MP Board Class 12th Biology Important Questions Chapter 14 Ecosystem
Ecosystem Important Questions
Ecosystem Objective Type Questions
Question 1.
Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
The flow of energy in ecosystem: (MP2011)
(a) Unidirection
(b) Bidirectional
(c) Tridirectional
(d) Four directional
Answer:
(a) Unidirection
Question 2.
Chief source of energy in ecosystem :
(a) Solar energy
(b) Green plants
(c) Food substances
(d) All of these.
Answer:
(a) Solar energy
Question 3.
The term ‘ecosystem’ was used for the first time by : (MP 2015)
(a) Tansley
(b) Odum
(c) Reiter
(d) Mishra and Puri.
Answer:
(a) Tansley
![]()
Question 4.
The pyramid of number of tree ecosystem is :
(a) Inverted
(b) Upright
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) Inverted
Question 5.
Correct food chain is :
(a) Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Hawk
(b) Grass → Frog → Snake → Peacock
(c) Grass → Peacock → Grasshopper → Hawk
(d) Grass → Snake → Rabbit.
Answer:
(a) Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Hawk
Question 6.
Pyramid of biomass of lake ecosystem is :
(a) Upright
(b) Inverted
(c) Upright or inverted
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Inverted
Question 7.
Vegetation present between two communities :
(a) Ecad
(b) Ecotype
(c) Ecotone
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) Ecotone
Question 8.
Xerosere is started from :
(a) Water
(b) Naked rock
(c) Swamp
(d) All of these.
(b) Naked rock
Question 9.
Serial development of plant community is called :
(a) Attack
(b) Succession
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Succession
Question 10.
Plants starting succession in any area are called :
(a) Pioneer
(b) Sere
(c) Displacer
(d) All of these.
Answer:
(a) Pioneer
Question 11.
In forest ecosystem, the pyramid of energy is : (MP 2012,17)
(a) Always inverted
(b) Always upright
(c) First upright then inverted
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Always upright
Question 12.
The study of ecology of a species is called :
(a) Ecology
(b) Autecology
(c) Synecology
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Autecology
![]()
Question 13.
Food chain starts from :
(a) Respiration
(b) Photosynthesis
(c) Decomposers
(d) Nitrogen fixation.
Answer:
(b) Photosynthesis
Question 14.
Man is:
(a) Autotrophic
(b) Carnivorous
(c) Herbivorous
(d) Omnivorous.
Answer:
(d) Omnivorous.
Question 15.
In any ecosystem, solar energy is conserved by :
(a) By producers
(b) By consumers
(c) By decomposers
(d) All of the above.
Answer:
(a) By producers
Question 16.
The two components of ecosystem are: (MP 2013)
(a) Organism and Plant
(b) Weeds and trees
(c) Frog and man
(d) Biotic and Abiotic.
Answer:
(d) Biotic and Abiotic.
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks:
- The transitional zone present between to adjacent communities is called ………………….
- All the plants of a particular area constitute …………………. of that place.
- Only …………………. % energy is transferred from one trophic level to another.
- Pyramid of …………………. is always upright. (MP 2013)
- …………………. and …………………. are the examples of omnivorous animals.
- The term ‘ecosystem’ was proposed by ………………….
- The chief source of energy ecosystems is (MP 2016)
- N2 fixing bacteria is called …………………. (MP 2009 Set A)
- All ecosystems are depended for energy on …………………. (MP 2009 Set D)
- In forest trees basically function as ………………….
- Establishment of organisms in new habitat is called ………………….
- A sereal development of plant community is called ………………….
- Succession which takes place in baren rock is called ………………….
- Succession in soil is called ………………….
Answer:
- Ecotone
- Flora
- 10
- Energy
- Man, Pig
- Tansley
- Sunlight
- Nitrifying bacteria
- Sun (solar energy)
- Producers
- Ecesis
- Succession
- Lithosere
- Psamosere.
Question 3.
Match the followings:
I.

Answer:
- (e)
- (d)
- (a)
- (c)
- (b)
II.

Answer:
- (b)
- (c)
- (d)
- (a)
![]()
Question 4.
Write the answer in one word/sentances:
- What is called the study of ecology of a species?
