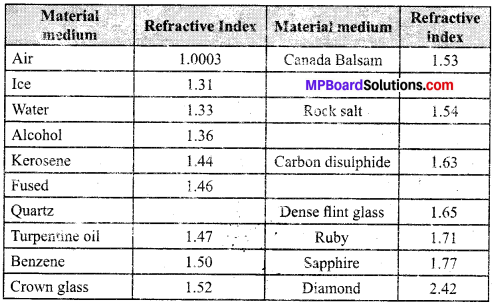
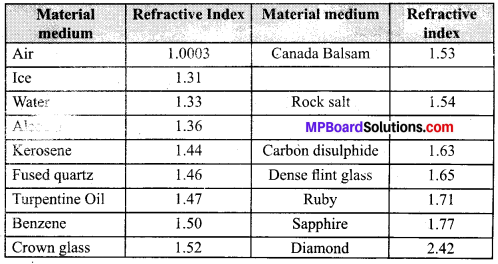
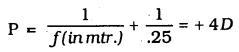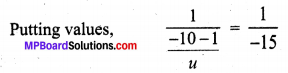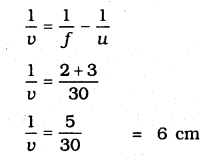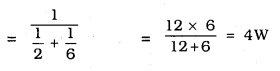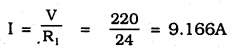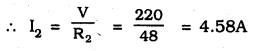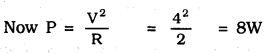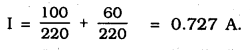MP Board Class 10th Science Solutions Chapter 14 Sources of Energy
MP Board Class 10th Science Chapter 14 Intext Questions
Class 10th Science Chapter 14 Intext Questions Page No. 243
Question 1.
What is a good source of energy?
Answer:
We could then say that a good source of energy would be one.
- Which would do a large amount of work per unit volume or mass.
- be easily accessible.
- be easy to store and transport, and
- perhaps most importantly, be economical.
Question 2.
What is a good fuel?
Answer:
A good fuel is one which
- produces more heat per unit mass. It has high calorific value.
- produces less harmful gases on combustion.
- is cheap and easily available.
- is every to handle safe to transport and convenient to store.
Question 3.
If you could use any source of energy for heating your food, which one would you use and why?
Answer:
We should select which is easily available and it should be cheaper. Bio-gas is an excellent fuel as it contains. It burns without some. Its heating capacity is high. This gas is convenient for consumption and transportation.
![]()
Class 10th Science Chapter 14 Intext questions Page No. 248
Question 1.
What are the disadvantages of fossil fuels?
Answer:
Disadvantages of fossil fuels are as following:
- Fossil fuels are limited source and we can not use them for more than 110-120 years. From not so designing or making machines dependent on them will be a big failure after their loss.
- Fossil fuel generates big amount of pollution which will destroy our atmosphere and increase temperature of earth which lead to destruction of our ecosystem.
Question 2.
Why are we looking at alternate sources of energy?
Answer:
Fossil fuels are a non-renewable source of energy. So we need to conserve them. If we were to continue consuming these sources at such alarming rates, we would soon run out of energy. In order to avoid this, alternate sources of energy were explored.
Question 3.
How has the traditional use of wind and water energy been modified for our convenience?
Answer:
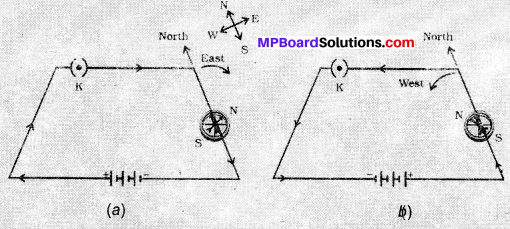
(1) Wind energy: The kinetic energy of the wind can be used to do work. This energy was harnessed by wind mills in the past to do mechanical work. For example in a water lifting pump, the rotatory motion of windmill is utilized to lift water from a well. Today wind energy is also used to generate electricity. A windmill essentially consists of a structure similar to a large electric fan that is erected at some height on a rigid support.
A number of windmills are erected over a large area, which is known as wind energy farm. The energy output of each windmill in a farm is coupled together to get electricity on a commercial scale wind energy farms can be established only at those places where wind blows for the greater part of a year. The wind speed should also be higher than 15 km/h to maintain the required speed of the turbine, since, the tower and blades are exposed to the vagaries of nature like rain, sun, storm and cyclone, they need a high level of maintenance.
