In this article, we will share MP Board Class 10th Social Science Book Solutions Chapter 15 आर्थिक विकास और नियोजन Pdf, These solutions are solved subject experts from the latest edition books.
MP Board Class 10th Social Science Solutions Chapter 15 आर्थिक विकास और नियोजन
MP Board Class 10th Social Science Chapter 15 पाठान्त अभ्यास
MP Board Class 10th Social Science Chapter 15 वस्तुनिष्ठ प्रश्न
सही विकल्प चुनकर लिखिए
प्रश्न 1.
आर्थिक विकास का परिणाम है – (2014)
(i) जीवन-स्तर में सुधार का
(ii) आर्थिक कल्याण में वृद्धि का
(iii) जीवन प्रत्याशा में वृद्धि का
(iv) उक्त सभी का।
उत्तर:
(iv) उक्त सभी का।
प्रश्न 2.
देश की प्रतिव्यक्ति आय की गणना किस आधार पर की जाती है ?
(i) उस देश की जनसंख्या
(ii) विश्व की जनसंख्या से
(iii) राज्यों की जनसंख्या से
(iv) अन्य देश की जनसंख्या से।
उत्तर:
(i) उस देश की जनसंख्या
प्रश्न 3.
प्रो. अमर्त्य सेन ने विकास का आधार क्या माना है ? (2009, 13)
(i) सम्पन्नता
(ii) आत्मनिर्भरता
(iii) जन-कल्याण
(iv) विदेशी व्यापार।
उत्तर:
(iii) जन-कल्याण
प्रश्न 4.
विकसित देशों में प्राकृतिक संसाधनों का उपयोग होता है –
(i) अतिअल्प
(ii) बिल्कुल नहीं
(iii) थोड़ा-बहुत
(iv) बहुत अधिक।
उत्तर:
(iv) बहुत अधिक।
प्रश्न 5.
अब तक भारत में कितनी पंचवर्षीय योजनाएँ पूर्ण हुई हैं ? (2010)
(i) 5
(ii) 10
(iii) 15
(iv) 11
उत्तर:
(iv) 11
रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति कीजिए
- आर्थिक विकास से जनता के …………………….. स्तर में वृद्धि होती है।
- इण्डिया विजन-2020 का प्रकाशन वर्ष …………………….. में हुआ था। (2011)
- जीवन की भौतिक गुणवत्ता सूचक का निर्माण …………………….. ने किया है। (2016)
- विश्व बैंक के अनुसार विकसित राष्ट्र वह है जिसकी प्रति व्यक्ति आय …………………….. प्रति वर्ष या उससे अधिक है।
- दसवीं योजना का कार्यकाल …………………….. से …………………….. तक था।
उत्तर:
- जीवन
- जनवरी 2003
- प्रो. मौरिस
- ₹4,53,000
- 1 अप्रैल, 2002, 31 मार्च, 2007
MP Board Class 10th Social Science Chapter 15 अति लघु उत्तरीय प्रश्न
प्रश्न 1.
वणिकवाद के अनुसार आर्थिक विकास का क्या अर्थ है ? लिखिए।
उत्तर:
जर्मनी एवं फ्रांस के वणिकवादी विचारक’ सोने एवं चाँदी की प्राप्ति को विकास का आधार मानते थे। विलियम पैटी ने लिखा है, “व्यापार का अन्तिम और महान् परिणाम धन नहीं बल्कि सोना-चाँदी और जवाहरात की प्रमुखता है जो नष्ट नहीं होते। इनको प्रत्येक समय और स्थान में प्रयुक्त किया जा सकता है।”
प्रश्न 2.
राष्ट्रीय आय की गणना किस समय अवधि में की जाती है ? लिखिए। (2017, 18)
उत्तर:
राष्ट्रीय आय की गणना देश में एक वर्ष (1 अप्रैल से 31 मार्च) में उत्पादित वस्तुओं तथा सेवाओं के मौद्रिक मूल्य को जोड़कर ज्ञात की जाती है।
प्रश्न 3.
मानव विकास सूचकांक की गणना किसके आधार पर की जाती है ? लिखिए।
उत्तर:
मानव विकास सूचकांक के निर्माण में जीवन के तीन आवश्यक मूलभूत घटकों का प्रयोग किया जाता है। ये घटक हैं –
- एक लम्बे और स्वस्थ जीवन के मापन हेतु जन्म के समय जीवन प्रत्याशा।
- वयस्क साक्षरता दर तथा कुल नामांकन अनुपात।
- प्रति व्यक्ति सकल घरेलू उत्पाद।
प्रश्न 4.
विश्व बैंक के अनुसार विकसित देशों की प्रति व्यक्ति आय कितनी होनी चाहिए ? लिखिए।
उत्तर:
विश्व बैंक ने अपनी विकास रिपोर्ट 2006 में विकसित एवं विकासशील राष्ट्रों के मध्य अन्तर करने के लिए प्रति व्यक्ति आय मापदण्ड का प्रयोग किया है। रिपोर्ट के अनुसार, वे राष्ट्र जिनकी वर्ष 2004 में प्रति व्यक्ति आय 4,53,000 रु. प्रतिवर्ष या उससे अधिक है, उसे विकसित राष्ट्र तथा वे राष्ट्र जिनकी प्रति व्यक्ति आय 37,000 रु. प्रतिवर्ष या उससे कम है, उन्हें विकासशील (निम्न आय) राष्ट्र माना गया है।
प्रश्न 5.
