Students get through the MP Board Class 11th Biology Important Questions Chapter 10 Cell Cycle and Cell Division which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
MP Board Class 11th Biology Important Questions Chapter 10 Cell Cycle and Cell Division
Cell Cycle and Cell Division Class 11 Important Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
What is the average cell cycle duration of cells of mammalia?
Answer:
Average cell cycle duration of cells of mammals is 24-25 hours.
Question 2.
What is the difference between cytokinesis and karyokinesis?
Answer:
Division of the cytoplasm is called as cytokinesis, whereas division of the nucleus is called as karyokinesis.
![]()
Question 3.
What is G0 phase of cell cycle?
Answer:
Cells which do not divide further and reaches to inactive phase, is called as G0 phase of cell cycle. At this stage cell shows high rate of (active) metabolism but does not divide. They divide depending upon requirement of the organism.
Question 4.
Why Mitosis cell division is called as similar division?
Answer:
At the end of this cell division daughter cells have same number of chromosomes like parent cell thus Mitosis division is called as similar cell division.
Question 5.
Where daughter cells formed by meiosis cell division are same and different?
Answer:
Four daughter cells formed by meiosis division in the testis are the spermatids which are same in size whereas in the ovary of female four daughter cells formed by meiosis are different in size, i.e. one ovum which is larger in size and three polar bodies, which are smaller in size.
Question 6.
Is Mitosis division possible without DNA replication in ‘S’ phase of cell cycle?
Answer:
No, Mitosis division is not possible without DNA replication in ‘S’ phase of cell cycle, because duplication of DNA is essential for Mitosis division.
Question 7.
Name the stage of cell division which involves crossing-over.
Answer:
Crossing-over occurs during pachytene stage of Prophase-I of meiosis cell division.
Question 8.
Name the stain used for staining chromosomes of the cells for study.
Answer:
Acetocarmine stain is used for staining chromosomes of the cell for study.
![]()
Question 9.
Name the cells exhibiting mitosis cell division.
Answer:
Mitosis is the characteristic feature of somatic cells.
Question 10.
Name the cells exhibiting meiosis cell division.
Answer:
Meiosis takes place in generative cells to produce gametes.
Question11.
What is chiasmata?
Answer:
The place of chromosomes where they come into contact with each other during crossing-over is called as chiasmata.
Question 12.
List the various phases of the first meiotic division.
Answer:
The following stages are found in the first meiotic division :
- 1. Prophase-I: It has following substages :
- Leptotene,
- Zygotene,
- Pachytene,
- Diplotene and
- Diakinesis.
- Metaphase-I,
- Anaphase-I,
- Telophase-I.
Question 13.
What is synapsis?
Answer:
Pairing of homologous chromosomes in zygotene stage of Prophase-I of meiosis cell division is known as synapsis. The paired structure formed by synapsis is called as bivalent.
Question 14.
What do you mean by Mitotic poison?
Answer:
Chemical substances which inhibit the mitotic division are called as Mitotic poison.
e.g.,
- Cholchicine : It stops formation of spindles during Metaphase.
- Ribonuclease : It stops Prophase stage.
- Mustard gas : It breaks chromosomes.
![]()
Question 15.
Name the parts of a flowering plant where meiosis cell division occurs.
Answer:
In the pollen sac of androecium and ovary of gynoecium meiosis division occurs to produce male and female gametes respectively.
Cell Cycle and Cell Division Class 11 Important Questions Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Describe the phenomenon occurs during interphase of cell cycle.
Answer:
Interphase is the period between two successive cell divisions. It has following three stages:
- G1-phase : RNA and protein synthesis occurs during this stage.
- S-phase : DNA synthesis occurs during this stage.
- G2-phase : Synthesis of protein and RNA continue in this stage.
Question 2.
What is the significance of Meiosis division?
Answer:
Significance of meiosis : The significance of meiosis are as follows :
- The number of chromosomes is stable generation to generation due to the meiotic division.
- The number of chromosomes is reduced to half in the gametes.
- The characters of parents are transmitted into offspring by this process.
- Crossing-over takes place during this stage which can produce new characters in the organisms.
- Variations are also occurred which help in the study of evolution.
- There are four haploid cells formed from one diploid cell.
Question 3.
Name the stage of cell cycle when following phenomenon occurs :
(i) Movement of chromosomes towards the equator of the cell.
(ii) Breaking of centromere and separation of chromosomal half.
(iii) Pairing of homologous chromosomes.
(iv) Exchange between homologous chromosomes.
Answer:
(i) Metaphase,
(ii) Anaphase,
(iii) Zygotene stage of Prophase-I of Meiosis-I,
(iv) Pachytene stage of Prophase-I of Meiosis-I.
Question 4.
Explain the following :
(i) Synapsis,
(ii) Bivalent,
(iii) Chiasmata.
Answer:
(i) Synapsis :
Pairing of homologous chromosomes in zygotene substage of prophase-I of meiosis cell division is known as synapsis. The paired structure formed as result of synapsis is called as bivalent.
(ii) Bivalent:
The pairs of homologous chromosome formed during zygotene stage of meiosis-I. The chromosomes contract and become short and thick.