(2) Water energy: In order to produce hydel electricity, high rise dams are constructed on the river to obstruct the flow of water and thereby collect water in larger reservoirs. The water level rises and in this process the kinetic energy of flowing water gets transformed into potential energy. The water from the high level in the dam is carried through pipes, to the turbine, at the bottom of the dam. Sine the water in the reservoir would be refilled each time. It rains (hydropower is a renewable source of energy) we would not have to worry about hydro electricity sources getting used up the way fossil fuels would get finished one day.
Class 10th Science Chapter 14 Intext Questions Page No. 253
Question 1.
Can any source of energy be pollution free? Why or why not?
Answer:
Yes, nature show itself some examples of energy conversion which arg pollution free as photosynthesis, as we know in this process photo energy is converted to chemical energy. Hence, solar energy is best way to produce pollution free energy.
Question 2.
Hydrogen has been used as rocket fuel. Would you consider it a cleaner fuel than CNG? Why or why not?
Answer:
Yes, it is cleaner because it does not create any residual hazardous product or chemicals which pollute environment or disbalance the ecosystem. But, handling such big amount of energy properly is required.
Class 10th Science Chapter 14 Intext Questions Page No. 254
Question 1.
Name two energy sources that you would consider to be renewable. Give reasons for your choices.
Answer:
Energy derived from water, wind, sun and ocean all are renewable. All these energies can be harnessed into usable form as long as the solar system exists.
Question 2.
Give the names of two energy sources that you would consider to be exhaustible. Give reasons for your choices.
Answer:
- fossil fuels
- Nuclear fuels
Fossil fuels are present in a limited. amount in the earth. Once exhausted, they will not be available to us again. It takes millions of years for fossil fuel to be formed. The nuclear materials which can be conveniently extracted from earth 7. are limited and hence they will get exhausted one day.
Class 10th Science Chapter 14 NCERT Textbook Exercises
Question 1.
A solar water heater cannot be used to get hot water on:
(a) A sunny day
(b) A cloudy day
(c) A hot day
(d) A windy day
Answer:
(b) A cloudy day
Question 2.
Which of the following is not an example of a bio-mass energy source?
(a) Wood
(b) Gobar-gas
(c) Nuclear energy
(d) Coal
Answer:
(c) Nuclear energy
Question 3.
Most of the sources of energy we use represent stored solar energy. Which of the following is not ultimately derived from the sun’s energy?
(a) Geothermal energy
(b) Wind energy
(c) Nuclear energy
(d) Bio-mass
Answer:
(c) Nuclear energy
Question 4.
Compare and contrast fossil fuels and the sun as direct sources of energy.
Answer:
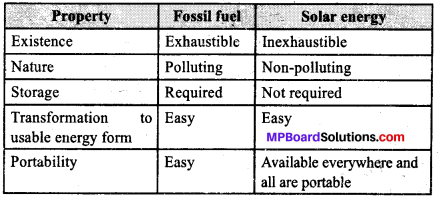
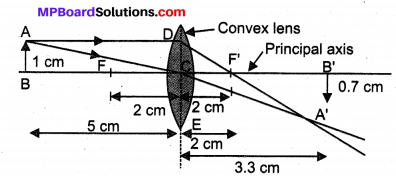
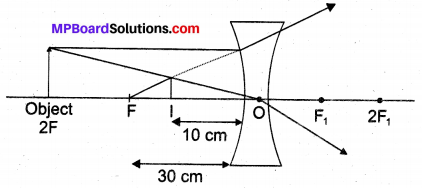
Question 5.
Compare and contrast bio-mass and hydro electricity as sources of energy.
Answer:
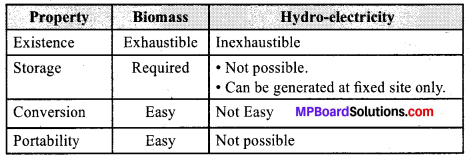
Question 6.
What are the limitations of extracting energy from—
(a) the wind?
(b) waves?
(c) tides?
Answer:
(a) The wind:
- Wind energy farms can be established only at those places where wind blows for the greater part of a year.
- The wind speed should also be higher than 15 km/h to maintain the required speed of the turbine.
