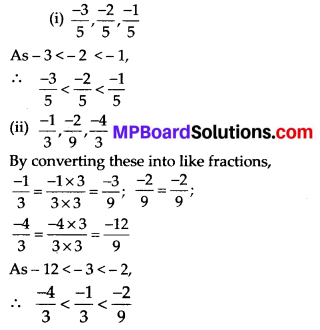
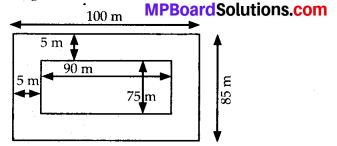
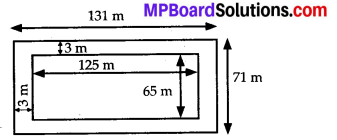
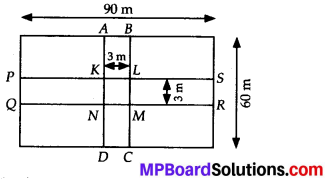
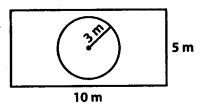
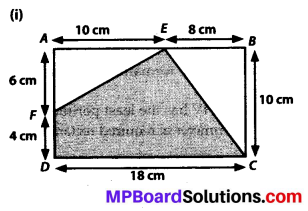
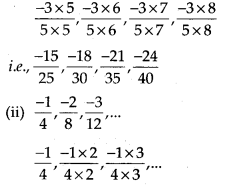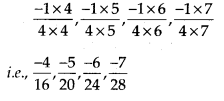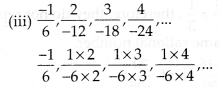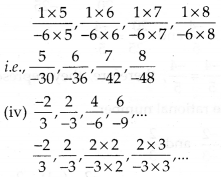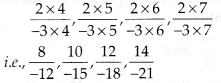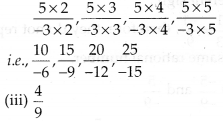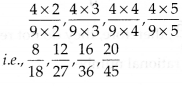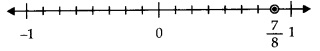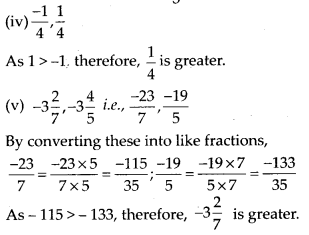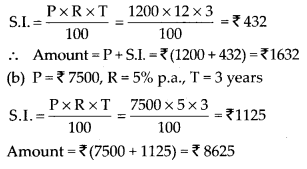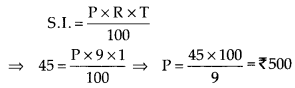MP Board Class 7th Special Hindi पत्र-लेखन
1. अवकाश के लिए प्रार्थना-पत्र
सेवा में,
श्रीमान् प्रधानाध्यापक महोदय,
शासकीय माध्यमिक विद्यालय,
चाँपा खेड़ा,
मन्दसौर (म. प्र.)
श्रीमान जी,
सविनय निवेदन है कि मेरे बड़े भाई का शुभ विवाह 15 अप्रैल, 20… को होना निश्चित हुआ है। भाई के विवाह में जाने के कारण मैं विद्यालय आने में असमर्थ हूँ। अत: मुझे पाँच दिन का अवकाश दिनांक 14.4.20… से 18.4.20… तक देने का कष्ट करें। आपकी बड़ी कृपा होगी।
दिनांक : 13.04.20…
प्रार्थी
सुमित राठी
कक्षा-7
![]()
2. फीस माफी (शुल्क मुक्ति) केलिए प्रार्थना-पत्र
सेवा में,
श्रीमान् प्रधानाध्यापक महोदय,
शासकीय माध्यमिक विद्यालय,
पीपल्या मंडी,
नीमच, (म. प्र.)
