MP Board Class 8th Sanskrit Solutions Surbhi Chapter 9 वसन्तोत्सवः
MP Board Class 8th Sanskrit Chapter 9 अभ्यासः
Mp Board Class 8 Sanskrit Chapter 9 प्रश्न 1.
एकपदेन उत्तरं लिखत(एक शब्द में उत्तर लिखो-)
(क) वसन्तपञ्चमी कस्य आगमनं सूचयति? (वसन्त पञ्चमी किसके आगमन को सूचित करती है?)
उत्तर:
ऋतुराजवसन्तस्य (ऋतुराज वसन्त के)
(ख) केषु नूतनकिसलयरागः राजते? (किन पर नये पत्तों की शोभा सुशोभित होती है?)
उत्तर:
वृक्षेषु। (पेड़ों पर)
(ग) केकिलानां मधुरस्वरः किम् आकर्षित? (कोयलों का मधुर स्वर किसको आकर्षित करता है?)
उत्तर:
चित्तम्। (मन को)
(घ) वसन्तोत्सवे कस्याः पूजनम् भवति? (वसन्त उत्सव में किसका पूजन होता है।)
उत्तर:
सरस्वत्याः। (सरस्वती का)
(ङ) ज्ञानस्य अधिष्ठात्री देवी का? (ज्ञान की मुख्य देवी कौन है?)
उत्तर:
शारदा। (सरस्वती)
Class 8 Sanskrit Chapter 9 Mp Board प्रश्न 2.
एकवाक्येन उत्तरं लिखत(एक वाक्य में उत्तर लिखो-)
(क) ऋतुराजवसन्तस्य आगमन-सूचना कदा भवति? (ऋतुराज वसन्त के आगमन की सूचना कब होती है?)
उत्तर:
ऋतुराजवसन्तस्य आगमन-सूचना माघमासस्य शुक्लपक्षस्य पञ्चम्यां तिथौ भवति। (ऋतुराज वसन्त के आगमन की सूचना माघ महीने के शुक्ल पक्ष की पंचमी तिथि को होती है।)
(ख) आमेषु कीदृशाःभ्रमराः दृश्यन्ते? (आमों पर कैसे भंवरे दिखाई देते है?)
उत्तर:
आनेषु भ्रमन्तः भ्रमराः दृश्यन्ते? (आमों पर घूमते हुए भंवरे दिखाई देते हैं।)
(ग) तमिलनाडुराज्ये जनाः शारदां कथम् अर्चयन्ति। (तमिलनाडु राज्य में लोग शारदा को कैसे पूजते हैं?)
उत्तर:
तमिलनाडुराज्ये जनाः प्रकाशितान् हस्तलिखितान् ग्रन्थान् एकस्याम् पीठिकायां संस्थाप्य विविधैः उपचारैः शारदां अर्चयन्ति। (तमिलनाडु राज्य में लोग प्रकाशित हस्तलिखित ग्रन्थों को एक चौकी पर रखकर विभिन्न पूजा की विधियों से शारदा की पूजा करते हैं।)
(घ) वसन्तोत्सवः किं किं द्योतयति? (वसन्तोत्सव क्या-क्या प्रकट करता है।)
उत्तर:
वसन्तोत्सवः भारतीयानां उत्सवप्रियतायाः शास्त्रीयं, सामाजिक तथा वैज्ञानिक चिन्तनं अपि द्योतयति। (वसन्तोत्सव भारतीयों की उत्सव प्रियता की शास्त्रीय, सामाजिक तथा वैज्ञानिक सोच को भी प्रकट करता है।)
(ङ) उत्तरभारते कुत्र-कुत्र सरस्वतीपूजनं बहुमान्यम् अस्ति? (उत्तरभारत में कहाँ-कहाँ सरस्वती पूजा बहुत मान्य है?)
उत्तर:
उत्तर भारते बिहार प्रान्ते, बङ्गालप्रान्ते तथा काश्मीर प्रदेशे सरस्वतीपूजनं बहुमान्यम् अस्ति। (उत्तर भारत में बिहार प्रान्त में, बंगाल प्रान्त में तथा कश्मीर प्रदेश में सरस्वती पूजा बहुत मान्य है।)
Mp Board Class 8 Sanskrit Solution Chapter 9 प्रश्न 3.
