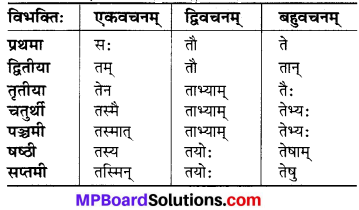
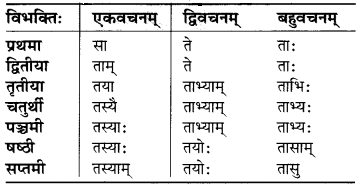
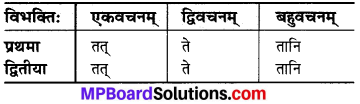
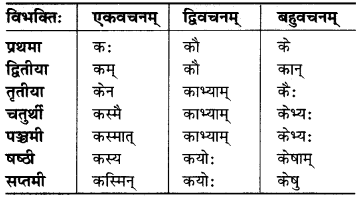
MP Board Class 6th Science Solutions Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits
Electricity and Circuits Textbook Exercises
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks:
- A device that is used to break an electric circuit is called ……………… terminals.
- An electric cell has ……………… terminals.
Answer:
- Switch
- Two.
![]()
Question 2.
Mark ‘True’ or ‘False’ for following statements:
- Electric current can flow through metals.
- Instead of metal wires, a jute string can be used to make a circuit.
- Electric current can pass through a sheet of thermo Col.
Answer:
- True
- False
- False.
Question 3.
Explain why the bulb would not glow in the arrangement show in Fig?
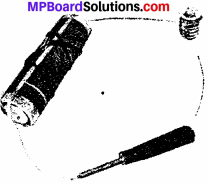
Answer:
The bulb will not glow because the circuit is not completed due to the presence of an insulator between the circuit. Here insulator is screw driver.
Question 4.
Complete the drawing shown in figure to indicate where the free ends of the two wires should be joined to make the bulb glow.
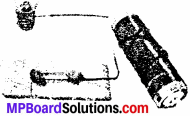
Answer:
The complete diagram in shown below:

Question 5.
What is the purpose of using an electric switch? Name some electrical gadgets that have switches built into them.
Answer:
An electric switch is used to open or close the circuit. Electric gadgets that have switches built into them are freezer, washing machines, microwaves, toaster, heaters, electric – bulb, tube – light, electric iron, etc.
![]()
Question 6.
Would the bulb glow after completing the circuit shown in Figure of Question 4 above if instead of safety pin we use an eraser?
Answer:
No.
Question 7.
Would the bulb glow in the circuit shown in Fig.

Answer:
No, because both of the terminal of battery is connecting with one terminal of bulb.
Question 8.
Using the “conduction tester” on an object it was found that the bulb begins to glow. Is that object a conductor or an insulator? Explain.
Answer:
That object is a conductor because electricity can pass through a conductor and not through an insulator. If the object is an insulator then bulb could not glow.
![]()
Question 9.
Why should an electrician use rubber gloves while repairing an electric switch at your home? Explain.
Answer:
An electrician use rubber gloves while repairing an electric switch because rubber is a bad conductor of electricity or in other words rubber is an insulator.
Question 10.
The handles of the tools like screwdrivers and pliers used by electricians for repair work usually have plastic or rubber covers on them. Can you explain why?
Answer:
Because plastic and rubber, both are the bad conductor of electricity. Hence, they protect electricians against electric shock.
Projects and Activities
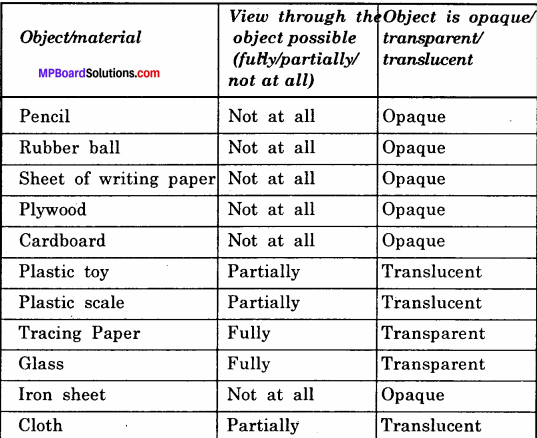
Activity 1.
