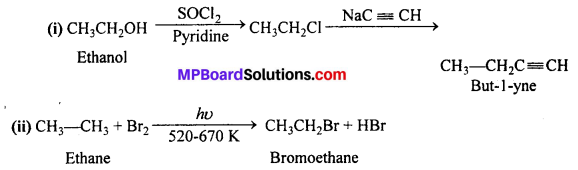
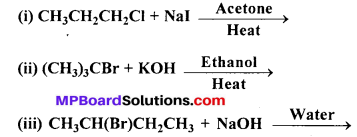
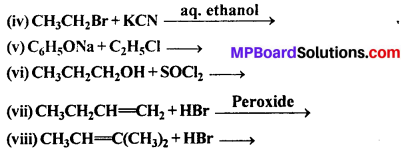
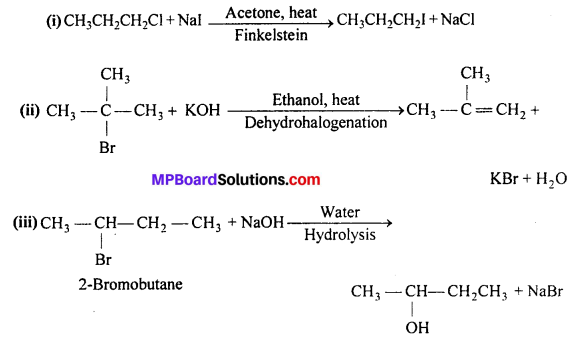
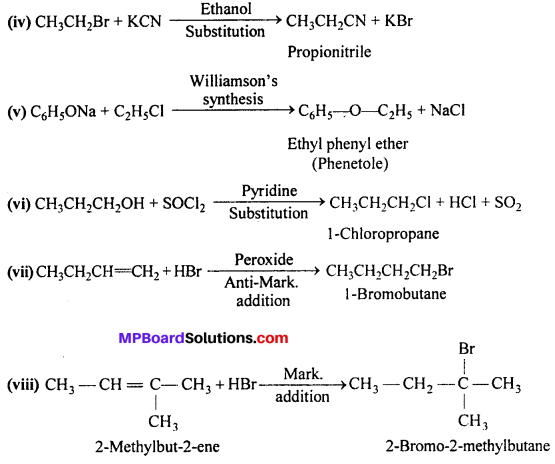
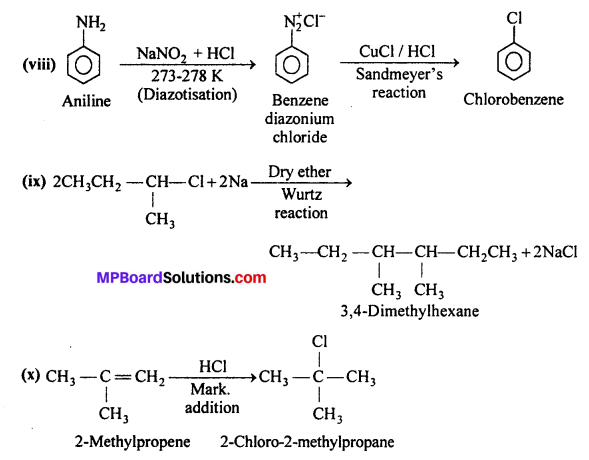
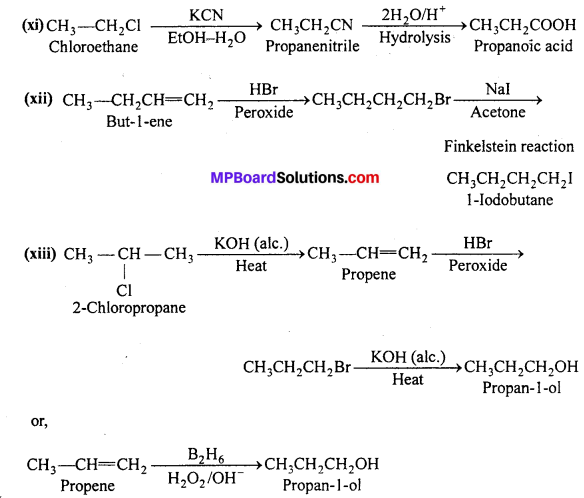
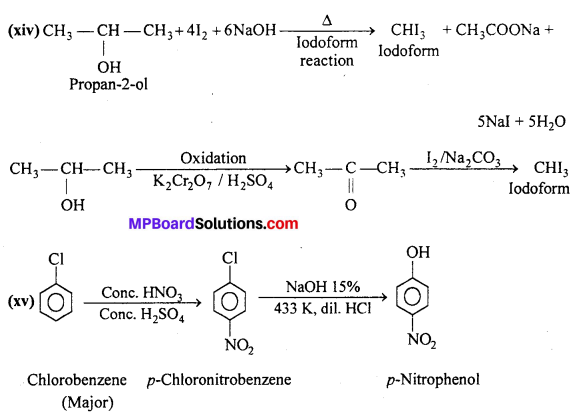
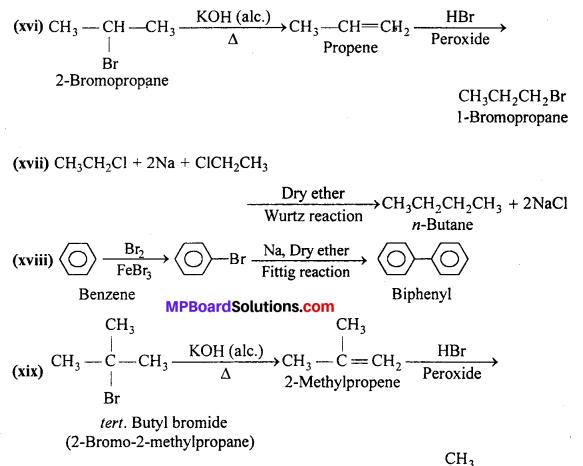
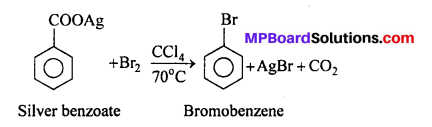
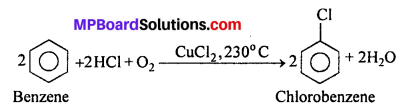
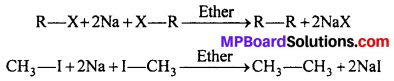
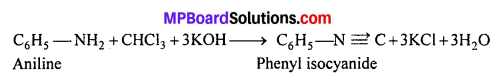
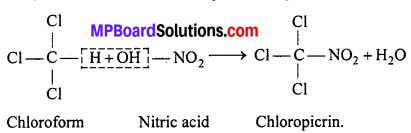
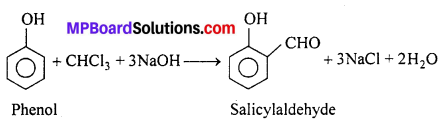
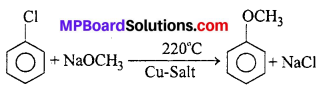
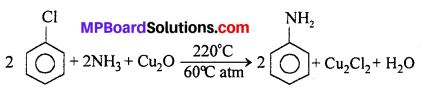
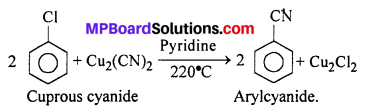
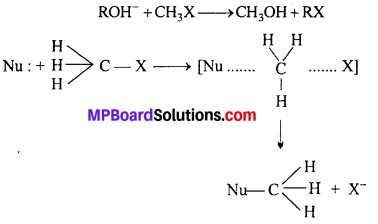
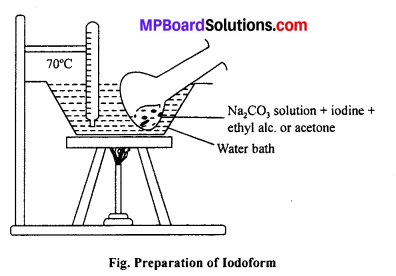
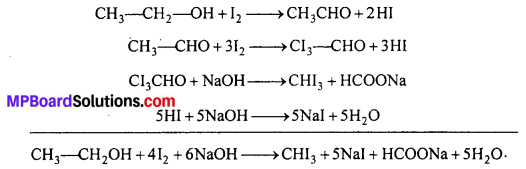
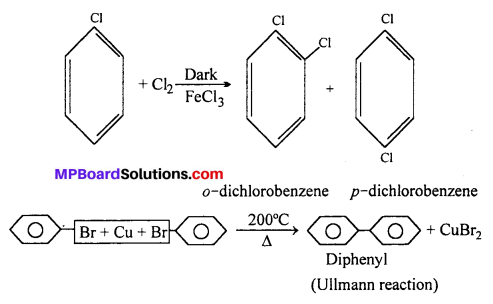
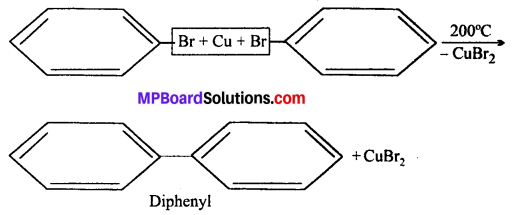
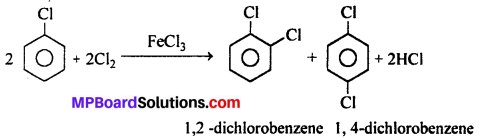
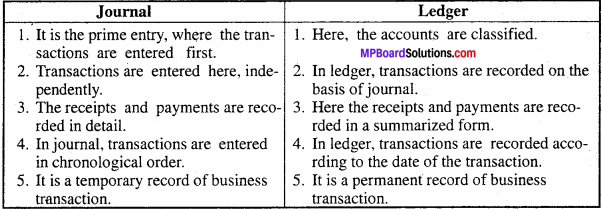
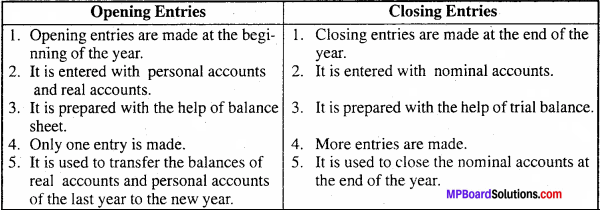
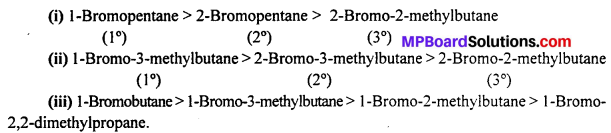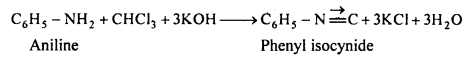MP Board Class 12th Business Studies Important Questions Chapter 2 Principles of Management
Principles of Management Important Questions
Principles of Management Very Short Answer Type Questions
Questions 1.
What do you understand by “Mental revolution” ?
Answer:
Principle of mental revolution assumes that even if there are large physical resources and other resources in an organization but if the human resources are not satisfied, there isn’t peace and prosperity and the moral of the human resources is not high till then the resources are simply resources. They can never take the form of production and services. Hence, managers must try to attain the maximum cooperation of the workers, to remove the gaps between labour and capital and to radicate mutual enmity.