आर्थिक विकास की माप के प्रमुख मापदण्ड कौन-कौनसे हैं ? लिखिए।
उत्तर:
आधुनिक अर्थशास्त्रियों ने आर्थिक विकास के कई मापदण्ड बताये हैं, जिनमें मुख्य निम्नलिखित हैं –
- राष्ट्रीय आय
- प्रति व्यक्ति आय
- आर्थिक कल्याण, तथा
- सामाजिक अभिसूचक।
MP Board Class 10th Social Science Chapter 15 लघु उत्तरीय प्रश्न
प्रश्न 1.
राष्ट्रीय आय क्या है व इसे कैसे ज्ञात किया जाता है ? लिखिए। (2009, 11, 15)
उत्तर:
राष्ट्रीय आय – किसी देश के श्रम एवं पूँजी उसके प्राकृतिक साधनों के साथ मिलकर एक वर्ष में जिन वस्तुओं और सेवाओं का शुद्ध वास्तविक उत्पादन करते हैं, के मौद्रिक मूल्य को राष्ट्रीय आय कहा जाता है। प्रो. मार्शल के अनुसार, “देश का श्रम एवं पूँजी उसके प्राकृतिक साधनों पर क्रियाशील होकर प्रतिवर्ष भौतिक एवं अभौतिक वस्तुओं के शुद्ध योग, जिसमें सभी प्रकार की सेवाएँ सम्मिलित होती हैं, का उत्पादन करते हैं। यही देश की वास्तविक शुद्ध आय या राष्ट्रीय लाभांश कहलाता है।”
राष्ट्रीय आय की गणना के सम्बन्ध में निम्न बातें महत्वपूर्ण हैं –
- राष्ट्रीय आय का सम्बन्ध किसी अवधि विशेष या एक वर्ष (1 अप्रैल से 31 मार्च) में उत्पादित समस्त वस्तुओं एवं सेवाओं की मात्रा से है।
- राष्ट्रीय आय में सभी प्रकार की वस्तुओं और सेवाओं की बाजार कीमतें सम्मिलित की जाती हैं, इसमें एक वस्तु की कीमत को एक ही बार गिना जाता है।
- इसमें विदेशों से प्राप्त आय को जोड़ा जाता है तथा विदेशियों द्वारा देश से प्राप्त आय को घटाया जाता है।
प्रश्न 2.
प्रति व्यक्ति आय क्या है ? इसकी गणना का सूत्र लिखिए। (2010, 14, 16)
उत्तर:
प्रति व्यक्ति आय (Per Capita Income) – एक देश की किसी वर्ष विशेष में औसत आय को ही प्रति व्यक्ति आय कहते हैं। इसे ज्ञात करने के लिए किसी एक वर्ष को राष्ट्रीय आय में वर्ष की जनसंख्या से भाग दे दिया जाता है।
संक्षेप में,
![]()
स्पष्ट है कि राष्ट्रीय आय में वृद्धि की दर जनसंख्या वृद्धि दर से अधिक होने पर ही प्रति व्यक्ति आय बढ़ेगी अन्यथा इसमें कमी हो जायेगी।
प्रति व्यक्ति आय हमें उस देश के निवासियों के जीवन-स्तर की जानकारी प्रदान करती है। यदि किसी राष्ट्र में प्रति व्यक्ति आय में बढ़ोत्तरी हो रही है तो इसका आशय है कि उस देश के निवासियों के जीवन-स्तर में सुधार हो रहा है।
प्रश्न 3.
मानव विकास के संकेतक बनाने के मुख्य उद्देश्य लिखिए। (2009)
उत्तर:
विकास के अन्तर्गत जनसामान्य को प्राप्त होने वाली स्वास्थ्य, शिक्षा, आवास, पोषक आहार, पेयजल जैसी सुविधाओं की उपलब्धता का भी समावेश होना चाहिए। फलतः आर्थिक विकास को मापने के लिए राष्ट्रीय आय एवं प्रति व्यक्ति आय के विकल्प के रूप में मानव विकास संकेतक’ को महत्व दिया गया।
मानव विकास संकेतकों में भौतिक एवं अभौतिक दोनों प्रकार के घटकों को सम्मिलित किया गया है। इनमें भौतिक घटक के रूप में सकल घरेलू उत्पाद और अभौतिक घटक के रूप में शिशु मृत्यु दर, जीवन की सम्भाव्यता और शैक्षणिक प्राप्तियाँ आदि को लिया गया है।
प्रश्न 4.
भारत के विकसित एवं विकासशील राज्य कौन-कौनसे हैं ? लिखिए।
उत्तर:
प्रति व्यक्ति आय मापदण्ड के आधार पर हम भारत के 15 बड़े राज्यों को दो वर्गों में बाँट सकते हैं-विकसित राज्य तथा विकासशील राज्य। इन 15 राज्यों में 2001 की जनगणना के अनुसार देश की कुल आबादी का 90 प्रतिशत हिस्सा निवास करता है। इसमें से 48 प्रतिशत जनसंख्या तुलनात्मक रूप से विकसित राज्यों में निवास करती है और 42 प्रतिशत आबादी विकासशील या पिछड़े राज्यों में रहती है। तुलनात्मक रूप से विकसित और विकासशील राज्यों को निम्न तालिका में दिखाया गया है।
भारत के विकसित एवं विकासशील राज्य
राज्यानुसार प्रति व्यक्ति निबल घरेलू उत्पाद 2014-15 (वर्तमान कीमतों पर)
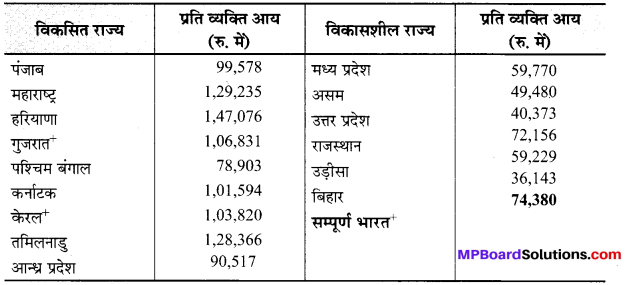
+ : 2012 – 13 के आँकड़े
स्रोत : आर्थिक समीक्षा-2015-16; A – 25
उपर्युक्त तालिका से स्पष्ट है कि भारत में तुलनात्मक रूप से विकसित राज्य वे हैं जिनकी प्रति व्यक्ति आय उस वर्ष की सम्पूर्ण भारत की प्रति व्यक्ति आय से अधिक है, जबकि विकासशील या पिछड़े राज्य वे हैं, जिनकी प्रति व्यक्ति आय सम्पूर्ण भारत की प्रति व्यक्ति आय की तुलना में कम है। 2014-15 में प्रति व्यक्ति आय के आधार पर विकसित राज्यों में हरियाणा का स्थान सबसे ऊपर है, जबकि विकासशील राज्यों में सबसे कम प्रति व्यक्ति आय बिहार राज्य की है।
प्रश्न 5.
