MP Board Class 9th Science Solutions Chapter 7 Diversity in Living Organisms
Diversity in Living Organisms Intext Questions
Diversity in Living Organisms Intext Questions Page No. 80
Question 1.
Why do we classify organisms?
Answer:
Classification of organism make it easy to study the millions of organisms on this earth. Similarities among them is the basis to classify them into different classes. Classification makes study easier.
![]()
Question 2.
Give three examples of the range of variations that you see in life – forms around you.
Answer:
Variations observed in life are:
- Size: Organisms vary greatly in size – from microscopic bacteria to elephants, whales and large trees.
- Appearance: The colour of various animals is quite different. Number of pigments are found in plants. Their body – built also varies.
- Life time: The life span of different organisms is varied.
Diversity in Living Organisms Intext Questions Page No. 82
Question 1.
Which do you think is a more basic characteristic for classifying organisms?
(a) the place where they live.
(b) the kind of cells they are made of. Why?
Answer:
(a) Different organisms may share same habitat but may have entirely different form and structure. So, the place where they live cannot be a basis of classification.
(b) The kind of cells they are. made of. Because placement of organism to other destination can create a easy confusion.
Question 2.
What is the primary characteristic on which the first division of organisms is made?
Answer:
The primary characteristic on which the first division of organisms is made is the nature of the cell – prokaryotic or eukaryotic cell.
Question 3.
On what basis are plants and animals put into different categories?
Answer:
Plants and animals are very different from each other but main basis to differentiate is “Mode of nutrition’’. Plants are autotrophs. They can make their food own while animals are heterotrophs which are dependent on others for food. Locomotion, absence of chloroplasts etc. also make them different.
Diversity in Living Organisms Intext Questions Page No. 83
Question 1.
Which organisms are called primitive and how are they different from the so-called advanced organisms?
Answer:
A primitive organism is the one which has a simple body structure and ancient body design or features that have not changed much over a period of time. As per the body design, the primitive organisms which have simple structures are different from those so – called advanced organisms which have complex body structure and organization.
![]()
Question 2.
Will advanced organisms be the same as complex organisms? Why?
Answer:
Yes, they are developed from same ancestor once. They have relatively acquired their complexity recently. There is a possibility that these advanced or ‘younger’ organisms acquire more complex structures during evolutionary time to compete and survive in the changing environment.
Diversity in Living Organisms Intext Questions Page No. 85
Question 1.
What is the criterion for classification of organisms as belonging to kingdom Monera or Protista?
Answer:
The organisms belonging to kingdom Monera are unicellular and prokaryotic whereas the organisms belonging to Kingdom Protista are unicellular and eukaryotic. This is the main criterion of their classification.
Question 2.
In which kingdom will you place an organism which is single – celled, eukaryotic and photosynthetic?
Answer:
Kingdom Protista.
Question 3.
In the hierarchy of classification, which grouping will have the smallest number of organisms with a maximum of characteristics in common and which will have the largest number of organisms?
Answer:
In the hierarchy of classification, “species” will have the smallest number of organisms with a maximum of characteristics in common whereas “the kingdom” will have the largest number of organisms a Arthropoda.
Diversity in Living Organisms Intext Questions Page No. 88
Question 1.
Which division among plants has the simplest organisms?
Answer:
Division thallophyta.
![]()
Question 2.
How are pteridophytes different from the phanerogams?
Answer:
1. Pteridophyta: They have inconspicuous or less differentiated reproductive organs. They produce naked embryos called spores.
Examples:
- Ferns
- marsilea
- equisetum, etc.
2. Phanerogams: They have well developed reproductive organs. They produce seeds.
Example:
- Pinus
- cycas
- fir etc.
Question 3.
How do gymnosperms and angiosperms differ from each other?
Answer:
Gymnosperm:
- They are non – flowering plants.
- Naked seeds not enclosed inside fruits are produced.
- Examples:
- Pinus
- Cedar
- Fir
- Cycas etc.
Angiosperm:
- They are flowering plants.
- Seeds are enclosed inside fruits.
- Examples:
- Coconut
- Palm
- Mango etc.
Diversity in Living Organisms Intext Questions Page No. 94
Question 1.
How do poriferan animals differ from coelenterate animals?
