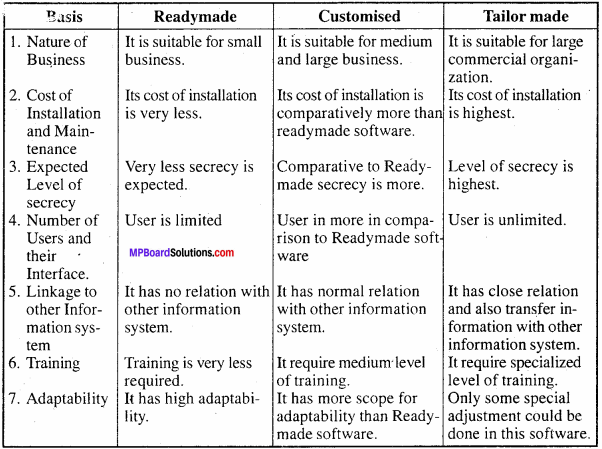
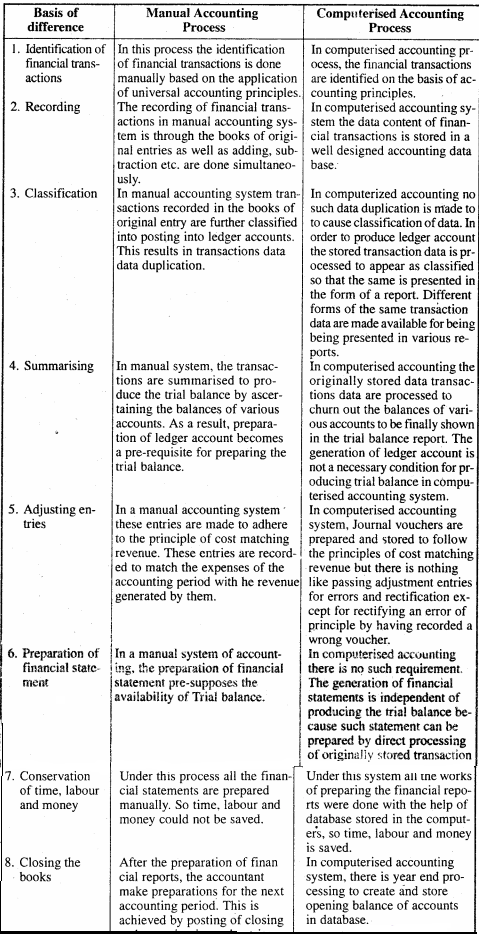
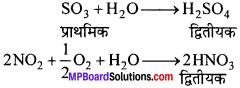
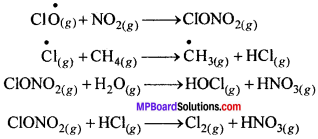
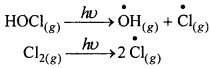MP Board Class 11th Physics Solutions Chapter 1 भौतिक जगत
भौतिक जगत अभ्यास के प्रश्न एवं उनके उत्तर
प्रश्न 1.1.
विज्ञान की प्रकृति से संबंधित कुछ अत्यंत पारंगत प्रकथन आज तक के महानतम वैज्ञानिकों में से एक अल्बर्ट आइंस्टाइन द्वारा प्रदान किए गए हैं। आपके विचार से आइंस्टाइन का उस समय क्या तात्पर्य था, जब उन्होंने कहा था “संसार के बारे में सबसे अधिक अबोधगम्य विषय यह है कि यह बोधगम्य है?