Question 2.
What do you understand by principles of management ?
Answer:
Principles of management represent the techniques and principles which are related to management tasks and to show the correct path for achievement of the main objectives of the organization.
Question 3.
Explain Fayols principle of Initiatives ?
Answer:
According to this principle Fayol has suggested that the officers and employees of an organization should be given freedom to work on the new plans and to upgrade the old plans in order to increase the productivity. The employees should take the initiative in order to give suggestions to increase the productivity of the firm.
Question 4.
What is principle of equity ?
Answer:
This principle was formulated by Henri Fayol. Equity means fair dealings, equality of treatment and cooperative attitude among the employees in the enterprise. Equity results from a combination of kindness and justice. Employees expect equity from management.
Question 5.
How is efficiency developed through division of labour ?
Answer:
According to Henri Fayol all employees is an organization or institution do not have same efficiency. So according to their efficiency and interest they should be assigned the work. Labour should be divided into various groups. By doing this workers are motivated and this helps in increasing their efficiency.
The object of division of work is to derive benefits from specialization. The various functions of management like planning, organization cannot be done alone.
Question 6.
Distinguish is between principles of unity of command and principle of unity of direction.
Answer:
Difference between Principles of unity of command and Principle of unity of direction
principal of unity command:
- it is concerned with the functioning of personnel.
- 2.this principal makes the relation of and officers (authority) strong.
princpals of unity of direction:
- it is concerned with the functioning of the department and sub-department comprising the business concern.
- the principals help the unification of plans.
Question 7.
What do you mean by decentralization ?
Answer:
When the top level management gives more role and importance to its subordinates in management and organization, it is known as decentralization. The intensity of centralization of decentralization is decided by the top level management.
![]()
Question 8.
What do you mean by standardization ?
Answer:
According to Taylor standardization is essential for high quality product with low cost of production. It involves the standardization of tools and equipment conditions of work and materials so that the best product can be produced at a minimum cost.
Question 9.
Explain the principle of unity of direction formulated by Henri Fayol.
Answer:
Principle of unity of direction means there should be one head and one plan for a group of activities having the same objectives. While unity of command is concerned with the functioning of personnel unity of direction is concerned with the functioning of the body corporate. The departments and subdepartments comprising the business concern.
Question 10.
Explain Principle of scientific selection, training and development.
Answer:
According to Taylor, selection of employees should be done very carefully, because wrong selection may create disaster. This does not mean that only well qualified persons should be employed, but that person should be employed who can do that work or is capable of -handling that work. Taylor in his book, “The principle of scientific management” has written, that no matter how good your selection procedure is, but without training, the working capacity of the employees cannot be increased. Therefore, along with scientific selection method, arrangement for training should also be made. “A person should do the work not mere know the work.”