- What is called the process of soil formation?
- What type of energy pyramid found in nature?
- Give one example of an omnivorous animal.
- Who proposed the term ecosystem?
- Who gave the 10% rule of ecosystem?
- In an ecosystem, producer is known as.
- What is the direction of the flow of energy in an ecosystem?
- When many food chains operate simultaneously and interlock such patterns is termed as?
- Give an example of autotrophic componant.
- Which gas is used by green plants in photosynthesis?
- Name the special nutrient which is present in metheonine amino acid.
- Name the cycle in which nitrogen is converted into multiple chemicals and circulated among atmosphere.
- Due to an ecosystem fungus and bacteria are known as.
- What is T2?
Answer:
- Autecology
- Pedogenesis
- Upright
- Man
- A.G. Tansley
- Lindman
- Biotic componant
- Leanear
- Food web
- Plants
- CO2
- Sulfer
- Nitrogen cycle
- Decomposer
- Herbivorous animal.
Ecosystem Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write the name and ratio of different components of biosphere.
Answer:
Name and ratio of different components of biosphere is:

Some gases are also found in biosphere example Helium, Neyon and Crypton are found in less quantity.
Question 2.
Differentiate between detritivore and decomposer.
Answer:
Detritivore are organisms which feed on detritus and break them into smaller particles, example earth worm. And decomposer are organisms which by secreting enzymes break down complex organic matter into in organic substance example some bacteria and fungi.
Question 3.
Explain consumers of ecosystem
Answer:
1. Producers – All the green plants.
2. Consumers – Depends on others for food.
- Primary consumer: Depends on plants called herbivores.
- Secondary consumers : Depends on herbivores for food.
- Tertiary consumers : Depends on secondary consumers.
3. Decomposers – They decomposed dead organic matter.
![]()
Question 4.
Differentiate between biome and ecosystem.
Answer:
An ecosystem is the interaction of living and non – living things in an environment. A biome is a specific geographic area notable for the species living there.
Question 5.
What are transducers according to some ecologists?
Answer:
Some ecologists call green plants as transducers of the ecosystem as they convert solar energy into chemical energy.
Question 6.
Name four submerged plants.
Answer:
- Hydrilla
- Vallisneria
- Elodea
- Potamogeton.
Question 7.
Name the stages of xerosere.
Answer:
Stages of xerosere:
- Crustose lichen stage
- Foliose lichen stage
- Moss stage
- Herb stage
- Shrub stage
- Climax forest stage.
Question 8.
When many food chain operate simultaneously and interlock such pattern is formed.
Answer:
Food web.
Question 9.
Name the ecosystem which shows most productivity.
Answer:
Tropical ecology.
Question 10.
What are fungi and bacteria called in an ecosystem?
Answer:
Micro – consumer or Decomposer.
![]()
Question 11.
Which part of the energy is transferred from one trophic level to other in ecosystem?
Answer:
10%.
Question 12.
Name the type of chemosynthetic bacteria.
Answer:
Autotrophic.
Question 13.
Name the word which is similar to ecosystem given by Prof. R. Mishra.
Answer:
Ecocosm.
Question 14.
Name the trophic level in which green plants are found.
Answer:
Primary trophic level.
Question 15.
Who gave the word transformer for producer?
Answer:
E.J. Kormondy.
Question 16.
Name any two sedimentary cycle.
Answer:
Phosphorus cycle
Sulphur cycle.
Question 17.
The energy pyramids are always.
Answer:
Upright.
Question 18.
Give examples of decomposers.
Answer:
Bacteria and Fungi.
Question 19.
Who gave 10% rule of energy?
Answer:
Lindeman.
Question 20.
Which form of nitrogen is absorbed by plants?
Answer:
In the form of nitrate ion (NO3–)
Ecosystem Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Draw a pyramid of energy of grassland ecosystem.
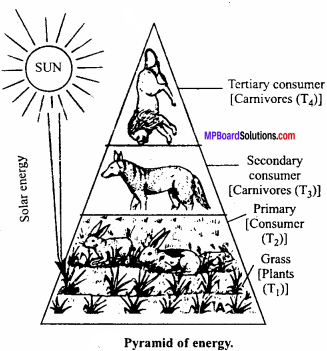
Answer:
Question 2.