प्रश्ननिर्माणं कुरुत (रेखांकितपदम् आधृत्य) [प्रश्न निर्माण करो (रेखांकित शब्द के आधार पर])
(क) विविधैः पुष्पैः ऋतुराजस्य स्वागतम् भवति। (विविध पुष्पों के द्वारा ऋतुराज का स्वागत होता है।)
उत्तर:
विविधैः पुष्पैः कस्य स्वागतम् भवति? (विविध पुष्पों के द्वारा किसका स्वागत होता है?)
(ख) पुस्तकानाम् अपि पूजनम् भवति। (पुस्तकों का भी पूजन होता है।)
उत्तर:
केषाम् अपि पूजनम् भवति? (किनका पूजन भी होता है?)
(ग) शारदाम् अर्चयन्ति। (शारदा की अर्चना करते हैं।)
उत्तर:
काम् अर्चयन्ति? (किसकी अर्चना करते हैं?)
(घ) सौन्दर्य कामयिंतु वसन्तपूजनम् भवति। (सुन्दरता की कामना के लिए वसन्त पूजा होती
उत्तर :
सौन्दर्य कामयितु किम् भवति? (सुन्दरता की कामना के लिए क्या होती है?)
(ङ) श्रीपञ्चमीनाम्ना वसन्तपञ्चमी ज्ञायते। (श्रीपंचमी नाम से वसन्तपंचमी जानी जाती है।)
उत्तर:
श्री पञ्चमीनाम्ना का ज्ञायते? (श्रीपंचमी नाम से क्या जानी जाती है।)
Sanskrit Class 8 Mp Board प्रश्न 4.
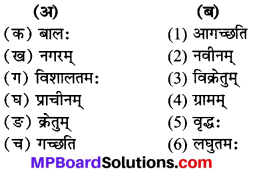
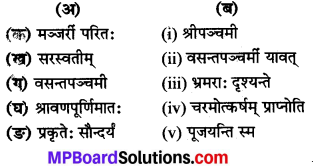
अर्थानुसारं युग्मानि योजयत (अर्थ के अनुसार जोड़े मिलाओ-)
उत्तर:
(क) → (iii)
(ख) → (v)
(ग) → (i)
(घ) → (ii)
(ङ) → (iv)
Mp Board Class 8 Sanskrit प्रश्न 5.
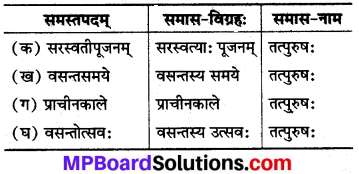
नामोल्लेखपूर्वकं समासविग्रह कुरुत (नाम का उल्लेख करते हुए समास विग्रह करो-)
(क) सरस्वतीपूजनम्
(ख) वसन्तसमये
(ग) प्राचीनकाले
(घ) वसन्तोत्सवः।
उत्तर:
एमपी बोर्ड क्लास 8th संस्कृत प्रश्न 6.
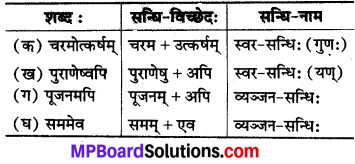
नामोल्लेखपूर्वकं सन्धिविच्छेदं कुरुत (नाम का उल्लेख करते हुए सन्धि-विच्छेद करो-)
(क) चरमोत्कर्षम्
(ख) पुराणेष्वपि
(ग) पूजनमपि
(घ) सममेव।
उत्तर:
Class 8 Sanskrit Mp Board प्रश्न 7.
