Students get through the MP Board Class 11th Biology Important Questions Chapter 8 Cell: The Unit of Life which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
MP Board Class 11th Biology Important Questions Chapter 8 Cell: The Unit of Life
Cell: The Unit of Life Class 11 Important Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
What is the mesosome of prokaryotic cells? Give its functions.
Answer:
Mesosome is a special fype of membrane produce by the growth of plasma membrane of prokaryotic cell.
Functions of Mesosome:
- Formation of cell wall.
- DNA replication and distribution in the daughter cells.
- Help in cellular secretion and respiration.
Question 2.
Give characteristics of prokaryotic cell.
Answer:
Characteristics of prokaryotic cells :
- Primitive type of cells.
- True nucleus is not found in them.
- Membrane bound cytoplasmic organelles are not found in them.
- 70 S type of ribosomes are found in them.
e.g. Blue green algae, Bacteria.
Question 3.
What are semiautonomous cell organelles ? Give at least one example.
Answer:
Organelles which can synthesize their protein can reproduce itself and have its own genetic material (DN A and RNA) are called as semiautonomous cell organelles, e.g., Chloroplast, mitochondria, etc.
![]()
Question 4.
Why lysosomes are called as the pocket of suicidal bag?
Answer:
In certain pathological conditions, the lysosomes start digesting the various organelles of cell and process is called autolysis. During this process, membrane of lysosome ruptures and enzymes are released into the cell which destroys and decomposes its own contents thus acting as suicidal bag.
Question 5.
Describe the significance of diffusion.
Answer:
Significance of diffusion :
- It involves in the gaseous exchanges during photosynthesis and respiration.
- During transpiration water is evaporated by the process of diffusion.
- Diffusion plays a vital role in the transport of substances in plants.
- It regulates body temperature.
Question 6.
What happens when R.B.Cs. are kept in hypertonic solution?
Answer:
When R.B.Cs. are placed in a hypertonic solution exosmosis of water takes place and they become plasmolysed. In other words, exosmosis causes shrunken appearance or crenation. A solution of NaCl having more than 0.9% concentration is hypertonic because their osmotic pressure is greater than the cytoplasm of the R.B.Cs.
Question 7.
What are nuclear pores? Give its functions.
Answer:
In some parts of nuclear membrane pores or gaps are found called as nucleopores or nucleus pore. It is formed by fusion of outer and inner nuclear membrane.
Function of nucleopores: RNA and proteins from the nucleus reaches to the cytoplasm through these pores.
Question 8.
How does neutral solvent passes through plasma membrane? Does polar solvent passes through plasma membrane in same way? If not then how does it transport it?
Answer:
Neutral solvent passes through plasma membrane according to concentration gradient, i.e. from higher concentration to lower concentration by diffusion process.
No, polar solvent can not pass through plasma membrane in same way. Since polar solvent can not pass through non-polar lipid, It binds with carrier protein to pass through plasma membrane.
![]()
Cell: The Unit of Life Class 11 Important Questions Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Define prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells with examples.
Answer:
Prokaryotic cells :
These are the primitive and underdeveloped cells. They do not have nucleolus and nuclear membrane. This type of nucleus is called as incipient nucleus. These cells do not possess double membraned cell organelles like mitochondria, chloroplast, golgi body and lysosomes. The genetic material is found only in the form of circular DNA molecule suspended in the cytoplasm itself. Cells bear only ribosomes to synthesize protein in the cytoplasm, e g., Bacteria and blue-green algae.
Eukaryotic cells :
These are the well-organized and well-developed cells. These cells contain nuclear membrane which surrounds the genetic material to form nucleus. Membrane bound cell organelles like mitochondria, golgi body, chloroplast are also present, e.g., cells of all organisms except bacteria and blue-green algae.
Question 2.
Name the scientist who discovered the cell, nucleus, pre-existing cell and organism composed of cell.
Answer:
- Cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665.
- Nucleus was discovered by Robert Brown in 1831.
- Rudolf Virchow (1885) discovered that cell exists from pre-existing cell by division.
- Organism composed of cell was discovered by Theodor Schwann in the year 1839.
Question 3.
Where is energy stored in the cell?
Answer:
Energy of the cell is stored in the high energy bonds of phosphate groups present in ATP (Adenosine triphosphate). After breakage these bonds release energy.
Question 4.
What is totipotency?
Answer:
The capability or potential of every cell of a plant to develop individually into a new plant is known as totipotency and the cells are called as totipotent cells. This idea was first proposed by Haberlandt in the year 1902. Later in 1950 Stecoard developed a new plant from the cells of the root of carrot plant. This technique is nowadays utilized in developing many plants.
Question 5.
How flow of information take place inside the cell? Explain.
Answer:
Flow of information : DNA is the hereditary material of most of the cells. The genetic informations are coded in the DNA. This DNA molecule synthesize RNA by the process of transcription. RNA can synthesize protein through the process of translation.
![]()
![]()
Question 6.
Draw a well labelled diagram of a prokaryotic cell.