(iii) Chiasmata :
In Pachytene stage of Prophase-I of Meiosis-I division, non-sister chromatids of two chromosomes, which come in contact of each other and fixes themselves tightly for crossing-over. These fixed parts are called as Chiasmata.
![]()
Question 5.
Write differences between cytokinesis in plant and animal cell.
Answer:
Cytokinesis : Division of cytoplasm after Karyokinesis to produce daughter cells is called as Cytokinesis.
(a) Cytokinesis in plant cell:
It immediately follows karyokinesis. In plant cells, a cell plate of dense cistemae is laid down at the equatorial plate. It grows centrifugally (external laterally) towards plasma membrane until it divides the cell into two parts. The space in between the two membranes of cistemae is filled by the deposition of pectates of calcium and magnesium to become middle lamella.
(b) Cytokinesis in animal cell:
In animal cell, cytokinesis occurs by an invagination of cell membrane almost in the middle of the cell. The furrow gradually depens and ultimately divides the cell into two parts.
Question 6.
Write differences between Anaphase of Mitosis and Meiosis cell division.
Answer:
Differences between Anaphase of Mitosis and Meiosis cell division
| Anaphase of Mitosis | Anaphase of Meiosis |
| One chromatid of one chromosome moves towards one pole and another chromatid of it moves towards the other pole. | In Anaphase-I complete chromosomes move towards their poles and in Anaphase-II movement occurs like Anaphase of Mitosis. |
Question 7.
Analyse each phase of cell division and explain how does following changes occurs in the cell:
(i) Number of chromosomes (N) in each cell.
(ii) Quantity of DNA in each cell.
Answer:
(i) In all cells during prophase, metaphase and anaphase stage of cell division, number of chromosomes become double and in telophase stage number of chromosomes become half again, i.e., (N).
(ii) During cell division quantity of DNA changes in all stages. During prophase, metaphase and anaphase number of DNA increases, it becomes double, but in telophase stage quantity of DNA becomes half.
Question 8.
Discuss following with your teacher :
(i) When cell division occurs in haploid seed and lower category of plants ?
(ii) Where cell division does not occur in the haploid cells of higher category of plant?
Answer:
(i) Haploid spores of lower category of plant divides by mitosis division to form gametophyte, whereas zygote develops to form sporophyte and meiosis division occurs for formation of haploid spores, e.g., moss, fern etc.
(ii) Synergids and antipodal cells found in the ovules of angiosperms are haploid. They do not show cell division. After completion of life span they dies.
Question 9.
What is crossing-over? Throw light on its significance.
Answer:
Crossing-over : Crossing-over is the exchange of chromosomal segments or genes between homologous chromosomes during diplotene stage of meiosis-I.
Significance of crossing-over :
- New characters are originated by this process,
- Variations occur in organisms,
- It plays an important role in organic evolution,
- It results in the production of adaptation in organisms.
![]()
Question 10.
Write the significance of mitosis.
Answer:
Significance of mitosis:
- Growth and development takes place due to mitosis,
- Some micro-organisms use this method for asexual reproduction,
- Dead cells are substituted by new cells by mitotic division,
- General repairing process is result of mitotic division,
- Genetic information are transferred from parents to offspring by this process.
Question 11.
What is the difference between anaphase-1 of meiosis and anaphase of mitosis ? What is its effect on the whole process?
Answer:
In meiotic anaphase-I, the two chromosomes of each bivalent separate from each other and move towards opposite poles of the spindle. But the two chromatids of each chromosome still continue to remain joined with one another with centromere. Thus, only one chromosome of each homologous chromosome pair reaches each pole and the number of chromosomes are reduced to half in daughter nuclei.
In mitotic anaphase-I, centromere of each chromosomes divides and permits the separation of two sister chromatids, each chromatid after separation is called daughter chromosomes. The daughter chromosomes move apart and migrate towards opposite poles. The centromere is pulled towards poles of the spindle and the arms of chromosomes are dragged behind.
Effect of whole process:
Anaphase-I of meiosis resulting in the formation of daughter nuclei having half of the chromosomes to their parents. Thus, the number of chromosomes is constant from generation to generation.
Question 12.
Write a note on necessity of two types of cell divisions in multicellular organisms.
Answer:
Necessity of two types of cell divisions :
There is complexity in structure and physiology of multicellular organisms. Thus, twc types of cell divisions are required in them. The process of meiosis cell division help in the maintenance of chromosome number in the species. Diploid (2x) organism produce haploid (x) gametes, which on fusion form diploid zygote, whereas zygote divides by mitosis division to form diploid organism. Healing of wound in multicellular organisms occurs by mitosis cell division.
Question 13.
Describe the prophase and anaphase of mitosis along with diagram.
Answer:
1. Prophase : (Pro = before, phasis – stage).
- In this stage chromosomes are found in the form of long threads which are called as chromatin net.

- Chromosomes become short and thick and each of them splits lengthwise forming two chromatids.
- At the ending of prophase nuclear membrane and nucleolus start to disappear.
2. Anaphase :
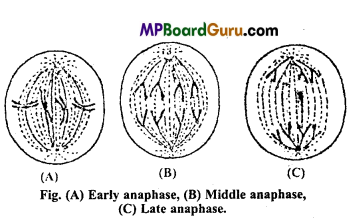
- During this stage the centromere of each chromosome gets divided into two which make the chromatids free from each other.