Question 11.
What is Taylor’s Eight Boss scheme ?
Answer:
Taylor has suggested functional organizational system. This organization is called Eight Boss scheme.
They are:
- Gang Boss
- Speed Boss
- Repair Boss
- Inspector
- Shop disciplinarian
- Route clerk
- Instruction card clerk
- Time and cost clerk.
Question 12.
ExpIain the principle of ‘I’ and ‘We’ propounded by Fayol ?
Answer:
According to this principle of Henry Fayol the industrialists should use the word we instead of ‘I’ in order to get maximum cooperation of the employees. Both the aspect should work in cave and harmony.
Question. 13.
Explain Taylor’s principle of task idea.
Answer:
Principle of task idea: This pertains to the norms of productivity of individual worker. It is a technique of forecasting and viewing ahead every step in a long series of separate operations. The standard task is the amount of work which an average worker does in congenial atmosphere during a working day. Taylor called it a fair day’s work. A worker usually works much below his capacity if no standard is set for him.
Question 14.
What do you mean by motion study ?
Answer:
It is the study of a machine operator and his movements for performing the job. The purpose is to eliminate useless motion and thereby establish a standard for performance. The study is undertook in order.
Question 15.
Explain the principle of unity of direction.
Answer:
Principle of unity of direction : It means, there should be one head and one plan for a group of activities having the same objectives while unity of command is concerned with the functioning of personnel, unity of direction is concerned with the functioning of the body corporate the departments and subdepartments comprising the business concern.
Question 16.
Who formulated scientific principles of management when and where did he die ?
Answer:
Principles of scientific management was formulated by F.W. Taylor. He died in 1915 at Filadalphiya.
Question 17.
How many parts did Henri Fayol divide the works of business ?
Answer:
Fayol has classified all the works of business in six parts :
- Technical work
- Commercial work
- Financial work
- Security work
- Administrative work
- Managerial work.
Question 18.
What do you mean by time study ?
Answer:
lt is done to observe and study the minimum time-period required to perform any task. Through time study the precise time required for man’s work is determined. It will help in fixing the standard time required to do a particular job.
![]()
Question 19.
what do you mean by Fatigue study ?
Answer:
Fatigue study : Excessive specialization of work and poor working conditions may cause monotony resulting in both physical and mental fatigue among industrial workers. Fatigue either a physical or mental always has an adverse effect on worker’s health and his efficiency. The idea of this study is to see that workers maintain their operational efficiency without any injury to their health and happiness.
![]()
Principles of Management Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name the 14 principles of management formulated by Henri Fayol.
Answer:
AnirFayol’s Principles of Administration of Management:
- Principle of division of work
- Principle of authority and responsibility
- Principle of discipline
- Principle of unity of command
- Principle of unity of direction
- Principle of priority to common interest
- Principle of remuneration of personnel
- Principle of centralization
- Principle of scalar chain
- Principle of order
- Principle of equity
- Principle of stability
- Principle of initiative and Esprit de corps
- Principle of coordination of management.
Question 2.
Differentiate the time study and motion study.
Answer:
Differences between time study and motion study :
Time study:
- Time study is done at first.
- In time study, study of time is done of time taken by machine and time taken by labours.
- Stopwatch is used in time study.
- Time study is related to increase the efficiency of labourers.
Motion study:
- Motion study is done after time study In motion study the study of work done by labours is done.
- Camera is used in motion study.
- The object of motion study is to minimize the movement of labours.
Question 3.
why the principles of scientific management opposed by labourers ? Give any six reasons.
Answer:
Opposition by labourers : The maximum opposition of scientific management has been done by the labourers. The reasons for opposition of scientific management are following: .
1. Increase of labourers work: To adopt the scientific management, it is necessary to increase the efficiency of a labour and so the work load on labour is increased. The increased work load creates bad effect on the health of labourer. Hence, it is opposed by the labourers.
2. Strict control: Under the scientific management, strictness has to be observed and so the labourers are kept under the strict control which they do not like.
3. Fear of unemployment: Increased use of machines create a sense of fear in the minds of the workers, thereby making them inefficient. This may further lead to retrench-ment. Hence, they are against being the standards set;
4. Exploitation of labourers : In scientific management, wages of the labourers are not increased in proportion to the increased production. So, in this system, exploitation of the labourers are maximum.
Question 4.
describe the similarities of opinions of Taylor and Fayol.
Answer:
Followings are the similarities of opinions Taylor and Fayol:
- Both wanted to bring change in managerial conditions
- Both were great supporters of human factor
- Both gave much importance to forecasting and planning
- Both were management experts of the same time, i.e., both were contemporaries
- Both accepted management as an earned talent
- Both were experts in their own fields
- Both emphasised working in a technical and scientific way
- Both formulated principles of management.