इण्डिया विजन-2020 क्या है ? लिखिए। (2009, 11, 13, 14)
उत्तर:
इण्डिया विजन-2020-आने वाले दो दशकों में अर्थव्यवस्था की प्रगति का पूर्वाकलन करने वाला महत्वपूर्ण दस्तावेज ‘इण्डिया विजन-2020’ योजना आयोग ने 23 जनवरी, 2003 को जारी किया। योजना आयोग के इस दस्तावेज में यह दर्शाने का प्रयत्न किया गया है कि दो दशकों के बाद क्या कुछ प्राप्त किया जा सकता है ? दस्तावेज के अनुसार 2020 तक देश की 1.35 अरब जनसंख्या बेहतर पोषित अच्छे रहन-सहन के स्तर वाली, अधिक शिक्षित व स्वस्थ तथा अधिक औसत आयु वाली होगी। निरक्षरता व प्रमुख संक्रामक रोगों का तब तक अन्त हो चुका होगा तथा 6-14 वर्ष आयु वर्ग के बच्चों का स्कूली पंजीकरण लगभग शत-प्रतिशत होगा। 2 प्रतिशत वार्षिक वृद्धि की दर से रोजगार के 20 करोड़ अतिरिक्त अवसर सृजित किए जा सकेंगे।
MP Board Class 10th Social Science Chapter 15 दीर्घ उत्तरीय प्रश्न
प्रश्न 1.
आर्थिक विकास की प्राचीन एवं नवीन अवधारणा को समझाइए। (2009)
उत्तर:
आर्थिक विकास की प्राचीन अवधारणा
प्राचीन काल में आर्थिक विकास के अन्तर्गत भौतिक सुख-सुविधाओं के साथ-साथ मानव मूल्यों को भी महत्वपूर्ण स्थान दिया गया था। महान् विचारक कौटिल्य ने अपनी पुस्तक ‘अर्थशास्त्र’ में इन विचारों की विस्तार से व्याख्या की है। भारत के प्राचीनतम ग्रन्थ वेदों में सबकी समृद्धि और बाहुल्यता की धारणा बताई गई है।
प्राचीनकाल में वैश्विक स्तर पर आर्थिक विकास के अन्तर्गत भौतिक सम्पन्नता को विशेष स्थान प्राप्त था। जर्मनी एवं फ्रांस के ‘वणिकवादी विचारक’ सोने एवं चाँदी की प्राप्ति को विकास का आधार मानते थे। समय के साथ-साथ विकास की अवधारणा भी बदलती रही। एडम स्मिथ का विचार था कि किसी राष्ट्र में वस्तुओं तथा सेवाओं की वृद्धि ही आर्थिक विकास है। कार्ल मार्क्स ने समाजवाद की स्थापना को आर्थिक विकास माना है परन्तु जे. एस. मिल ने लोककल्याण व आर्थिक विकास के लिए सहकारिता के सिद्धान्त को अपनाने को आर्थिक विकास माना।
आर्थिक विकास की नवीन अवधारणा
नवीन अर्थशास्त्रियों में पॉल एलबर्ट राष्ट्र के उत्पादन के साधनों के कुशलतम प्रयोग द्वारा राष्ट्रीय आय में वृद्धि को आर्थिक विकास मानते हैं जबकि विलियमसन और बॉडिक का विचार है कि राष्ट्र के निवासियों की प्रति व्यक्ति आय में वृद्धि आर्थिक विकास है। इनसे भिन्न डी. ब्राइट सिंह का विचार है कि यदि आय में वृद्धि के साथ-साथ समाज कल्याण में भी वृद्धि होती है तो वह आर्थिक विकास है। नोबेल पुरस्कार से सम्मानित ‘प्रो. अमर्त्य सेन’ ने भी आर्थिक कल्याण को विशेष महत्व दिया है।
आर्थिक विकास को परिभाषित करते हुए मेयर एवं बाल्डविन ने कहा है, “आर्थिक विकास एक ऐसी प्रक्रिया है जिसमें दीर्घकाल में अर्थव्यवस्था की वास्तविक राष्ट्रीय आय में वृद्धि होती है।”
प्रश्न 2.