उत्तर:
ब्रह्माण्ड अत्यन्त जटिल है एवं इसमें होने वाली घटनाएँ भी बहुत जटिल हैं लेकिन विज्ञान के अनेक नियम ऐसे हैं जो इन सभी घटनाओं की व्याख्या पूर्णत: करते हैं। अतः जब प्रथम बार कोई घटना देखते या सुनते हैं तब वह अबोधगम्य होती है लेकिन जब हम उस घटना से जुड़े सिद्धान्त नियम इत्यादि का गहन विश्लेषण करते हैं तो वह घटना हमारे लिए बोधगम्य हो जाती है। इस प्रकार भौतिक जगत से जुड़े प्रत्येक तथ्य की सुस्पष्ट व्याख्या विज्ञान विषय में उपलब्ध है। जब कभी भी हम किसी तथ्य से जुड़े वैज्ञानिक दृष्टिकोण को जानना चाहते हैं तो हम उसे जान लेते हैं। इसी कारण जटिलतम परिघटना भी हमारे लिए आश्चर्यजनक नहीं होती है। इस प्रकार हम कह सकते हैं कि आइंसटाइन का कथन तर्क संगत है।
प्रश्न 1.2.
“प्रत्येक महान भौतिक सिद्धान्त अपसिद्धांत से आरंभ होकर धर्मसिद्धांत के रूप में समाप्त होता है”। इस तीक्ष्ण टिप्पणी की वैधता के लिए विज्ञान के इतिहास से कुछ उदाहरण लिखिए।
उत्तर:
अपसिद्धान्त ऐसे तथ्य हैं जो स्थापित नहीं होते हैं जबकि धर्म सिद्धान्त से अर्थ स्थापित विचार हैं जिन पर सामान्यत: कोई प्रश्न नहीं उठता है। जैसे – प्रकाश – वैद्युत नियम प्रारम्भ में एक अपसिद्धान्त के रूप में आया था लेकिन अन्तत: यह एक धर्म सिद्धान्त के रूप में परिवर्तित हो गया था।
प्रश्न 1.3.
“संभव की कला ही राजनीति है”। इसी प्रकार “समाधान की कला ही विज्ञान है”। विज्ञान की प्रकृति तथा व्यवहार पर इस सुन्दर सूक्ति की व्याख्या कीजिए।
उत्तर:
सभी राजनीतिज्ञ, चाहे वे दुनिया के किसी भी भाग से सम्बन्धित हों, हमेशा कुछ भी कहने को तैयार रहते हैं। राजनीतिज्ञों के अनुसार, प्रत्येक कार्य, घटना इत्यादि सभी कुछ सम्भव है एवम् इसके पीछे जो कारण है वह सिर्फ उनके शब्दों का जाल होता है। इसी कला से वे जनता में अपनी प्रसिद्धि प्राप्त करते हैं। अर्थात् राजनीति सम्भव की कला है। जो कार्य किसी भी तरह होना सम्भव न हो उसे भी राजनीतिज्ञ अपनी बात के माध्यम से सम्भव बना सकते हैं। हालांकि विज्ञान में ऐसा नहीं होता है। विज्ञान में प्रश्न का तार्किक उत्तर उपलब्ध है जिसकी जाँच बार-बार की जा सकती है।
उदाहरण के लिए विज्ञान कहता है कि प्रकाश सरल रेखा में गमन करता है, तो इसका कारण एवम् इसकी जाँच हम कभी भी और कितनी ही बार कर सकते हैं। इसके अलावा वैज्ञानिक अध्ययन के बाद असम्भव एवम् जटिल प्रक्रियाओं को भी बोधगम्य कर सकते हैं। अर्थात् हम कह सकते हैं कि विज्ञान समाधान की कला है जबकि राजनीति सम्भव की कला है।
प्रश्न 1.4.
यद्यपि अब भारत में विज्ञान तथा प्रौद्योगिकी का विस्तृत आधार है तथा यह तीव्रता से फैल भी रहा है, परन्तु फिर भी इसे विज्ञान के क्षेत्र में विश्व नेता बनने की अपनी क्षमता को कार्यान्वित करने में काफी दूरी तय करनी है। ऐसे कुछ महत्वपूर्ण कारक लिखिए जो आपके विचार से भारत में विज्ञान के विकास में बाधक रहे हैं?