Question 5.
To increase the production efficiency in industrial organization many principles were developed by Taylor. Explain them.
Answer:
To increase the production efficiency in industrial organization following principle are adopted by Taylor :
Principle of modern machines and equipment: Modem machines and equipments yield good quality of goods. Cost incurred is also reduced, therefore under production management, best of modem machines and equipments should be used.
Principle of standardization : Taylor says that, “For production, standard material, standard method, proper procedure and good workers qualifying the standard requirements should be made available, such that good quality of goods can be produced at lesser cost.”
Principle of ideal cost accounting system : For controlling the wastage in expenditure and misuse of materials suitable system of cost accounting should be adopted. Capable and experienced cost accounts should so appointed in the organization.
Question 6.
What are the dissimilarities in study of Taylor and Fayol ?
Answer:
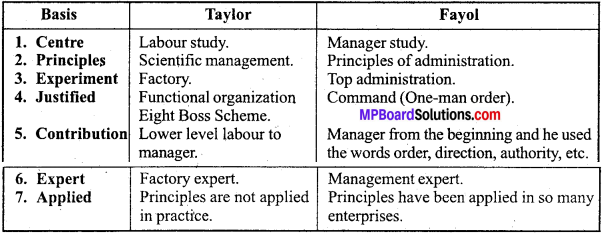
Dissimilarity of Opinions : Taylor and Fayol
- Taylor’s centre of study was labour whereas Fayol’s centre of study was manager.
- Taylor’s principles were Principles of Scientific Management whereas Fayol’s Principles were known as Principles of Administration.
- Taylor’s experiment point was factory whereas Fayol’s experiment point was top administration.
- Taylor justified functional organization (Eight Boss Scheme) for an enterprise whereas Fayol justified unity of command (One-man order).
- Taylor’s study and contribution was lower level, labour to manager whereas Fayol’s_ study and contribution was manager from the beginning and he used the words order, direction, authority, etc.
- Taylor is called as Factory Expert whereas Fayol is known as Management Expert.
- Taylor’s principles are not applied in practice whereas Fayol’s principles have been applied in so many enterprises.
![]()
Question 7.
Mention the objectives of scientific management.
Answer:
Following are the main objectives of scientific management: .
- Increase in the rate of production by use of standardized tools, equipments and methods
- Increase in quality of goods by research, quality control and inspection devices
- Reduction in the cost of production by rational planning and regulation and using cost control techniques.
Question 8.
“Principles of management are concentrated on human behaviour”. Explain.
Answer:
Management is totally related with human behaviour. The success of principles of management is affected by human behaviour. Management is related with persons. Management gives proper directions to human behaviour. Management is also done by human being and the consumer for whom the organization, is prepared is also human being. So it is said that principles of “Management are concentrated on human behaviour”.
Question 9.
The work of Taylor and Fayol are complementary.’ Explain
Answer:
F. W. Taylor is regarded as “father of scientific management and Henry Payol is regarded as “father of modern principles of industrial management”. Both were contemporaries and both were top class engineers. Both emphasized working in a technical and scientific way. Both have contributed a lot in the field of management. These existed a difference in thinking and working method of both. Economics for instance, Taylor focussed on improving efficiency of labourers while Fayol focussed on management work. The both realised that in every stage. Employees and their management will be the basis of success of an industrial Concern. To solve such problem both suggested scientific solutions and their implementation.
Despit of dissimilarities between the principles propounded by both learned economists. We can say that their work is complementary to each other.
Question 10.
Write the importance of principles of management is three points.
Or
Explain the importance of principle of management.
Answer:
Significance of Importance of Principles of Management: The principles of management are very useful as they provide useful guidelines to managerial behaviour and influence managerial practices. Actually, principles guide Them in taking and implementing decisions. Their importance can be understood by the discussion of the following points :
1. They provide useful In-sights : The principles provide the managers with useful insights into real world situations. Following these principles they increase their knowledge, ability and understanding and can face adverse situations effectively. Thus, the principles increase managerial efficiency.
2. They help in utilization to Resources of the optimum : As we know resources both human and material are limited. They have to be put to optimum use. They should be uses in such a way that they give maximum benefit with minimum cost. Principles equip the managers foresee the.cause and effect relationships of their decisions and actions. Thus, the wastage associated with a trial-and-error approach can be overcome.
3. Highlight the True Nature of Management: Lack of understanding of management principles makes it difficult to define clearly the nature and scope of the managerial job. Principles are necessary if the true nature of management is to be clearly understood. Principles act as a checklist of the meaning and contents of management. They highlight the role of managers in concrete terms and serve as a criteria to judge the appropriateness of managerial decisions and actions.
