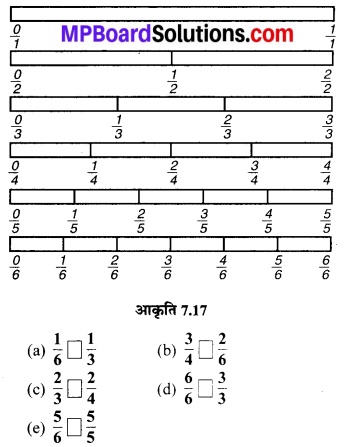
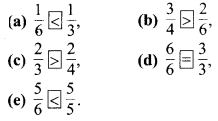
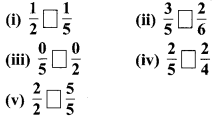
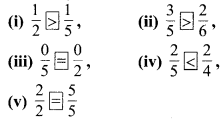
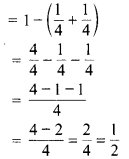
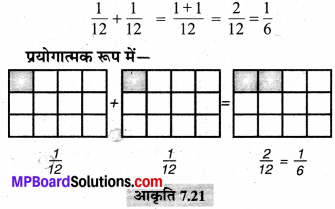
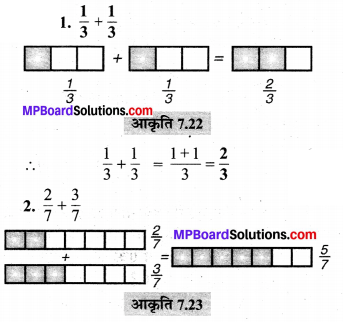
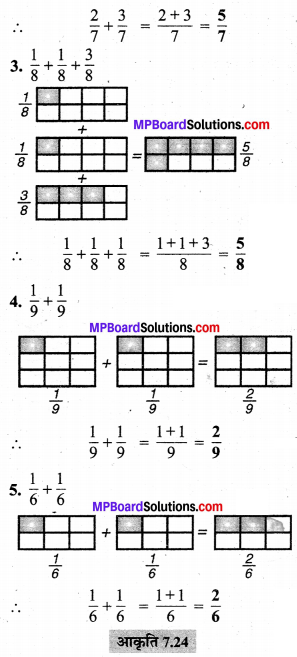
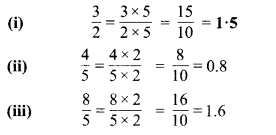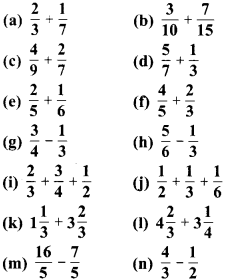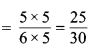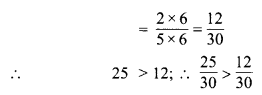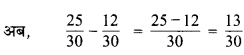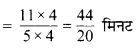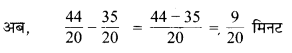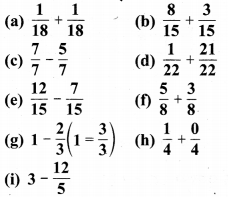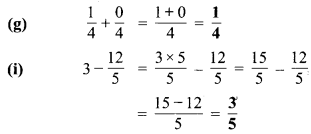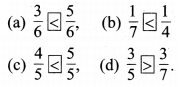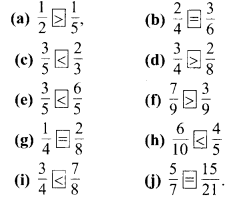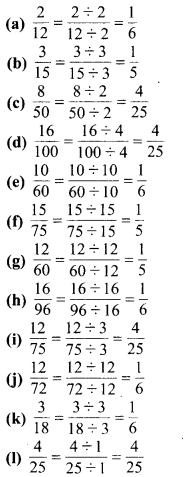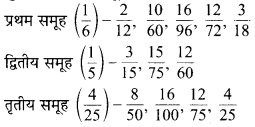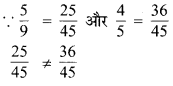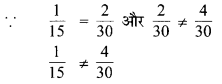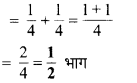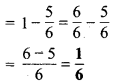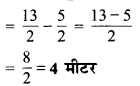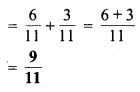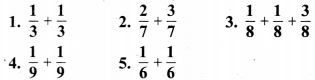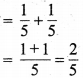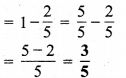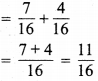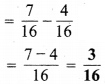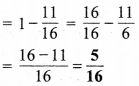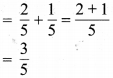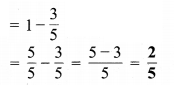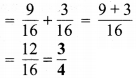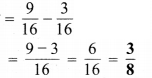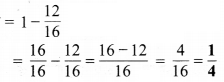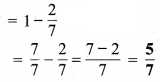MP Board Class 6th Maths Solutions Chapter 8 दशमलव Ex 8.1
पाठ्य-पुस्तक पृष्ठ संख्या # 181-183
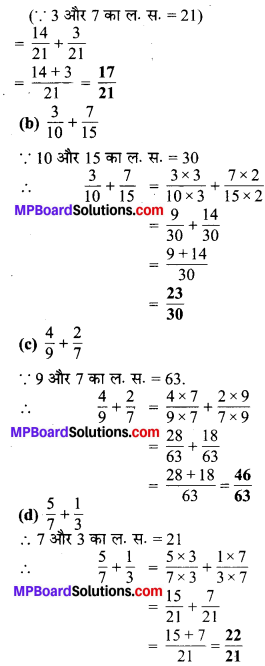
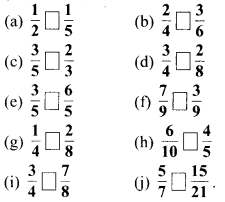
प्रश्न 1.
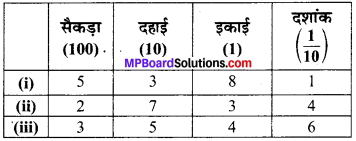
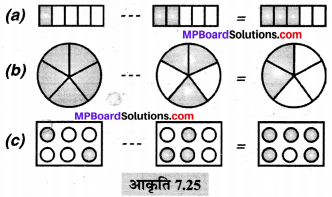
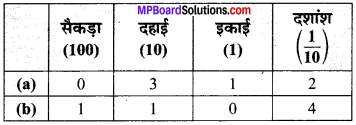
पाठ्य-पुस्तक में दिये गये चित्रों के लिए दी गई सारणी में संख्याएँ लिखिए
हल :
(a) पाठ्य-पुस्तक में 3 टॉवर हैं प्रत्येक में 10 इकाई हैं, 4 ब्लॉक हैं (1 इकाई) और 2 छोटे भाग (प्रत्येक दशांश के बराबर है)।
(b) पाठ्य-पुस्तक में 1 सैकड़ा, 1 दहाई, 0 इकाई और 4 दशांश हैं।
सारणी –
प्रश्न 2.
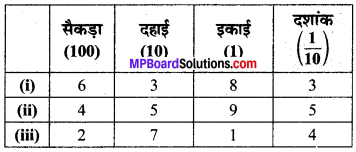
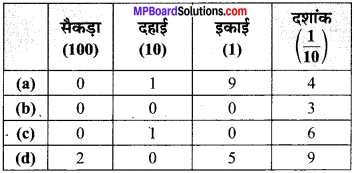
निम्न दशमलव संख्याओं को स्थानीय मान सारणी में लिखिए
(a) 19.4
(b) 0.3
(c) 10.6
(d) 205.9
हल:
प्रश्न 3.
निम्न में से प्रत्येक को दशमलव रूप में लिखिए
(a) 7 दशांश
(b) 2 दहाई, 9 दशांश
(c) चौदह दशमलव छः
(d) एक सौ और 2 इकाई
(e) छः सौ दशमलव आठ।
हल :
(a) 7 दशांश = 7 x \(\frac { 1 }{ 10 }\) = 0.7
(b) 2 दहाई, 9 दशांश = 2 x 10 + 9 x \(\frac { 1 }{ 10 }\)
= 20 + \(\frac { 9 }{ 10 }\)
= 20 + 0.9
= 20.9
(c) चौदह दशमलव छः = 14.6
(d)एक सौ और 2 इकाई = 1 सौ + 0 दहाई + 2 इकाई + 0 दशांश
= 100 + 0 + 2 + 0.0
= 102.0
(e) छः सौ दशमलव आठ = 600.8
![]()
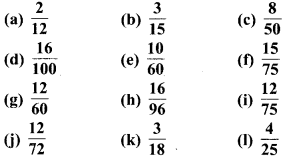
प्रश्न 4.