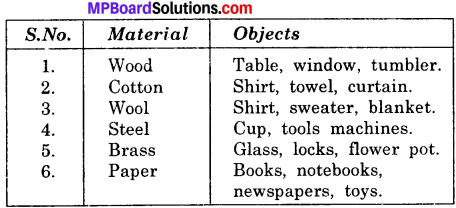
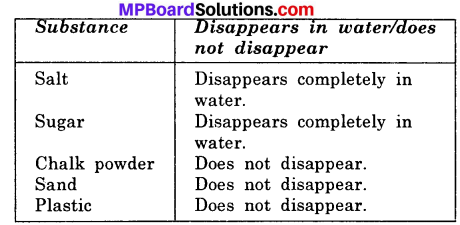
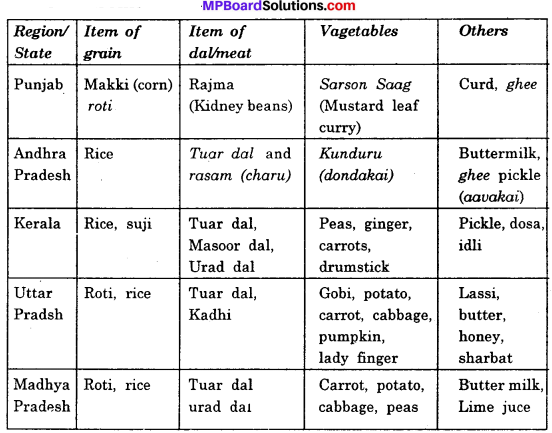
Make a table to show different materials allows current to pass through it or not.
Answer:
Conductors and Insulators:
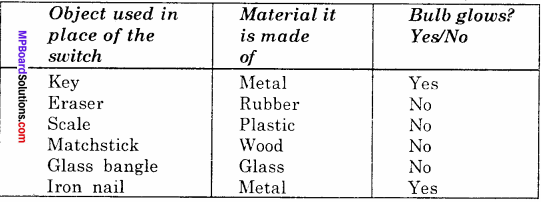
Activity 2.
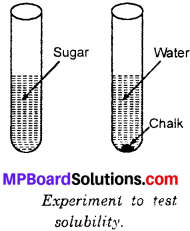
Describe a simple experiment to test whether a given material is a conductor or an insulator.
Answer:
To identify given material is a conductor or an insulator.
Requirements:
Pencil, matchstick, alpin, rubber tube, cell wire, bulb.
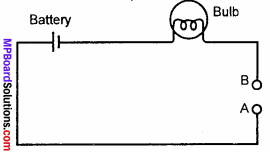
Procedure:
Take a small bulb, a battery and a length of wire and connect them in a circuit as show in figure. This circuit is not closed and no current will pass through it. Close the gap between the points A and B by inserting the graphite of your pencil between them. Repeat this by successively replacing the graphite by rubber tube, alpin and matchstick. Record the observations in the table given below.
Table

Electricity and Circuits Additional Important Questions
Electricity and Circuits Objective Type Questions
Question 1.
Choose the correct answer:
Question (i)
S.I. unit of electic current is –
(a) Farad
(b) Volt
(c) Ampere
(d) Coulomb.
Answer:
(c) Ampere
Question (ii)
The types of charges are –
(a) Two
(b) Three
(c) Four
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) Two
Question (iii)
Voltaic cell was invented by –
(a) Alessandro Volta
(b) J. F. Volta
(c) Georges Leclanche
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) Alessandro Volta
![]()
Question (iv)
The principle of a voltaic cell was used by –
(a) J. F. Daniel
(b) Alessandro Volta
(c) Georges Leclanche
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) J. F. Daniel
Question (v)
The primary cells are –
(a) Voltaic cell
(b) Daniel cell
(c) Dry cell
(d) All of these.
Answer:
(d) All of these.
Question (vi)
Electric current is the flow of particles with –
(a) A negative charge
(b) A positive charge
(c) Both positive and negative charges flowing opposite to each other.
(d) Either positive or negative charge depending on the material.
Answer:
(a) A negative charge
Question (vii)
The conductors of electricity are –
(a) mica
(6) wood
(c) glass
(d) none of these.
Answer:
(d) none of these.
![]()
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks:
- Flow of ………….. through a conductor, when a potential difference is applied across its terminals, is called electric current.
- The actual direction of current flowing through a circuit is from negative to positive electrode, whereas the …………….. direction is from negative to positive.