पाठात् पञ्च अव्ययानि चित्वा लिखत। (पाठ में से पाँच अव्यय चुनकर लिखो।)
उत्तर:
(क) अपि:
(ख) सर्वत्र
(ग) च
(घ) अधुना
(ङ) एव।
वसन्तोत्सवः हिन्दी अनुवाद
माघमासस्य शुक्लपक्षस्य पञ्चम्यां तिथौ ऋतुराजवसन्तस्य आगमनसूचना भवति। वसन्तपञ्चमी श्रीपञ्चमी नाम्ना अपि. ज्ञायते। अस्मिन् समये प्रकृतेः सौन्दर्यं चरमोत्कर्ष प्राप्नोति। सर्वत्र रमणीयतायाः दर्शनं भवति। वृक्षेषु नूतनकिसलयरागः राजते। क्षेत्रेषु सर्षपपुष्याणां सुषमा पीतिमा च मनोहारिणी दृश्यते। आनेषु मञ्जरीम् परितः भ्रमन्तः भ्रमराः दृश्यन्ते। कोकिलानां मधुरस्वरः चित्तम् आकर्षति। वसन्तसमये सर्वत्र रमणीयतायाः दर्शनम् भवति। वसन्तोत्सवे शीतकालस्य अनन्तरम् परम्परया सौन्दर्यस्य पूजनं क्रियते। विविधैः पुष्पैः, नवान्नैः, फलैः च ऋतुराजस्य वसन्तस्य स्वागतम् भवति। एषः उत्सवः सौन्दर्यस्य रमणीयतायाः पुष्याणां, किसलयानां मधुरागमनस्य च उत्सवः अस्ति।
अनुवाद :
माघ के महीने की शुक्ल पक्ष की पंचमी तिथि को ऋतुओं के राजा वसन्त के आगमन की सूचना होती है वसन्त पंचमी को ‘श्री पंचमी’ के नाम से भी जाना जाता है। इस समय प्रकृति की सुन्दरता अत्यधिक उन्नति को प्राप्त करती है। सब जगह सुन्दरता के दर्शन होते हैं। पेड़ों पर नवीन पत्तों की शोभा सुशोभित होती है। खेतों में सरसों के फूलों की अत्यधिक शोभा और पीलापन मन को हरने वाला दिखाई देता है। आम के पेड़ों पर बौरों के चारों ओर घूमते हुए भँवरे दिखाई देते हैं। कोयलों का मधुर स्वर मन को आकर्षित करता है। वसन्त के समय में सब जगह सुन्दरता के दर्शन होते हैं। वसन्त के उत्सव में शीतकाल के बाद परम्परा से सुन्दरता का पूजन किया जाता है। अनेक फूलों, नये अन्नों और फलों से ऋतुओं के राजा वसन्त का स्वागत होता है। यह उत्सव सुन्दरता मनोहरता फूलों और पल्लवों के मधुर आगमन का उत्सव होता है।
वसन्तोत्सवस्य द्वितीयपक्षः अधिकः महनीयः अस्ति। भारते वसन्तवेलायां भगवत्याः सरस्वत्याः आराधनस्य अपि परम्परा विद्यते। वसन्तपञ्चमी ज्ञानस्य उपासनायाः आराधनायाः उत्सवः अस्ति। प्राचीनकाले वसन्तपञ्चम्यां ज्ञानयज्ञतपस्वरूपां सरस्वतीं जनाः पूजयन्ति स्म। अधुना अपि सम्पूर्णे देशे आध्यात्मिकजिज्ञासया अस्मिन् दिने जनाः ज्ञानस्य अधिष्ठात्रीं शारदां पूजयन्ति।
अनुवाद :
वसन्त उत्सव का द्वितीय पक्ष अधिक सम्मान के योग्य होता है। भारत में वसन्त की बेला में देवी सरस्वती की आराधना भी परम्परा है। वसन्त पंचमी ज्ञान की उपासना। (और) आराधना का उत्सव है। प्राचीन समय में वसन्त पंचमी पर ज्ञानयज्ञ (और) तप स्वरूप सरस्वती को लोग पूजते थे। अब भी सम्पूर्ण देश में आध्यात्मिक जिज्ञासा से इस दिन लोग ज्ञान की मुख्य देवी शारदा (सरस्वती) को पूजते हैं।
वसन्तोत्सवः वस्तुतः सांस्कृतिकः उत्सवः अस्ति। वैदिककालात् एव अस्मिन् दिने सरस्वत्याः उपासना भवति। महाभारते पुराणेष्वपि वसन्तोत्सवः सरस्वत्याः उपासनायाः उत्सवरूपेण दर्शितः। वसन्तपञ्चम्यां आगमविधिना महाशक्त्याः सरस्वत्याः वार्षिकपूजायाः विधानम् भवति।