- Every chromatid with its centromere moves towards its poles.
- Termination of anaphase movement occurs when the chromosomes form a densely packed group at the two poles.
![]()
Question 14.
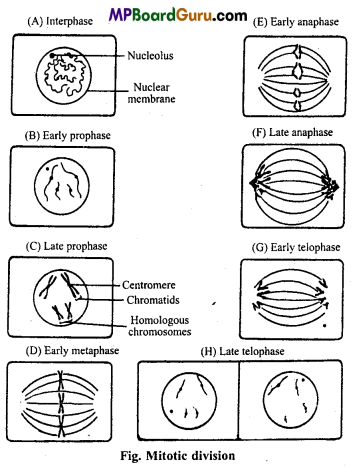
Draw labelled diagram of different stages of Mitosis cell division.
Answer:
Question 15.
Describe the metaphase of mitosis along with diagram.
Answer:
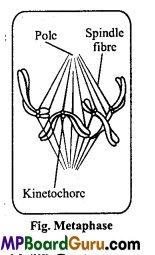
Metaphase : The following events occur during mitotic metaphase: ‘
- Nuclear membrane and nucleolus disappear during this stage.
- Chromosomes move towards equatorial plane of the cell.
- Chromatids of chromosomes become dense and separated from each other except centromere.
- Spindle fibres are formed.
- The centromeres of the chromosomes are arranged on equator and chromatid towards the opposite poles. Fig Metaphase
Question 16.
Write differences between following :
(i) Mitosis and Meiosis cell division,
(ii) Chromatin and Chromatid,
(iii) Centromere and centriole,
(iv) Centromere and Chromomere,
(v) Metaphase-I and Metaphase-II,
(vi) Zygotene and Pachytene,
(vii) Cell furrow and Cell plate.
Answer:
(i) Differences between Mitosis and Meiosis cell division :
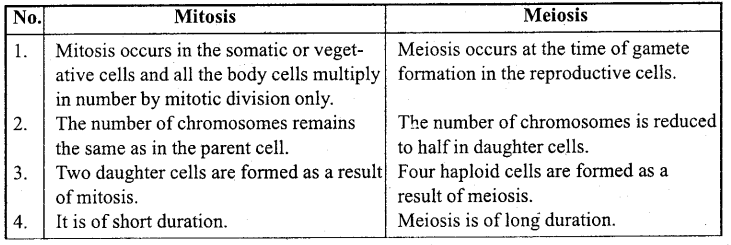
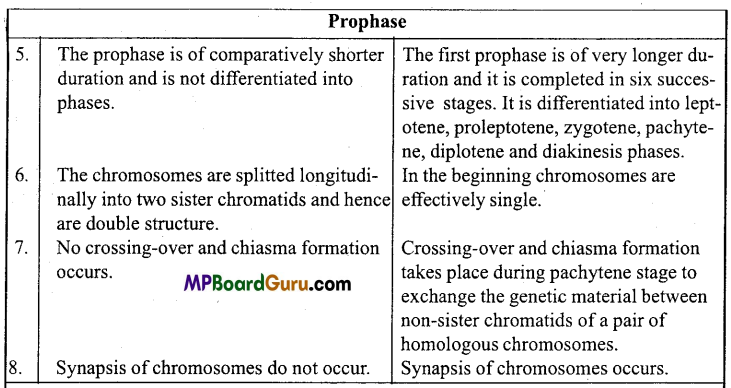
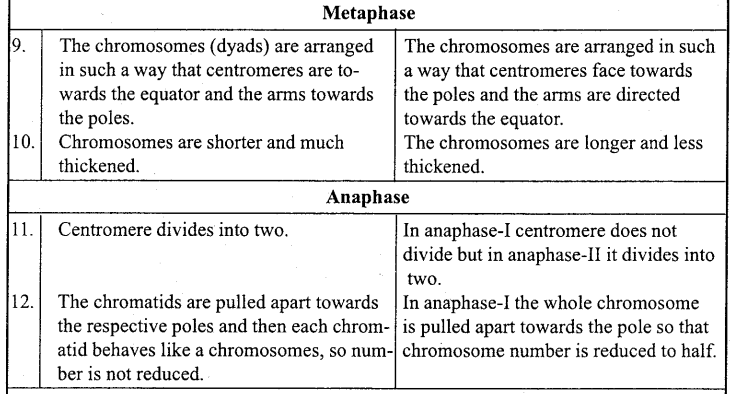
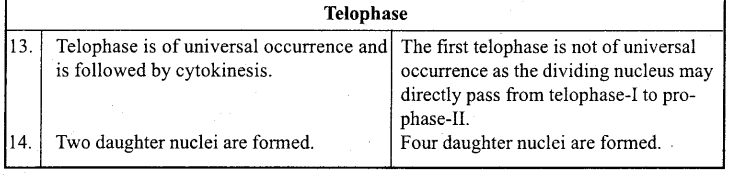
(ii) Differences between Chromatin and Chromatid
| Chromatin | Chromatid |
| 1. It is the diffused deep staining hereditary material. | It is longitudinally split half of a chromosome. It is light staining hereditary material. |
| 2. It is metabolically inert and its crossing-over frequency is less. | It is very active metabolically and its crossing over frequency is more. |
(iii) Differences between Centromere and Centriole
| Centromere | Centriole |
| 1. It is the region of attachment of the sister chromatids and also the site of attachment to the spindle fibres. | It is the minute self replicating body lying near the nucleus in the animal cell. It radiates astral rays and spindle fibres during cell division. |
(iv) Differences between Centromere and Chromomere
| Centromere | Chromomere |
| 1. It is the region of attachment of the sister chromatids and also the site of attachment to spindle fibres. | The beaded and knot like structure present on chromonemata are called as chromomeres. |
(v) Differences between Metaphase-I and Metaphase-II
| Metaphase-I | Metaphase-II |
| 1. Pair of homologous chromosomes are arranged at the equator of the cell. | Single chromosomes are arranged at the middle part of the cell. |
| 2.Centromere do not divide. | Centromere divides to form chromatids. |
(vi) Differences between Zygotene and Pachytene