4. Based on Objective Assessment: Management principles help in thoughtful decision making. They emphasis logic rather than blind faith. Management decisions taken on the basis of principles are free from bias and prejudice. They are based on the objective assessment of the situation
5. To Guide Research : Principles of management indicate the lines along, which research should be carried out to develop new guidelines and to ascertain the validity of existing guidelines. Thus, management principles serve as focal points for useful research in management.
6. To attain Social Goals: Manager coordinate the efforts of people so that individual objectives get translated into social attainments. The standard of living of people depends upon the quality of management. If management is efficient, the resources of society are better utilized and quality of life is improved. Development of management principle by increasing, efficiency, in the use of resources, would definitely have a revolutionary impact on the cultural level of society and on human progress.
Question 11.
Distinguish between managerial principles and managerial techniques.
Answer:
Differences between Managerial principles and Managerial techniques
Managerial principles:
- Managerial principle is flexible.
- Managerial principles are directions for managerial work.
Managerial techniques:
- Managerial techniques are less flexible
- These are managerial techniques which are made fulfil the targets.
Question 12.
How are principles of management arises ?
Answer:
Principles of management arises due to following reasons :
1. Deep observation: In every business in front of management some problems arises. During this time managers observe working of employees. They see their reactions. On the basis of these observations principles are made.
2. Experiments done again and again : In this method experiments are done on various employees frequently. On the basis of results the principles are made.
Question 13.
Explain the principle of “Esprit De Corps”
Answer:
By ‘Esprit De Corps’ we mean “Power of Organization”. According to this principle each employee should consider himself/herself as the member of teach. He/she should try to achieve the target of team. Management should try to create feeling of cooperation among the workers. By following this target group target is achieved.
Question 14.
While fixing the proper wages which points are to be kept in mind ?
Answer:
While fixing the proper wages these points are kept in mind :
- Financial situation of institution or organization.
- Minimum wages act of government.
- Payment of bonus and wages done by competent.
Question 15.
How principles of management make administration more effective ? Explain with example.
Answer:
Principles of management discourages partiality and prejudice. It makes administration more effective. These principles encourages the scientific principles.
For example “Principle of unity of command” and “Principle of unity of direction” lead the orderly working of the organization. Principle of direction do assimilation of effort made by workers in a specific direction. Principle of scalar chain do the flow of information in a proper way.
Question 16.
Recognize those techniques of scientific management which are analysed by the following statements :
- When any expert supervises each labour.
- To know the best solution of doing any work.
- Different wages paid to labours.
- When equality is brought in material, machines tools and working methods and conditions after proper experimentation.
- To fix the standard time for completing the fixed work.
- Employee is for the enterprise and enterprise is for the employee.
Answer:
- Creative foremanship
- Method study
- Differential wages
- Stan-dardization of work
- Time study
- Mental revolution.
Question 17.
Distinguish between principle of unity of command and functional foremanship.
Answer:
The differences between principle of unity of command and functional foremanship:
Principle of unity of command
- This principle requires that the employees should receive orders from one superior only for any action or activity.
- In it planning and performing work is same.
- It means workers in a department are required to be accountable to one superior for orders.
Functional foremanship
- Under it each worker has to takeorder for performance of any work from foreman.
- Under it planning and performance of work is different, (excutation of function)
- This concept was extended to the lower level.
Question 18.
Distinguish between principles of management and principles of pure science
Answer:
Principles of management:
- Principles of management are of more flexible nature.
- These changes in business environment according to change.
- These principles are implemented with creativity.
Principles of puree science:
- These principles are more strong.
- These principles do not change according to time.
- These are implemented with fixed or proposed way.
Question 19.
When a salesman gets order from two high authority then what bad effects may take place ?
Answer:
When a salesman gets order from two different authorities then following bad effects may be found:
- Suspicion may take place in mind of salesman.
- He tries to avoid the work.
- There may be difference of opinion regarding the orders by two persons.
- It may be difficult to maintain discipline.
Question 20.
It is seen that in organization present position is due to the non-violation of principles of management. What is this present position ?
Answer:
Due to violation of principles of management following positions may be in the organization:
- Necessary material may not be made available at die time of requirement of it. In search of material much time will be wasted.
- Conditions may increases.
- Possibility of accidents may increase.
![]()
Question 21.
Write the names of those officers who work under foremanship the following works:
- To examine the quality of produced goods. To check the standard of goods and if the goods are of not standardize, then finding the reason of it.
- To cheek if all the labours are working their own work according to fixed rate.
- To ensure what will be the order of any work in completing the specific work.
- To keep the machines and tools in working conditions.
- To give direction to workers to do work by a specific method.
- To ensure that each work is done in proper way.
Answer:
- Inspector
- Speed Boss
- Rote clerk
- Repairs Boss
- Card clerk
- Displinarian.