अनुवाद :
वसन्त उत्सव वास्तव में सांस्कृतिक उत्सव है। वैदिक काल से ही इस दिन सरस्वती की उपासना होती है। महाभारत में पुराणों में भी वसन्त उत्सव सरस्वती की उपासना के उत्सव के रूप में दिखाया गया है। वसन्त पंचमी पर शास्त्र में वर्णित विधि से महाशक्ति सरस्वती की वार्षिक पूजा का विधान होता है।
विशेषतः उत्तरभारते बिहारप्रान्ते, बङ्गालप्रान्ते तथा काश्मीरप्रदेशे सरस्वतीपूजनं बहुमान्यम् अस्ति। दक्षिणे तमिलनाडुक्षेत्रे अपि एतस्य महत्त्वं विद्यते। तत्र आबालवृद्धपरिजनाः प्रकाशितान् हस्तलिखितान् ग्रन्थान् एकस्याम् पीठिकायां संस्थाप्य विविधैः उपचारैः शारदाम् अर्चयन्ति। एतेन सममेव वाद्ययन्त्राणां वीणादीनाम् पूजनमपि भवति। कुत्रचित् दक्षिणभारते शिल्पिनः स्वयन्त्राणाम् अपि अस्मिन् दिने पूजनं कुर्वन्ति।
अनुवाद :
विशेष रूप से उत्तर भारत में बिहार 7 में, बंगाल प्रान्त में तथा कश्मीर प्रदेश में सरस्वती पूजन ब न्य है। दक्षिण में तमिलनाडु क्षेत्र में भी इसका महत्त्व है. वहाँ बच्चों से लेकर वृद्ध तक (सभी) परिवार के लोग प्रकाशित (छपे) हाथ से लिखे ग्रन्थों को एक चौकी पर रखकर विविध पूजा की विधियों से शारदा की पूजा करते हैं। इसी समय वाद्य यन्त्र वीणा आदि का पूजन भी होती है। वहीं दक्षिण भारत में शिल्पी (कारीगर) अपने यन्त्रों (औजारों) का भी इसी दिन पूजन करते हैं।
सरस्वतीपूजनस्य वेदाध्ययन सत्रं श्रावणीपूर्णिमातः आरभ्य वसन्तपञ्चमी यावत् भवति। सरस्वती पूजयित्वा ऋतुपरिवर्तनस्यारम्भे जीवने हर्षोल्लासं, सौन्दर्य, शृंङ्गारं च कामयितु वसन्तस्य, कामदेवस्य अपि पूजनं परम्परा भवति। वस्तुतः भारतीयपरम्परायां वसन्तोत्सवः सौन्दर्यस्य, उल्लासस्य, ज्ञानस्य उपासनायाः उत्सवः। एषः भारतीयानां उत्सवप्रियतायाः शास्त्रीय, सामाजिक तथा वैज्ञानिक चिन्तनम् अपि द्योतयति।
अनुवाद :
सरस्वती की पूजा वेद के अध्ययन की अवधि श्रावणी पूर्णिमा से आरम्भ होकर वसन्तपंचमी तक होती है। सरस्वती को पूजकर ऋतु परिवर्तन के आरम्भ में जीवन में हर्षोल्लास, सौन्दर्य और श्रृंगार की कामना के लिए वसन्त का (और) कामदेव का भी पूजन परम्परा से होता है। वस्तुतः भारतीय परम्परा में वसन्तोत्सव सौन्दर्य की, उल्लास की (और) ज्ञान की उपासना का उत्सव है। यह भारतीयों की उत्सव प्रियता की शास्त्रीय, सामाजिक तथा वैज्ञानिक सोच को भी प्रकट करता है।
वसन्तोत्सवः शब्दार्थाः
चरमोत्कर्षम् = अत्यधिक उन्नत। उल्लासः = हर्ष। नूतनकिसलयरागः = नवीन पत्तों की शोभा। आबालवृद्धाः = बच्चों से लेकर वृद्ध तक। मञ्जरी = बौर (आम के बौर)। अधिष्ठात्रीम्=मुख्यदेवीको।पीठिका-चौकी।वाद्ययन्त्राणाम् – (वाद्योपकरणानाम्) = बजाये जाने वाले यन्त्रों का (वीणा आदि। विधानम् = विधि। उपचारैः = पूजा विधि से। महनीयः = महत्तर। वेदाध्ययनसत्रम् = वेद की अध्ययन की अवधि। आगमविधिना = शास्त्रवर्णित विधि से।