| Zygotenw | Pachytene |
| 1. Pairing of homologous chromosomes occurs (synapsis) to form Bivalent | Chromosomes split lengthwise but still remain attached at the point of centromere to form tetrad followed by crossing-over. |
(vii) Differences between Cell furrow and Cell plate
| Cell furrow | Cell plate |
| 1. It is a constriction formed at the middle part of a cell, which grows to divide parent cell into two daughter cells. | It is a cell wall formed at the equator formed by accumulation of vesicles of dictyosomes and elements of endoplasmic reticulum to form two daughter cells. |
| 2. Cell furrow formation occurs in animal cells. | Cell plate formation occurs in plant cell. |
![]()
Question 17.
Define the following :
1. Homologous chromosomes,
2. Synapsis,
3. G2alent,
5. Tetrad.
Answer:
1. Homologous chromosomes :
Homologous chromosomes are paired during zygotene and then form chiasmata at some places where crossing over takes place between them and finally resulting in the production of new characters and possibilities of organic evolution.
2. Synapsis:
Pairing of homologous chromosomes in zygotene substage of prophase-I of meiosis cell division is known as synapsis. The paired structure formed as result of synapsis is called as bivalent.
3. G2-Phase :
In this phase, RNA and protein continues to be synthesised. The cell is now ready to enter the mitotic phase. The cells of this stage contain double amount of DNA.
4. Bivalent:
The pairs of homologous chromosome formed during meiosis-I. The chromosomes contract and become short and thick.
5. Tetrad:
In Pachytene stage of Prophase-I of Meiosis-I, Chromosomes split lengthwise but still remain attached at the point of centromere to form four chromatids called as Tetrad.
Question 18.
Which of the following statement is associated with :
(a) Prophase,
(b) Metaphase,
(c) Anaphase,
(d) Telophase,
(e) Interphase of mito-sis.
1. The nuclear membrane reappears.
2. Chromosomes are thickest and shortest.
3. Chromosomes begin to coil.
4. Centromere divides into two.
5. Nucleus is active, but chromosomes are not distinct.
6. Followed by cytokinesis.
7. Each chromosome consists of two chromatids.
Answer:
1. (d) Telophase
2. (b) Metaphase
3. (c) Anaphase
4. (c) Anaphase
5. (e) Interphase of mito-sis
6. (d) Telophase
7. (c) Anaphase
Cell Cycle and Cell Division Class 11 Important Questions Long Answer Type
Question 1.
Write important differences between Mitosis and Meiosis cell division.
Answer:
Differences between Mitosis and Meiosis
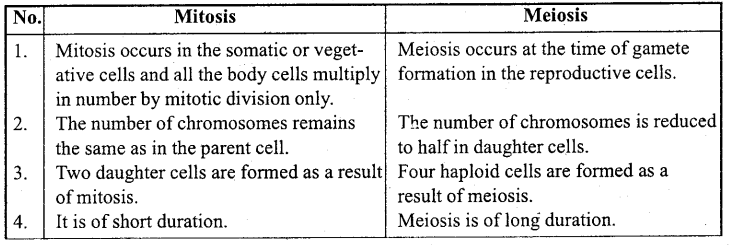
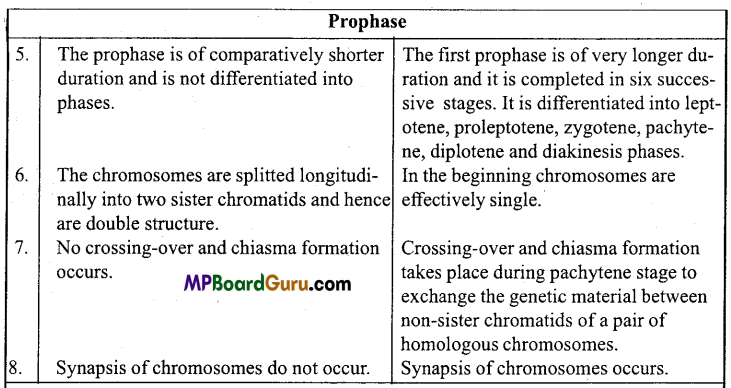
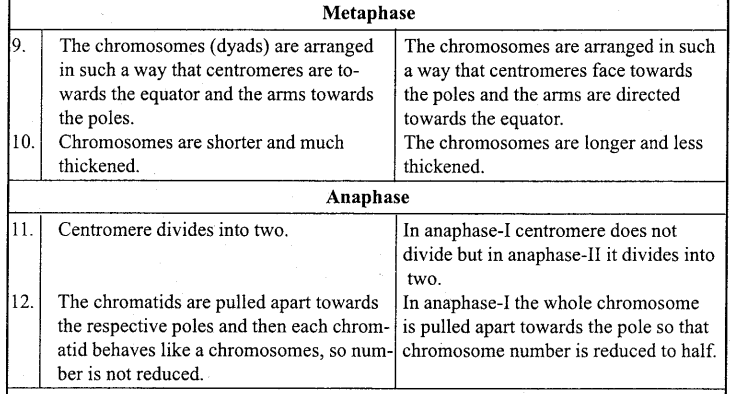
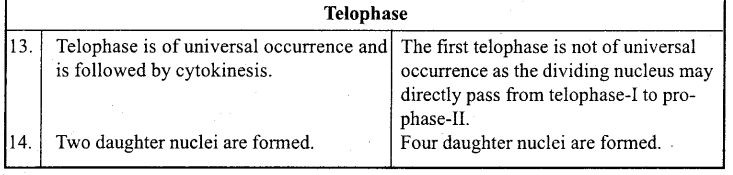
![]()
Question 2.