![]()
Principles of Management Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain some merits of scientific management.
Answer:
some merits of scientific management are as follows :
- Division of work : It stress on specialization and division of work. It helps the producer in completing of work effectively.
- Industrial peace: The conflicts among labours are solved scientifically under scientific management. There is no place for conflicts which helps in main taining industrial peace.
- Maximum work: It helps in getting the maximum work done from laboures. This helps in increase in profit as well.
- Reduction in cost of production : If reduce the cost of production, it can achieve .success. ‘
- Increase in Income: It increases the efficiency of worker which increase the income of labours.
- Stability in employment: Efficient and able worker provide their service regularly it will increasestability in employment.
Question .2
What do you understand by scientific management ? Write its characteristics.
Answer:
Meaning of Scientific Management: Scientific management is made of two words science and management. Science is the application of logic, reasoning and it gives a new dimension to our study approach to different problems of life. When we apply scientific approach towards management concepts this is called as scientific management.
Following are the characteristics of scientific management:
- The objectives of every job in scientific management is fixed and predetermined,
- There is a fixed plan to attain objectives
- Mutual cooperation among employees is essential in scientific management
- Scientific management works on the objective of maximum production at minimum cast
- Motivation is considered necessary for the completion of work
- Scientific control system is implemented under scientific management
- Time to time evaluation of standards is performed
- Increase in efficiency of employees helps in increase in the income of employees
- Researches and experiments plays an important role in the field of scientific management
- Specialisation and division of work is also given importance
- Much stress is given on right person for the right job
- Responsibilities are assigned or fixed for every level of work.
Question 3.
Discuss the elements of scientific management. (Imp)
Answer:
In order to implement the principles of scientific management, Taylor and his associates developed the following techniques :
1. Time Study : In refers to the technique used to measure the time that may be taken by a worker of reasonable skill and efficiency to perform various elements of a job. The aim of time study is to fix ‘Time standards’ for each operation.
2. Motion Study : It refers to have close observation of the movements of a worker’s body involved in performing a job. The purpose of motion study is to avoid wasteful motions in working.
3. Fatigue Study ; Fatigue study seeks to find out how long a person can perform the standard task without any adverse effect on this health and efficiency. It helps to determine the mount and frequency of rest intervals in completing a job.
4. Method Study : The aim of this study is to maximize efficiency in the use of materials, machinery, manpower, and capital by improving work methods.
5. Scientific Task Setting : Scientific planning of a task is the technique of forecast¬ing and viewing ahead every step in a long series of separate operations. Each step has to be taken in the right place, of the right degree, and at the right time, so that work can be done with maximum possible efficiency. Scientific task is the amount of work which an average worker working under proper working conditions can perform during a working day.
6. Standardization : Standardization is the process of fixing well thought-out and tasted norms with a view to maximise efficiency of work standardization eliminates needles variety and thereby simplifies the process of production.
7. Scientific Selection and Training : Under scientific management right men are selected for right jobs. Employees are selected according to predetermined standard in an impartial way. Workers are specifically trained for the jobs, so that they can perform their jobs effectively and efficiently.
8. Mental Revolution : It requires that there should be perfect cooperation,coordination and adjustment between the efforts of labour and management.
Question 4.
describe the principles formulated by Taylor.
Answer:
‘The principles formulated by Taylor are in fact the principles of scientific management. Sir Taylor has formulated the principles of management after studying the scientific management minutely and deeply. Taylor has presented the principles of management in L scientific way. So, it is called as principles of scientific management. The following principles have been formulated by Taylor.
1. Principle of task idea : This pertains to the norms of productivity of individual worker. It is a technique of forecasting and viewing ahead every step in a long series of separate operations. The standard task is the amount of work which an average worker does in congenial atmosphere during a working day. Taylor called it a fair day’s work. A worker usually works much below his capacity if no standard is set for him.
2. Principles of experiment: Taylor suggested that the following studies be conducted by an organization so that it has an insight in knowing the method of doing a job, movement of a machine, time required for its completion and the fatigue that is associated with performing the job.
(i) Time study : It is done to observe and study the minimum time required to perform any task. Through time study, the precise time required for man’s work is determined. It will help in fixing the standard time required to do a particular job.
(ii) Motion study : It is the study of a machine operator and his movements for performing the job. The purpose is to eliminate useless motion and thereby establish a standard for performance. This study is undertook in order to develop a less time consuming system for accomplishing the work.
(iii) Fatigue study : Excessive specialization of work and poor working conditions may cause monotony resulting in both the physical and mental fatigue among the industrial workers. Fatigue either a physical or mental always has an adverse effect on worker’s health and his efficiency. The idea of this study is to see that workers maintain their operational efficiency without any injury to their health and happiness.