- S.I. unit of electric current is ……………..
- …………….. is used to measure current flowing through a conductor and voltmeter is used to measure ……………. difference across the ends of a conductor.
- The bulb with broken filament is called a …………… bulb.
- The thin tiny wire inside the glass cover in a bulb is called ……………….
- The bulb does not glow when the ……………. is open.
Answer:
- Free electrons
- Conventional
- Ampere,
- Ammeter, potential difference
- Fused
- Filament
- Switch.
Question 3.
Which of the following statements are true (T) or false (F):
- Materials which do not allow an electric current to flow through them are called conductors.
- In an electric press which effect of electric current used is heating effect.
- Rate of flow of charge is called electric current.
- Electric cell converts chemical energy to mechanical energy.
- Voltaic cell was invented by Volta.
- Dry cell is portable.
- An electric cell cannot to be used in a wrist watch.
Answer:
- False
- True
- True
- False
- True,
- True
- False.
Electricity and Circuits Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are the essential components of an electric circuit?
Answer:
The essential components of an electric circuit are battery or cell, conductor and a key.
Question 2.
What is an electric circuit?
Answer:
The path of an electric current is referred to as electric circuit.
Question 3.
Can we see electricity?
Answer:
No, we cannot see electricity but can observe its effects.
![]()
Question 4.
Name two sources of electric current?
Answer:
The two sources of electric current are Voltaic cell and Daniel cell.
Question 5.
What is a conductor? Give two examples.
Answer:
Substances, such as metals, that can conduct electric current are called conductors. For examples, Copper, Aluminium.
Question 6.
What is an insulator? Give three examples.
Answer:
The materials that do not allow current to pass through them are called insulators. For examples, Mica, Wood and Rubber.
Question 7.
Make a list of materials around you which conduct electricity and a list of those that do not.
Answer:
Conductors of electricity are:
All metals, acid base and salt solutions, aluminium, iron, copper and nickel.
Do not conduct electricity are:
Paper, rubber, wool, nylon, polythene and backelite.
Question 8.
Who supplies electricity to tourch bulb?
Answer:
Electric cell supplies electricity to torch bulb.
Question 9.
What are the ready sources of electric current?
Answer:
The ready sources of electric current are dry cell and battery. Every dry cell and battery had got two terminals or connection points marked (+) and (-).
Question 10.
Which scientist made earliest attempts to obtain an electric current?
Answer:
The earliest attempts to obtain electric current was made in the year 1790 by Alessandro Volta an Italian scientist.
![]()
Question 11.
What is a fused bulb?
Answer:
When the filament is broken in a bulb, it is called the fused bulb.
Question 12.
Define an open circuit?
Answer:
When there is a gap between two terminals, it is called an open circuit.
Question 13.
Define a closed circuit?
Answer:
A circuit where there is no gap between two terminals is called a closed circuit.
Question 14.
Draw symbol of (i) a cell, (ii) battery and (iii) a key.
Answer:
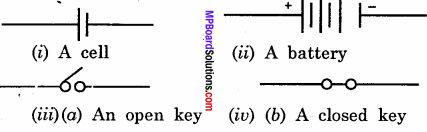
Question 15.
Name two insulators?
Answer:
Plastics and rubber.
Question 16.
Who discovered the dry cell?
Answer:
Georges Leclanche discovered the dry cell.
![]()
Question 17.
What is meant by battery?
Answer:
The positive terminal of one cell is kept in contact with the negative terminal of the other cell. When two or more then two cells are joined together in this way, we get a battery.
Question 18.
What energy is converted to electrical energy in an electric cell?
Answer:
The chemicals in a cell produce chemical energy. This chemical energy is converted to electrical energy in a cell.
Question 19.
What are the uses of storage batteries?
Answer:
Storage batteries are used where electric current is needed for longer time of more voltage. For examples, in cars, trucks, buses. It is also used in submarines, radars and satellites.
![]()
Question 20.
Give some uses of dry cells?
Answer:
Uses of dry cells. In radio, transistor, tourches, remote, camera and calculator.
Question 21.
What is filament of a bulb?
Answer:
The thin wire that gives off light is called the filament of the bulb.
Electricity and Circuits Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is current?
Answer:
The rate of flow of electric charge through a conductor per unit time is called electric current. In other words, we can say that the amount of electric current is the ratio of charge flowing through a conductor to the time taken in the flowing of the charge.