Answer:
| Poriferan | Coelenterate |
| 1. Mostly marine, non – motile. | 1. Motile marine animals that either live in colonies or have a solitary life – span. |
| 2. Cellular level of organisation. | 2. Tissue level of organisation. |
| 3. Spongilla, Euplectella etc. | 3. Hydra, sea anemone. |
Question 2.
How do annelid animals differ from arthropods?
Answer:
| Annelids | Arthropods |
| 1. Closed circulatory system | 1. An open circulatory system |
| 2. The body is divided into several identical segments | 2. The body is divided into few specialized segments |
Question 3.
What are the differences between amphibians and reptiles?
Answer:
| Amphibian | Reptiles |
| 1. They live at land and water both. | 1. They are completely terrestrial. |
| 2. Scales are absent. | 2. Skin is covered with scales. |
| 3. They lay eggs in water. | 3. They lay eggs on land. |
| 4. Example: frogs, toads and salamanders. | 4. Example: lizards, snakes, turtles, chameleons etc. |
Question 4.
What are the differences between animals belonging to the Aves group and those in the mammalia group?
Answer:
Most birds have feathers and they possess a beak.Mammals do not have feathers and the beak is also absent. Birds lay eggs. Hence, they are oviparous. Some mammals lay eggs and some give birth to young ones. Hence, they are both oviparous and viviparous.
Diversity in Living Organisms NCERT Textbook Exercises
Question 1.
What are the advantages of classifying organisms?
Answer:
Advantages of classification:
- Better categorization of living beings based on common characters.
- Easier study for scientific research.
- Better understanding of human’s relation and dependency on other organisms.
- Helps in cross breeding and genetic engineering for commercial purposes.
Question 2.
How would you choose between two characteristics to be used for developing a hierarchy in classification?
Answer:
Gross character will form the basis of start of the hierarchy and fine character will form the basis of further steps of single hierarchy.
Examples:
- Presence of vertebral column in human beings can be taken under vertebrata.
- Presence of four limbs makes them members of Tetrapoda.
- Presence of mammary glands keeps them under mammalia.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the basis for grouping organisms into five kingdoms.
Answer:
Basis of classification:
- Number of cells: unicellular or multicellular.
- Complexity of cell structure: Prokaryote and Eukaryote.
- Presence or absence of cell wall.
- Mode of nutrition.
- Level of organization.
Question 4.
What are the major divisions in the Plantae? What is the basis for these divisions?
Answer:
Major divisions of Kingdom Plantae:
| Division | Basis for classification |
| 1. Thallophyta or Algae | 1. Thallus like body, plant body is not differentiated into roots, stems etc. |
| 2. Bryophyta | 2. Body is divided into leaf and stem, lack vascular tissue. |
| 3. Pteridophyta | 3. Body is divided into root, stem and leaf, lack seeds. |
| 4. Gymnosperm | 4. Seed bearing, naked seeds, lack flowers. |
| 5. Angiosperm | 5. Seed bearing covered seeds, produce flowers. |
Question 5.
How are the criteria for deciding divisions in plants different from the criteria for deciding the subgroups among animals?
Answer:
In plants, basic structure of their body is a major criteria based on which thallophytes are different from bryophytes. Apart from this, absence or presence of seeds is another important criteria. Gymnosperms and angiosperms are further segregated based on if seeds are covered or not. It is clear that it is the morphological character which makes the basis for classification of plants.
In animal, classification is based on more minute structural variations. So in place of morphology, cytology forms the basis. Animals are classified based on layers of cells, presence or absence of coelom. Further, higher hierarchy animals are classified based on the presence or absence of smaller features, like presence or absence of four legs.
Question 6.
Explain how animals in Vertebrata are classified into further subgroups.
Answer:
Vertebrata is divided into two super classes, viz. Pisces and Tetrapoda. Animals of pisces have streamlined body with fins and tails to assist in swimming. Animals of tetrapoda have four limbs for locomotion.
Tetrapoda is further classified into following classes:
- Amphibia: Amphibians are adapted to live in water and on land. They can breathe oxygen through kin when under water.
- Reptilia: These are crawling animals. Skin is hard to withstand extreme temperatures.
- Aves: Forelimbs are modified into wings to assist in flying. Beaks are present. Body is covered with feathers.
- Mammalia: Mammary glands are present to nurture young ones. Skin is covered with hair. Most of the animals are viviparous.
Diversity in Living Organisms Additional Questions
Diversity in Living Organisms Tissues Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Find out incorrect sentence.
