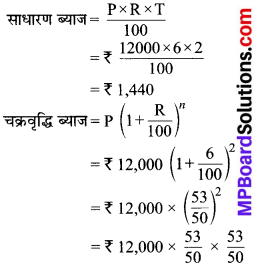
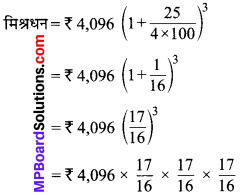
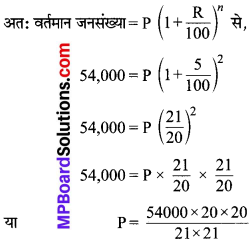
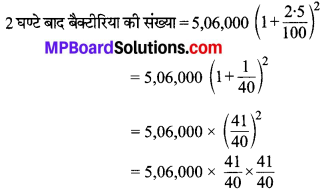
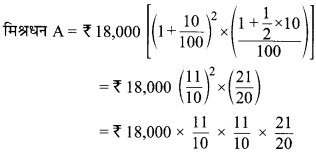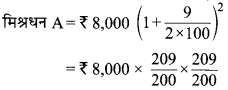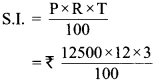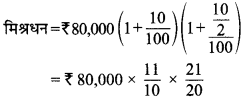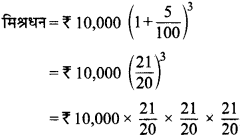MP Board Class 7th Social Science Solutions Miscellaneous Questions 1
Choose the correct alternative from the following:
Question 1.
The medieval period in India begins form:
(a) The 13th century
(b) 7th century
(c) 8th century
(d) 12th century
Answer:
(c) 8th century
Question 2.
The famous Raja Rajeshwara temple of Tanjavur was built by:
(a) Raja raja – I
(b) Rajendra -I
(c) Krishna – I
(d) Krishna – II
Answer:
(a) Raja raja – I
Question 3.
The President of the constituent assembly was:
(a) Dr. Harising Gaur
(b) Dr. Bhimrao Ambedekar
(c) Dr. Rajendra Prasad
(d) Pt. Jawaharlal Nehru.
Answer:
(c) Dr. Rajendra Prasad
Question 4.
The total no. of the members of the Rajya Sabha is:
(a) 238
(b) 250
(c) 230
(d) 260
Answer:
(c) 230
Question 5.
Day and night are equal on:
(a) 21 March and 25th Dec
(b) 21 June and 22 Dec
(c) 25 Dec & 25 June
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(d) none of the above
Question 7.
The percentage of oxygen percent in the atmosphere is:
(a) 78%
(b) 21%
(c) 28%
(d) 71%
Answer:
(b) 21%
![]()
Fill in the blanks:
- India was in continuous contact with …………… through trade.
- ……………. translated Ramayana into Tamil
- The ancient name of the capital of Madhya Pradesh was …………….
- The Constitution of India is a written and ……………. Constitution.
- The earth’s axis makes an angle of ……………… from its plane.
Answer:
- Arabs
- Kamban
- Bhojpal
- Comprehensive
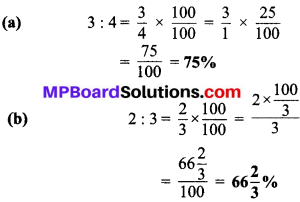
- 23 \(\frac { 1 }{2 }\)°
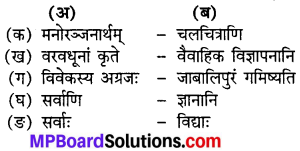
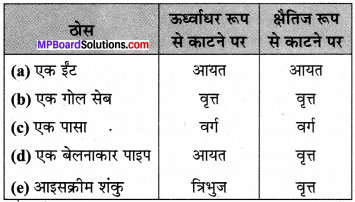
Make correct pairs:

Answer:
1. (b) Uttar Ram charit
2. (a) Geetgovind
3. (d) Siddhata shiromani
4. (c) Life saving gas
Answer the following in brief:
Question 1.
Write the names of the important rulers of the Chouhan dynasty.
Answer:
Ajayraj Chouhan and Prithiviraj Chouhan.
Question 2.
Write any three features of the Chola administration.
Answer:
- The king was the head of the government
- The empire was divided into provinces.
- The village was the lowest unit of administration.
Question 3.
What do you understand by Secularism?
Answer:
Secularism means that from point of view of the government all religious are equal and the state shall not discriminate between the people of different facilities.
Question 4.
Write any three qualifications required to be a member of the RajyaSabha.
Answer:
A person must be 30 years or above in age.
- His name must be in the voter is list of the constituency to which he belongs.
- He must not be insolvent, bankrupt and must be same.
Question 5.
What do you know about die Ionosphere?
Answer:
It is one of the layers of gases found in thermosphere. It is found at a height of 80 to 400 km from the earth.
![]()
Question 6.
What do you mean by the axis of the earth?
Answer:
The axis of the earth is the point on which die earth rotates.
Question 7.
What is meant by change of season?
Answer:
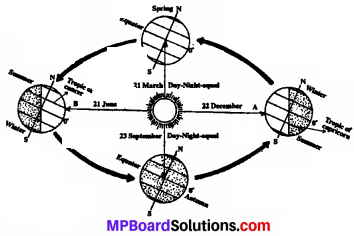
Because of the title of the earth’s axis one hemisphere comes to face to the sun first and then comes the other hemisphere. Therefore variations in the weather phenomenon occur. Change in temperature is die bases for change in seasons. The earth gets heat from sun. Due to its tilt of 23\(\frac { 1 }{2 }\)° degrees on its axis and its revolution round the sun the quantity of temperature received differs. This brings about changes in seasons.