मानव विकास संकेतक का अर्थ बताते हुए इसके घटकों की व्याख्या कीजिए।
उत्तर:
मानव विकास संकेतक (या सूचक)
[Human Development Index-HDI]
मानव विकास ही मानव का साध्य है तथा आर्थिक विकास का श्रेष्ठ मापक है, क्योंकि राष्ट्रीय आय सम्बन्धी आँकड़े अनेक दृष्टियों से उपयोगी होने के बावजूद राष्ट्रीय आय की संरचना व उससे वास्तव में लाभान्वित होने वाले निवासियों पर प्रकाश नहीं डालते। मानव विकास रिपोर्ट के अनुसार, ‘मानव विकास लोगों की पसन्दगी को व्यापक करने की एक प्रक्रिया है।’ ये पसन्दगियाँ अनेक हो सकती हैं और इन पसन्दगियों में समय के साथ परिवर्तन हो सकता है।
इस दिशा में प्रो. मौरिस ने जीवन के भौतिक गुणों के सूचकांक (Physical Quality of Life Index या POLI) का विकास किया। इसी प्रकार प्रो. पॉल स्ट्रीटन (Paul Streetan) के मूल आवश्यकता दृष्टिकोण को अपनाने पर जोर दिया। इन विचारों को मूर्त रूप देते हुए सन् 1990 में संयुक्त राष्ट्र संघ ने मानव विकास संकेतक या सूचकांक (HDI) प्रकाशित किये। इसके बाद आर्थिक विकास के ये संकेतक प्रति वर्ष मानव विकास संकेतक रिपोर्ट में प्रकाशित किये जा रहे हैं।
मानव विकास सूचक की गणना करने के लिए सबसे पहले उपरोक्त तीनों घटकों के अलग-अलग सूचक तैयार किये जाते हैं। तदोपरान्त उनका औसत ज्ञात करके उनके मूल्य को 0 से 1 के मध्य प्रदर्शित किया जाता है। सबसे अधिक विकसित राष्ट्र का सूचक एक तथा सबसे अधिक पिछड़े राष्ट्र का सूचक शून्य के निकट होता है। इस आधार पर विश्व के सभी राष्ट्रों को उनके विकास के स्तर के अनुसार निम्नलिखित तीन वर्गों में वर्गीकृत किया जाता है –
- उच्च मानवीय विकास वाले राष्ट्र-जिन राष्ट्रों के सूचक का माप 0.8 का या इससे अधिक होता है, उन्हें उच्च मानवीय विकास वाले राष्ट्र कहा जाता है।
- मध्यम मानवीय विकास वाले राष्ट्र-जिन राष्ट्रों के सूचक का माप 0.5 से 0.8 होता है उन्हें मध्यम मानवीय विकास वाले राष्ट्र माना जाता है।
- निम्न मानवीय विकास वाले राष्ट्र-जिन राष्ट्रों के सूचक का मान 0-5 से कम होता है उन्हें निम्न मानवीय विकास वाले राष्ट्र माना जाता है।
प्रश्न 3.
विकसित एवं विकासशील अर्थव्यवस्था में अन्तर बताइए।
उत्तर:
विकसित अर्थव्यवस्था – विकसित अर्थव्यवस्था में वे राष्ट्र आते हैं, जहाँ नागरिक अपनी भोजन, कपड़ा व मानवं की आवश्यकताएँ सरलतापूर्वक पूरी कर रहे हैं। इन राष्ट्रों में निर्धनता व बेरोजगारी नियन्त्रण में है। विकसित राष्ट्रों में जापान, अमेरिका, इंग्लैण्ड आदि देश आते हैं।
विकासशील राष्ट्र – ऐसे राष्ट्र जहाँ नागरिकों को भरपेट भोजन भी प्राप्त नहीं होता, पहनने को सीमित मात्रा में कपड़े मिलते हैं, नागरिकों का जीवन-स्तर बहुत निम्न है-इन राष्ट्रों में व्यापक बेरोजगारी व अशिक्षा पायी जाती है। इन राष्ट्रों को अल्पविकसित या विकासशील राष्ट्र कहा जाता है। भारत, पाकिस्तान, बांग्लादेश, श्रीलंका तथा म्यांमार आदि को इस श्रेणी में रखा जाता है।
विकसित तथा विकासशील (अर्द्धविकसित) राष्ट्रों की अर्थव्यवस्था में प्रमुख अन्तर निम्नलिखित हैं –
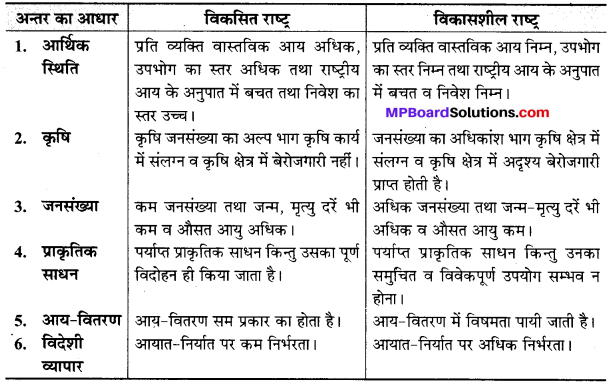
प्रश्न 4.