उत्तर:
भारत में विज्ञान के विकास में बाधा उत्पन्न करने वाले कुछ महत्वपूर्ण कारक निम्नलिखित हैं
- हमारे देश में वैज्ञानिकों को लक्ष्यों की प्राप्ति करने के लिए शैक्षणिक स्वतन्त्रता प्राप्त नहीं है।
- विदेशों में वैज्ञानिकों, इन्जीनियों, डॉक्टर्स इत्यादि का देशान्तर भ्रमण, क्योंकि विदेशों में उन्हें उत्कृष्ट सुविधाएँ, वेतन इत्यादि प्राप्त हो जाते हैं जबकि हमारे देश में इन सुविधाओं एवम् उच्च वेतन का प्राप्त करना आज भी सम्भव नहीं है।
- हमारे देश में अनुसन्धान एवम् तकनीक के प्रबन्धन में प्रशासनिक हस्तक्षेप की अधिकता भी विज्ञान के विकास में बाधा है।
- हमारे देश में अनुसन्धानकर्ताओं एवम् उद्यमियों के मध्य सामंजस्य स्थापित नहीं है।
प्रश्न 1.5.
किसी भी भौतिक विज्ञानी ने इलेक्ट्रॉन के कभी भी दर्शन नहीं किए हैं। परन्तु फिर भी सभी भौतिक विज्ञानियों का इलेक्ट्रॉन के अस्तित्व में विश्वास है। कोई बुद्धिमान परन्तु अंधविश्वासी व्यक्ति इसी तुल्यरूपता को इस तर्क के साथ आगे बढ़ाता है कि यद्यपि किसी ने देखा’ नहीं है परन्तु ‘भूतों’ का अस्तित्व है। आप इस तर्क का खंडन किस प्रकार करेंगे?
उत्तर:
किसी भी भौतिक विज्ञानियों ने इलेक्ट्रॉन के कभी दर्शन नहीं किए हैं, परन्तु फिर भी सभी भौतिक विज्ञानियों का इलेक्ट्रॉन के अस्तित्व में विश्वास है। इसका मुख्य कारण है कि इस कण के अस्तित्व के पक्ष में बहुत – से प्रमाण उपलब्ध हैं जैसे विद्युत धारा का प्रवाह, अणुओं की विभिन्न आकृतियों एवम् आकारों का होना, विभिन्न रासायनिक यौगिकों में ध्रुवणता होना, क्षम का होना इत्यादि। जबकि भूतों का कोई भी भौतिक प्रभाव नहीं होता है, जिसे प्रायोगिक रूप से सत्यापित कर सके। अतः हम कह सकते हैं कि इन दोनों की पारस्परिक तुलना एक निरर्थक कार्य है।
परश्न 1.6.
जापान के एक विशेष समुद्र तटीय क्षेत्र में पाए जाने वाले केकड़े के कवचों (खोल) में से अधिकांश समुरई के अनुश्रुत चेहरे से मिलते जुलते प्रतीत होते हैं। नीचे इस प्रेक्षित तथ्य की दो व्याख्याएँ दी गई हैं। इनमें से आपको कौन – सा वैज्ञानिक स्पष्टीकरण लगता है?
1. कई शताब्दियों पूर्व किसी भयानक समुद्री दुर्घटना में एक । युवा समुरई डूब गया। उसकी बहादुरी के लिए श्रद्धांजलि के रूप में प्रकृति ने अबोधगम्य ढंगों द्वारा उसके चेहरे को केकड़े के कवचों पर अंकित करके उसे उस क्षेत्र में अमर बना दिया।
2. समुद्री दुर्घटना के पश्चात् उस क्षेत्र के मछुआरे अपने मृत नेता के सम्मान में सद्भावना प्रदर्शन के लिए उस हर केकड़े के कवच को जिसकी आकृति संयोगवश समुरई से मिलती-जुलती प्रतीत होती थी, उसे वापस समुद्र में फेंक देते थे। परिणामस्वरूप केकड़े के कवचों की इस प्रकार की विशेष आकृतियाँ अधिक समय तक विद्यमान रहीं और इसीलिए कालान्तर में इसी आकृति का आनुवंशत: जनन हुआ। यह कृत्रिम वरण द्वारा विकास का एक उदाहरण है।
(नोट : यह रोचक उदाहरण कार्ल सागन की पुस्तक “दि कॉस्मॉस” से लिया गया है। यह इस तथ्य पर प्रकाश डालता है कि प्रायः विलक्षण तथा अबोधगम्य तथ्य जो प्रथम दृष्टि में अलौकिक प्रतीत होते हैं वास्तव में साधारण वैज्ञानिक व्याख्याओं द्वारा स्पष्ट होने योग्य बन जाते हैं। इसी प्रकार के अन्य उदाहरणों पर विचार कीजिए)
उत्तर:
- दिए गये प्रश्न में दोनों कथनों में से कथन
- प्रेक्षित तथ्य का वैज्ञानिक स्पष्टीकरण देने में पर्याप्त रूप में समर्थ है।
प्रश्न 1.7.