- Establishment of wind energy farms require large are of land.
These are the limitations of extracting energy from the wind.
(b) Limitations of extracting waves energy: The waves are generated by strong winds blowing across the sea. Wave energy would be a viable proposition only where waves are very strong.
(c) Limitations of extracting tidal energy: The locations where such dams can be built are limited.
Question 7.
On what basis would you classify energy sources as
(a) renewable and non-renewable?
(b) exhaustible and inexhaustible?
Are the options given in (a) and (b) the same?
Answer:
The options given in (a) and (b) are the same.
Question 8.
What are the qualities of an ideal source of energy?
Answer:
The qualities of an ideal source of energy are as follows:
- Which would do a large amount of work per unit volume or mass.
- Be easily accessible.
- Be easy to store and transport, and
- Perhaps most importantly, be economical.
Question 9.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using a solar cooker? Are there places where solar cookers would have limited utility?
Answer:
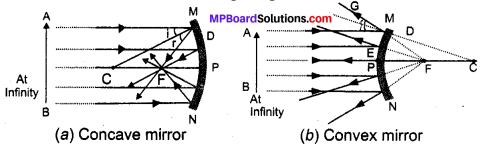
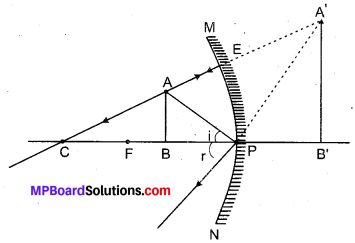
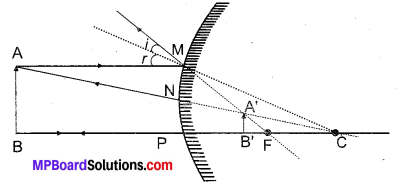
Solar cooker is a device used to trap solar energy and utilize it to cook food. It consists of a box painted black from inside to absorb heat of the Sun (black colour is the best absorber of heat). A thick glass lid is placed over the box to trap heat energy of the sun. A plane mirror reflector is also attached to the box so that a strong beam of sunlight falls over the cooker’s top.
The reflector of the solar cooker sends strong beams of sunlight over the top of the cooker. Sunlight consists of about 1/3 rd infra-red rays which have a heating effect. These infra-red rays are of shorter wavelength as these are produced by a very hot source of heat. The glass lid over the cooker allows these infra-red rays of short wavelength into the cooker but does not allow the infra-red rays which are emitted by the black surface of the cooker to escape as these are of longer wavelength. Thus, heat energy of the sun gets trapped in the black box of the solar cooker. This heat cooks the food material kept in the black box.
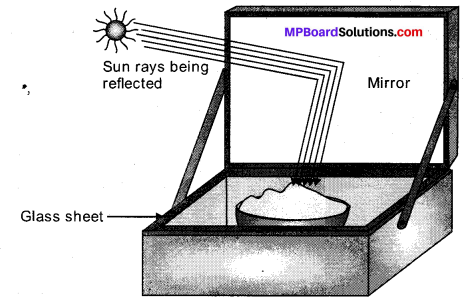
Fig. 14.1: Solar heating device (solar cooker).
Advantages of solar cooker:
- It is used to cook food and saves precious fossil fuel.
- It does not cause any pollution.
- No smoke is produced during the working of a solar cooker.
- Nutrients of food material, which is to be cooked in the solar cooker, do not get destroyed.
- Four food items can be cooked at the same time.
Disadvantages:
- It cannot be used to cook food during the night.
- It cannot be used to cook food on a cloudy day.
- The direction of the reflector has to be changed after a small interval of time with the change of position of the sun.
Question 10.
What are the environmental consequences of the increasing demand for energy? What steps would you suggest to reduce energy consumption?
Answer:
They are:
- Burning of fossil fuels to meet the increasing demand for energy causes air pollution.
- Construction of dams and rivers to generate hydroelectricity destroys large ecosystems which get submerged underwater in the dams further, a large amount of methane [which is a green house gas] is produced when submerged vegetation rots under anaerobic conditions.
In order to reduce energy consumption
- Fossil fuel should be used with care and caution to derive maximum benefit out of them.
- Fuel saving devices such as pressure cookers etc should be used.
- Efficiency of energy sources should be maintained be getting them regularly serviced.