Question 2.
List the appliances around you that depend on electricity for their operation. List the appliances that do not use electrical energy?
Answer:
Appliances that depend on electricity are:
Electric press, geyser, washing machine, television, radio, fan, cooler etc.
Appliances that do not depend on electricity are:
Cooking gas, stove, solar cooker, sewing machine, cycle, rickshaw, etc.
![]()
Question 3.
We selectively choose certain materials to make a path and reject others. Why?
Answer:
Some materials do not allow an electric current to pass through them. Such materials are called insulators. Materials which allow electric current to pass through them are called conductors.
Question 4.
What happens when a charged electroscope is connected to a uncharged electroscope by a wire? What is that called?
Answer:
When a charged electroscope is joined to an uncharged electroscope by a wire, charges flow from the charged to the uncharged electroscope through the wire till they are equalised. This flow of charges forms an electric current. It is measured in ampere.
Question 5.
What is the nature of electric current?
Answer:
As water flows from higher level to lower level in a pipe, electric current also flows from the source of electric current to the target where it is needed through metal wires.
Question 6.
Define an electric switch?
Answer:
A switch is a simple device that either breaks the circuit or completes it. When the switch is open, the circuit is not complete and the current does not flow. In the other position, when the switch is closed, the circuit is complete and current can flow through the circuit.
![]()
Question 7.
On what principle scientist Volta made his cell?
Answer:
The principle was that when two strips of different metals are dipped in an acid solution an electric current begins to flow through them. Such a simple source of current, or a cell is called as a voltaic cell in honour of its inventor.
Question 8.
What are the draw backs in voltaic cell? Who then improved the design?
Answer:
Voltaic cell is not a good source of current as the flow through the wire in such a cell is not smooth and steady. J. F. Daniel (1790 – 1845) made an improved design of voltaic cell in the year 1836.
Electricity and Circuits Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain an electric cell with suitable diagram and their construction.
Answer:
Electricity to the bulb in a torch is provided by the electric cells. Electric cells are also used in alarm clocks, wristwatches, transistor, radios, cameras and many other devices. In an electric cell their is a small metal cap on one side and a metal disc on the other side. The metal cap is the positive terminal of the electric cell while the metal disc is the negative terminal.

All electric cells have two terminals one positive and another negative terminal. An electric cell produces electricity from the chemical stored inside it. When the chemicals in the electric cell are used up, the electric cell stops producing electricity. The electric cell then has to be replaced with a new one.
![]()
Question 2.
What is meant by an electric circuit?
Answer:
When we connect the two ends of a cell to a bulb using copper wires, the bulb lights up. This is because we have provided a path for electrons to flow the negative terminal of the battery to the positive terminal through a bulb. Such a path of an electric current is known as a electric circuit.
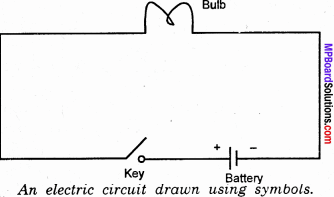
Question 3.
Find the various ways in which two batteries and two bulbs can be connected in a working circuit.
Answer:
Two batteries and two bulbs can be connected in working circuit in two ways.
1. In series as shown in figure.
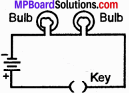
2. In parallel as shown in figure.
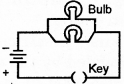
Question 4.
Draw a diagram of a torch bulb?
Answer:
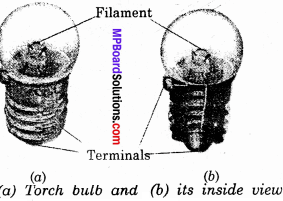
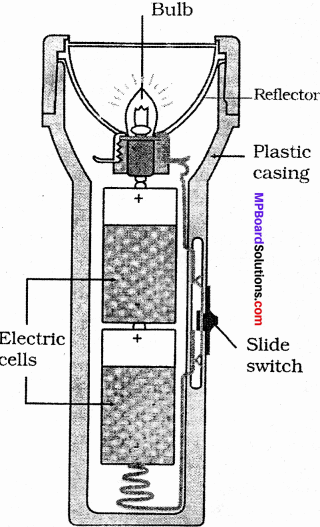
Question 5.
Draw a neat diagram to show the inside view of a torch?
Answer: