These MP Board Class 11th Chemistry Notes for Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons help students to get a brief overview of all the concepts.
MP Board Class 11th Chemistry Notes Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons
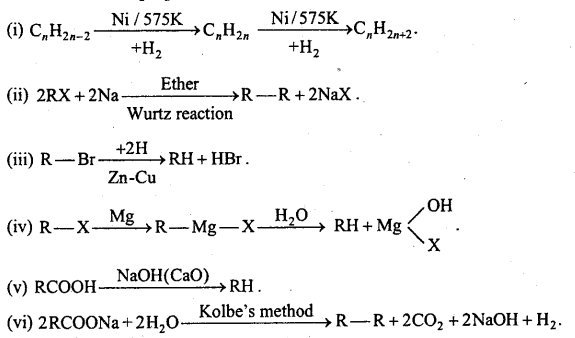
Main methods of preparation of alkanes :
→ Main methods of preparation of alkenes :
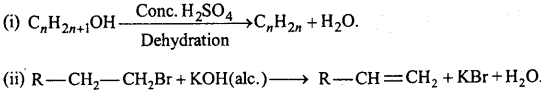
→ Main methods of preparation of alkynes:
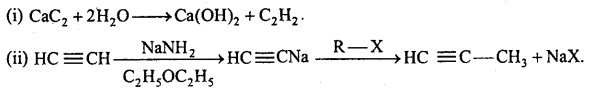
![]()
→ Physical properties of alkanes :
- Boiling point increases with increase in molecular mass, b.p. of branched chain compounds are lower than that of straight chain compounds.
- Melting points also increases with increasing molecular mass. Compounds having odd number of carbon atoms have lower value of m.p.
- Insoluble in water or polar solvents but soluble in non-polar solvents like ether, benzene, etc.
- Generally, density increases with increasing molecular mass.
→ Chemical properties of hydrocarbons;
- Combustion: Exothermic reactions, give CO2 and water vapours.
- Alkenes and alkynes decolorize alcoholic KMnO4 solution.
- Alkyl benzene oxidize into benzoic acid.
- Unsaturated hydrocarbons give addition reactions (H2, Cl2, HCI, etc.).
- Addition of HX in unsaturated hydrocarbons is according to MarkownikofFs rule but opposite in presence of peroxide.
- Alkenes, alkynes and arenes ozonolyze and form carbonyl compounds.
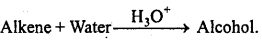
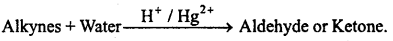
- Polymerization: (a) Ethylene → polyethylene, (b) Propylene → polypropylene, (c) Isoprene → polyisoprene, (d) Vinyl chloride → polyvinyl chloride (PVC), (e) Styrene → polystyrene, (f) Tetrafluoroethene → teflon (PTFE).
(x) Substitution reactions: (a) In alkanes substitution of all hydrogen atoms by halogen atoms take place in presence of sunlight.
(b) Benzene gives halogenation, nitration, sulphonation, alkylation and Friedel-Crafts reaction.
(c) Acetylene and other alkynes give substitution reactions with silver(I) and Cu(I) ions in ammoniacal medium and white and red coloured precipitates of acetylides are formed.
→ Acetylene and others : Alkynes undergo substitution reactions in ammoniacal medium with Silver(I) and Copper(II) ions and form white and red precipitate of acetylides. The ≡ C—H group is of acidic nature.
![]()
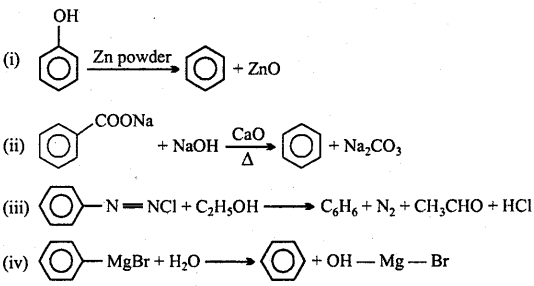
→ Methods of preparation of Benzene :
→ Alkanes undergo free radical substitution reactions.
→ Alkenes and Alkynes undergo electrophilic addition reaction.
→ Main chemical reaction of benzene is electrophilic substitution reaction.
→ Conformation: Due to free rotation around C – C (single bond), formation of different special arrangements.
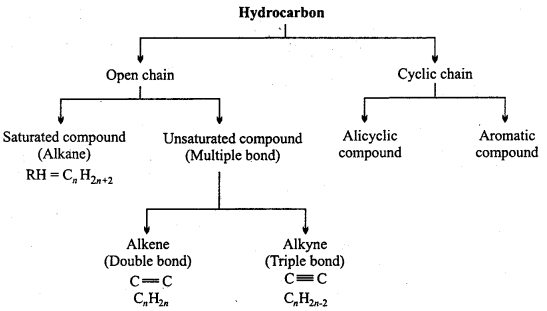
→ Alkanes : Saturated hydrocarbons or paraffins, general formula CnH2n+2tetrahedral structure, sp3 hybridization, H – C – H bond angle is 109° 28′.
→ Alkenes : Unsaturated hydrocarbons whose general fonnula is CnH2n. Carbon-carbon double bond is present.
→ Alkynes : Unsaturated hydrocarbons whose general formula is CnH2n – 2. Carbon-carbon triple bond is present.
![]()
→ Chirality : Compounds not superimposable on their mirror images.
→ Unsymmetrical carbon atom : Such carbon atom to which four different atoms or groups are linked.
→ Optical isomers : Mirror image isomers which rotate the plane of polarised light in opposite direction equally.
→ Racemic mixture : Mixture of equal amount of d and f forms which is optically inactive.
→ Meso form : Symmetrical molecule with more than one chiral centre which is optically inactive.
→ Markownikoff’s rule : The negative part of polar molecule adds to that carbon atom of an unsymmetrical double bond which contains less number of hydrogen atoms.
→ Kharasch effect: Addition reaction on unsymmetrical alkene in presence of peroxide occurs against Markownikoff’s rule.
→ Huckel’s rule : Compound behaves as Aromatic compound if it contains (4n + 2) π-electrons, mete directing groups : — CHO, – COOH, – NO2, – C ≡ N,- SO3H, — COR, — COOR. ortho and para directing groups: – OH, – NH2, – X, – OR, – R, – NHR, – NHCOCH3, – CH3, – C2H5.
→ meta directing groups makes the ring inactive towards electrophilic substitution reactions.
→ ortho and para directing groups make the ring active towards electrophilic substitution reagents.
→ Dienes : These are unsaturated hydrocarbons. They contain carbon-carbon double bond.
![]()
→ Hydrocarbons are compounds of carbon and hydrogen only. They are mainly obtained from coal and petroleum which are main sources of energy.
→ Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) and Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) which is a domestic fuel and are main source of energy for automobiles. These are also obtained from petroleum.
→ Classification of hydrocarbons on the basis of structure :