Describe different stages of Meiosis and its significance also.
Answer:
Meiosis-I division :
1. Prophase-I (Gk., pro = before, phasis = stage) : The prophase of first meiotic division is a complex phase of longer duration which is further divided into following five substages:
(i) Leptotene or Leptonema (Gk., leptos = thin, nema = thread) :
At this stage condensation of chromatin starts and the fine chromatin fibres appear with granule like chromomeres on them. The chromomeres are the regions where chromatin fibres are highly coiled.
(ii) Zygotene or Zygonema (Gk., zygo = paired, tiema = thread):
At zygotene stage two homologous chromosomes (one paternal and other maternal) lie side by side which is known as pairing of homologous chromosomes or synapsis. Each pair is called as a bivalent, they are similar in length and in position of their centromere.
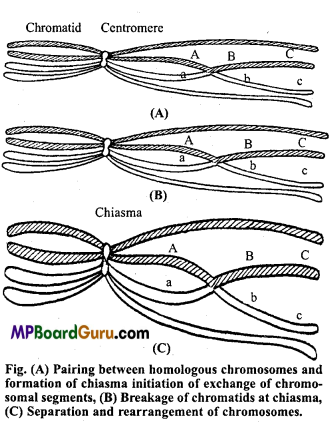
The process of synapsis can take place in many ways. It may start from the ends of homologous chromosomes and proceed towards the centromere or it may start from centromere and proceed towards the ends. It may also begin at one point or many points simultaneously. It is believed that synapsis is initiated by some sort of attraction force.
(iii) Pachytene or Pachynema (Gk., pachus = yolked or thick, nema = thread): At pachytene chromosomes contract longitudinally, resulting in shorter and thicker threads. Each unit is a bivalent or tetrad which is composed of two homologous chromosomes in close longitudinal union and which contains four chromatids. Each chromatid has its own centromere. The chromatids of each homologue is called sister chromatids.
During pachytene two of the homologous chromosome exchange their segments. This process is called as crossing-over. During this process, two non-sister chromatids, one from each bivalent partially coil around each other. Then both chromatids break at contact place and reunite in this way that exchange of chromosomal segments take place. This event is called crossing-over. The points of crossing-over are called chiasmata.
(iv) Diplotene or Diplonema (Gk., diplos = double, nema = thread):
In diplotene, the two chromosomes of each bivalent move away from each other and the chiasmata finally disappear. This event is terminalization of chiasmata. The two homologous chromosomes, thus separate from each other, however not completely because both remain united at the point of interchange or chiasmata.
(v) Diakinesis (Gk., dia = through, kinesis = division or movement):
During this stage the bivalents condense further, i.e., continue shortening and also become more thicker. Homologous chromosomes move apart. The nucleolus and nuclear membrane begin to dis¬appear. In animal cell both the centrioles travel to opposite poles. Astral rays emerge out from the centriole and the structure appear like aster or star and spindle formation starts.
2. Metaphase-I (Gk., meta = between) :
This stage begins with disappearance of nuclear membrane and nucleolus. The bivalents arrange themselves at the equatorial plane in such a way that one chromosome faces one pole of the spindle apparatus and the other one another pole. The spindle fibres get attached to bivalents at the centromere.
3. Anaphase-I (Gk,, ana = up,phasis = stage):
Due to contraction of spindles the two chromosomes of each bivalent separate from each other and move towards opposite poles of the spindle. But the two chromatids of each chromosome still continue to remain jointed with one another with centromere. Thus, only one chromosome of each homologous pair reaches at each pole and the number of chromosomes are reduced to half in daughter nuclei.