(a) Protista includes unicellular eukaryotic organisms.
(b) Whittaker considered cell structure, mode and source of nutrition for classifying the organisms in five kingdoms.
(c) Both Monera and Protista may be autotrophic and heterotrophic.
(d) Monerans have well defined nucleus.
Answer:
(d) Monerans have well defined nucleus.
Question 2.
Which among the following has specialised tissue for conduction of water?
(i) Thallophyta
(ii) Bryophyta
(iii) Pteridophyta
(iv) Gymnosperms
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv).
Answer:
(c) (iii) and (iv)
Question 3.
Which among the following produce seeds?
(a) Thallophyta
(b) Bryophyta
(c) Pteridophyta
(d) Gymnosperms.
Answer:
(d) Gymnosperms.
![]()
Question 4.
Which one is a true fish?
(a) Jellyfish
(b) Starfish
(c) Dogfish
(d) Silverfish.
Answer:
(c) Dogfish
Question 5.
Which among the following is exclusively marine?
(a) Porifera
(b) Echinodermata
(c) Mollusca
(d) Pisces.
Answer:
(b) Echinodermata
Question 6.
Which among the following animals have pores all over their body?
(a) Porifera
(b) Aves
(c) Mollusca
(d) Pisces.
Answer:
(a) Porifera
Question 7.
Which among the following have chi tin as cell wall?
(a) Sycon
(b) Yeast
(c) Jelly fish
(d) Euplectella.
Answer:
(c) Jelly fish
Question 8.
Which among the following is not a Monocotyledonous plant?
(a) Wheat
(b) Rice
(c) Maize
(d) Gram.
Answer:
(d) Gram.
Question 9.
Which among the following is not a dicotyledonous plant?
(a) Wheat
(b) Sunflower
(c) Mango
(d) Gram.
Answer:
(a) Wheat
Question 10.
An organism with a single cell is called _______ .
(a) Thallophyta
(b) Bryophyta
(c) Unicellular
(d) Multicellular.
Answer:
(c) Unicellular
![]()
Question 11.
The amphibians of the plant is _______ .
(a) Thallophyta
(b) Bryophyta
(c) Unicellular
(d) Multicellular.
Answer:
(b) Bryophyta
Question 12.
Plant bearing naked seeds are _______ .
(a) Thallophyta
(b) Bryophyta
(c) Unicellular
(d) Gymnosperm.
Answer:
(d) Gymnosperm.
Diversity in Living Organisms Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name a saprophyte and also tell, why are they called so.
Answer:
Aspergillus: They are called so because they obtain their nutrition from dead and decaying matter.
Question 2.
Why are lichens called dual organisms?
Answer:
Lichens are permanent symbiotic association between algae and fungi. Therefore, they are called dual organisms.
Question 3.
State the phylum to which centipede and prawn belong.
Answer:
Arthropoda.
Question 4.
Name one reptile with four – chambered heart.
Answer:
Crocodile.
Question 5.
Identify kingdom in which organisms do not have well defined nucleus and do not show multicellular body designs.
Answer:
Monera.
Diversity in Living Organisms Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Why do we differentiate organism, give two main basis?
Answer:
Due to variation in various characteristics, we differentiate organism. Two main basis are mode of nutrition and habitat.
Question 2.
Which kingdom generate food on earth and initiate food chain?
Answer:
Plantae.
![]()
Question 3.
Which kingdom do not have cell wall to their cell?
Answer:
Animalia.
Question 4.
What do you understand by biodiversity?
Answer:
Biodiversity: The variety of living beings found in a particular geographical area is called biodiversity of that area. Amazon rainforests is the largest biodiversity hotspot in the world.
Question 5.
Why classification is required?
Answer:
Classification is necessary for the study of living beings in easy way. Without proper classification, it would be impossible to study millions of organisms which exist on this earth.
Question 6.
What was the basis of classification of Ancient Greek philosopher Aristotle?
Answer:
Aristotle classified living beings on the basis of their habitat. He classified them into two groups, i.e. those living in water and those living on land.
Question 7.
How can we divide organism on the basis of mode of nutrition ?
Answer:
On this basis, organisms can be divided into two broad groups, i.e. autotrophs and heterotrophs.
Question 8.
Define Monocotyledonous plants. Give examples.
Answer:
Monocotyledonous: There is single seed leaf in a seed. A seed leaf is a baby plant.