दो शताब्दियों से भी अधिक समय पूर्व इंग्लैण्ड तथा पश्चिमी यूरोप में जो औद्योगिक क्रांति हुई थी उसकी चिंगारी का कारण कुछ प्रमुख वैज्ञानिक तथा प्रौद्योगिक उपलब्धियाँ थीं। ये उपलब्धियाँ क्या थीं?
उत्तर:
सन् 1750 से अर्थात् औद्योगिक क्रान्ति से पूर्व, कुछ सरल यन्त्र एवं मशीनें ही प्रचलन में थीं, जिनके कार्य करने की दर काफी कम एवम उत्पादित माल का स्तर काफी खराब था लेकिन औद्योगिक क्रान्ति के परिणामस्वरूप कुछ नवीन मशीनों का विकास हुआ जिनके द्वारा उत्पादन लागत में कमी आई एवम् वैमार माल की उत्कृष्टता में उन्नति हुई। औद्योगिक क्रान्ति की प्रमुख वैज्ञानिक एवम् प्रौद्योगिकीय उपलब्धियाँ निम्नवत् हैं
- स्पिनिंग गेनी (Spinning Genny) सन् 1764 में हारग्रीव्ज ने इस मशीन का आविष्कार किया। इससे कटाई – कार्य में तेजी आई।
- भाप इंजन (Steam Engine) सन् 1769 में जेम्सवॉट ने इसका आविष्कार किया। इसकी सहायता से औद्योगिक इकाइयों को देश के भीतरी भागों में समुद्री किनारों से दूर स्थान प्राप्त हो सका था।.
- पावरलूम (Powerloom) सन् 1785 में कार्ल-राइट ने इसका आविष्कार किया। यह माप शक्ति चालित मशीन है। इसे चलाकर कपड़ों की बुनाई का कार्य किया जाता था।
- विस्फोटक पदार्थ की खोज से ना सिर्फ आर्मी में सहायता मिली बल्कि इससे खनिज विस्फोट में भी सहायता मिली है।
प्रश्न 1.8.
प्रायः यह कहा जाता है कि संसार अब दूसरी औद्योगिकी क्रांति के दौर से गुजर रहा है, जो समाज में पहली क्रांति की भाँति आमूल परिवर्तन ला देगी। विज्ञान तथा प्रौद्योगिकी के उन प्रमुख समकालीन क्षेत्रों की सूची बनाइए जो इस क्रांति के लिए उत्तरदायी हैं।
उत्तर:
विज्ञान तथा प्रौद्योगिकी के उन प्रमख समकालीन क्षेत्रों की सूची निम्नवत् है जो इस क्रांति के लिए उत्तरदायी हैं, जो समाज में पहली क्रांति की भाँति आकूल परिवर्तन ला देगी
- जैव प्रौद्योगिकी
- सुपर कम्प्यूटर
- सूचना प्रौद्योगिकी
- विद्युत दुर्बल बल के सिद्धान्त का विकास
- प्रकाशिक तन्तु।
प्रश्न 1.9.