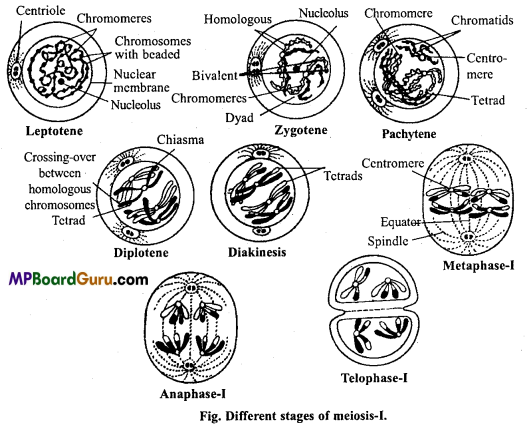
4. Telophase-I (Gk, telo = end,phasis = stage):
As soon as the chromosomes reach the poles decondensation starts and they lose their identity. Nuclear envelope is formed around the daughter nuclei and nucleolus also reappears.
Cytokinesis :
Telophase-I is generally followed by cytokinesis (similar to mitosis) to form two haploid (n) daughter cells.
Interphase:
A short interphase called interkinesis may intervene between meiosis-I and meiosis-II. However, replication of DNA does not take place in this phase. Sometimes the daughter nuclei are not fully constituted in telophase-I. Instead the chromosomes reachng the opposite poles may progress directly to prophase-II.
Meiosis-II division:
It is similar to mitosis and is also known as equational division. It consists of following phases:
1. Prophase-II:
Sister chromatids of each chromosome begin to condense and chromosomes reappear. Nuclear envelope and nucleolus disappear. Spindle fibres begin to disappear.
2. Metaphase-II:
The haploid number of chromosomes become arranged at the equatorial plane of spindle apparatus, each chromosome gets attached to spindle fibre by its centromere.
3. Anaphase-II:
The centromere divides and sister chromatids by the shortening of spindle fibres are pulled apart to their respective poles. Each half chromosome (chromatid) move towards the opposite pole.
4. Telophase-II:
The chromosomes on the respective poles uncoil and form chromatin network again. Nuclear membrane and nucleolus reappear. Finally, at the end of meio- sis-II four haploid nuclei are produced.
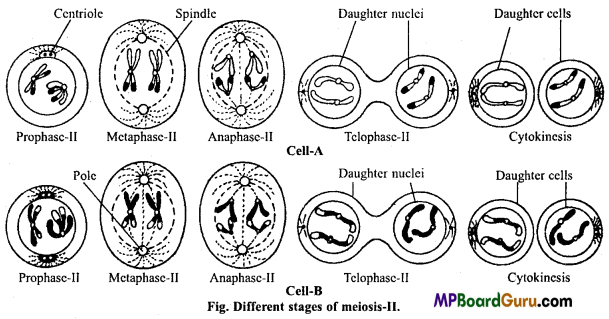
Cytokinesis : It is similar to mitosis, in animal cell by furrow formation and in plant cell by cell plate formation.
This way each daughter cell of meiosis-I produces two haploid daughter cells at the end of meiosis-II. In other words we can say that four haploid cells are formed from a diploid cell by the process of meiosis.
Significance of meiosis :
- It plays an important role in sexual reproduction of both the lower as well as higher organisms. Gametes are produced by this process.
- The process of meiosis helps in the maintenance of chromosome number in the species. Diploid (2n) organisms produce haploid (n) gametes which on fusion form diploid organism again.
![]()
Question 3.
Give necessity and significance of cell cycle and describe the phenomenon occurs in its various stages.
Answer:
Cell cycle :
Complete life cycle of any cell is called as cell cycle. Cell cycle includes various phases of the growth, development and reproduction of the cell. It is a continuous process.
Significance of cell cycle :
The cell, after its formation from pre-existing cell takes sometime to undergo further division. In this ‘resting period’ the cell grows in size, its nuclear materials increases and thus cell get ready for the next division. Hence, cell cycle is a cyclic process from the existence of a new cell to the division of cell. The total duration of a cell cycle constitutes one generation time.
Duration of cell cycle :
The duration of cell cycle varies from 25-30 hours in different cells. In case of E. coli the cell cycle is completed in 20 minutes, in rat 22-25 hours, in root tip of onion 20 hours and in human it is completed in 26 hours.
Stages of cell cycle :
Howard and Pele in 1953 discovered various stages of cell cycle. According to them cell cycle is completed in two phases :
1. Interpbase: Interphase is the interval period between the two successive divisions, when cell does not show any division. But it prepares itself for it by synthesizing new proteins and nucleic acids. In interphase chromosomes are not distinguished, they are in the fonn of chromatin network. This phase is also called as preparatory phase.
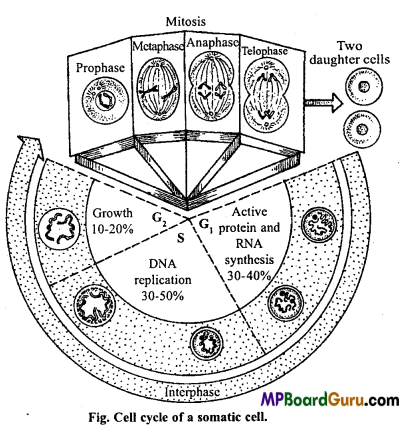
Interphase is divided into following three subphases, i.e., G1, S and G2phase :
(i) Presynthetic or G1– phase : This phase is also known as the period of initial growth as the young daughter cell grow in size during this phase. Synthesis of new proteins and RNA needed for various activities of growing cell also occurs in this phase. G1 -phase in most of the cells lasts for about 10-12 hours. Non-dividing cells remain permanently in this stage. There is no change in the DNA contents of the cell at this stage.
