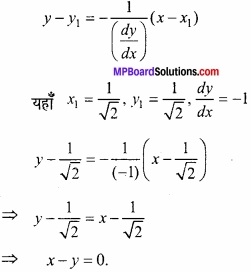
(B) वक्र 16x2 + 9y2 = 145 के बिन्दु (x1, y1) पर स्पर्श रेखा तथा अभिलंब के समीकरण ज्ञात कीजिये, जहाँ x1 = 2 तथा y1 > 0। (CBSE 2018)
हल:
वक्र का समीकरण है –
16x2 + 9y2 = 145
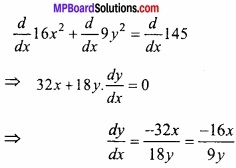
समी. (1) में x = 2 रखने पर,
16. (2)2 + 9y2 = 145
⇒ 64 + 9y2 = 145
⇒ 9y2 = 145 – 64 = 81
⇒ y2 = 9 [y ≠ -3 ∵y1 > 0]
⇒ y = 3
बिन्दु (2, 3) पर \(\frac{dy}{dx}\) = – \(\frac{16}{9}\).\(\frac{2}{3}\) = – \(\frac{32}{27}\)
बिन्दु (2, 3) पर वक्र (1) की स्पर्श रेखा
y – y1 = \(\frac{dy}{dx}\) (x – x1)
⇒ y – 3 = \(\frac{-32}{7}\) (x – 2)
⇒ 27y – 81 = -32x + 64
⇒ 32x + 27y = 145
बिन्दु (2, 3) पर वक्र (1) का अभिलम्ब

⇒ 32y – 96 = 27x – 54
⇒ 27x – 32y = 42
![]()
प्रश्न 27.
(25)1/3 का सन्निकट करने के लिए अवकल का प्रयोग कीजिए। (NCERT)
हल:
माना y = x1/3
जहाँ x = 27 और ∆x = -2

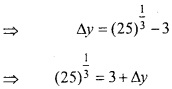
∆y सन्निकटतः dy के बराबर है।
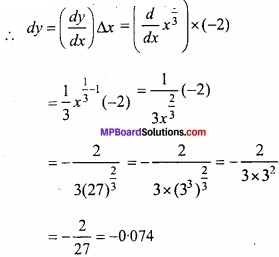
(25)1/3 का सन्निकट मान
= 3 + ∆y
= 3 – 0.074
= 2.926.
प्रश्न 28.
\(\sqrt { 36.6 } \) का सन्निकटन करने के लिए अवकल का प्रयोग कीजिए।
हल:
माना y = \(\sqrt{x}\)
जहाँ x = 36 और ∆x = 0.6

∆y सन्निकटतः dy के बराबर है।
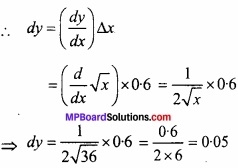
\(\sqrt { 36.6 } \) का सन्निकट मान = ∆y + 6
= 0.05 + 6 = 6.05.
![]()
प्रश्न 29.
(15)1/4 का सन्निकट करने के लिए अवकल का प्रयोग कीजिए। (NCERT)
हल:
माना y = x1/4
जहाँ x = 16 और ∆x = -1

∆y सन्निकटतः dy के बराबर है।
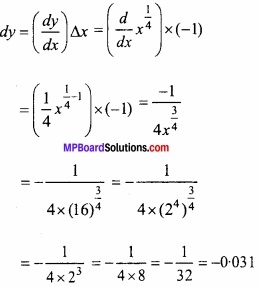
(15)1/4 का सन्निकट मान = ∆y + 2 = 2 – 0.031 = 1.969.
प्रश्न 30.
(26)1/3 का सन्निकट करने के लिए अवकलज का प्रयोग कीजिए। (NCERT)
हल:
माना y = x1/3
जहाँ x = 27 और ∆x = -1

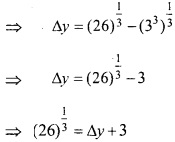
∆y सन्निकटतः dy के बराबर है।
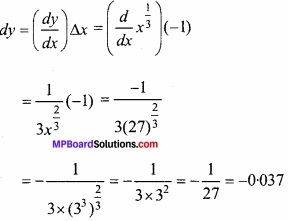
(26)1/3 का सन्निकट मान = ∆y+3
= 3 – 0.037 = 2.963.
![]()
प्रश्न 31.
एक गोले की त्रिज्या 9 सेमी मापी जाती है जिसमें 0.03 सेमी की त्रुटि है। इसके पृष्ठ के क्षेत्रफल के परिकलन में सन्निकट त्रुटि ज्ञात कीजिए। (NCERT)
हल:
माना गोले की त्रिज्या r तथा त्रिज्या मापन में त्रुटि ∆r है
दिया है:
r = 9 सेमी, ∆r = 0.03 सेमी
गोले का पृष्ठ S = 4πr2
\(\frac{dS}{dr}\) = 4π \(\frac{d}{dr}\)r2
⇒ \(\frac{dS}{dr}\) = 8πr
∆S = ( \(\frac{dS}{dr}\) ) ∆r
= (8πr) × 0.03 = 8π × 9 × 0.03 = 2.16 मी2
पृष्ठ क्षेत्रफल के परिकलन में सन्निकट त्रुटि 2.16 मी2 है।
प्रश्न 32.
एक गोले की त्रिज्या 7 मी मापी जाती है जिसमें 0.02 मी की त्रुटि है। इसके आयतन के परिकलन में सन्निकट त्रुटि ज्ञात कीजिए। (NCERT)
हल:
माना गोले की त्रिज्या r तथा त्रिज्या मापन में त्रुटि ∆r है
दिया है:
r = 7 मी, ∆r = 0.02 मी
गोले का आयतन V = \(\frac{4}{3}\)πr3

आयतन के परिकलन में सन्निकट त्रुटि 3.9π मी3 है।
![]()
प्रश्न 33.
x मी भुजा वाले घन की भुजा में 1% वृद्धि के कारण घन के आयतन में होने वाला सन्निकट परिवर्तन ज्ञात कीजिए। (NCERT)
हल:
घन की भुजा x मी है
घन का आयतन V = x3, ∆x = x का 1% = \(\frac{x}{100}\)
\(\frac{dV}{dx}\) = \(\frac{d}{dx}\) x3 = 3x2
आयतन में परिवर्तन ∆V = ( \(\frac{dV}{dx}\) ) ∆x
= 3x2 × \(\frac{x}{100}\) = 0.03 x3 मी3
आयतन में सन्निकट परिवर्तन 0.03x3 मी3 है।
प्रश्न 34.
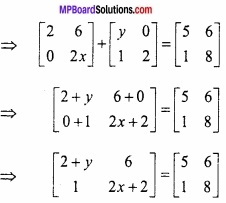
x मीटर भुजा वाले घन की भुजा में 2% वृद्धि के कारण से घन के आयतन में सन्निकट परिवर्तन ज्ञात कीजिए। (NCERT)
हल:
घन की भुजा x मीटर है।
∆x = x का 2% = \(\frac { x\times 2 }{ 100 } \) = 0.02x
घन का आयतन V = x3
\(\frac{dV}{dx}\) = \(\frac{d}{dx}\) x3 = 3x2
dV = ( \(\frac{dV}{dx}\) ) ∆x = 3x2 × 0.02x = 0.06 x3 मी3
आयतन में सन्निकट परिवर्तन 0.06x3 मी3 है।