Explain nitrogen cycle in nature.
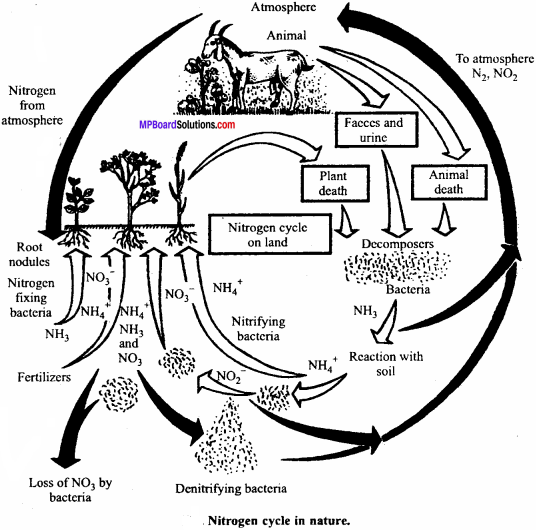
Answer:
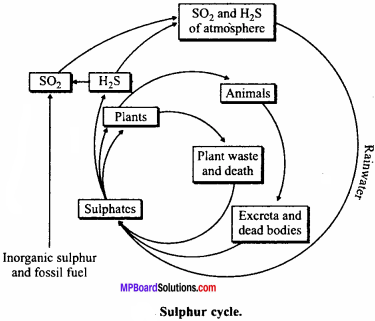
Question 3.
Explain sulphur cycle by diagram.
Answer:
Question 4.
Explain the effect of light on plants.
Answer:
Effect of light on plants:
Light is the source of energy. It is essential for life. It is an important factor of an ecosystem. The existence of life on earth is because of light obtained from sun. Sunlight is essential for photosynthesis, help in preparation of food for the whole living world. Light effects biological activities of plants by its intensity, period and duration. Plants are classified into following two categories on the basis of requirement of light intensity:
- Heliophytes – Plants, which can grow better in bright light are called heliophytes.
- Sciophytes – Plants, which require relatively less of light and they can grow better in shades are called sciophytes.
![]()
Question 5.
Explain the meaning of food web and draw its diagram.
Answer:
Food Web:
In nature, foodchains are not isolated sequences, but are interrelated and interconnected with one another. When many foodchains operate simultaneously and interlock such pattern is termed as food web. Thus, the food web is a description of feeding connections between the organisms which make up a community. Energy passes through one trophic level to next via these food web links, example a rat feeds on various kinds of grains, fruits, stems, roots, etc.
A rat in its turn is consumed by a snake which is eaten by a falcon. The snakes feed on both frogs and rats. Thus, a network of food – chains exists and this is called food web. The food web gets more complicated because of variability in taste and preference availability and compulsion and several other factors at each level. For example, tigers normally do not feed on fishes or crabs but in Sunderbans they are forced to eat them.
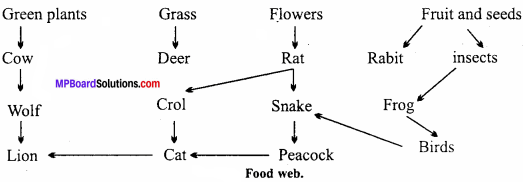
Question 6.
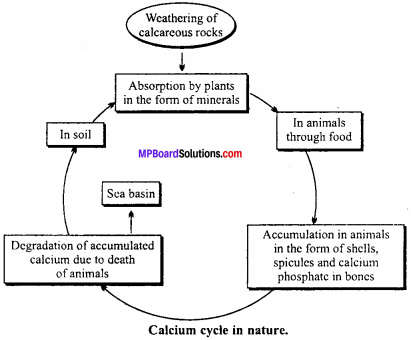
Explain calcium cycle with well labelled diagram.
Answer:
Question 7.