Mitochondria, chloroplast, lysosome, Golgi body, vacuoles, ribosomes, etc. are formed in this phase.
(ii) Synthetic phase or S-phase :
This phase is characterized by the replication of DNA molecules. Thus, each chromosome now carries a duplicate set of genes. Each chro¬mosome is now composed of two sister chromatids held together by a common centromere. The cell thus retains the original diploid (2n) number of chromosomes but it has duplicate set of genes. It lasts for about 6-8 hours.
(iii) Post-synthetic or G2-phase :
In this phase nucleus increases in its size. The synthesis of protein and RNA continues in this phase, r RNA and m RNA required for cell division are synthesized in this phase and the cell prepares itself for the cell division. Mito¬chondria and chloroplasts are duplicated in this phase. Centriole begins to form proteins required for the formation of spindle fibres.
2. Phase of cell division or M-Phase :
In this phase, a cell tends to divide and generating two daughter cells. It is completed in following two stages :
- (i) Karyokinesis : It is the stage of division of nucleus, which is completed in four stages :
- Prophase,
- Metaphase,
- Anaphase and
- Telophase.
- (ii) Cytokinesis : It is the stage of division of cytoplasm to form daughter cells.
Question 4.
Write short note on Karyotype and Idiogram.
Answer:
Karyotype:
We have well studied earlier that each and every eukaryotic organism including plants and animals is characterised by a set of chromosomes which have certain
constant features. The chromosomes of a particular organism or species are identified on the basis of following important features :
- Number of chromosomes,
- Shape and size of chromosomes,
- Position of centromere,
- Length and ratio of two arms of a chromosome, (v) Presence of secondary constriction,
- Size of satellite bodies on chromosomes.
Example : Karyotype of Ginkgo biloba.
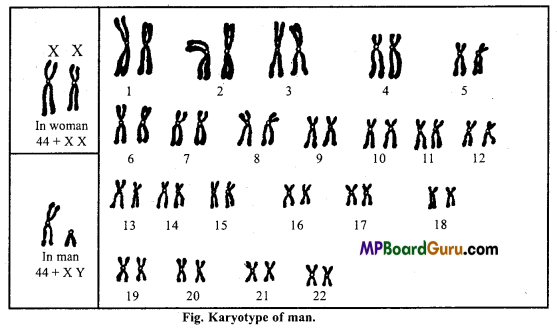
The term karyotype has been proposed for “the group of characteristics that identifies a chromosome set (haploid) of a particular species.” This karyotype is represented by a diagram called idiogram.
Idiogram :
The idiogram of an organism is prepared by arranging the chromosomes of somatic cells in a descending order of size keeping their centromeres in a straight line (Fig.).
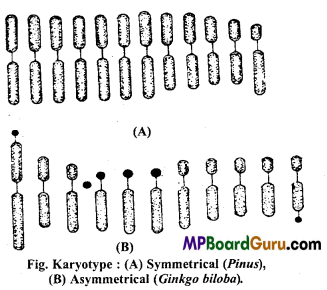
Thus, the longest chromosome is placed on the extreme left and the smallest one on the extreme right. In organisms having sex chromosomes, the sex chromosomes are sometimes placed at the extreme right but more commonly they are placed at their appropriate position according to their size and marked by X and Y. Each chromosome in a karyotype is designated by a serial number according to its position. (44 + XY) (44 + XX).
![]()
Cell Cycle and Cell Division Class 11 Important Questions Objective Type
1. Choose the correct answers:
Question 1.
Chiasmata formation takes place during:
(a) Diplotene
(b) Leptotene
(c) Pachytene
(d) Diakinesis.
Answer:
(c) Pachytene
Question 2.
Duplication of chromosomes takes place during mitosis in:
(a) Early prophase
(b) Late prophase
(c) Interphase
(d) Late telophase.
Answer:
(b) Late prophase
Question 3.
Centromere in the first metaphase of meiosis:
(a) Divide
(b) Do not divide
(c) Divide but do not separated
(d) Are not similar.
Answer:
(c) Divide but do not separated
Question 4.
Spindle fibres are attached with chromosomes at:
(a) Telomere
(b) Chromomere
(c) Centromere
(d) Kinetochore.
Answer:
(c) Centromere
Question 5.
Part of the chromosome where crossing-over takes place is:
(a) Chromomeres
(b) Bivalent
(c) Chiasmata
(d) Centromere.
Answer:
(c) Chiasmata
Question 6.
Number of chromosomes becomes half during:
(a) Prophase-1
(b) Anaphase-I
(c) Metaphase-1
(d) Metaphase-lI.
Answer:
(b) Anaphase-I
Question 7.
Reduction division takes place ¡n:
(a) Pollen grains
(b) Pollen tube
(c) Pollen mother cell
(d) Generative cell.
Answer:
(c) Pollen mother cell
Question 8.
