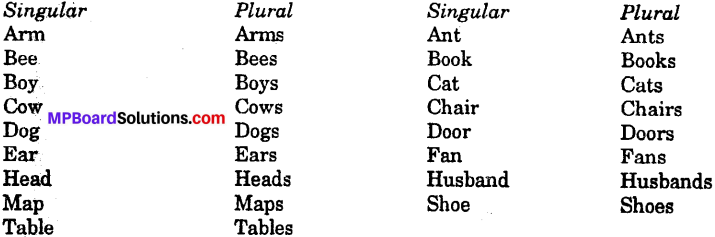
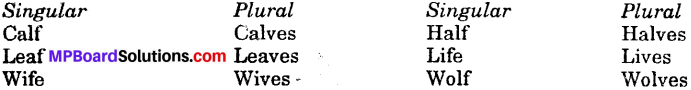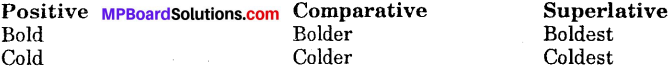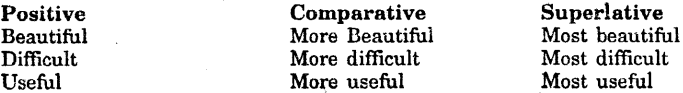Get Updated MP Board Solutions for Class 7 Special English Short Essay Writing Questions and Answers in PDF Format and download them free of cost. These are provided as per the latest exam pattern and syllabus. Access the topics of Chapter wise and communication skills, grammer part through the direct links available depending on the need. You can Download MP Board Class 7 English Solutions and can score highest grade in examination. Clear all your queries on the Mp Board Solutions for Class 7 English Chapter 21 Tansen Questions and Answers Subject by using the Madhya Pradesh State Board Solutions for existing.
MP Board Class 7th Special English Short Essay Writing
If you are eager to know about the Madhya Pradesh State Board Solutions for Class 7 English you will find all of them here. You can identify the knowledge gap using these MP Board Solutions for English PDF and plan accordingly. Don’t worry about the accuracy as they are given after extensive research by people having subject knowledge along side from the latest English Syllabus.
My School
I read in Sarvadaya Senior Secondary School, Bhopal, It is situated out of the town in a grove of trees.
The building of my school is’ very grand. There are twenty five class-rooms and a big hall. We have our library and the reading room in the hall. All the rooms are airy, neat and clean. We have electric light and’fans in each room
There are about twenty-five teachers in my school. Shri R.N. Goel is our Principal. All the teachers and the Principal are well qualified and trained. They are very hard working. All of them love us.
In front of the building there is the school garden. It is full of flower, plants and trees. There are many grassy lawns in the garden. Our school has a big play-ground. We play games there.
Vocabulary :
Grove – कुँज। Grand – शानदार। Airy – हवादार। Trained – प्रशिक्षित। Hard working परिश्रमी। Grass – घासवाला।
My Best Friend
I have many boys in my school. I like them all. But of all of them I like Harish the most. He is almost as old as I am He is tall, strong and handsome. He has a smiling face.
He likes all sorts of games. He does not care much for books. He likes jokes.
Both of us read in the same class. We sit together at the same bench. We have many habits in common. Both of us are good players. I generally stand
first in my class. My friends never feels jealous.
Both of us are helpful to each other. I often go to his village. His mother loves me just like her son. She is very glad to see me. His father is also a gentleman.
I like my friend because of his simple and noble nature. He is honest in all his dealings, he possesses a kind heart. He is God-fearing. He is always ready to help the poor and needy.
Vocabulary :
All sorts of – सब प्रकार के – In common-एक सी – Jealous-इर्ष्यालु – Thorough पूर्ण। Nature – स्वभाव। Dealings – व्यवहार। God-fearing – ईश्वर से डरने वाला।
The Postman
The postman is a useful public servant. He does an important duty. He brings our letters, parcels and money-orders. He goes from door to door. He knows each and every house of the street.
The postman wears a Khaki dress. He keeps a bag with him. He keeps the letters, parcels and money-orders in this bag. He knocks at the door. People wait for him He brings news from our friends and relatives.
The postman does more work. He reads out the letters for the villagers. Sometimes, he writes letters for them. The postman’s life is very hard. He gets a small salary. The prices of things are rising. The postman cannot support his family. So he gets some money from the people as gift.
The government should raise his salary.
Vocabulary :
Important – महत्त्वपूर्ण। Knocks at – खटखटाता है। Relatives – सम्बन्धी। Bitter – अघि क। Salary – वेतन। Support – पालन करना। Gift – उपहार। Raise – बढ़ाना।
The Policeman
The policeman is a useful public servant, he has an important work to do. He helps us in many ways. He keeps peace wherever he is on dut&
The policeman wears a khaki dress. He ties a red turban on his head. A whistle is a part of his dress. The dress of a traffic policeman is different. The policeman guards our property. He keeps law and order. He is on duty when we are sleeping. Thieves are afraid of him.
The traffic policeman controls the traffic. Without him, traffic cannot move safely on the roads.