- And last of all, we should be economical in our energy consumption as energy saved is energy produced.
![]()
MP Board Class 10th Science Chapter 14 Additional Important Questions
MP Board Class 10th Science Chapter 14 Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Can we convert any form of energy to its other form?
(a) Yes
(b) No
(c) May be Yes
(d) None
Answer:
(a) Yes
Question 2.
Photosynthesis represents what kind of conversion of energy:
(a) Conversion of photo-energy to chemical energy
(b) Conversion of chemical energy to photo-energy
(c) Conversion of physical energy to photo-energy
(d) Conversion of chemical energy to electrical energy
Answer:
(a) Conversion of photo-energy to chemical energy
Question 3.
Which one of the following is good source of energy?
(a) Burning wood
(b) Burning cooking oil
(c) Burning wax
(d) Burning petroleum
Answer:
(d) Burning petroleum
Question 4.
Fuel not used for cooking is:
(a) LPG
(b) Coal
(c) Petrol
(d) PNG
Answer:
(c) Petrol
Question 5.
Renewable source of energy is:
(a) Diesel
(b) Water
(c) Coal
(d) Petrol
Answer:
(b) Water
Question 6.
Physical energy is changed to electrical energy in:
(a) Thermal power plant
(b) Hydro power plant
(c) Photosynthesis
(d) None
Answer:
(a) Thermal power plant
Question 7.
Which one among following is not a property of biomass fuel?
(a) It contains 75% methane
(b) Bum without smoke
(c) Leaves no residue
(d) Easy to install
Answer:
(c) Leaves no residue
Question 8.
What kind of energy is used in wind energy form?
(a) Potential energy
(b) Kinetic energy
(c) Chemical energy
(d) Photo-energy
Answer:
(b) Kinetic energy
Question 9.
Which one is among alternative non-conventional source of energy?
(a) Fossil fuel
(b) Biomass
(c) Solar energy
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Solar energy
Question 10.
What percent of total of solar energy is absorbed on earth:
(a) 10%
(b) 50%
(c) 100%
(d) Can’t calculate
Answer:
(a) 10%
Question 11.
Ultimate source of energy on earth is:
(a) Electricity
(b) Nuclear energy
(c) Fossil fuel
(d) Sun
Answer:
(d) Sun
Question 12.
To maintain a wind energy farm, the wind speed should be:
(a) 1-2 km/h
(b) 180-200 km/h
(c) 15-20 km/h
(d) Can’t be calculated
Answer:
(c) 15-20 km/h
Question 13.
Which of the following element is chosen for generating nuclear energy?
(a) Uranium
(b) Silicon
(c) Germanium
(d) Carbon
Answer:
(c) Germanium
Question 14.
How bio gas is generated in biomass plant?
(a) By distillation
(b) By anaerobic fermenting
(c) By reduction
(d) By simple burning
Answer:
(b) By anaerobic fermenting
Question 15.
Natural gas contains:
(a) CO2
(b) H2O
(c) CH4
(d) NH3
Answer:
(c) CH4
Question 16
…………. is used in a solar cell for storing energy.
(a) Gold
(b) Silver
(c) Germanium
(d) Silicon
Answer:
(d) Silicon
Question 17.
The stored heat in the earth is harnessed as:
(a) Fuel
(b) Geothermal energy
(c) Solar energy
(d) Biomass
Answer:
(b) Geothermal energy
Question 18.
Main constituent of LPG is:
(a) Butane
(b) Methane
(c) Propane
(d) Ethane
Answer:
(c) Propane
Question 19.
High calorific value of a material represents:
(a) A good manure
(b) A good fuel
(c) Protein rich material
(d) A good conductor of electricity
Answer:
(b) A good fuel
Question 20.
…………………… is a coal with highest carbon content
(a) Bituminous
(b) Peat
(c) Anthracite
(d) None
Answer:
(c) Anthracite
![]()
MP Board Class 10th Science Chapter 14 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name two things which are considered as good source of energy.
Answer:
Coal and petrol.
Question 2.
Write a main characteristic of a good fuel.
Answer:
It should release a large amount of energy per unit volume.
Question 3.
Which food product can be used to produce light energy?
Answer:
Cooking oil and fodder.
Question 4.
What kind of energy source can be used with the help of concave mirror?
Answer:
Solar energy when being used in solar appliances.