बाईसवीं शताब्दी के विज्ञान तथा प्रौद्योगिकी पर अपनी निराधार कल्पनाओं को आधार मानकर लगभग 1000 शब्दों में कोई कथा लिखिए।
उत्तर:
माना कि एक हवाई जहाज 500 प्रकाश वर्ष दूर स्थित तारे की ओर गतिमान है। माना यह हवाई जहाज विद्युत मोटर जिसमें अतिचालक तार लगा है, में संचित धारा से चलता है। ब्रह्माण्ड में, माना कि एक क्षेत्र ऐसा है जहाँ इतना अधिक ताप है, जिस कारण मोटर के विद्युत तारों का अतिचालक गुण नष्ट हो जाता है। इस स्थिति में, एक अन्य हवाई जहाज जिसमें द्रव्य तथा अद्रव्य भरा है, पहले हवाई जहाज को चलाता है जिस कारण यह तारे की ओर गतिमान रहता है।
प्रश्न 1.10.
‘विज्ञान के व्यवहार’ पर अपने ‘नैतिक दृष्टिकोणों’ को रचने का प्रयास कीजिए। कल्पना कीजिए कि आप स्वयं किसी संयोगवश ऐसी खोज में लगे हैं जो शैक्षिक दृष्टि से सेचक है परन्तु उसके परिणाम निश्चित रूप से मानव समाज के लिए भयंकर होने के अतिरिक्त कुछ नहीं होंगे। फिर भी यदि ऐसा है तो आप इस दुविधा के हल के लिए क्या करेंगे?
उत्तर:
प्रत्येक वैज्ञानिक खोज, प्रकृति के रहस्यों को प्रदर्शित करती है एवम् इन रहस्यों के सत्य को समाज के सामने रखता है। सत्य एक सापेक्षिक पद है। सत्य का प्रदर्शन इस प्रकार होना चाहिए कि कोई भी खोज जो मानव समाज के नैतिक मूल्यों को हानि पहुँचा सकती हो, उसे एकदम रोक देना चाहिए। जैव – प्रौद्योगिकी मानव-कल्याण हेतु बहुत उपयोगी है लेकिन जीवित प्राणियों की क्लोनिंग नीति-असंगत है। इस अनुसंधान को आगे बढ़ाने से पूर्व हमें समाज के सामने यह तथ्य रखना चाहिए कि क्या यह अनुसन्धान जारी रखना मानव के लिए भयंकर तो नहीं है। यदि ऐसा है तो अनुसन्धान को एकदम से रोक देना चाहिए।
इसके अलावा कोई खोज आज भयंकर हो लेकिन भविष्य में यह लाभप्रद सिद्ध हो सकती है। इसके लिए, सबसे पहले यह जरूरी है कि वैज्ञानिक खोज के गलत प्रयोग के सम्बन्ध में लोक विचार लेने चाहिए। यह सार्थक कदम किसी वैज्ञानिक खोज के गलत प्रयोग को रोक सकता है। अतः उन वैज्ञानिक खोजों जो समाज के नैतिक मूल्यों के लिए भयंकर साबित हो सकती हैं, को समाज की अच्छाई के लिए रोक देना चाहिए।
प्रश्न 1.11.
किसी भी ज्ञान की भाँति विज्ञान का उपयोग भी, उपयोग करने वाले पर निर्भर करते हुए, अच्छा अथवा बुरा हो सकता है। नीचे विज्ञान के कुछ अनुप्रयोग दिए गए हैं। विशेषकर कौन-सा अनुप्रयोग अच्छा है, बुरा है अथवा ऐसा है कि जिसे स्पष्ट रूप से वर्गबद्ध नहीं किया जा सकता। इसके बारे में अपने दृष्टिकोणों को सूचीबद्ध कीजिए
- आम जनता को चेचक के टीके लगाकर इस रोग को दबाना और अन्ततः इस रोग से जनता को मुक्ति दिलाना। (भारत में इसे पहले ही प्रतिपादित किया जा चुका है।
- निरक्षरता का विनाश करने तथा समाचारों एवं धारणाओं के जनसंचार के लिए टेलीविजन।
- जन्म से पूर्व लिंग – निर्धारण।
- कार्यदक्षता में वृद्धि के लिए कम्प्यूटर।
- पृथ्वी के परितः कक्षाओं में मानव-निर्मित उपग्रहों की स्थापना।
- नाभिकीय शस्त्रों का विकास।
- रासायनिक तथा जैव-युद्ध की नवीन तथा शक्तिशाली तकनीकों का विकास।
- पीने के लिए जल का शोधन।
- प्लास्टिक शल्य क्रिया।
- क्लोनिंग।
उत्तर:
- अच्छा
- अच्छा
- बरा.