आर्थिक नियोजन का अर्थ बताते हुए भारत में नियोजन के प्रमुख उद्देश्य बताइए।
उत्तर
आर्थिक नियोजन का आशय
आर्थिक नियोजन का आशय एक केन्द्रीय सत्ता द्वारा देश में उपलब्ध प्राकृतिक एवं मानवीय संसाधनों का सन्तुलित ढंग से, एक निश्चित अवधि के अन्तर्गत निर्धारित लक्ष्यों की प्राप्ति करना है जिससे देश का तीव्र गति से आर्थिक विकास किया जा सके। इस प्रकार आर्थिक नियोजन के लिए दो बातें होनी चाहिए-(1) निर्धारित लक्ष्य, जिन्हें प्राप्त करना है तथा (2) इन लक्ष्यों को प्राप्त करने के लिए उपलब्ध संसाधन तथा उनके उपयोग के ढाँचे का विवरण।
आर्थिक नियोजन में सरकार द्वारा यह सुनिश्चित किया जाता है कि किस प्रकार समाज की अधिकतम सन्तुष्टि के लिए देश के संसाधनों का प्रयोग किया जाता है। नियोजन से पूर्व देश के आर्थिक संसाधनों का आकलन किया जाता है। इसमें घरेलू संसाधनों के साथ-साथ विदेशों से प्राप्त होने वाले साधनों को भी शामिल किया जाता है। इसके बाद आर्थिक लक्ष्यों का निर्धारण कर, देश में उपलब्ध संसाधनों को श्रेष्ठतम प्रयोग करते हुए लक्ष्यों को प्राप्त करने का प्रयास किया जाता है।
भारत में आर्थिक नियोजन के उद्देश्य
भारत में आर्थिक नियोजन के प्रमुख उद्देश्य निम्न प्रकार हैं –
(1) आर्थिक संवृद्धि या विकास – भारत की सभी पंचवर्षीय योजनाओं का मुख्य उद्देश्य आर्थिक संवद्धि रहा है। आर्थिक विकास की गति को तेज करके ही आत्मनिर्भरता की स्थिति को प्राप्त किया जा सकता है तथा गरीबी और बेरोजगारी जैसी आधारभूत समस्याओं का समाधान किया जा सकता है।
(2) आत्मनिर्भरता – आत्मनिर्भरता प्राप्त करना आर्थिक नियोजन का प्रमुख उद्देश्य है। तीसरी योजना के बाद से इस उद्देश्य पर विशेष बल दिया गया। छठी योजना में तो इस लक्ष्य की प्राप्ति पर अधिक जोर दिया गया। इस योजना में निम्नलिखित बातें इस लक्ष्य की प्राप्ति हेतु कही गई
- विदेशी सहायता पर निर्भरता में कमी,
- घरेलू उत्पादन में विविधता और इसके परिणामस्वरूप कुछ महत्त्वपूर्ण वस्तुओं के आयात में कमी, तथा
- निर्यात को प्रोत्साहित करना ताकि हम अपने साधनों से आयातों का भुगतान कर सकें।
(3) रोजगार के अवसरों में वृद्धि करना – सभी को रोजगार प्रदान करना आर्थिक नियोजन का महत्त्वपूर्ण लक्ष्य है। इसलिए प्रत्येक योजना में रोजगार के अवसरों को बढ़ाने तथा अर्द्ध-बेरोजगारी को दूर करने के कार्यक्रमों पर विशेष ध्यान दिया गया है।
(4) आर्थिक असमानताओं में कमी – आयोजन का एक अन्य महत्त्वपूर्ण उद्देश्य आर्थिक समानता है ताकि देश में सामाजिक न्याय की स्थापना की जा सके। धन व आय की असमानताएँ सामान्य जीवन-स्तर को ऊपर उठाने में बाधक होती हैं। स्वस्थ आर्थिक विकास के लिए आवश्यक है कि इन असमानताओं को दूर किया जाये। आयोजन का मुख्य उद्देश्य देश में समाजवादी ढंग के समाज की स्थापना है।।
(5) आर्थिक स्थिरता – आर्थिक आयोजन का एक अन्य महत्त्वपूर्ण उद्देश्य अर्थव्यवस्था में स्थिरता लाना और उसे बनाये रखना है।आर्थिक स्थिरता से अभिप्राय है कि अर्थव्यवस्था में होने वाले अनियमित उतार-चढ़ाव को समाप्त किया जाए जिससे अर्थव्यवस्था ठीक ढंग से आगे बढ़ सके और जनसाधारण के जीवन-स्तर में समय के साथ सुनिश्चित सुधार लाए जा सकें।
प्रश्न 5.
भारत में नियोजन की सफलताएँ और असफलताएँ लिखिए।
अथवा
भारत के नियोजन की सफलताओं की संक्षिप्त वर्णन कीजिए। (2010)
उत्तर:
भारत में नियोजन की सफलताएँ एवं असफलताएँ
भारत में आर्थिक नियोजन 1 अप्रैल, 1951 से प्रारम्भ हुआ। अभी तक 10 पंचवर्षीय योजनाएँ पूर्ण हो गई हैं। इस अवधि में देश का औद्योगिक ढाँचा सुदृढ़ हुआ और कृषि के क्षेत्र में आत्मनिर्भरता प्राप्त हुई। शिक्षा, स्वास्थ्य एवं अन्य सामाजिक क्षेत्रों में तेजी से विस्तार हुआ। भारत में नियोजन से प्राप्त प्रमुख सफलताएँ निम्न प्रकार रहीं –
(1) राष्ट्रीय एवं प्रति व्यक्ति आय में वृद्धि – भारत की राष्ट्रीय आय वर्ष 1950-51 में वर्तमान कीमतों पर केवल 10,360 करोड़ रुपये थी जो वर्ष 2015-16 में बढ़कर 1,34,09,892 करोड़ रुपये हो गई। इसी प्रकार प्रति व्यक्ति आय इस अवधि में 274 रुपये से बढ़कर 93,231 रुपये हो गई। इस प्रकार स्पष्ट है कि नियोजन की अवधि में राष्ट्रीय एवं प्रति व्यक्ति आय में तेजी से वृद्धि हुई है।
(2) पूँजी निर्माण की दर – अर्थव्यवस्था में योजनाकाल के प्रारम्भिक वर्षों में पूँजी निर्माण की दर कम रही है, परन्तु अब पूँजी निर्माण की दर में सुधार है। वर्ष 1950-51 में पूँजी निर्माण की दर सकल घरेलू उत्पाद का 9:3% थी जो वर्ष 2014-15 में बढ़कर 34-2% हो गई।2
(3) कृषि क्षेत्र – नियोजन काल में कृषि के उत्पादन में उल्लेखनीय वृद्धि हुई है। खाद्यान्न उत्पादन जो वर्ष 1950-51 में 508 लाख टन था, वह वर्ष 2014-15 में बढ़कर 2,527 लाख टन हो गया।
(4) विद्युत उत्पादन – योजना काल के दौरान विद्युत का उत्पादन तेजी से बढ़ा है। अनेक नई विद्युत परियोजनाओं का निर्माण किया गया। ताप-विद्युत और अणु शक्ति के विकास का प्रयत्न किया गया। विद्युत उत्पादन वर्ष 1950-51 में 5.1 बिलियन किलोवाट था जो वर्ष 2014-15 में 1105-2 बिलियन किलोवाट हो गया।
(5) औद्योगिक क्षेत्र – योजनावधियों में औद्योगिक प्रगति संतोषजनक रही। औद्योगिक उत्पादन की वृद्धि को हम सूचकांक की सहायता से मापते हैं। भारत में औद्योगिक उत्पादन का सूचकांक जो 1950-51 में मात्र 7.9 (आधार वर्ष 2004-5) था, वह 2014-15 में बढ़कर 176.9 हो गया जो इस बात का सूचक है कि औद्योगिक उत्पादन के क्षेत्र में भारत ने तेजी से प्रगति की है। स्वतन्त्रता के समय भारत सुई से लेकर वायुयान तक विदेशों से आयात करता था। आज भारत न केवल सभी तरह की औद्योगिक वस्तुओं का उत्पादन अपनी आवश्यकताओं की पूर्ति के लिए करता है, बल्कि इनका विदेशों को निर्यात भी करता है।
(6) स्वास्थ्य और परिवार कल्याण योजना काल के दौरान देश में स्वास्थ्य और परिवार कल्याण की सुविधाओं में विस्तार हुआ है। देश भर में अस्पतालों और ग्रामीण डिस्पेन्सरियों की संख्या में वृद्धि हुई है।
- आर्थिक समीक्षा, 2015-16
- पुनः वही।
मृत्यु-दर में कमी स्वास्थ्य सेवाओं के विस्तार का परिणाम है। वर्ष 1950-51 में मृत्यु-दर 27.4 प्रति हजार थी जो वर्ष 2013 में 7 प्रति हजार हो गयी।
(7) शिक्षा – शिक्षा के क्षेत्र में योजना काल में पर्याप्त प्रगति हुई है। नए स्कूलों, कॉलेजों, प्रशिक्षण केन्द्रों, विश्वविद्यालय और छात्रों की बढ़ती हुई संख्या से इस प्रगति का आभास होता है। वर्ष 1950-51 में केवल 30 विश्वविद्यालय एवं 700 महाविद्यालय थे जिनमें लगभग 2.50 लाख छात्र अध्ययन कर रहे थे, जबकि इस समय 757 विश्वविद्यालयों में लगभग 296 लाख छात्र पंजीकृत हैं। स्वतन्त्रता प्राप्ति के बाद से उच्चतर शिक्षा प्रणाली में विश्वविद्यालयों तथा कॉलेजों की संख्या में 38 गुना वृद्धि हई है।
(8) बैंकिंग क्षेत्र में प्रगति – देश ने बैंकिंग क्षेत्र में भी पर्याप्त प्रगति की है। 30 जून, 1969 को वाणिज्य बैंकों की संख्या 8,262 थी जो 30 जून, 2015 को बढ़कर 1,31,750 तक पहुँच गई।
भारत में आर्थिक नियोजन की असफलता के कारण
भारत में आयोजन की सीमित सफलता के अनेक कारण हैं, जिनमें प्रमुख निम्न प्रकार हैं –
(1) प्राकृतिक कारण – भारत में प्राकृतिक दुर्घटनाएँ समय-समय पर अपना प्रभाव दिखाती रही हैं। कभी देश को बाढ़ की मुसीबत झेलनी पड़ती है, कभी सूखे की। कृषि पर इसका विशेष रूप से प्रतिकूल प्रभाव पड़ता है। कृषि उत्पादन में कमी अर्थव्यवस्था के सभी क्षेत्रों को प्रभावित करती है। इसलिए देश में आयोजन को पूरी सफलता नहीं मिलती है।