Question 5.
What kind of energy is heat energy of molten rock present inside earth core?
Answer:
Geothermal energy.
Question 6.
Name two energy sources which are conventional and renewable in nature.
Answer:
Biomass and hydroelectricity.
Question 7.
Write one limitation of use of fossil fuels.
Answer:
Pollution.
Question 8.
How much percent of CH4 is present in Bio gas?
Answer:
75%.
Question 9.
Write two kind of solar energy manifestation to oceans.
Answer:
Wave energy and ocean thermal energy.
Question 10.
What percentage of nuclear energy is contributed in total energy production in India?
Answer:
Approximately 3-4%.
Question 11.
What is main source of solar energy?
Answer:
Sun is the main source of energy.
Question 12.
Give one cause of limitation of solar energy.
Answer:
Solar energy is costly.
Question 13.
What is nuclear energy?
Answer:
Nuclear fission is the process during which two nucleus fuse to form one nucleus. The energy which is produced in this process called nuclear energy.
Question 14.
Give three examples of energy which is produced from sea.
Answer:
Tidal Energy, wave energy and Ocean thermal energy.
![]()
MP Board Class 10th Science Chapter 14 Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Why it is important to consume energy wisely?
Answer:
When we use energy in its usable form we convert the form of energy and get our work done during the process. Since, we cannot reverse . the change involved in this process so we cannot get back the original usable form of energy. Due to this, it becomes important to think about energy shortage and the related energy crisis.
Question 2.
Write characteristics of a good source of energy.
Answer:
Characteristics of a good source of energy are:
- It should be effective i.e., able to do large amount of work in mass or volume.
- It should be easily accessible.
- It should be easily transported from one place to other.
- It should be economical.
Question 3.
What are conventional sources of energy?
Answer:
The sources of energy which have been in knowledge since a long time are conventional sources of energy. Firewood, coal, petroleum, natural gas, hydel energy, wind energy and nuclear energy are considered to be the conventional sources of energy.
Question 4.
Give two examples of fossil fuels.
Answer:
Two examples of fossil fuels used commercially for producing energy are:
Coal: The plants buried under swamps after death for very long time and due to high pressure and high temperature inside the earth; they are converted into coal. Coal is the highest used energy source in India.
Petroleum: The animals body after death get buried under the ocean surface and due to high pressure and high tempera lure inside the water were converted into petroleum; in due course of time Petroleum is among the major source of energy. Petroleum products are used as automobile fire! and also in the chemical industries.
Question 5.
Differentiate between non-renewable and renewable sources of Energy.
Answer:
Non-renewable sources of Energy: It takes millions of years for the formation of fossils fuels. Since, they cannot be replenished in the foreseeable future, they are known as non-renewable sources of energy.
Renewable sources of Energy: Those sources of energy which can be replenished quickly are called renewable sources of energy. Hydel energy, wind energy and solar energy are examples of renewable sources of energy.
Question 6.
What is hydel energy?
Answer:
Hydel Energy: Hydel energy is produced by utilizing the kinetic energy of flowing water. Huge dams are built over a source of water. Water is collected behind ‘the dam and released. When the water falls on the turbine; the turbine moves; because of kinetic energy of water. Electricity is generated by the turbine. Electricity; thus generated is called hydel energy of hydroelectricity. Water in the reservoir is replenished with rainwater and so, availability of water is, not a problem for hydroelectricity.
Question 7.
How electricity is generated in thermal power plant?
Answer:
In a thermal power plant, coal or petroleum is used for converting water into steam. The steam is used to run the turbine and thus, electricity in generated.
Question 8.
Define biomass.
Answer:
Biomass: The plants and animals constitute the biomass. Farm waste; such as stalks of harvested plants and dung of cattle; can be used to generate methane. The decomposition of biomass produces methane; which can be channelized for useful purposes.
Question 9.
What is bio-gas plant? How it is channelized?
Answer:
Bio-gas plant: Bio-gas plant can be very useful in solving the energy need of rural areas. A bio gas plant is a dome like structure which is usually built from bricks and concrete. In the mixing tank; the slurry is made from cow dung and water. The slurry then goes to the digester; which is a closed chamber. Since oxygen is absent in the digester, the anaerobes carry on their work of decomposition. The process of decomposition produces bio gas. Bio gas has about 70% of methane and the rest is composed of other gases.