- अच्छा
- अच्छा
- बुरा
- बुरा
- अच्छा
- अच्छा
- इसे स्पष्ट रूप से वर्गबद्ध नहीं किया जा सकता।
प्रश्न 1.12.
भारत में गणित, खगोलिकी, भाषा विज्ञान, तर्क तथा नैतिकता में महान विद्वत्ता की एक लंबी एवं अटूट परम्परा रही है। फिर भी इसके साथ एवं समान्तर, हमारे समाज में बहुत – से अंधविश्वासी तथा रूढ़िवादी दृष्टिकोण व परम्पराएँ फली – फूली हैं और दुर्भाग्यवश ऐसा अभी भी हो रहा है और बहुत – से शिक्षित लोगों में व्याप्त हैं। इन दृष्टिकोणों का विरोध करने के लिए अपनी रणनीति बनाने में आप अपने विज्ञान के ज्ञान का उपयोग किस प्रकार करेंगे?
उत्तर:
हमारे देश में समाज में व्याप्त अन्धविश्वासी एवम् रूढ़िवादी दृष्टिकोण व परम्पराएँ दूर करने के लिए रणनीति बनाने में विज्ञान के ज्ञान का उपयोग निम्नवत् रूप में किया जा सकता
1. स्थानीय स्तर पर जनता को आपसी बातचीत, सभाओं, क्लबों इत्यादि के माध्यम से गलत एवम् असत्य विश्वासों को दूर करने के लिए जानकारियों का प्रचार करना लाभदायक होगा।
2. छात्रों को दी जाने वाली विद्यालयी शिक्षा के पाठ्यक्रम में दैनिक जीवन से जुड़े अनुभवों की स्पष्ट व्याख्या देने वाली पाठ्य सामग्री का समावेश अति आवश्यक है अर्थात् शिक्षा की दैनिक जीवन में व्यक्त विभिन्न घटनाओं की व्याख्या देने में समर्थ होना चाहिए। इस प्रकार शिक्षा का उद्देश्य तर्कसंगत हो जाएगा एवम् वह भविष्य में भी लाभदायक सिद्ध होगी।
3. इन्जीनियर्स, वैज्ञानिकों, शिक्षाविदों, एवम् डॉक्टर्स इत्यादि द्वारा विभिन्न परिघटनाओं के सही-सही कारणों एवम् अन्धविश्वासों व गलत धारणाओं को समाप्त करने के लिए प्रदान की गई जानकारियों के अलग – अलग कार्यक्रमों द्वारा शहरी व ग्रामीण जनता के सामने प्रस्तुत करना लाभदायक होगा।
4. समाचार पत्र, रेडियो, टेलीविजन, इण्टरनेट इत्यादि माध्यमों द्वारा लोगों में व्याप्त अपूर्ण ज्ञान, भ्रान्तियों, रूढ़िवादिता, अन्धविश्वास इत्यादि को समाप्त करने में किया जाना एक हितकारी प्रयास है। इस कार्य के लिए विभिन्न कार्यक्रमों जैसेनाटकों, क्विज, विचार-गोष्ठियों, वर्कशॉप, समर स्कूल, विन्टर-स्कूल आदि का आयोजन कर संकेत दें।
प्रश्न 1.13.