Examples:
- wheat
- rice
- maize, etc.
Question 9.
Give example of Dicotyledonous plants.
Answer:
Dicotyledonous plants: Mustard, gram, mango etc.
Question 10.
Give one difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes
Answer:
- Prokaryotes: When nucleus is not organized, i.e., nuclear materials are not membrane bound; the organism is called prokaryote.
- Eukaryotes: When nucleus is organized, i.e., nuclear materials are membrane bound; the organism is called eukaryote.
Question 11.
What is the difference between unicellular and multicellular organism?
Answer:
- Unicellular organism: An organism with a single cell is called unicellular organism.
- Multicellular organism: An organism with more than one cell is called multicellular organism.
![]()
Question 12.
Write short notes on the following:
(a) Thallophyta
(b) Bryophyta
Answer:
(a) Thallophyta: The plant body is thallus type. The plant body is not differentiated into root, stem and leaves. They are known as algae also.
Examples:
- Spirogyra
- chara
- volvox
- ulothtrix etc.
(b) Bryophyta: Plant body is differentiated into stem and leaf like structure. Vascular system is absent, which means there is no specialized tissue for transportation of water, minerals and food. Bryophytes are known as the amphibians of the plant kingdom, because they need water to complete a part of their life cycle.
Examples:
- Moss
- marchantia.
Question 13.
What are cryptogams and phanerogams?
Answer:
Plant body is differentiated into root, stem and leaf. Vascular system is present. They do not bear seeds and hence are called cryptogams. Plants of rest of the divisions bear seeds and hence are called phanerogams.
Examples:
- Marsilear
- ferns
- horse tails etc.
Question 14.
How gymnosperms are different from angiosperms?
Answer:
- Gymnosperms: They bear seeds. Seeds are naked i.e., are not covered. The word ‘gymnos’ means naked and ‘sperma’ means seed.
- Angiosperms: The seeds are covered. The word ‘angios’ means covered. There is great diversity in species of angiosperm.
Question 15.
What is porifera?
Answer:
Porifera: These animals have pores all over their body. The pores lead into the canal system. They are marine animals. Examples:
- Sycon
- Spongilla
- Euplectella, etc.
Question 16.
What is coelenterata?
Answer:
Coelenterata: The body is made up of a coelom (cavity) with a single opening. The body wall is made up of two layers of cells (diploblastic).
Examples:
- Hydra
- jelly fish
- sea anemone, etc.
Question 17.
What is Platyhelminthes?
Answer:
The body is flattened from top to bottom and hence the name platyhelminthes. These are commonly known as flatworms. The body wall is composed of three layers of cells (triploblastic).
Example:
- Planaria
- liver fluke
- tapeworm etc.
Question 18.
What is Nematohelminthes and Annelida?
Answer:
Nematohelminthes: Animals are cylindrical in shape and the body is bilaterally symmetric and there are three layers in the body wall.
Example:
- Roundworms
- pinworms
- filarial parasite (Wuchereria) etc.
Annelida: True body cavity is present in these animals. The body is divided into segments and hence the name annelida.
Example:
- Earthworm
- leech etc.
![]()
Question 19.
Explain the followings:
(a) Arthropoda
(b) Mollusca
(c) Echinodermata
(d) Protochordata
(e) Chordata.
Answer:
(a) Arthropoda: Animals have jointed appendages which gives the name arthropoda. Exoskeleton is present which is made of chitin. This is the largest group of animals; in terms of number of species.
Examples:
- cockroach
- housefly
- spider
- prawn
- scorpion etc.
(b) Mollusca: The animal has soft body; which is enclosed in a hard shell. The shell is made of calcium carbonate.
Examples:
- Snail
- mussels
- octopus etc.
(c) Echinodermata: The body is covered with spines, which gives the name echinodermata. Body is radially symmetrical. The animals have well developed water canal system, which is used for locomotion.
Examples:
- Starfish
- sea urchins etc.
(d) Protochordata: Animals are bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic and ceolomate. Notochord is present at least at some stages of life.
Examples:
- Balanoglossus
- herdmania
- amphioxus etc.
(e) Chordata: Animals have notochord, pharyngeal gill slits and post anal tail; for at least some stages of life. Phylum chordata is divided into many sub – phyla; out of which we shall focus on vertebrata.
Diversity in Living Organisms Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is the different levels of organizations in case multicellular organism?