The bio gas is channelized through a pipe and can be utilitzed as kitchen fuel and also as fuel for getting light. The slurry; left behind; is removed. It is used as manure, once it dries.
Question 10.
What is wind energy?
Answer:
Wind energy has been in use since ages. The sail boats of the pre-industrialisation era used to run on wind power. Windmills have been in use; especially in Holland; since the medieval period. Nowadays, windmills are being used to generate electricity. The kinetic energy of wind is utilized to run the turbines; which generate electricity.
Question 11.
What is non-conventional sources of energy?
Answer:
Energy sources which are relatively new are called non-conventional sources of energy, e.g., nuclear power and solar energy.
Question 12.
Explain solar energy.
Answer:
The sun is the main source of energy for all living beings on this earth. Even the energy in the fossil fuels has come from the sun. The sun is an endless reservoir of energy which would be available as long as the solar system is in existence. Technologies for harnessing the solar energy have been developed in recent times.
Question 13.
What is solar cooker and how food is cooked in it?
Answer:
Solar cooker is very simple in design and mode of function. It is usually made from mirrors. Plane mirrors are placed inside a rectangular box. The light reflected from the plane mirrors concentrates the solar energy inside the solar cooker which generates enough heat to cook food.
Question 14.
What are solar cells?
Answer:
Solar cells: Solar cells are made from silicon. The solar panel converts solar energy into electrical energy which is stored in a battery; for later use.
Question 15.
What is tidal energy?
Answer:
Due to the gravitational pull of the moon, tides happen near seashores. Water rushes up near the seashore during a high tide and goes down during a low tide. Dams are built near seashores to collect the water which comes during a high tide. When the water runs back to the ocean, the flow of water can be utilized to generate electricity.
Question 16.
How energy is generated from molten rocks?
Answer:
The molten rocks from the inside the earth are pushed in certain regions of the earth. Such regions are called the hot spots of the earth. When groundwater comes in contact with such hot spots, lot of steam is generated. This steam can be harnessed to produce energy which is called Geothermal Energy.
Question 17.
What is nuclear energy?
Answer:
Nuclear fission is the process during which two nucleus fuse to form one . nucleus. The process generates a huge amount of energy. This phenomenon is utilized in nuclear power plants. Nuclear power is safest for the environment but the risk of damage due to accidental leaks of radiation is pretty high. Further, storage of nuclear waste is a big problem because of potential risk of radiation involved. Nonetheless, many countries are using nuclear power in a big way.
![]()
MP Board Class 10th Science Chapter 14 Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Define biomass. What is Bio gas plant? How it is channelized?
Answer:
Biomass: The plants and animals constitute the biomass. Farm waste; such as stalks of harvested plants and dung of cattle; can be used to generate methane. The decomposition of biomass produces methane; which can be channelized for useful purposes.
Bio gas plant: Bio gas plant can be very useful in solving the energy need of rural areas. A bio gas plant is a dome like structure which is usually built from bricks and concrete. In the mixing tank; the slurry is made from cow dung and water. The slurry then goes to the digester; which is a closed chamber. Since oxygen is absent in the digester, the anaerobes carry on their work of decomposition. The process of decomposition produces bio gas, has about 70% of methane and the rest ‘is composed of other gases. The bio gas is channelized through a pipe and can be utilized as kitchen fuel and also as fuel for getting light. The slurry; left behind; is removed. It is used as manure, once it dries.
Question 2.
What is wind energy? Write limitations of wind energy.
Answer:
Wind energy has been in use since ages. The sail boats of the re-industrialization era used to run on wind power. Windmills have been in use; especially in Holland; since the medieval period.
Nowadays, windmills are being used to generate electricity. The kinetic energy of wind is utilized to run the turbines; which generate electricity.
Limitations of wind Energy: Wind farms can only be established at those places where the wind speed is high enough and is more than 15 km/hr for most parts of the year. Wind farms need to be established on large tracts of land. The fan of the windmill has many moving parts; so cost of maintenance and repair is quite high. The fact, that it has to suffer the vagaries of the nature, further compounds the problem. Initial cost of establishing a wind farm is very high.
Question 3.
Briefly explain energy from sea.