Question 8.
Which season does India experience when die sun is directly on the tropic of Cancer?
Answer:
Summer season.
Answer the following questions in detail:
Question 1.
Describe die political condition of India in the beginning of the early part of the medieval period.
Answer:
The Arabs made great contribution in the development of the Medieval civilization. They were expert traders. Trade had made them rich and they used the wealth for the development of art, science and literature.
They spread knowledge, which they acquired from the countries with which they had trade relations, to distant lands. They also made important contribution in the field of Geometry, Algebra, Geography and Astronomy. They also carried new inventions of China like Gun Powder, Paper and Compass to countries of Europe.
Question 2.
Write about the main features of the Pallava dynasty.
Answer:
Main features of the Pallava dynasty:
- Pollar administration was well – managed.
- Education, literature and art flourished greatly.
- The local language was Tamil in which high quality literature was produced.
- The Pollar kings were Shaivas and the Hindu religion flourished there well.
- The Pollar as got many famous temples built there. Some of the very famous are ‘Dharmraj’ and Kailashnath temple at Kanchi, the rock – cut Rathmandir at the sea coast of Mahabalipuram.
![]()
Question 3.
Describe the freedoms given in the Rights to freedom.
Answer:
Right to freedom guarantees six basic freedoms. Two freedoms are given here:
1. Freedom to express thoughts – All die citizens of India has the freedom to express his / her thoughts, to give speech and to know about the thought of others and to propagate it The citizens have the freedom to write articles etc. in newspapers.
2. Freedom to live and settle in any part of India – All the citizens of India have die freedom to settle in any part of the country permanently or temporarily as per their wish.
Question 4.
Explain the process of framing a law.
Answer:
Every bill has to go through three stages in the Parliament. These stages are:
- The first reading of the bill – In it, copies of the bill are given to the members. The person or minister who introduces the bill in the House, gives a speech explaining die purpose of die bill.
- The second reading – In the second reading, a clause / by – clause discussion takes place on the bill.
- The third reading – in the third reading the bill as a whole is finally discussed and put to vote.
If the majority of the members are in its favor, the bill is passed. Now the bill is sent to the other House. After the bill is sent to the other House, it goes through all the three stages as mentioned above. After toe other House passes toe bill, it is sent to toe President for his assent The bill becomes a law after it is signed by toe President
Question 5.
Describe die composition of die atmosphere
Answer:
The changes in temperature at various attitudes divide the atmosphere into 5 layers.
1. Troposphere
2. Stratosphere
3. Mesosphere
4. Thermosphere
5. Exosphere
1. Troposphere:
It extends to a height of 8 km at the poles and 18 km on equator. Dust particles and water vapor are found in this layer. All kinds of weather phenomenon like clouds, rainstorm etc. is observed in this layer. All types of life forms are found in this layer. This layer is also known as dynamic layer.
2. Stratosphere:
The second layer of the atmosphere is known as stratosphere. The temperature in this layer is constant till 20 kms. height and then slowly increases.
3. Mesosphere:
The height of this layer is 50 to 80 km from the sea level. The variation in temperature is less in this layer as water vapor, clouds and dust are found less and fast wind blows here.
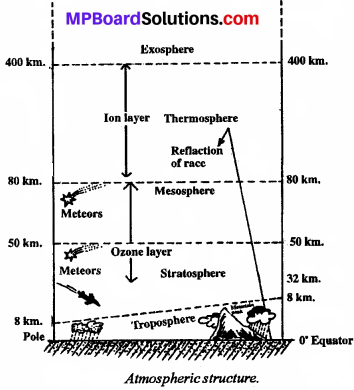
4. Thermosphere:
The thermosphere starts from the height of 80 km from sea level. The density of air is very less in this layer. The
temperature increases with height in this layer. Two layers of gases are found here. One is the ozone layer and the other is the ion layer.
The ozone layer is spread at a height of 32 to 80 km from the earth. The ion layer is found at a height of 80 to 400 km. from earth. The electrically charged particles stop the radio waves transmitted from the earth and return it back to the earth. In this way we can listen to various radio programmers.
5. Exosphere:
This is the outermost layer of die atmosphere the upper limit of this layer is uncertain. The density of air is the least here.
![]()
Question 6.
Describe the different types of permanent winds.
Answer:
Winds are the natural horizontal movement of air over the earth’s surface.
Difference between air and wind:
- When air moves vertically downwards or upwards, it is known as air. But when it moves horizontally, it is known as wind.
- Airis calm-but when it becomes dynamic it take / the form of wind. Wind always blows from high pressure to low pressure.
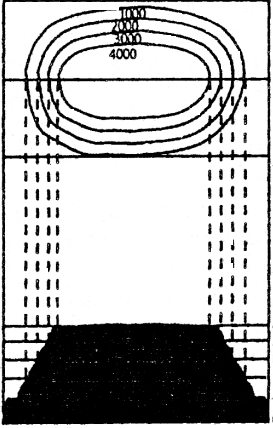
Question 7.
Explain with the help of a diagram the changing seasons of the earth.
Answer:
The earth’s axis forms an angle of 66 \(\frac { 1 }{2 }\) with the plane of the earths orbit and the earth tilts at 23 1/2 degree on its axis. Let us understand how seasons occurs on earth.