3. Principles of scientific selection and training : Scientific management requires a radical change in the methods and procedures of selecting workers for the plan. Hence, it is essential to entrust the task of selection to a central personnel department. After having selected the workers, every job must be entrusted to the’best worker in the factory. This depends upon the workers aptitude, skill and intelligence.
Under scientific management, the management has to undertake the training of workmen before allotting them certain tasks. Training should be imparted from time to time to improve the efficiency of labour.
4. Principles of justified division of work : According to the principle of division of work, work should be allotted to the right worker according to his choice and efficiency. This is called as right job to the right person.
5. Principles of incentive wage system : Taylor assumes that in addition to good wages, proper incentive should be given to the employees for getting proper attention towards the work. Taylor introduced ‘Differential Wage System’ in this regard. This implies that a worker who works as per the standards set should be paid more, in comparison to the inefficient worker, who does not work as per the standards set. In simple words, a worker who works more should receive more wages than the person who doesn’t.
![]()
Question 5.
Explain the principles of Fayol.
Answer:
Principles of administration or Management of Fayol: Fayol has mentioned 14 principles in his book, ‘General and Industrial Management’. As he has accepted administration and management as being synonyms, we can say it as principles of management.
These principles are as follows :
1. Principle of division of work : The object of division of work is to derive benefits from specialization. The various functions of management like planning, organization, coordination, control, etc., cannot be performed by a single proprietor or by a group of directors and they have to be entrusted to specialists in the related fields.
2. Principle of authority and responsibility: As management consists of getting the work done through others, it implies that the manager should have the right to give orders and the power to exact obedience. Thus, the manager gives order to his subordinates to perform the job as per his direction. A manager may exercise official authority and also personal authority. An individual to whom authority is given to exercise power must also be prepared to bear responsibility to perform the work.
3. Principle of discipline : Discipline is absolutely essential for the smooth running of the business. By discipline, we mean the obedience to authority, observance of the rules of service and norms of performance, respect for agreements, sincere efforts for completing the given job, respect to the superiors, etc.
Question 6.
Explain the nature of principles of management.
Or
Describe any six characteristics which clarify the nature of the principle of management.
Answer:
Nature/Characteristics of management principles: Management includes the qualities of both science and art that’s why management is called as a science or an art. The principles of management are not rigid and fixed like the principles of physics and chemistry. The main characteristics which highlight the nature of management principles are as follows:
(1) Universality of principles: Management principles can be applied to all manage
rial situations irrespective of the size (Small or large) and nature (Business government or social organization). That’s why Henri Fayol stressed on universality of management principles. Every organization or persons tries to achieve objectives through group efforts. Management principles can be implemented by the managers or directors in any level of management.
(2) Dynamic nature of principles : Management principles are dynamic in nature and flexible. These principles are not rigid and fixed like the principles of mathematics, physics and chemistry. Management principle changes due to cause and effect relationship. Management principles which were earlier important now have changed due to social changes. Management principles are dynamic in nature because these principles are directly related with human beings.
(3) Concentrated on human behavior: Management is totally related with human behavior. Management is related with persons. The success of management principles is affected by human behavior. Principles of management are directed towards enhancing human behavior so that the persons in organization give their best performance.
(4) Relative principles : Management principles are relative not absolute. These principles are implemented according to the needs of organization. It is not compulsory to apply these principles. Every organization, enterprise or society is having different type of nature. Thus due to different circumstances, assumptions, needs etc. accordingly the principles are applied in enterprises and organizations.
(5) Equal importance : All the principles of management are having equal importance. This is true that some principles are important for one organization while other principles may be important for other organization. But these principles are having some importance in all the organization.
(6) Cause and effect relationship : Management principles are always affected by cause and effect (result). Management principles establishes relationship between cause and result. These principles indicates the effect of an important decision on the activities of enterprise.
Question 7.
Write the characterstics of scientific management.
Answer:
Meaning of Scientific Management: Scientific management is made of two words science and management. Science is the application of logic, reasoning and it gives a new dimension to our study approach to different problems of life. When we apply scientific approach towards management concepts this is called as scientific management.
Following are the characteristics of scientific management:
- The objectives of every job in scientific management is fixed and predetermined,
- There is a fixed plan to attain objectives
- Mutal cooperation among employees is essential in scientific management
- Scientific management works on the objective of maximum production at minimum cast
- Motivation is considered necessary for the completion of work
- Scientific control system is implemented under scientific management
- Time to time evaluation of standards is performed
- Increase in efficiency of employees helps in increase in the income of employees
- Researches and experiments plays an important role in the field of scientific management
- Specialisation and division of work is also given importance
- Much stress is given on right person for the right job
- Responsibilities are assigned or fixed for every level of work.