Spindle fibres are formed from :
(a) Protein
(b) Lipid
(c) Cellulose
(d) Pectin.
Answer:
(a) Protein
![]()
Question 9.
Synapsis takes place between :
(a) Similar chromosomes
(b) Two homologous chromosomes
(c) Non-homologous chromosomes
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Two homologous chromosomes
Question 10.
In animals, spindle fibres are formed from :
(a) Centriole
(b) Centromere
(c) Nucleus
(d) Mitochondria.
Answer:
(a) Centriole
Question 11.
Formation of synaptical complex takes place during :
(a) Leptotene
(b) Zygotene
(c) Pachytene
(d) Diplotene.
Answer:
(b) Zygotene
Question 12.
Diploid number of chromosomes in an organism is 8. Then find out the number of chromatids in each daughter cell will be :
(a) 2
(b) 4
(c) 8
(d) 16.
Answer:
(c) 8
Question 13.
Stage of meiosis in which synapsis takes place is :
(a) Leptotene
(b) Pachytene
(c) Zygotene
(d) Metaphase-I.
Answer:
(c) Zygotene
Question 14.
Stage of meiosis in which centromere divide :
(a) Diplotene
(b) Metaphase-I
(c) Pachytene
(d) Anaphase-II
Answer:
(d) Anaphase-II
![]()
Question 15.
During interphase RNA and protein are synthesized :
(a) In S-phase
(b) In G1phase
(c) In G2-phase
(d) Both (b) and (c).
Answer:
(d) Both (b) and (c).
Question 16.
In which stage of meiosis centromere divides :
(a) Early prophase
(b) Early metaphase
(c) Early anaphase
(d) Post anaphase.
Answer:
(d) Post anaphase.
Question 17.
In which stage chromonemata begins to form paired chromosome :
(a) Zygotene
(b) Leptotene
(c) Pachytene
(d) Diplotene.
Answer:
(a) Zygotene
Question 18.
In which type of cell division number of chromosomes reduces :
(a) Meiosis
(b) Mitosis
(c) Amitosis
(d) Cleavage.
Answer:
(a) Meiosis
Question 19.
Which organ of the cell disappear during mitosis cell division :
(a) Plastid
(b) Plasma membrane
(c) Nucleus
(d) None.
Answer:
(c) Nucleus
Question 20.
How many chromosomes are present in a cell of human being after meiosis : (a) 46
(b) 23
(c) 20
(d) 48.
Answer:
(b) 23
Question 21.
Life of multicellular organisms begin from :
(a) Sperm
(b) Egg
(c) Zygote
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) Zygote
Question 22.
Diploid chromosome number in human is :
(a) 23
(b) 46
(c) 92
(D) 48
Answer:
(b) 46
![]()
Question 23.
Synapsis between chromosomes takes place during :
(a) Leptotene
(b) Pachytene
(c) Zygotene
(d) Diakinesis.
Answer:
(c) Zygotene
Question 24.
Stage of mitosis in which centromere divides :
(a) Anaphase
(b) Prophase
(c) Metaphase
(d) Telophase.
Answer:
(a) Anaphase
Question 25.
Which of the following divide during karyokinesis :
(a) Pollen grain
(b) Nucleus
(c) Cell wall
(d) Cytoplasm.
Answer:
(b) Nucleus
2. Fill in the blanks:
1. Somatic cells multiply by ……………….
Answer:
Mitosis
2. Mitosis results in the formation of nuclei having ………………. number of chromosomes.
Answer:
Same (identical)
3. The second division of meiosis can be described as ………………. division.
Answer:
Mitotic
4. The region of attachment of chromosomes to spindle fibres is called ………………….
Answer:
Centromere
![]()
5. The haploid condition is reached by ……………. stage.
Answer:
Anaphase
6. In parent and daughter cell, number of chromosomes are same, thus this type of cell division is called as ………………….
Answer:
Mitosis division
7. Chromosomes arrange themselves during metaphase at the ………………… of the cell.
Answer:
Equator
3. Match the following:
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Pachytene | (a) Mitosis |
| 2. Zygotene | (b) Metaphase |
| 3. Equational division | (c) S-phase |
| 4. Spindle formation | (d) Crossing-over |
| 5. DNA replication | (e) Homologous pairing. |
1. (d) Crossing-over
2. (e) Homologous pairing,
3. (a) Mitosis,
4. (b) Metaphase,
5. (c) S-phase.
4. Write true or false:
1. Interphase is the stage in between Prophase-I and Metaphase-I.
Answer:
False
2. Mitosis is also called as Reductional Division.
Answer:
False
3. Meiosis results in the formation of two haploid cells.
Answer:
False
4. Meiosis takes place in reproductive cells.
Answer:
True
5. During Prophase-I of Meiosis-I, the nuclear membrane and nucleolus disappear in Diakinesis stage.
Answer:
True
![]()
5. Answer in one word:
1. Short Interphase between Meiosis-I and Meiosis-II.
Answer:
Interkinesis
2. Division which takes place in somatic cells.
Answer:
Mitosis
3. The process of interchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatid.
Answer:
Crossing-over
4. The term given to each bivalent containing four chromatids at pachytene stage.
Answer:
Tetrad
5. The name of cell division taking place in reproductive cells.
Answer:
Meiosis