Answer:
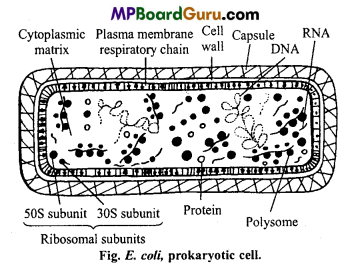
Question 7.
What do you understand by cell theory? Explain.
Answer:
In 1838 and 1839, Schleiden and Schwann proposed a theory about cell which is known as cell theory. The main postulates of the cell theory are as follows :
- Each living body is made up of single or many cells.
- New cells arise from pre-existing cells.
- Structural composition of all cells is basically similar and hence they perform similar metabolic activities.
- The activities shown by an organism is the result of total sum of the activities performed by the cell of its body.
Question 8.
Define cell.
Answer:
According to cell theory Schleiden and Schwann, “Cell is the structural and functional unit of all organisms”. In other words, cell is the smallest living unit which is capable of maintaining its independent existence.
In 1963, Loewy and Siekevity defined cell as, “Cell is a biological unit delimited by a semipermeable membrane and capable of self-reproduction in a medium free of other living system.
Question 9.
What is hybridization? What are its advantages?
Answer:
Hybridization is a technique in which the protoplasm of organisms of different species with different genetic constituency are fused to get a new species. In 1977, Y.P.S. Bajaj obtained a new variety of plant by fusing the cells of Petunia and tobacco.
Advantages :
- New improved varieties can be produced in plants.
- Plants of useful breed can be fielded by this technique.
![]()
Question 10.
Write down the advantages of Multicellularity.
Answer:
Advantages of multicellularity :
- Multicellular organisms are adapted in better way by division of labour as cells of these organisms organize into kinds of tissues and organs to perform specialized functions such as respiration, digestion, excretion, reproduction, etc.
- In multicellular organisms, in many activities number of cells work in coordination. e.g., heart pumps the blood by well coordinated movement of all its muscles.
- In a multicellular organism, cell has a dual existence as an individual and as a part of community.
- The life span of multicellular organisms is comparatively greater than unicellular organisms due to following reasons :
- They can work more efficiently due to division of labour.
- In spite of death of few cells the organism remains alive.
- They have capacity of replacement of dead cells.
- They have capacity to adapt themselves according to its environment.
- They have various developed systems for performing different functions.
Question 11.
Draw a well labelled diagram of PPLO cell.
Answer:
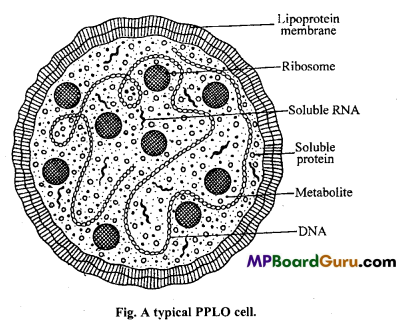
Question 12.
Write down the difference between :
(a) Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic molecule
(b) Passive and Active transport.
(c) Pinocytosis and Phagocytosis.
Answer:
(a) Difference between hydrophilic and hydrophobic molecule :
Molecules which has a very strong liking for water are called as hydrophilic molecules, whereas the molecules which has fear from water molecules are called as hydrophobic molecules. Ex. Bilayered lipid of plasma membrane consists of lipid molecules with two ends hydrophilic and hydrophobics ends. The hydrophilc ends of phospholipid molecules face each other where as hydrophilic ends face the outer protein layer.
(b) Difference between passive and active transport:
Passive transport is kind of physical process and does not involve neither movement of cell nor consumption of energy. e.g., Transport by diffusion and osmosis.
Active transport is the movement of ions or molecules across plasma membrane against concentration gradient. The transport of molecules against concentration gradient involves consumption of energy, e.g., Transport of K+ through plasma membrane.
(c) Difference between pinocytosis and phagocytosis :
Pinocytosis is non-specific intake by a cell of a tiny droplets of extracellular fluid which cannot otherwise pass through the cell membrane. It is also called cell drinking.
In this process, a small region of plasma membrane invaginates and a fluid droplet passes into the pocket so formed. The pocket deepens and finally nips off as a fluid-filled vacuole, the pinocytotic vesicle or pinosome.
Phagocytosis :
The process of engulfing large sized particles of solid food by cell through the plasma membrane is known as phagocytosis. This process is easily seen in protozoa and in certain cells of metazoa.
![]()
Question 13.
Write down the functions of Active Transport.
Answer:
Functions of Active Transport :
- Active transport helps in maintaining a definite ion concentration and definite osmotic pressure within the living system.
- It helps in maintaining water and ionic balance between cell and extracellular fluids.
- Active transport also helps in maintaining membrane potential by keeping the inner side of the membrane relatively electronegative to its outer side.
- It helps for transport of nutrient materials at higher rate.
- Harmful substances are removed from the cell due to this process.
- As this process is selective, it helps in maintaining the chemical composition of the protoplasm.
Question 14.
Explain the importance of osmosis.
Answer:
Importance of osmosis :
- Water is absorbed by root hairs from soil by the process of osmosis,
- Different organs of plant show growth and turgidity only through osmosis,
- The opening and closing of stomata takes place through endosmosis and exosmosis,
- Water moves in the plant body from cell to cell through osmosis.