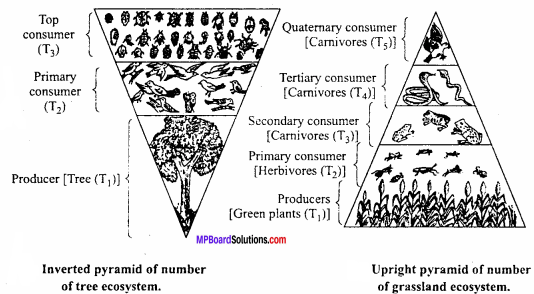
Draw ecological pyramid of number of a tree ecosystem and grassland ecosystem.
Answer:
Question 8.
What do you mean by ecosystem? Describe the important components of a pond ecosystem.
Or
Write about role of decomposers in an ecosystem with example.
Answer:
Ecosystem:
The system resulting from the interaction between organisms and their environment is called as ecosystem.
Components of a pond ecosystem:
A pond ecosystem should contain all components of ecosystems like:
1. Producers:
Organism, which can synthesize their own food are included under producers, example Volvox, Pandorina, Oedogonium, Saggitaria, Utricularia, Azolla, Trapa, Lemna, Typha, Nymphaea etc. form the producer class of the pond ecosystem.
2. Consumers:
- Primary consumer – Animals, which feed on producers are included into this category example Daphnia, Cyclops, Paramoecium, Amoeba and small fishes.
- Secondary consumers – Primary consumers also serve as food for water snakes, a few tortoise, few types of fish etc. hence, these are carnivores.
- Tertiary consumers – Secondary consumers also serve as food for aquatic birds like kingfisher, cranes, big fish and these together form a top class carnivorous group and called as tertiary consumers.
3. Decomposers:
All producers and consumers die and accumulate on the floor of the pond. Even the waste material and faeces of these animals get accumulated on the floor of the pond. Similarly, the floor of pond is also occupied by decomposers, which include bacteria and fungi. These decomposers decompose complex organic compounds of their bodies into simpler forms which are finally mixed with soil of floor of ponds. These are again absorbed by the roots of producer plants and thus matter is recycled.
![]()
Question 9.
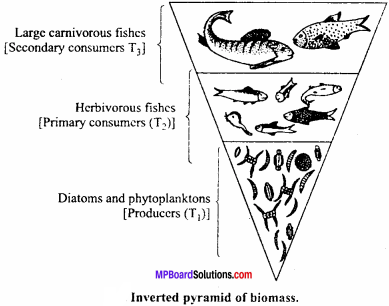
Explain pyramid of biomass of pond ecosystem.
Answer:
The biomass, i.e., the living weight of the organisms in the foodchain present at different trophic levels in an ecosystem forms the pyramid of biomass. When biomass of consumers is greater than biomass of producer then pyramid is called as inverted pyramid of biomass. example pyramid of biomass of pond ecosysyem is always inverted.
Ecosystem:
The system resulting from the interaction between organisms and their environment is called as ecosystem.
Question 10.
Distinguish between:
- Grazing food chain and Detritus food chain
- Production and Decomposition
- Upright and Inverted pyramid
- Food chain and Food web
- Litter and Detritus,
- Primary and Secondary productivity
Answer:
1. Differences between Grazing food chain and Detritus food chain :
Grazing food chain:
- Energy for the food chain comes from the sun.
- First trophic level organisms are producers.
Detritus food chain:
- Energy comes from detritus (organic matter).
- First trophic level organisms are detritivores and decomposers.
2. Differences between Production and Decomposition :
Production:
- It refers to the process of synthesis of organic compounds from inorganic substances utilising sunlight.
- Example: Plants perform the function of production of food.
Decomposition:
- It is the phenomenon of degradation of waste biomass.
- Example : Bacteria and fungi decompose dead organic matter.
3. Differences between Upright pyramid and Inverted pyramid:
Upright pyramid:
When the number of producers or theirbiomass is maximum in an ecosystem and it decreases progressively at each trophic level in a food chain, an uprightpyramid is formed.
Inverted pyramid:
When the number of individuals or their biomass at the producer level is minimum and it Increases progressively at each trophic level in a food chain, an inverted pyramid is formed.
4. Differences between Food chain and Food web:
Food chain:
- A food chain is a single pathway where energy is transferred from producers to successive orders of consumers.
- All food chains start with green plants which are the original source of all food.
- Energy flow is unidirectional.
Food web:
- A food web is a network of various food chains which are interconnected with each other like an interlocking pattern.