निम्न को दशमलव रूप में व्यक्त कीजिए
![]()
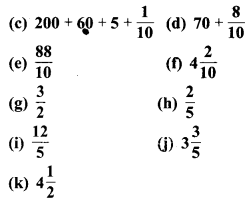
हल :
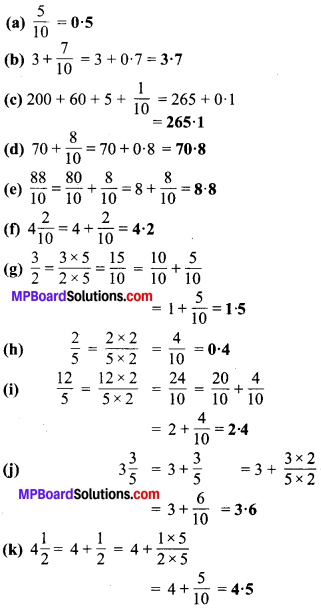
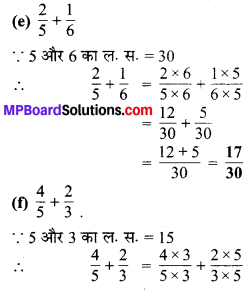
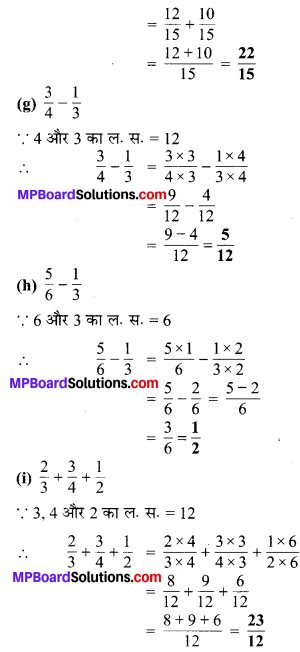
प्रश्न 5.
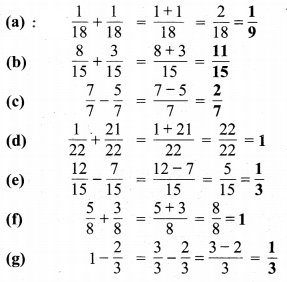
निम्न दशमलव संख्याओं को भिन्न के रूप में लिखकर न्यूनतम (सरलतम) रूप में बदलिए
(a) 0.6
(b) 2.5
(c) 1.0
(d) 3.8
(e) 13.7
(f) 21.2
(g) 6.4
हल :
(a) भिन्न = 0.6 = \(\frac { 6 }{ 10 }\)
सरलतम रूप = \(\frac{6 \div 2}{10 \div 2}=\frac{3}{5}\)
(b) भिन्न 2.5 = \(\frac { 25 }{ 10 }\)
सरलतम रूप = \(\frac{25 \div 5}{10 \div 5}=\frac{5}{2}\)
(c) भिन्न 1.0 = \(\frac { 10 }{ 10 }\) = 1
सरलतम रुप = \(\frac{10 \div 10}{10 \div 10}=\frac{1}{1}=1\)
(d) भिन्न = 3.8 = \(\frac { 38 }{ 10 }\)
सरलतम रूप = \(\frac{38 \div 2}{10 \div 2}=\frac{19}{5}\)
(e) भिन्न = 13.7 = \(\frac { 137 }{ 10 }\)
सरलतम रूप = \(\frac { 137 }{ 10 }\)
(f) भिन्न = 21.2 = \(\frac { 212 }{ 10 }\)
सरलतम रूप = \(\frac{212 \div 2}{10 \div 2}=\frac{106}{5}\)
(g) भिन्न = 6.4 = \(\frac { 64 }{ 10 }\)
सरलतम रूप = \(\frac{64 \div 2}{10 \div 2}=\frac{32}{5}\)
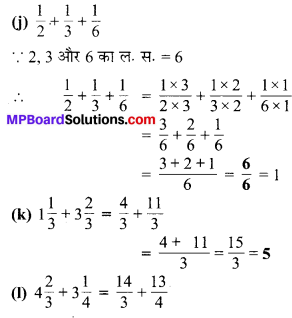
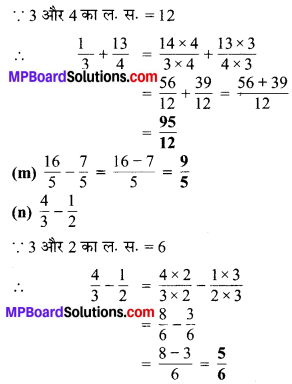
प्रश्न 6.