Answer:
Level of organization: Even in case of multicellular organisms, there can be different levels of organization:
(a) Cellular level of organization: When a cell is responsible for all the life processes, it is called cellular level of organization.
(b) Tissue level of organization: When some cells group together to perform specific function, it is called tissue level of organization.
(c) Organ level of organization: When tissues group together to form some organs, it is called organ level of organization. Similarly organ system level of organization is seen in complex organisms.
Question 2.
“Classification of living organism is based on evolution.” Explain.
Answer:
It is a well – established fact that all the life forms have evolved . from a common ancestor. Scientists have proved that the life begun on the earth in the form of simple life forms. During the course of time, complex organism evolved from them. So, classification is also based on evolution. A simple organism is considered to be primitive while a complex organism is considered to be advanced.
Question 3.
Explain five kingdom classification by Robert Whittaker (1959).
Answer:
Five Kingdom Classification by Robert Whittaker (1959):
This is the most accepted system of classification. The five kingdoms and their key characteristics are given below:
1. Monera: These are prokaryotes; which means nuclear materials are not membrane bound in them. They may or may not have cell wall. They can be autotrophic or heterotrophic. All organisms of this kingdom are unicellular. Examples: bacteria, blue green algae (cyanobacteria) and mycoplasma.

2. Protista: These are eukaryotes and unicellular. Some organisms use cilia or flagella for locomotion. They can be autotrophic or heterotrophic. Examples: unicellular algae, diatoms and protozoans.
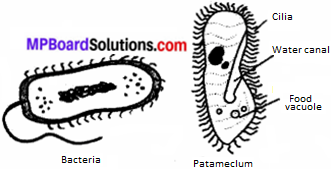
3. Fungi: These are heterotrohic and have cell wall. The cell wall is made of chitin. Most of the fungi are unicellular. Many of them have the capacity to become multicellular at certain stage in saprophytic. Some fungi live in symbiotic relationship with other organisms, while some are parasites as well.
Examples:
- Yeast
- penicillum
- aspergillus
- mucor etc.
4. Plantae: These are multicellular and autotrophs. The presence of chlorophyll is a distinct characteristic of plants, because of which they are capable of doing photosynthesis. Cell wall is present.
5. Animalia: These are multicellular and heterotophs. Cell wall is absent. They feed on decaying organic materials.
Diversity in Living Organisms Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS)
Question 1.
What are the differences between Platyhelminthes and Nematohelminthes?
Answer:
| Platyhelminthes | Nematohelminthes |
| 1. Form: They are flat in shape and are called flat worms. | 1. They are cylindrical in form and are called round worms. |
| 2. Sexuality: Animals are hermaphrodite. | 2. Animals are uni – sexual. |
| 3. Coelom: Platyhelminthes are acoelomate. | 3. Nematohelminthes are pseudocoelomate. |
| 4. Digestive Tract: It is incomplete. | 4. It is complete |
Question 2.
Differentiate between animals belonging to the Mammalia group and those in the Aves group.
Answer:
Differences between mammals and aves.
| Mammals | Aves |
| 1. Give birth to young ones except platypus and the echidna. | 1. Lay eggs. |
| 2. Mammary glands are present. | 2. Mammary glands are absent. |
| 3. Body covered with hair. | 3. Body covered with feathers. |
| 4. Sweat and sebaceous glands are present in the skin. | 4. Sweat and sebaceous glands are not present in the skin. |
Diversity in Living Organisms Value Based Questions
Question 1.
Ashish, a IX class student, was studying chapter, ‘Diversity in Living Organisms’. He thought that all the fungi are harmful as these spoil food and cause various diseases. However, his elder sister Dimple told him that not all fungi are harmful as these are also used in making bread, vitamins and medicines.
- Name any fungus which is the source of some medicine.
- Name any fungus which is used in bread making.
- What value are displayed by Ashish’s sister?
Answer:
- Pencillium.
- Yeast.
- Dimple acted as elder sister and enhanced his younger brother’s scientific knowledge about fungi and their functions.
Question 2.
Coral is getting diminished in all the oceans due to global warming. People in Goa island protects their coral by not allowing people / tourist to take it away.
- What is the phylum of coral?
- What is coral made up of?
- What value of people in Goa island is reflected here?
Answer:
- Coelenterates is the phylum of coral.
- It is made up of calcium carbonate.
- They reflect the value of being responsible citizen, respecting environment and nature.