- It has many linkages and intercrosscs among producers and consumers.
- Energy flow in multidirectional.
5. Differences between Litter and Detritus:
Litter:
The dead remains of plants (leaves, flowers etc.) and animals excreta which falls on the surface of the earth in terrestrial ecosystems is called litter.
Detritus:
The dead remains of plants and animals constitute detritus. It is differentiated into litter fall (above ground detritus) and below ground detritus.
![]()
6. Differences between Primary and Secondary productivity:
Primary productivity:
- It is the rate at which organic matter is built up by producers.
- It is due to photosynthesis.
- Primary productivity is two types :
Gross Primary Productivity (GPP) and Net Primary Productivity (NPP) GPP – R = NPP (R = loss in Respiration)
Secondary productivity:
- It is the rate of synthesis of organic matter by consumers.
- It is due to herbivory and predation.
- Secondary productivity is two types :
Gross Secondary Productivity (GSP) and Net Secondary Productivity (NSP) NSP = GSP – R (Loss in Respiration)
Question 11.
What is primary productivity ? Give brief description of factors that affect primary productivity.
Answer:
The rate of biomass production is called productivity.
It is expressed in terms of g-2yr-1 or (kcal – m-2) yr-1 to compare the productivity of ecosystems. It can be divided into Gross Primary Productivity (GPP) and Net Primary Productivity (NPP).
Gross primary productivity of an ecosystem is the rate of production of organic matter during photosynthesis. A considerable amount of GPP is utilized by plants in respiration. Gross primary productivity minus respiration losses (R), is the Net Primary Productivity (NPP). GPP – R = NPP
Primary productivity depends on:
- The plant species inhabiting a particular area.
- The environmental factors.
- Availability of nutrients.
- Photosynthetic capacity of plants.
Question 12.
Define decomposition and describe the processes and products of decomposition.
Answer:
Decomposition:
Decomposition is the process that involves the breakdown of complex organic matter or biomass from the body of dead plants and animals with the help of decomposers into inorganic raw materials such as carbon dioxide, water, and other nutrients.
The various processes involved in decomposition are as follows :
1. Fragmentation:
It is the first step in the process of decomposition. It involves the breakdown of detritus into smaller pieces by the action of detritivores such as earthworms.
2.Leaching:
It is a process where the water soluble nutrients go down into the soil layers and get locked as unavailable salts.
3. Catabolism:
It is a process in which bacteria and fungi degrade detritus through various enzymes into smaller pieces.
4. Humification:
The next step is humification which leads to the formation of a dark coloured colloidal substance called humus, which acts as reservoir of nutrients for plants.
5. Mineralization:
The humus is further degraded by the action of microbes, which finally leads to the release of inorganic nutrients into the soil. This process of releasing inorganic nutrients from the humus is known as mineralization. Decomposition produces a dark coloured, nutrient rich substance called humus. Humus finally degrades and releases inorganic raw materials such as CO2, water, and other nutrient in the soil.
![]()
Question 13.
Given account of explain energy flow in ecosystem.
Answer:
Energy flow:
In the ecosystem, energy is transferred in an orderly sequence. The flow of solar energy from producers to consumers and to decomposers subsequently in an ecosystem is known as energy flow. Energy flow is an ecosystem is always unidirectional. Sun is the sole source of solar energy in an ecosystem. Green plants utilize this energy in photosynthesis and convert it in the form of chemical energy and store it.
Plants utilize maximum part of this energy to do its biological functions. Some of it is converted into heat and released in the environment. Remaining part of the energy is stored in various components of the body. When a consumer eats these producer plants, the energy is then transferred into its body.
In any food chain energy flows from primary producers to primary consumers, from primary consumers to secondary consumers and secondary consumers to tertiary consumers and so on. Because every organism of a trophic level continuously converts chemical energy into heat, there is always a loss of energy with each step in a food – chain. According to an estimate only 10% of the total energy obtained is transferred from one trophic level to another.
Question 14.
Write important features of a sedimentary cycle in an ecosystem.