सेमी का प्रयोग कर निम्न को दशमलव रूप में बदलिए
(a) 2 मिमी
(b) 30 मिमी
(c) 116 मिमी
(d) 4 सेमी 2 मिमी
(e) 11 सेमी 52 मिमी
(f) 83 मिमी
हल :
(a) 2 मिमी = \(\frac { 2 }{ 10 }\) सेमी = 0.2 सेमी
(b) 30 मिमी = \(\frac { 30 }{ 10 }\) सेमी = 3.0 सेमी
(c) 116 मिमी = \(\frac { 116 }{ 10 }\) सेमी = 11.6 सेमी
(d) 4 सेमी 2 मिमी = 4 सेमी + \(\frac { 2 }{ 10 }\) सेमी
= 4 सेमी + 0.2 सेमी
= 4.2 सेमी
(e) 11 सेमी 52 मिमी = 11 सेमी + \(\frac { 52 }{ 10 }\) सेमी
= 11 सेमी + 5.2 सेमी
= 16.2 सेमी
(f) 83 मिमी = \(\frac { 80 }{ 10 }\) सेमी + \(\frac { 3 }{ 10 }\) सेमी
= 8 सेमी + 0.3 सेमी
= 8.3 सेमी
![]()
प्रश्न 7.
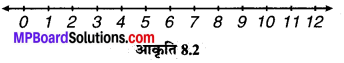
संख्या रेखा पर किन दो पूर्ण संख्याओं के बीच निम्न संख्याएँ स्थित हैं ? इनमें से कौन-सी पूर्ण संख्या दी हुई दशमलव संख्या के अधिक निकट है ?
(a) 0.8
(b) 5.1
(c) 2.6
(d) 6.4
(e) 9.0
(f) 4.9
हल :
(a) 0.8 संख्या 0 और 1 के बीच में स्थित है और 1, 0.8 के अधिक निकट है।
(b) 5.1 संख्या 5 और 6 के बीच में स्थित है और 5, 5.1 के अधिक निकट है।
(c) 2.6 संख्या 2 और 3 के बीच में स्थित है और 3, 2.6 के अधिक निकट है।
(d) 6.4 संख्या 6 और 7 के बीच में स्थित है और 6, 6.4 के अधिक निकट है।
(e) 9.0 स्वयं 9 पूर्ण संख्या है।
(f) 4.9 संख्या 4 और 5 के बीच में स्थित है और 5, – 4.9 के अधिक निकट है।
प्रश्न 8.
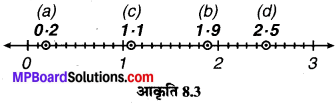
निम्न को संख्या रेखा पर दर्शाओ
(a) 0.2
(b) 1.9
(c) 1.1
(d) 2.5
हल :
संख्या रेखा
प्रश्न 9.
दी हुई संख्या रेखा स्थित A, B, C, D बिन्दुओं के लिए दशमलव संख्या लिखिए

हल :
A → 0.8,
B → 1.3,
C → 2.2,
D → 2.9.
प्रश्न 10.
(a) रमेश की कॉपी की लम्बाई 9 सेमी 5 मिमी है। सेमी में इसकी लम्बाई क्या होगी?
(b) चने के एक छोटे पौधे की लम्बाई 65 मिमी है। इसकी लम्बाई सेमी में व्यक्त कीजिए।
हल :
(a) रमेश की कॉपी की लम्बाई
= 9 सेमी 5 मिमी
= 9 सेमी + \(\frac { 5 }{ 10 }\) सेमी
= 9 सेमी + 0.5 सेमी
= 9.5 सेमी
अतः रमेश की कॉपी की लम्बाई = 9.5 सेमी
(b) चने के पौधे की लम्बाई = 65 मिमी = \(\frac { 65 }{ 10 }\) सेमी
= \(\frac { 60 }{ 10 }\) सेमी + \(\frac { 5 }{ 10 }\) सेमी
= 6.5 सेमी
अतः चने के पौधे की लम्बाई = 6.5 सेमी।
![]()
पाठ्य-पुस्तक पृष्ठ संख्या # 183
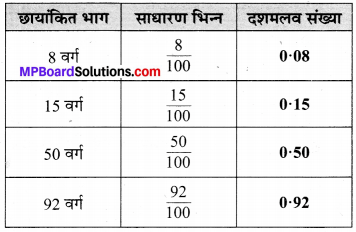
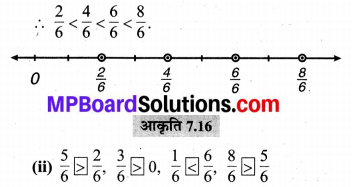
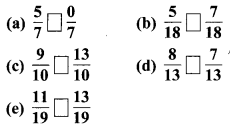
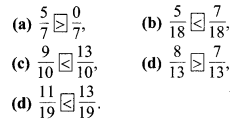
प्रश्न 1.
पाठ्य-पुस्तक में पृष्ठ संख्या 184 पर दी गई आकृतियों में यदि हम बड़े वर्ग के 8 वर्ग छायांकित करें, 15 वर्ग छायांकित करें, 50 वर्ग छायांकित करें, 92 वर्ग छायांकित करें तो वह पूरे वर्ग का कौन-सा भाग होगा ?
हल :