(2) जनसंख्या में भारी वृद्धि – सन् 1951 से 2011 तक भारत की जनसंख्या में 85 करोड़ की वृद्धि हुई अर्थात जनसंख्या तीन गुना हो गई। इस अवधि में उत्पादन में जो वृद्धि हुई उसे बढ़ी हुई जनसंख्या खा गई जो नियोजन काल में बाधक रही।
(3) सार्वजनिक क्षेत्र की अकुशलता – भारत में आयोजन की सफलता बहुत कुछ सार्वजनिक क्षेत्र की कुशलता पर निर्भर थी। भारत के लोकतान्त्रिक राजनैतिक ढाँचे में सार्वजनिक क्षेत्र की योजनाओं को बनाना, उन पर लोकसभा में विचार होना, उसमें बार-बार काँट-छाँट होना आदि में समय की हानि हुई। अधिकारियों में आपसी तालमेल का अभाव रहा। कभी-कभी विभिन्न परस्पर विरोधी नीतियों को अपनाते रहे। इन सबका संयुक्त परिणाम हुआ आर्थिक आयोजन की सीमित सफलता।
(4) प्रतिरक्षा का भारी बोझ – शान्तिप्रिय राष्ट्र होने के बावजूद भारत पर युद्ध के बादल सदा मँडराते रहे हैं जिससे निपटने के लिए आवश्यक है कि भारत अपनी प्रतिरक्षा व्यवस्था मजबूत करे। साथ ही, युद्ध की आधुनिक तकनीक में अनेक महत्त्वपूर्ण परिवर्तन होते जा रहे हैं। फलस्वरूप, प्रतिरक्षा की व्यवस्था पर होने वाले व्यय की राशि निरन्तर बढ़ती जा रही है।
(5) अन्य आर्थिक कारण – किसी राष्ट्र के तीव्र आर्थिक विकास के लिए कुछ मौलिक सुविधाओं की आवश्यकता होती है; जैसे-यातायात एवं संचार के विकसित साधन, शक्ति के साधनों की उपलब्धि, प्रशिक्षित कारीगर, इन्जीनियर, तकनीशियन और वैज्ञानिक, उन्नत बैंकिंग व्यवस्था और पर्याप्त मात्रा में पूँजी निर्माण। स्वतन्त्रता के समय देश में इन मौलिक आवश्यकताओं का अभाव था। पूँजी निर्माण की दर केवल 5% वार्षिक थी, जबकि विकास के लिए कम-से-कम 25 प्रतिशत होनी चाहिए। प्रशिक्षित कारीगर तथा इन्जीनियर नहीं थे। बहुत-सा समय और साधन इन मौलिक आवश्यकताओं के निर्माण में व्यय हो गए। इस प्रकार आर्थिक विकास की गति धीमी रही और योजनाओं में सफलता भी सीमित ही रही।
उपर्युक्त विवेचन से स्पष्ट है कि नियोजनकाल में कृषि, उद्योग, शिक्षा आदि के क्षेत्रों में जहाँ विकास हुआ है वहीं बेरोजगारी, निर्धनता तथा असमानताओं आदि के क्षेत्र में असफलता रही है। अतः नियोजनकाल की सफलताएँ सीमित रही हैं।
- आर्थिक समीक्षा 2015-16; A – 155.
- आर्थिक समीक्षा 2015-16; A – 69.
MP Board Class 10th Social Science Chapter 15 अन्य परीक्षोपयोगी प्रश्न
MP Board Class 10th Social Science Chapter 15 वस्तुनिष्ठ प्रश्न
बहु-विकल्पीय
प्रश्न 1.
ग्यारहवीं योजना प्रारम्भ हुई
(i) 1 अप्रैल, 2005 से
(ii) 1 अप्रैल, 2006 से
(iii) 1 अप्रैल, 2007 से
(iv) 1 अप्रैल, 2008 से।
उत्तर:
(iii) 1 अप्रैल, 2007 से
प्रश्न 2.
प्राचीन काल में भारत को कहा जाता था -(2009)
(i) सोने का घड़ा
(ii) सोने की चिड़िया
(iii) सोने का देश
(iv) सोने का घर।
उत्तर:
(ii) सोने की चिड़िया
प्रश्न 3.
भारत में आर्थिक नियोजन प्रारम्भ किया गया है
(i) 1 अप्रैल, 1948 से
(ii) 1अप्रैल, 1949 से
(iii) 1 अप्रैल, 1951 से
(iv) 1 अप्रैल, 1955 से।
उत्तर:
(iii) 1 अप्रैल, 1951 से
रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति कीजिए
- आर्थिक विकास एक ………….. प्रक्रिया है।
- व्यक्ति के जीवित रहने की औसत आयु को ………….. कहते हैं।
- वस्तुओं के थोक बाजार में पाए जाने वाले मूल्य को ………….. कहा जाता है।
उत्तर:
- सतत्
- जीवन प्रत्याशा
- थोक मूल्य।
सत्य/असत्य
प्रश्न 1.
जे. एस. मिल ने सहकारिता की स्थापना को आर्थिक विकास का मापदण्ड माना है।
उत्तर:
सत्य
प्रश्न 2.
उत्पादक कार्यों में पूँजी लगाने को विनियोग कहा जाता है। (2014)
उत्तर:
सत्य
प्रश्न 3.
कार्ल मार्क्स ने पूँजी की स्थापना को आर्थिक विकास माना है।
उत्तर:
असत्य
प्रश्न 4.
आर्थिक विकास एक सतत् एवं निरन्तर चलने वाली प्रक्रिया है। (2017)
उत्तर:
सत्य
प्रश्न 5.
भारत में आर्थिक नियोजन के अन्तर्गत अब तक दस पंचवर्षीय योजनाओं को पूरा किया जा चुका है।
उत्तर:
सत्य
जोड़ी मिलाइए

उत्तर:
- → (ग)
- → (क)
- → (ख)
- → (ङ)
- → (घ)
एक शब्द/वाक्य में उत्तर
प्रश्न 1.
कौटिल्य द्वारा लिखी गई पुस्तक का क्या नाम है ?
उत्तर:
अर्थशास्त्र
प्रश्न 2.
भारतीय योजना आयोग का गठन कब किया गया था ? (2017)
उत्तर:
15 मार्च, 1950 को
प्रश्न 3.
मानवीय विकास सूचकांक की गणना किसके आधार पर की जाती है ? कोई एक लिखिए। (2014)
उत्तर:
जीवन प्रत्याशा
प्रश्न 4.
मानव विकास सूचकांक किस अन्तर्राष्ट्रीय संस्था ने तैयार किया है ?
उत्तर:
संयुक्त राष्ट्र संघ ने
प्रश्न 5.
PQLI का पूरा नाम बताइए।
उत्तर:
जीवन का भौतिक गुणवत्ता सूचक
प्रश्न 6.
विश्व बैंक के अनुसार विकासशील राष्ट्रों की प्रति व्यक्ति आय कितनी होनी चाहिए?
उत्तर:
37,000 रुपये प्रतिवर्ष या उससे कम है
प्रश्न 7.
वर्ष 2004-05 में प्रति व्यक्ति आय के आधार पर विकसित राज्यों में किस राज्य का स्थान सबसे ऊपर है ?
उत्तर:
हरियाणा
प्रश्न 8.
देश में सार्वजनिक क्षेत्र में उद्यमों की संख्या कितनी है ?
उत्तर:
242
प्रश्न 9.
भारत में प्रथम पंचवर्षीय योजना कब लागू की गयी है ? (2015)
उत्तर:
1 अप्रैल 1951
MP Board Class 10th Social Science Chapter 15 अति लघु उत्तरीय प्रश्न
प्रश्न 1.
वणिकवाद से क्या आशय है ?
उत्तर:
वणिकवाद से आशय उस आर्थिक विचारधारा से है जो 16वीं शताब्दी से लेकर 18वीं शताब्दी के मध्य तक यूरोप के राष्ट्रों में लोकप्रिय रही।
प्रश्न 2.
आर्थिक कल्याण क्या है ?
उत्तर:
आर्थिक कल्याण, सामाजिक कल्याण का वह भाग है, जिसे मुद्रा के मापदण्ड से प्रत्यक्ष रूप से मापा जा सके।
प्रश्न 3.
नियोजन किसे कहा जाता है ?
उत्तर:
एक निश्चित अवधि में राष्ट्र में उपलब्ध संसाधनों के द्वारा निर्धारित लक्ष्यों का प्राप्त करने की प्रक्रिया को नियोजन कहा जाता है।
प्रश्न 4.
शिशु मृत्यु दर क्या है ?
उत्तर:
एक वर्ष की आयु से पहले हुई मृत्यु, शिशु मृत्यु दर कहलाती है। शिशु मृत्यु दर प्रतिवर्ष हजार जीवित जन्मे शिशुओं में से मृत शिशुओं की संख्या है।
प्रश्न 5.
क्षेत्रीय असन्तुलन से क्या आशय है ?
उत्तर:
जब कुछ क्षेत्रों में उद्योग-धन्धों का केन्द्रीयकरण हो जाता है तथा अन्य क्षेत्र पिछड़े रह जाते हैं तो उसे क्षेत्रीय असन्तुलन कहा जाता है।
MP Board Class 10th Social Science Chapter 15 दीर्घ उत्तरीय प्रश्न
प्रश्न 1.
आर्थिक विकास की प्रमुख विशेषताओं को स्पष्ट कीजिए।
उत्तर:
आर्थिक विकास की विशेषताएँ
आर्थिक विकास के प्रमुख लक्षण (या विशेषताएँ) निम्नलिखित हैं –
- सतत् प्रक्रिया – आर्थिक विकास एक सतत एवं निरन्तर चलने वाली प्रक्रिया है जिसके परिणामस्वरूप राष्ट्रीय आय में क्रमशः वृद्धि होती रहती है। इस प्रक्रिया के परिणामस्वरूप अर्थव्यवस्था में वस्तुओं की माँग और पूर्ति में निरन्तरता बनी रहती है।
- राष्ट्रीय आय और प्रति व्यक्ति आय में वृद्धि – आर्थिक विकास के परिणामस्वरूप राष्ट्रीय आय व प्रति व्यक्ति आय में निरन्तर वृद्धि होती है।
- दीर्घकालीन प्रक्रिया – आर्थिक विकास की निरन्तर प्रक्रिया में वास्तविक राष्ट्रीय आय में निरन्तर वृद्धि होनी चाहिए। इस वृद्धि का सम्बन्ध दीर्घकाल से है जिसमें कम-से-कम 15-20 वर्षों का समय लगता है। आर्थिक विकास का सम्बन्ध अल्पकाल या एक या दो वर्षों में होने वाले परिवर्तनों से नहीं है। इसलिए अगर किसी अर्थव्यवस्था में किन्हीं अस्थायी कारणों से देश की आर्थिक स्थिति में सुधार हो जाता है; जैसे-अच्छी फसल, अप्रत्याशित निर्यात आदि का होना तो इसे आर्थिक विकास नहीं समझना चाहिए।
- संसाधनों का समुचित विदोहन – आर्थिक विकास में देश में उपलब्ध संसाधनों का कुशलतापूर्वक विदोहन किया जाता है।
- उच्च जीवन स्तर की प्राप्ति – आर्थिक विकास के दौरान प्रति व्यक्ति आय में वृद्धि के फलस्वरूप जनसाधारण के जीवन-स्तर में सुधार आता है। आर्थिक विषमता में कमी आती है तथा सरकार द्वारा शिक्षा सार्वजनिक स्वास्थ्य आदि जनकल्याण कार्यक्रमों में वृद्धि की जाती है। इससे लोगों के रहन-सहन का स्तर ऊँचा उठता है। आर्थिक विकास के परिणामस्वरूप राष्ट्र की आय एवं उसमें रहने वाले लोगों की आय में वृद्धि होती है जिसे हम राष्ट्रीय आय एवं प्रति व्यक्ति आय के रूप में जानते हैं।