Answer:
Sedimentary cycles have their reservoirs in the earth’s crust or rocks. Nutrient elements are found in the sediments of the earth. Elements such as sulphur, phosphorus, potassium, and calcium have sedimentary cycles. Sedimentary cycles are very slow. They take a long – time to complete their circulation and are considered as less perfect cycles. This is because during recycling, nutrient elements may get locked in the reservoir pool, thereby taking a very long – time to come out and continue circulation. Thus, it usually goes out of circulation for a long – time.
Ecosystem Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Describe various components of ecosystem.
Answer:
Ecosystem has following components:
1. Abiotic components:
The physical conditions of the ecosystem depends upon latitude, overall climatic and edaphic factors. The physical deficiencies are overcome by artificial irrigation and use of fertilizers. Thus, like natural ecosystem all organic, inorganic substances and climatic factors together forms abiotic component of the ecosystem.
- Organic substances : Such as carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, etc.
- Inorganic substances : Such as C, H, N, P, K, Ca, I, etc.
- Climatic factors : Such as temperature, light, water, humidity, wind, pH, minerals, soil structure, etc.
2. Biotic factors:
Three types are there
(a) Producers :
This type of crop (dominant species) depends upon the climate, season and the choice of the farmer.
(b) Consumers:
- Primary consumers : Insects, beetles, fishes, etc.
- Secondary consumers : Frog and fishes.
- Tertiary consumers : Snakes and cranes.
(c) Decomposers:
Bacteria, fungi etc.
Question 2.
Explain consumer components ecosystem of a pond in brief.
Answer:
Consumers:
They feed on producers directly or indirectly. It is of following categories:
1. Primary consumers:
Varied forms of zooplanktons are found in the water surface. Most of them are unicellular protists, such as Amoeba, Paramoecium whereas some are multicellular crustaceans, such as Daphnia, Cyclops, etc. Animals which are found under the surface of water are called as benthos, such as many types of fishes, crustaceans, molluscs, insects, beetles, etc. They too feed on producers.
2. Secondary consumers:
They feed on primary consumers, example big fishes, water snakes, etc.
3. Tertiary consumers:
They feed on secondary consumers, example kingfisher, cranes, omnivorous man, etc.
Question 3.
Describe carbon cycle in an ecosystem.
Answer:
Carbon Cycle:
Importance of carbon:
Carbon is considered as the basis of life. Carbon is the most important constituent of proteins, fats and nucleic acids which form the essential constituents of protoplasm.
Sources of carbon – The three sources of carbon in non – living world are:
- The carbon dioxide of the air and that which is dissolved in water.
- The rocks of the earth crust containing carbonates.
- The fossil fuel like coal and petroleum.
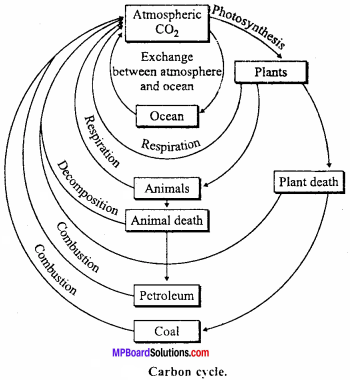
Recycling of carbon:
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the main source of carbon for the living beings. The carbon of coal, graphite, petroleum are insoluble and carbonates are not available to the organism until they are burnt or chemically changed. Most of the carbon dioxide enters the living world through photosynthesis. In this process green plants trap CO2 from atmosphere and convert it into carbohydrates by using water and solar energy.
![]()
The amount of the carbon fixed by photosynthesis is nearly 7 x 1013 kg/year. The organic compounds synthesized in photosynthesis are passed from plants to the herbivores and carnivores. It is estimated that one hectare of a healthy forest produces about 10 tonnes of oxygen and absorbs 30 tonnes of carbon dioxide annually.
![]()
Question 4.
What do you mean by trophic levels? What are ecological pyramids ? Explain various types of ecological pyramids.
Answer:
Trophic level:
In an ecosystem, the producer consumer arrangement is a kind of structure known as trophic structure and each food level in the food chain is called as trophic level or energy level. In other words each level of food in food chain is called its trophic level. The first trophic level (T1) in an ecosystem is occupied by producers. Herbivores (primary consumers) form second trophic level (T2), secondary consumers form third trophic level (T3), tertiary consumers form fourth trophic level (T4) and decomposers form fifth trophic level (T5) in an ecosystem.