Answer:
Tidal energy: Due to the gravitational pull of the moon, tides happen at seashores. Water rushes up near the seashore during a high tide and goes down during a low tide. Dams are built near seashores to collect the water which comes during a high tide. When the water runs back to the ocean, the flow of water can be utilized to generate electricity.
Wave Energy: Waves can also be a good source of energy. Many devices are being designed and tested to produce wave energy. For example; a hollow tower is built near the seashore. When water gushes in the tube because of wave, it forces the air upwards. The kinetic energy of air in the tube is used to run a turbine. When the wave goes down; air from up goes down the tube which is also used in running the turbine.
Ocean Thermal Energy. The water at sea surface is hot during daytime, while the water at lower level is cold. The temperature differential in water levels can be utilized to generate energy. If the temperature differential is more than 20°C, then ocean thermal energy can be utilized from that place. For this, a volatile liquid; like ammonia; is boiled using the heat from the hot water at the surface. The steam of the volatile liquid is utilized to run the turbine to generate electricity. Colder water from the surface below is utilized to condense ammonia vapour which is then channelized to the surface to repeat the cycle.
Question 4.
Explain Solar Energy. How is food cooked with help of solar energy and also explain its limitations.
Answer:
The sun is the main source of energy for all living beings on this earth. Even the energy in the fossil fuels has come from the sun. The sun has an endless reservoir of energy which would be available as long as the solar system is in existence. Technologies for harnessing the solar energy hav been developed in recent times.
Solar cooker is very simple in design and mode of function. It is usually made from mirrors. Plane mirrors are placed inside a rectangular box. The light reflected from the plane mirrors concentrates the solar energy inside the solar cooker which generates enough heat to cook food.
Limitations of solar Energy: The technologies for harnessing solar energy are at a nascent stage. At present, the cost benefit ratio for using solar energy is not conducive. Using solar energy is exhorbitantly costly.
![]()
MP Board Class 10th Science Chapter 14 NCERT Textbook Activities
Class 10 Science Activity 14.1 Page No. 242
- List four forms of energy that you use from morning, when you wake up, till you reach the school.
- From where do we get these different forms of energy?
- Can we call these ‘sources’ of energy? Why or why not?
Observations:
- Forms of energy that we use are electrical energy, mechanical energy, chemical energy for vehicles, chemical energy from food.
- Energy can neither created nor destroyed. It is just transferred from one form to the other.
- The ‘sources’ of energy are the one which releases energy to be used in such forms.
Class 10 Science Activity 14.2 Page No. 243
- Consider the various options we have when we choose a fuel for cooking our food.
- What are the criteria you would consider when trying to categories something as a good fuel?
- Would your choice be different if you lived:
(a) in a forest?
(b) in a remote mountain village or small island?
(c) in New Delhi?
(d) lived five centuries ago?
- How are the factors different in each case?
Observations:
- The criteria for good fuel inducts amount of energy released upon combustion, smoke produced or not, easily accessible, economical and easy be store and transport.
- In forest or remote village, wood from forests can be used as fuel.
- In new Delhi, electrical energy would be a choice.
- Five centuries ago, may be mechanical energy would have been used.
- Factors includes availability of the sunrises and case in utilizing them.
Class 10 Science Activity 14.3 Pages No. 244-245
- Take a table-tennis ball and make three slits into it.
- put semicircular
 fins cut out a metal sheet into these slits.
fins cut out a metal sheet into these slits. - Pivot the tennis ball on an axle through its centre with a straight metal wire fixed to a rigid support. Ensure that the tennis ball rotates freely about the axle.
- Now connect a cycle dynamo to this,
- Connect a bulb in series.
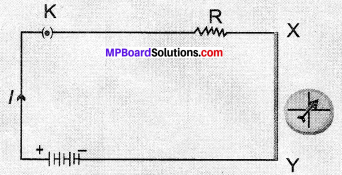
- Direct a jet of water or steam produced in a pressure cooker at the fins (Fig. 14.2). What do you observe?
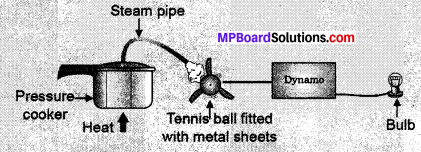
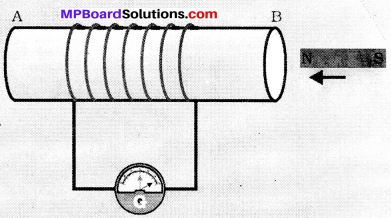
Fig. 14.2: A model to demonstrate the process – of thermo – electric production.