यद्यपि भारत में स्त्री तथा पुरुषों को समान अधिकार प्राप्त हैं, फिर भी बहुत-से लोग महिलाओं की स्वाभाविक प्रकृति, क्षमता, बुद्धिमत्ता के बारे में अवैज्ञानिक विचार रखते हैं तथा व्यवहार में उन्हें गौण महत्व तथा भूमिका देते हैं। वैज्ञानिक तर्कों तथा विज्ञान एवं अन्य क्षेत्रों में महान महिलाओं का उदाहरण देकर इन विचारों को धराशायी करिए, तथा अपने को स्वयं, तथा दूसरों को भी समझाइए कि समान अवसर दिए जाने पर महिलाएँ पुरुषों के समकक्ष होती हैं।
उत्तर:
प्राकृतिक रूप से स्त्री तथा पुरुषों में कुछ अन्तर अवश्य होते हैं। परन्तु जिम्मेदारी निभाने, कार्य करने, बुद्धिमत्ता तथा सोच समझने में स्त्री व पुरुष में कोई अन्तर नहीं होता है। जन्म से पूर्व एवम् जन्म के पश्चात् आहार के पोषक तत्वों का एक बड़ा भाग मानव मस्तिष्क के विकास में महत्वपूर्ण योगदान करता है। यह मस्तिष्क स्त्री अथवा पुरुष किसी का भी हो सकता है। जब हम स्त्रियों के प्राचीन इतिहास एवम् वर्तमान स्थिति का अध्ययन करें तो हम देखते हैं कि स्त्रियों की स्थिति हमेशा से ही सम्मानजनक. रही है एवम् उन्होंने अनेक उत्कृष्ट कार्य किए हैं। ये स्त्रियाँ हर कार्य करने में सक्षम हैं एवम् किसी भी रूप में पुरुषों से कम नहीं है। जब कभी भी स्त्रियों को अवसर मिलता है चौंकाने वाले परिणाम सामने आए हैं।
महर्षि अत्रि की पत्नी सती अनुसूइया, झाँसी की रानी लक्ष्मीबाई, रानी कर्मवती, नूरजहाँ, मैडम क्यूरी, सरोजिनी नायडू, कल्पना चावला, प्रिंसेज डायना, मार्गेट थ्रेचर, इन्दिरा गाँधी, श्रीमती भण्डानाइके, श्रीमती चन्द्रिका कुमार तुंगे, बछेन्द्री पाल इत्यादि अनेक नाम स्त्रियों के स्वर्णिम इतिहास का उल्लेख करते हैं। आजकल सानिया मिर्जा का नाम भी शीर्षस्थ स्थान पर है। इसका तात्पर्य है कि इन स्त्रियों को अवसर मिलने पर, इन्होंने अपनी अपूर्व क्षमता का परिचय दिया। आज हमारे देश में रक्षा सेवाओं के द्वार भी स्त्रियों के लिए खुले हुए हैं। इस क्षेत्र में भी स्त्रियों ने अपनी कार्यदक्षता सिद्ध की है।
अतः हम कह सकते हैं कि समान अवसर दिए जाने पर महिलाएँ भी पुरुषों के समकक्ष परिणाम देती हैं।
प्रश्न 1.14.
“भौतिकी के समीकरणों में सुन्दरता होना उनका प्रयोगों के साथ सहमत होने की अपेक्षा अधिक महत्वपूर्ण है।” यह मत महान ब्रिटिश वैज्ञानिक पी० ए० एम० डिरैक का था। इस दृष्टिकोण की समीक्षा कीजिए। इस पुस्तक में ऐसे संबंधों तथा समीकरणों को खोजिए जो आपको सुन्दर लगते हैं।
उत्तर:
डिरैक के कथन में कोई विसंगति नहीं है। भौतिकी में एक समीकरण जो प्रयोगों के साथ सहमत है, उसे निश्चित ही सरल एवम् बोधगम्य होना चाहिए। यही उसकी सुन्दरता की कसौटी है। इसका तात्पर्य है कि जो समीकरण सरल एवम् समझने योग्य होगी, वह सुन्दर मानी जाएगी। जैसे आइन्सटीन की द्रव्यमान ऊर्जा समतुल्यता समीकरण E = mc2, द्रव्यमान के ऊर्जा तथा ऊर्जा के द्रव्यमान में स्थानान्तरण को समझाती है। यह समीकरण सरल एवम् समझने योग्य है। अर्थात् यह एक सुन्दर समीकरण है।
प्रश्न 1.15.