Question 15.
Why did shrunken grapes or raisins become swollen when kept in water?
Answer:
When shrunken grapes are placed in water, they absorb water by the process of endosmosis through plasma membrane because of their higher concentration. Here plasma membrane acts as semipermeable membrane.
Question 16.
What is cell-wall, explain it?
Answer:
Cell wall is thick, rigid, non-living envelop which surrounds the plasma membrane. It is composed of network of microfibrils embedded in a gel matrix. The microfibrils are mainly cellulosic in nature, but in bacteria and blue green algae, they are formed of protein and polysaccharides. The gel matrix contains protein, pectin, hemicellulose and lignin. The cell wall is found in plant cells and in bacterial cells.
![]()
Question 17.
Write down two chemical components of plasma membrane.
Answer:
Protein and lipid.
Question 18.
Write down the difference between:
(i) Exosmosis and Endosmosis,
(ii) Exocytosis and Endocytosis,
(iii) Cell wall and Cell membrane,
(iv) Semipermeable and Selective permeable membrane
Answer:
(1) Differences between Exosmosis and Endosmosis:
| Exosmosis | Endosmosis |
| 1. Water moves towards outside the solution. | Water moves towards inside the solution. |
| 2. This process is completed in hypertonicsolution. | This process is completed in hypotonie solution. |
| 3 The turgor pressure of the cell is decreased and DPD is increased. | The turgor pressure of the cell is increased and DPD is decreased. |
| 4. Plasmolysis occurs in the cell. | Plasmolysis does not occur in the cell. |
(ii) Difference between Exocytosis and Endocytosis : The secretory products moved
outside the cell cytoplasm is called as Exocytosis. This process requires energy from ATP.
e.g., Transpiration, where as in Endocytosis is the process of engulfing large sized particles
of food substances, e.g., movement of cell and cell sap.
(iii) Differences between Cell wall and Cell Membrane:
| Cell wall | Cell membrane |
| 1. It is the outermost layer or boundary of cell. | It is the outermost layer or boundary of cytoplasm, |
| 2. It is found only in the plant cells. | It is found in all living cells. |
| 3. It is made up of cellulose and lignin. | It is made up of lipid and proteins. |
| 4. It is hard. | It is thin and elastic. |
| 5. It is permeable. | It is selectively permeable. |
(iv) Semipermeable and Selective permeable membrane: Membrane which allow only the solvent to pass through it not the solute are called as semipermeable membrane, where as selective permeable membrane allow only certain selective ions and molecules to pass through it.
Question 19.
Which membrane is known as “Protein iceberg in a sea of lipids” and why?
Answer:
According to Fluid mosaic model, plasma membrane is made up of lipid and protein, in which lipid is present at normal temperature (37°C) in the form of fluid in which solid particles of protein floats. Thus plasma membrane is known as “Protein iceberg in a sea of lipids”.
Question 20.
What are raphides?
Answer:
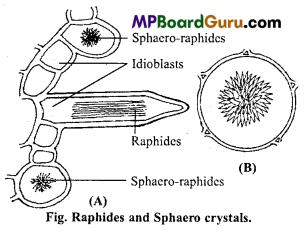
Raphides are excretory materials of plants which are found in the form of crystals of calcium oxalate.
When calcium oxalate crystals are needle shaped they are called as raphides e.g.,
Pistia. If calcium oxalate crystals are more or less star shaped, they are called as Sphaero raphides e.g., Opuntia.
![]()
Question 21.
Write the functions of plasma membrane.
Answer:
Functions of plasma membrane :
- It provides shape of the cell.
- It protects the cell from external forces.
- It helps in the cellular exchange.
- It forms organelles of the cell.
- The inpushing help intake of materials.
Question 22.
Describe plasmolysis.
Answer:
Plasmolysis:
When a living cell is placed in a hypertonic solution then exosmosis of water takes place hence the water of cell comes out into outer solution. Due to exosmosis of water the protoplasm shrinks away from the cell wall and an irregular mass at the centre. This shrinkage of protoplasm is known as plasmolysis.
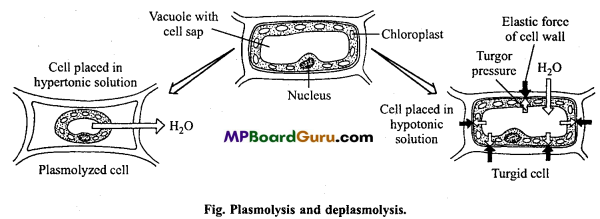
When plasmolysed cell is placed in water, the water enters into the cell sap, the cell becomes turgid and the protoplasm again assumes its normal sap and position. This phenomenon is called as deplasmolysis.
Question 23.
Write down the difference between Diffusion and Osmosis.
Answer:
Differences between Diffusion and Osmosis :
| Diffusion | Osmosis |
| 1. It is the movement of solute particles from higher concentration to lower concentration. | It is the movement of solvent from the region of lower concentration to higher concentration across a semipermeable membrane. |
| 2. It occurs in solids, liquids and gases. | It occurs only in liquids. |
| 3. Semipermeable membrane is not required for this process. | This process requires semipermeable membrane. |
| 4. Diffusion is physical process. | Osmosis is a vital process. |
Question 24.
Give exceptions of cell theory.
Answer:
Exception of cell theory :
- Viruses do not have cellular struture.
- In RBCs aerobic respiration do not occur.
- RBCs are incomplete cells, as they do not have nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum etc.
- Well developed neuron can not show cell division.
- Inspite of capacity cells of liver and muscles do not shows cell division but can regenerate lost or damaged part.
![]()
Question 25.
Define Bio-membrane.
Answer:
The cytoplasm of every cell is enclosed by a layer of lipo-protein membrane called as plasma membrane. The plasma membrane and the subcellular membranes are collectively known as Biological membranes or Bio-membrane.
Question 26.
Sometime plants wilts after addition of fertilizers to the soil. Why?
Answer:
If excess quantity of fertilizers added to the soil then concentration of soil become more as compared to cell-sap of rootcells, thus water from the plantcells is drawn out by exosmosis process and the plant wilts.
Question 27.
What happens when RBCs are kept in hypotonic solution.
Answer:
When RBCs are kept in hypotonic solution endosomosis occurs, If the concentration of hypotonic solution is less than 0-9%, then water or solvent continously enters into RBCs due to which cells of RBCs may burst.
Question 28.
What are trophoplasm?
Answer:
Part of the cytoplasm which contain metabolically active organelles like mitochondria, golgi complex, plastids, endoplasmic reticulum etc. is called as trophoplasm.
Question 29.
Both Lysosomes and vacuoles are bounded by single unit membrane but functionally both are different. Write a note on it.
Answer:
Lysosomes are formed from gogli complex. It consists of many spherical tiny bags filled with hydrolytic enzymes like hydrolases, lipases, proteases etc. All these enzymes become active in acidic medium and help for digestion of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids etc.
Where as Vacuoles are also bounded by single membrane called as Tonoplast, which encloses excess water, excretory materials and cellular products. Ions and other substances enters into vacuole through tonoplast against concentration gradient in plant cells. Thus concentration of vacuoles is always greater than the concentration of cytoplasm.
Question 30.
Describe division of labour in multicellular organisms.
Answer:
Multicellular organisms are made up of different types of cells. In multicellular organisms, cells are interdependent on each other for their survival. They interact and cooperate with one another. In a multicellular organism different functions are performed by different tissues. This is known as division of labour whereas in unicellular organism, all the vital functions are performed by a single cell.
Division of labour in multicellular organisms can be explained by following points :
- Some cells produces additional substances which help to connect different organs with each other.
- Some cells help to carry impulses.
- In multicellular organisms different life processes like respiration, excretion and circulation etc. are performed by different organ systems formed by different types of tis¬sues.
- Many cells dies everyday in the body but new cells are continuously formed in the body. For ex. life span of RBCs is 120 days but new RBCs are continuously formed by bone marrow.
Thus worn out and death of cells in multicellular oiganism does not cause any harm to the organism because new cells are regularly formed in them,
![]()
Cell: The Unit of Life Class 11 Important Questions Long Answer Type
Question 1.
Give names of two cytoplasmic organelles which are surrounded by double membrane. Give characteristics and functions with labelled diagram.
Answer:
Two cytoplasmic organelles surrounded by double membrane are :
(i) Golgi body,
(ii) Endoplasmic reticulum.
(i) Golgi body :
Golgi bodies are found in all eukaryotic cells except RBCs. Golgi body is made up of double layered unit membrane. Under electron microscope, three components are seen:
1. Cisternae : These are flat sacs having 4 to 7 in numbers. Each sac is 60A thick.
2. Vesicles : These are produced by budding or constriction of sacs and are 60n in diameter.
3. Vacuoles : These develop over the body as rounded structure.
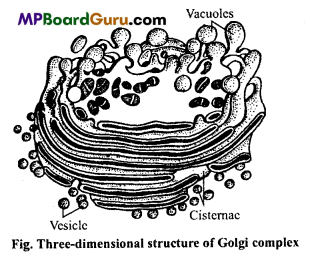
Functions of Golgi body : Some of the most important functions of Golgi body are the following:
- Formation of secretory vesicles.
- Formation of complex molecules of carbohydrate from simple sugars.
- Formation of cell wall and cell plate in plant cell during cell division.
- They form lysosomes which form acrosome after modification.
- They form glycoprotein by aggregation of carbohydrates and proteins.
- Golgi body also helps in the secretion of hormones from endocrine cells.
- It stimulates mitochondria to produce ATP.
- Formation of plasma membrane.
(ii) Endoplasmic reticulum :
Under electron microscope cytoplasmic matrix is seen to be traversed by a complex network of interconnecting membranes of different shapes and sizes. Since this network is concentrated in the endoplasm it is known as endoplasmic reticulum (ER). The endoplasmic reticulum was reported for the first time by Porter and Kallman in 1945.
Endoplasmic reticulum is a complex vacuolar system extending from the nucleus throughout cytoplasm to the cell wall. This vacuolar system is nothing else but spaces enclosed by double membrane.
Types of ER: Depending upon the nature of its membranes, ER is of two main types, i.e., smooth and rough surface.
(i) Smooth surface ER or Agranular ER:
It is formed of smooth membranes. There are no ribosomes attached to its membranes. Smooth surface ER is found in those cells which are almost inactive in protein synthesis. It is generally found in adipose cells, interstitial cells, glycogen storing cells of liver, leucocytes, mature spermatocytes and retinal cells.
(ii) Rough surface ER or Granular ER:
The granular or rough surface endoplasmic reticulum possesses rough walls because the ribosomes are attached with its membranes. Granular ER is found in those cells which are actively involved in protein synthesis, e.g., pancreatic cells, plasma cells, goblet cells and liver cells.
Structure of ER :
Endoplasmic reticulum consists of membrane lined channels or space containing a fluid called endoplasmic matrix. It is composed of three kinds of structures :
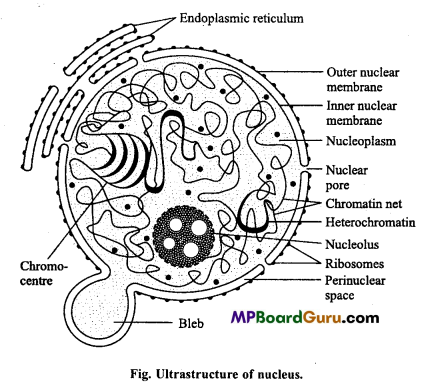
Heterochromatin is the dark stained, condensed end region of chromatin fibres whereas ettchromatin is the light stained and diffused regions of the chromatin. Nucleus also contains a large, spherical acidophilic dense granules called as nucleolus.
Functions of nucleus :
- Nucleus regulates all the activities of the cell.
- It synthesizes all types of cellular RNA, which are necessary forprotein synthesis.
- It plays an important role in cell division and controls growth of the cell.
- It contains genes and chromosomes which carries genetic information from generation to generation.
(ii) Centriole or Centrosome : Centrosomes are found in all the animal cells except mature RBCs but absent in plant cells.
Structure :
Centrioles and basal bodies are cylindrical structures which are 0.15 to 0.25 μ in diameter and usually 0.3-0.7 μ in length. The wall of each centriole and also of the basal body is formed of nine groups of triplet microtubules or fibres. These are equally spaced on the periphery of imaginary cylinder the space between and around the triplet microtubules is filled with the amorphous electron dense material.
All the nine triplet microtubules which form the walls are identical. Each microtubule is formed of three subtubules or subfibrils. The innermost subunit is designated by A, the middle one by B and the outer one by C. Only the A subunit tubule is round, the others are partial and share their wall with the preceding tubule. Often the triplets are thought to run parallel to one another and to the long axis of the cylinder but this is not always true.
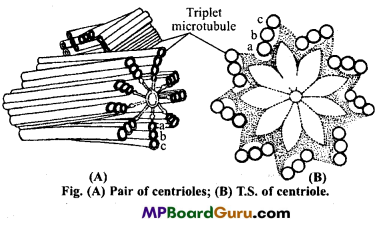
The A tube of each triplet is linked with the C-tube of the neighbouring triplet by a dense link. A-C linkers are responsible for the radial tilt of the triplets. At
(a) Cisternae:
These are elongated, flattened sac like unbranched tubules arranged in parallel rows having the diameter of 40 to 50 mμ Cisternae are found in the cells of liver, pancreas, notochord and brain which are actively involved in protein synthesis.
(b) Vesicles :
These are round, ovoid membrane bound vacuolar spaces having the diameter of 25 to 500 mμ. They are also called microsomes. They generally remain isolated in the cytoplasm and occur in most cells but especially abundant in the pancreatic cells.
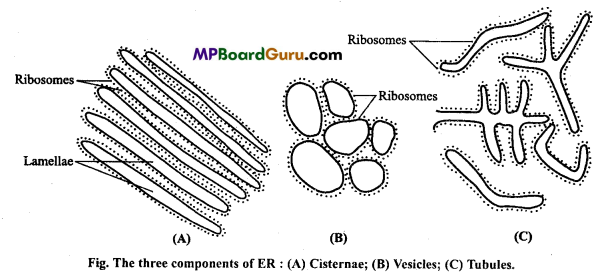
(c) Tubules: Tubules are small, smooth walled, branched, tubular spaces of 50-100 μ diameter. These are found in the cells which are engaged in the synthesis of steroids like cholesterol, glycerides and hormones.
Functions of Endoplasmic Reticulum:
- It forms ultrastructural framework in the cytoplasm and provides mechanical support to the cell.
- Rough endoplasmic reticulum provides surface for the attachment of ribosome, which are involved in protein synthesis thus indirectly they help for protein synthesis.
- It helps in intracellular transport.
- During cell division, it helps for formation of nuclear membrane.
- It stores protein.
- It helps for exchange of material between inner and outer part of the cell.
- It provides surface for various enzymatic activities.
- Smooth endoplasmic reticulum helps in the lipid and glycogen synthesis with the help of enzymes stored in it.
- In liver cells, it helps in glycogenolysis.
![]()
Question 2.
Describe structure of following with labelled diagrams :
(i) Nucleus,
(ii) Centrosome.
Answer:
(i) Nucleus :
All eukaryotic cells normally contain a rounded, circular or oval structure which is called nucleus. It was discovered by Robert Brown in 1831. According to Beller, “Nucleus is a structure surrounded by cytoplasm and which produces chromosomes during cell division”.
Each nucleus is surrounded by a bilayered cell membrane which contains numerous pores.
The outer membrane of nucleus possesses numerous ribosomes. Each nucleus is filled with nucleoplasm, which contains a network of chromatin. During cell division these chromatin fibres condense to form chromosomes. In nucleus two types of chromatin have been identified:
- Heterochromatin and
- Euchromatin.
the proximal end of centrioles and basal bodies is found a cartwheel structure composed of central rod or hub in the centre and radiating from it are nine spokes. These spokes end in the dense feet. Cells of plants lack centrioles.
Functions of centriole :
- During the cell division they help in the formation of spindles.
- Centriole serve as foci for the production of new centrioles and basal bodies.
- The microtubules of cilia and flagella originate and bear by basal bodies.
Question 3.
“Cell is the basic unit of life”. Explain the statement.
Answer:
Each cell is an autonomous unit. It independently carries out all fundamental processes like respiration, excretion, energy utilization, etc. It oxidizes food molecules to release energy to perform its functions like synthesis of materials for body movement, secretion and transport. Cell exchange gases like O2 and CO2. It synthesizes DNA for its duplication. The cell maintains its internal physico-chemical conditions. Each cell has its own life span.
The above facts will prove cell as self-contained autonomous unit.
In multicellular organisms cells are interdependent on each other for their survival. They interact and co-ordinate with one another, but they shows the capacity of independent existance and multiplication. This can be demonstrated by isolating cells of multicellular organism and growing them in a culture medium under controlled conditions, then like unicellular orgnanisms these cells can perform all life activities independently control and coordination is done by the materials present within the cell.
Each cell is found surrounded by plasma membrane, which encloses protoplasm, thus separate protoplasm from the environment and acts as an indepdent unit. Thus cell is called as “basic unit of life”.
![]()
Question 4.
Write differences between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells.
Or,
Write five differences between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells on the basis of complexity.
Answer:
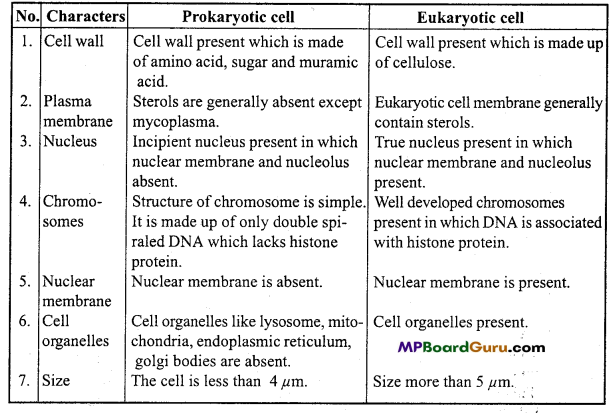
Question 5.
Distinguish between Plant and Animal cell.
Or,
Write five differences between Plant cell and Animal cell.
Answer:
Differences between Plant and Animal cells
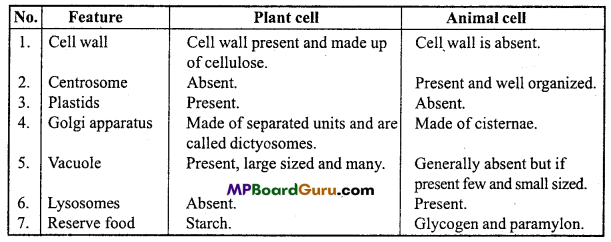
Question 6.
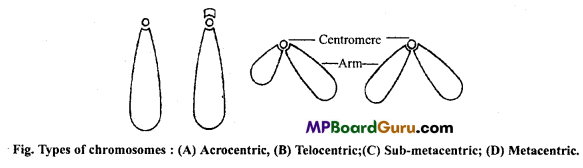
What is centromere? How classification of chromosomes is done on the basis of location of centromere? Describe with diagrams.
Answer:
Centromere :
The chromatids of chromosomes are held together at a point is called Centromere. It divides chromosome into two equal or unequal halves.
There are four types of chromosomes on the basis of position of centromere.
- Acrocentric : These are rod shaped chromosomes which has terminal centromere, so they possess only one arm.
- Telocentric : These are rod shaped chromosomes having subterminal centromere. One arm of the chromosome is very long and other is very short.
- Sub-metacentric : These are ‘L’ shaped chromosomes with centromere slightly away from the mid point so that two arms are unequal.
- Metacentric : These are ‘V’ shaped chromosomes in which centromere is located at the middle of the chromosome so that the two arms are almost equal.
![]()
Cell: The Unit of Life Class 11 Important Questions Objective Type
1. Choose the correct answers:
Question 1.
Cell is discovered by :
(a) Robert Hooke
(b) Robert Brown
(c) Schleiden
(d) Schwann.
Answer:
(a) Robert Hooke
Question 2.
Nucleus is discovered by :
(a) Schleiden
(b) Schwann
(c) Robert Brown
(d) Mendel.
Answer:
(c) Robert Brown
Question 3.
Cell theory was proposed by :
(a) Schleiden and Schwann
(b) Lamarck and Traviranus
(c) Muir and associates
(d) Maheshwari and Guha.
Answer:
(a) Schleiden and Schwann
Question 4.
Scientist associated with totipotency is :
(a) Lamarck
(b) Haberlandt
(c) Schleiden
(d) Schwann.
Answer:
(b) Haberlandt
Question 5.
Formation of a well developed organism from a vegetative cell is called :
(a) Somatic hybridization
(b) Somatic reproduction
(c) Totipotency
(d) Plasmolysis.
Answer:
(c) Totipotency
Question 6.
Cell is an autonomous unit because :
(a) It possesses the capacity of locomotion
(b) It can reproduce
(c) It contains nucleus
(d) It possesses the capacity of regulation and direction of all vital processes.
Answer:
(d) It possesses the capacity of regulation and direction of all vital processes.
Question 7.
Prokaryotic cell does not contain :
(a) Cell wall
(b) Nuclear membrane
(c) Plasma membrane
(d) Vacuole.
Answer:
(b) Nuclear membrane
![]()
Question 8.
Which prokaryotic cell having very minute cell structure :
(a) Rhizobium
(b) Mycoplasma
(c) Nostoc
(d) Bacillus.
Answer:
(b) Mycoplasma
Question 9.
Which statement is not correct:
(a) Cell was discovered by Robert Brown.
(b) Cell theory was proposed by Schleiclen and Schwann.
(c) According to Virchow new cells develop from the division of pre-existing cells, [omnis cellula e cellula]
(d) Unicellular organisms perform all the activites in single cell.
Answer:
(a) Cell was discovered by Robert Brown.
Question 10.
New cells are formed :
(a) By bacterial fermentation
(b) By reproduction of old cells
(c) From pre-existing cells
(d) From non-living substances.
Answer:
(c) From pre-existing cells
Question 11.
Which statement is correct:
(a) All genes are found in the nucleus
(b) Plasma membrane is not found in both plant and animal cell
(c) Membrane bound organelles are found, in the cell membrane of prokaryotic cell.
(d) Production of cell occurs from non-living materials.
Answer:
(a) All genes are found in the nucleus
Question 12.
Ingestion of solid particles by plasma membrane is called :
(a) Pinocytosis
(b) Exocytosis
(c) Endocytosis
(d) Phagocytosis.
Answer:
(d) Phagocytosis.
Question 13.
What is cell omitting :
(a) Active transport
(b) Diffusion
(c) Osmosis
(d) Inactive transport.
Answer:
(a) Active transport
Question 14.
Ingestion of liquids by cell membrane is called :
(a) Endocytosis
(b) Pinocytosis
(c) Osmosis
(d) Diffusion.
Answer:
(b) Pinocytosis
![]()
Question 15.
Amount of proteins in plasma membrane is about:
(a) 30-40%
(b) 10-20%
(c) 5%
(d) 60-80%.
Answer:
(d) 60-80%.
Question 16.
Percentage of lipid in plasma membrane is about:
(a) 20-40%
(b) 60-80%
(c) 5%
(d) 10-20%.
Answer:
(a) 20-40%
Question 17.
Outer and inner layer of plasma membrane is made up of:
(a) Lipid
(b) Protein
(c) Carbohydrate
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Protein
Question 18.
Desmosomes are:
(a) Pores present in plasma membrane
(b) Special area of plasma membrane where other plasma membrane attached
(c) Substance take part in the constitution of plasma membrane
(d) Chemical which j oin two cells.
Answer:
(b) Special area of plasma membrane where other plasma membrane attached
Question 19.
Lamellar model of plasma membrane was proposed by :
(a) Danielli and Davson
(b) Robertson
(c) Robert Brown
(d) Singer and Nicholson.
Answer:
(a) Danielli and Davson
Question 20.
The cell membrane is composed of:
(a) Phospholipid
(b) Nucleoprotein
(c) Polysaccharides
(d) Lipoprotein.
Answer:
(d) Lipoprotein.
Question 21.
All are membrane bounded cell organelles :
(a) Mitochondria
(b) Lysosomes
(c) Spherosomes
(d) Ribosomes.
Answer:
(d) Ribosomes.
![]()
Question 22.
Robertson’s model of cell membrane is similar to that of Danielli and Davson’s
in:
(a) Types of protein
(b) Lamellar structure
(c) Permeases
(d) Carrier particles.
Answer:
(b) Lamellar structure
Question 23.
‘Power house of the cell’ is:
(a) Nucleus
(b) Mitochondria
(c) Golgi body
(d) Chioroplast.
Answer:
(b) Mitochondria
Question 24.
Which of the following is called as ‘Suicidal bag of the cell’:
(a) Lysosome
(b) Mitochondria
(c) Peroxisomes
(d) Golgi body.
Answer:
(a) Lysosome
Question 25.
The word chromosome was coined by :
(a) Balbiani
(b) Waldeyer
(c) Sutton
(d) Purkinje.
Answer:
(b) Waldeyer
2. Fill in the blanks:
1. Cell theory was proposed for the first time ………………..
Answer:
Schleiden and Schwann
2. Nucleus was discovered by …………………..
Answer:
Robert Brown
3. ……………….. is present in animal cell not in plant cell.
Answer:
Centrosome
4. …………………. is the main constituent of cell wall.
Answer:
Cellulose
5. ……………….. are called suicidal bags of cell.
Answer:
Lysosomes
6. Polymorphism phenomenon occurs in a cell organelle called as ……………………
Answer:
Lysosome
7. In plant cells, golgi complex is formed of unconnected units called ……………………
Answer:
Dictyosome
8. …………………. is engaged in the synthesis of glycogen, lipids and steroids.
Answer:
Photorespiration
9. The tubular arrangement in cilia and flagella is …………………………..
Answer:
9 + 2
10. …………………. form spindle fibres at the time of cell division.
Answer:
Centrosome
11. The thickness of cell membrane is about ……………….
Answer:
75 Å
12. …………….. is called a protein factory of the cell.
Answer:
Ribosome
![]()
3. Match the following:
(A)
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Mitochondria | (a) Cellulose |
| 2. Nucleus | (b) Lysosoine |
| 3. Cell wall | (c) R.N.A. and Protein |
| 4. Engine of cell | (d) Power house of cell |
| 5. Nucleolus | (e) Director of the cell |
Answer:
1. (d) Power house of cell
2. (e) Director of the cell
3. (a) Cellulose
4. (b) Lysosoine
5. (c) R.N.A. and Protein
(B)
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Cistemae | (a) Green Algae |
| 2. Stroma | (b) Dictyosome |
| 3. Animal cell | (c) Endoplasmic Reticulum |
| 4. Centriole | (d) R.N.A. + Protein |
| 5. Ribosome | (e) Sperm. |
Answer:
1. (b) Dictyosome
2. (a) Green Algae
3. (d) R.N.A. + Protein
4. (e) Sperm.
5. (c) Endoplasmic Reticulum
(C)
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Amyloplast | (a) Polyribosomes |
| 2. Golgi complex | (b) Passive transport |
| 3. Known as Bioblast | (c) Starch grains |
| 4. Cluster of Ribosomes | (d) Secretion |
| 5. Saves energy | (e) Mitochondria. |
Answer:
1. (c) Starch grains
2. (d) Secretion
3. (e) Mitochondria.
4. (a) Polyribosomes
5. (b) Passive transport
![]()
(D)
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Semiautonomous organelle | (a) Ribosome |
| 2. Suicidal bag | (b) Chioroplast and Mitochondria |
| 3. Physical basis of life | (e) Mitochondria |
| 4. Protein factory | (d) Lysosome |
| 5. Power house of the cell | (e) Protoplasm |
| 6. Cell theory | (f) Schleiden and Schwann. |
Answer:
1. (b) Chioroplast and Mitochondria
2. (d) Lysosome
3. (e) Protoplasm
4. (a) Ribosome
5. (e) Protoplasm
6. (f) Schleiden and Schwann
(E)
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| I. Cristae | (a) Disc like flat membranous component in grana |
| 2. Vacuole | (b) Finger like projection in the rnìtochondria |
| 3. Thylakoid | (c) Large specious rounded sac like structure of Golgi complex. |
Answer:
1. (b) Finger like projection in the rnìtochondria
2. (c) Large specious rounded sac like structure of Golgi complex.
3. (a) Disc like flat membranous component in grana
4. Write true or false:
1. Small bodies have more surface unit volume.
Answer:
True
2. Golgi body help in protein synthesis.
Answer:
False
3. Osmoregulatory organelle is vacuole.
Answer:
True
4. Skeleton of cell are endoplasmic reticulum.
Answer:
True
5. Ribosome was discovered by Palade.
Answer:
True
6. The outermost layer of cellwall is called middle lamella.
Answer:
True
7. The chief role of nucleolus in a nucleus concerns with DNA replication.
Answer:
False
8. Cilia are formed by lysosome.
Answer:
False
9. Mitochondria are called the Power house of the cell.
Answer:
True
10. Centrosome forms asters during cell division.
Answer:
True
![]()
5. Answer in one word:
1. What will you call a cell not having E.R., golgi body, mitochondria, nuclear membrane etc.?
Answer:
Prokaryotic cell
2. In which cell, plastids and cell wall are present?
Answer:
Plant cell
3. What will you call the fusion product of protoplast of two somatic cells?
Answer:
Heterokaryon
4. Which of the following is dead-plasma membrane or cell wall?
Answer:
Cell wall
5. Which mature body cell are/is capable of reproduction?
Answer:
Nerve cells
6. RER occurs more abundantly in cells which are synthesizing .
Answer:
Protein
7. Inner membrane of cristae which bears enzymes necessary for electron transport chain.
Answer:
Oxisomes
8. The protein present in microtubules are ………………
Answer:
Tubulin
9. Proteins associated with chromosomes are ………………….
Answer:
Histone and Non-histone
10. Recent name of bioblasts is ………………..
Answer:
Mitochondria