Observations:
- We observe that fan starts morning. The rotor blade also moves with speed that turn the shaft of the dynamo and concert the mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Class 10 Science Activity 14.4 Page No. 248
- Find out from your grand-parents or other elders:
- (a) how did they go to school?
- (b) how did they get water for their daily needs when they were young?
- (c) what means of entertainment did they use?
- Compare the above answers with how you do these tasks now.
- Is there a difference? If yes, in which case more energy from external sources is consumed? _
Observations:
- Earlier, people used to go school on-foot.
- The water were drawn from wells from far off places and carried on head in pots to the home.
- Means of entertainment includes folk dances, songs etc.
- The scenario has totally changed, nowadays, people are being separately and generally, not in noses as were done decades ago. More energy from internal sources is consumed these days to fulfill the demands of energy which is inversed a lot.
Class 10 Science Activity 14.5 Page No. 249
- Take two conical flasks and paint one white and the other black. Fill both with water.
- Place the conical flasks in direct sunlight for half an hour to one hour.
- Touch the conical flasks. Which one is hotter? You could also measure the temperature of the water in the two conical flasks with a thermometer.
- Can you think of ways in which this finding could be used in your daily life?
Observations:
- The one with black colour is hotter as black absorbs more heat as compared to white one.
- In daily life, we apply this on the colour we wear. The days which are that, we avoid black colours as they absorb more heat. Sincerity for cooling effect, white colours used.
Class 10 Science Activity 14.6 Pages No. 249-250
- Study the structure and working of a solar cooker and/or a solar water- heater, particularly with regard to how it is insulated and maximum heat absorption is ensured.
- Design and build a solar cooker or water-heater using low-cost material available and check what temperatures are achieved in vour system.
- Discuss what would be the advantages and limitations of using the solar cooker or water-heater.
Observations:
- The minimum heat absorption is ensured by painting it black in colour. The glass used on the lop traps the infrared rays from the sun and do not allow them the escape.
- Advantages includes no wastage of energy as solar energy is a trapped to be used further. It is a renewable some of energy that do not create any pollution.
- Limitations includes plausibility of solar rays at certain times of day only. It will not work on sunny days.
Class 10 Science Activity 14.7 Page No. 252
- Discuss in class the question of what is the ultimate source of energy for bio-mass, wind and ocean thermal energy.
- Is geothermal energy and nuclear energy different in this respect? Why ?
- Where would you place hydro electricity and wave energy?
Observations:
- The cleaner source of energy is the sun. Yes, cleaner energy is obtained from fusion or fission of molecules whereas geothermal energy is the energy present in the earth. The energy from geological changes is harnessed to be used in various ways.
- Hydro electricity and wave energy are also form of renewable energy.
Class 10 Science Activity 14.8 Page No. 253
- Gather information about various energy sources and how each one affects the environment.
- Debate the merits and demerits of each source and select the best source of energy on this basis.
Observations:
- Among the various source of energy, renewable sources of energy are the best as they do not harm the environment and this energy can be reused and when required. Non-renewable resources of’energy are harmful to the environment and causes pollution.
- Best sources of energy arc renewable sources of energy like solar, hydro, tidal, wave energy etc.
Class 10 Science Activity 14.9 Page No. 254
- Debate the following two issues in class.
(a) The estimated coal reserves are said to be enough to last us for another two hundred years. Do you think we need to worry about coal getting depleted in this case? Why or why not?
(b) It is estimated that the Sun will last for another five billion years. Do we have to worry about solar energy getting exhausted? Why or why not?
- One the basis of the debate, decide which energy sources can be considered
- exhaustible
- inexhaustible
- renewable
- non-renewable.
Give your reasons for each choice.
Observations:
- Yes, we need to worry about availability of coal as resources are limited they are made from fossil fuels which take millions of years to be formed. Also, they cause pollution and harm the environment.
- Sun will least for another five billion years but we should use this to the maximum as there are still so many years in which it can be utilized, harness eat and stored.
- Exhaustible are those energy sources which will get exhausted soon from fossil fuel inexhaustible are the one like solar, tidal etc. Renewable can be used whereas non-renewable are not used again and again.