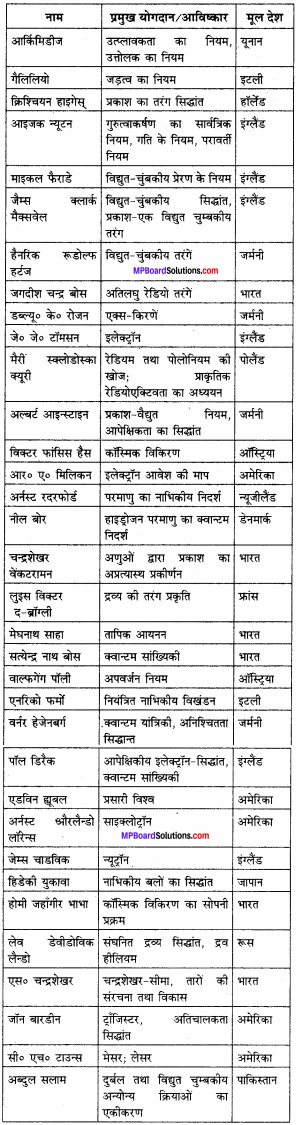
यद्यपि उपरोक्त प्रकथन विवादास्पद हो सकता है, परन्तु अधिकांश भौतिक विज्ञानियों का यह मत है कि भौतिकी के महान नियम एक ही साथ सरल एवं सुन्दर होते हैं। डिरैक के अतिरिक्त जिन सुप्रसिद्ध भौतिक विज्ञानियों ने ऐसा अनुभव किया, उनमें से कुछ के नाम इस प्रकार हैं : आइंस्टाइन, बोर, हाइसेनबर्ग, चन्द्रशेखर तथा फाइनमैन। आपसे अनुरोध है कि आप भौतिकी के इन विद्वानों तथा अन्य महानायकों द्वारा रचित सामान्य पुस्तकों एवं लेखों तक पहुँचने के लिए विशेष प्रयास अवश्य करें। (इस पुस्तक के अंत में दी गई ग्रंथ – सूची देखिए)। इनके लेख सचमुच प्रेरक हैं।
उत्तर:
प्रश्न 1.16.
विज्ञान की पाठ्य पुस्तकें आपके मन में यह गलत धारणा उत्पन्न कर सकती हैं कि विज्ञान पढ़ना शुष्क तथा. पूर्णतः अत्यंत गंभीर हैं एवं वैज्ञानिक भुलक्कड़, अंतर्मुखी, कभी न हँसने वाले अथवा खीसें निकालने वाले व्यक्ति होते हैं। विज्ञान तथा वैज्ञानिकों का यह चित्रण पूर्णतः आधारहीन है। अन्य समुदाय के मनुष्यों की भाँति वैज्ञानिक भी विनोदी होते हैं तथा बहुत-से वैज्ञानिकों ने तो अपने वैज्ञानिक कार्यों को गंभीरता से पूरा करते हुए अत्यंत विनोदी प्रकृति तथा साहसिक कार्य करके अपना जीवन व्यतीत किया है। गैमो तथा फाइनमैन इसी शैली के दो भौतिक विज्ञानी हैं। ग्रंथ सूची में इनके द्वारा रचित पुस्तकों को पढ़ने में आपको आनन्द प्राप्त होगा।
उत्तर:
गैमो एवं फाइमैन द्वारा रचित पुस्तक निम्नलिखित हैं
1. गैमो द्वारा रचित ‘Mr Tompkins in paperback : Cambridge Universing Press (1987)”
2.फाइनमैन द्वारा रचित “Surely you are joing : Mr. Reynman, Bantan Books (1986)”.
उपरोक्त पुस्तकों के पढ़ने पर ज्ञात होता है कि वैज्ञानिक भी अन्य मनुष्यों की भाँति ही विनोदी होते हैं। इनके अलावा सी० वी० रमन, होमी जे० भाभा, भी विनोदी स्वभाव के भौतिकवादी रहे हैं। हमारे देश के कुछ नेता जैसे-मुरली मनोहर जोशी, वी० पी० सिंह इत्यादि भी भौतिकविद् रहे हैं।