श्रीमान् जी,
सविनय निवेदन है कि मैं आपके विद्यालय की कक्षा 7 का छात्र हूँ। मेरी पढ़ने में अत्यधिक रुचि है और अपनी कक्षा का मॉनीटर भी हूँ। मेरे पिता एक दफ्तर में चतुर्थी श्रेणी के कर्मचारी हैं। घर में पिताजी-माताजी सहित छः सदस्य हैं। सभी भाई-बहन आपके विद्यालय में ही शिक्षा प्राप्त कर रहे हैं। फीस देने में असमर्थ होने के कारण मुझे शुल्क से पूर्ण मुक्ति देने की कृपा करें।
दिनांक : 13.07.20…
विनीत
सावन कुमार
कक्षा-7
![]()
3. पत्र मित्र को (समाचार-पत्र का महत्व बताते हुए)
अहिल्याबाई हॉस्टल
माध्यमिक विद्यालय
हवाई अड्डा मार्ग, इसौर
दिनांक : 15.03.20…
प्रिय मित्र मोहन,
सप्रेम नमस्ते।
मैं अपने सहपाठियों सहित हॉस्टल में कुशल हूँ। आशा | करता हूँ कि तुम भी सकुशल होंगे। अपनी पढ़ाई ठीक तरह कर रहे होंगे। मैंने अपने विद्यालय में होने वाली सामान्य ज्ञान परीक्षा दी। उसमें मैंने सबसे अच्छे अंक प्राप्त किए। इसका कारण था, मेरी वह आदत जिससे में प्रतिदिन समाचार-पत्र पढ़ता हूँ और एकत्रित सूचनाओं के आधार पर ही मैंने परीक्षा दी। मैं तुम्हें समाचार-पत्र पढ़ने के महत्व को बताता हूँ।
समाचार-पत्र पढ़ने से हमें सामाजिक, राजनैतिक, आर्थिक और धार्मिक जीवन के प्रत्येक पहलू से सम्बन्धित जानकारी – मिलती है। विज्ञान के आविष्कारों की जानकारी व लाभों से – अवगत होते हैं। भाषा-साहित्य का प्रचार और प्रसार भी इन्हीं से होता है। दूसरों के दृष्टिकोण की भी जानकारी मिलती है।
व्यापारियों के विज्ञापन भी आते हैं जिससे वस्तुओं की कीमतें आदि की भी जानकारी मिलती है। राष्ट्रीय जागरण व चेतना जगाने में समाचार-पत्रों का बड़ा महत्व है। शासन-प्रशासन की बुराइयों और भलाइयों को भी नागरिकों तक पहुँचाते हैं। सरकार के द्वारा बनाये गये कानून भी समाचार-पत्रों द्वारा जनता में प्रसारित होते हैं। इनसे ही जनता की राय भी जानी जाती है।
इस तरह समाचार-पत्रों का प्रतिदिन पढ़ना एक अच्छे छात्र के लिए बहुत ही लाभकारी है। अतः मैं तुम्हें इस पत्र के द्वारा – यह बताना चाहता हूँ कि तुम अवश्य ही प्रतिदिन समाचार-पत्र पढ़ा करो। इति
तुम्हारा मित्र
रवीन्द्र सहाय
कक्षा-7
![]()
4. जन्मदिन पर बधाई पत्र (मित्र को)
दौलतगंज,
भोपाल (म. प्र.)
दिनांक : 21.06.20…
प्रिय मित्र प्रवीण शर्मा,
जय हिन्द
आज तुम्हारी 13वीं वर्षगाँठ है। इसके लिए मैं तुम्हें बधाई देता हूँ। तुम दीर्घायु हो, स्वस्थ रहो, ऐसी मेरी कामना है। उपहार के रूप में, तुम्हारे लिए अपने छोटे भाई के द्वारा मिठाई और फल भेज रहा हूँ। स्वीकार करें।
तुम्हारी स्नेही
राकेश मोहन
![]()
5. निमंत्रण-पत्र (प्रीतिभोज हेतु)
प्रिय बन्धु अजय गोपाल,
सादर नमस्ते।
आपको यह जानकर बड़ी प्रसन्नता होगी कि मेरे छोटे भाई का विवाह 10 जून, 20… को सम्पन्न हो रहा है। इस उपलक्ष्य में प्रतिभोज का आयोजन 12 जून, 20… को होगा। प्रीतिभोज का समय 5 बजे सायंकाल है।
अत: निवेदन है कि इस शुभ अवसर पर आप अपने माता-पिता सहित पधार कर आयोजन को सफल बनायें।
दिनांक : 06.06.20…
भवदीय
भुवन प्रकाश मंडी
रामदास, इन्दौर
![]()
6. अवकाश के लिए प्रार्थना-पत्र (मलेरिया से पीड़ित होने पर)
सेवा में,
श्रीमान् प्रधानाध्यापक महोदय,
शासकीय माध्यमिक विद्यालय,
चौपा खेड़ा,
मन्दसौर (म. प्र.)
श्रीमान् जी,
सविनय निवेदन है कि मैं आपके विद्यालय की कक्षा-7 का छात्र हूँ। कल सायंकाल से मुझे ज्वर आ रहा है। सारी रात बेचैन रहा। प्रातः होने पर मैंने वैद्य जी से परामर्श कराया। उन्होंने मेरी नाड़ी जाँच की तो वे इस निष्कर्ष पर पहुँचे कि मैं मलेरिया से पीड़ित हूँ। उनका इलाज निरन्तर जारी है। अत: मैं विद्यालय आकर कक्षा में उपस्थित होने में असमर्थ हूँ। कृपया मुझे दिनांक 12.04.20… से 14.04.20… का अवकाश देने का कष्ट करें। ठीक होने पर वैद्य जी का चिकित्सा प्रमाण-पत्र प्रस्तुत कर दूंगा। पढ़ाई की हानि की भी पूर्ति सहपाठियों से सहायता लेकर कर लूँगा। यह मैं आपको विश्वास दिलाता हूँ।
दिनांक : 13.04.20…
प्रार्थी
स्वतन्त्र कुमार
कक्षा-7