![]()
Food or Ecological pyramids:
If we express the organisms of various trophic levels according to their number, biomass and ratio of energy stores within it, then we obtain a cone or pyramid like structure which is known as food or ecological pyramid. Ecological pyramids represent the trophic structure and function of an ecosystem. In base and successive trophic levels the tiers which make up the apex. Ecological pyramids are of the following three types:
- Pyramid of biomass
- Pyramid of number
- Pyramid of energy.
1. Pyramid of Biomass:
Biomass is the dry weight of living organisms per unit of space. The ecological pyramid, which shows the quantitative relationship of the standing crop at each trophic level/The pyramid of biomass shows gradual reduction in biomass at each trophic level from base to apex.
The pyramid of biomass may be :
- Upright – example all terrestrial ecosystems.
- Inverted – example all aquatic ecosystems.

2. Pyramid of Number:
The ecological pyramid which shows the number of individual organisms at each trophic level. It represents numerical relationship between different trophic level of a food chain. In this pyramid more abundant species from the first trophic level and from the base of pyramid and the less abundant species remain near the top. The pyramid of number may be:
- Upright : example grassland, pond, forest ecosystem.
- Inverted : example ecosystem of tree.

3. Pyramid of Energy:
It indicates the total amount of energy at each trophic level of the food chain. At each producer level, the total energy available is relatively more than at the higher trophic levels because of the loss of the energy at each trophic level. Thus, there is a gradual loss of energy at each trophic level. The pyramid of energy of each types of ecosystem is always upright.

Question 5.
What is meant by terrestrial biomes? What are its types? Explain any one biomes in detail.
Answer:
Terrestrial biome:
Large area occupying ecosystems in nature are called biomes. If biomes are on land than they are called terrestrial biomes.
Terrestrial biomes may be :
1. Forest biomes – They may be as below :
- Topical rain forest
- Cold tropical forest
- Taiga forest.
2. Grassland biomes – They may be as below:
- Tropical rain forest
- Cold tropical forest
3. Desert biomes
4. Tundra biomes.
Grassland biome – Grassland biome or ecosystem has long grasses, Its, land is fertile. It receives approximately 25 to 75 cm average rainfall. Its component are:
1. Abiotic component:
All organic, inorganic substances and climatic factors together form abiotic component.
2. Biotic component:
- Producers – Grasses, herb, shrubs.
- Primary consumers – Herbivore like cow, buffalo, goats, sheep, deer, rabbit, rat insect.
- Secondary consumers – Carnivore animals which eat primary consumers, like snake, birds, foxes, jackal etc.
- Tertiary consumers – These organism which eat secondary consumers because no other one eats them, like Hawk, Peacock etc.
- Decomposers – Micro fungus, Bacteria, Actinomycetes are decomposer of grassland biomes and recycle the material back to soil and used by producers.
![]()
Question 6.
What are biogeochemical cycles? Write in short sulphur and calcium cycle.
Answer:
Biogeochemical cycles:
All living organisms get matter from the biosphere components i.e., lithosphere, hydrosphere and atmosphere. Essential elements or inorganic substances are provided by earth and are required by organisms for their body building and metabolism, they are known as biogeochemicals or biogenetic nutrients.
Sulphur cycle:
Producers (green plants) need sulphur in the form of sulphates from soil or from water (aquatic plants). The animals get sulphur through food. Some animals get sulphur from water also. Sulphur is found in three amino acids hence, sulphur is component of most proteins, some vitamins and enzymes. Plants pick up sulphur in the form of sulphates. They are converted to organic form mostly as component of some amino acids. It is found in nature as element and also as sulphates in soil, water and rocks. After the death of plants and animals, they are decomposed by microbes like Asperigillus, Neurospora and Escherichia releasing hydrogen sulphide.

Calcium cycle:
Calcium is slowly released from the rocks by water and wind action. These are either blown into the air or absorbed by plants through their roots. Animals obtain it directly as compounds and also from plants. Calcium is released from plant and animal bodies by decomposition after death. Molluscs and Corals deposit a large quantity of calcium in their shells and skeletons making it unavailable for quick cycling.