His life is very hard. He is always ready for duty. He puts himself in dangers. He faces the dacoits. Sometimes, he loses his life in accidents.
The policeman does not get a good salary. He cannot support his family well. He cannot give good education to his children. So he takes bribe.
The government should raise his salary.
Vocabulary :
Peace – शांति। Turban – पगड़ी। Whistle – सीटी। Traffic – यातायात। Different – भिन्न। Guards – रक्षा करता है। property – सम्पत्ति। Controls – नियंत्रित करता है। Dacoits – डाकू। Bribe – रिश्वत
A Hockey Match that I Saw
Last Sunday a hockey match was played between the Kisan School and D.A.V. School. It was a very interesting match. It was played at the Ramlila ground. Many boys came to see the match.
At 4 p.m. the referee called the captains of the teams. The Kisan School won the toss. After this both the teams entered the ground. They were wearing colourful uniforms.
The players took their positions. The game started. It was very interesting. Both the teams were equal. The ball was running to and fro.
The players played with full force. Both the teams tried hard. But none could make a goal in the first half.
The players took oranges during the interval. Then the game started again. This time the fight was very hard.
The captain of the Kisan School team took the ball: He hit it. The goal keeper of the D.AV. School team tried to save the goal. But he failed. Thus the Kisan School team made a goal.
There were shouting of joy form the crowd. The time was over. The match ended. The Kisan School team won it. It was really an interesting match.
Vocabulary :
Interesting – रोचक। Colourful – रंग-बिरंगे। Uniform – पोशाक। To and from – इधर-उध पर। Crowd – भीड़। Interesting – मजेदार।
The Diwali Festival
Diwali is one of the most important Hindu festivals. It falls in the middle of Kartik. It means a ‘row of earthen lamps’. Every Hindu householder lights up earthen lamps at night. It marks the coming of winter.
The Hindus believe that God Ram returned to Ayodhya on this day after defeating Ravan. He was given a warm welcome by the people of Ayodhya. Lamps were lit up in his honour.
The Sikhs celebrate it because their Guru Govind Singh was set free by the Mughals on this day. The jains believe that Mahavir Swami got salvation on this day.
Many days before the festival people begin to clean, white wash afid decorate their houses. On the day of festival all schools, offices and courts are closed. All people, young and old, put on new clothes. There is loud noise of crackers on this day.
At night ‘Lakshmi’, the Goddess of wealth is worshipped. There is a great hustle and bustle in bazaars. The sweet-sellers earn money. Many businessmen close their old accounts and begin their new business year on this day.
Some people gamble to try their luek. But they are often^ruined. We should try to keep away from this evil practice.
Vocabulary :
Festival – त्यौहार। Falls – पड़ता है। Earthen-lamp – मिट्टी के दीपक। Marks – आरम्भ करता है। Salvation – निर्वाण। Decorate – सजाना। Crackers – पटाखे। Hustle and Bustle – शोर-गुल। Gamble – जुआ खेलना।
Prize Distribution Function in My School
Today is our prize distribution -day. Every year our school gives away prizes to pupils of merit. I was waiting early for the day. I was in high spirits on that day. The Director of Education was our chief guest He was to give away the prizes. He came at 5 p.m. The Principal received him The school band played a welcome tune. He took his seat and the function began.
Prayers were sung. Then came the welcome song. The principal read out the school’s annual report.
The chief guest rose. He addressed the audience. He spoke about the progress of the school. He praised the pupils and the staff. He gave some suggestions for more progress. He sat down. The audience clapped.
Then the prize distribution began. The winners walked up to the chief guest. They saluted him and received their prizes with smiles on their faces. They marched to their places.
I was among the winners. I had to go to the stage six times to get my prizes. My parents were proud of me. The function ended at 7 p.m There was a light refreshment for guests.
We left the school in gay mood. On the successful function the Principal declared one day’s holiday.
Vacabulary :
Merit – योग्यता। In high spirirt – उत्साहपूर्ण। Audience – श्रोतागण। Suggestion – प्रस्ताव।
A Cricket Match that I saw
Cricket is a good game. It has become very popular. It is played all over the world: Thousands of people see a cricket test match for hours together.
Last year our college played a cricket match against S. A.V. Inter College. The match was played on our ground. S.A.V. Inter College team won the toss and went in.
The match started at lo’clock. The two opening batsmen went in to bat. Our players took position for fielding. Our captain bowled. And lo ! the first ball knocked the wicket down. It was a bad start for S.A.V. Inter College team Another player walked in to bat, he played carefully. But after half an hour wickets began to fall rapidly. The whole team was out after securing 80 runs. Now lunch began.
After lunch our team started batting. Our opening batsmen played well. They secured 80 runs in an hour. After this our team scored 60 runs for the loss of six wickets. Our captain hit the sixers. The crowd cheered the team oiir team was out for 120 runs.
S.AV. Inter College team did not come next day to play the second innings. We won match.
Vocabulary :
Popular – लोकप्रिय। carefully – सावधानीपूर्व। Rapidly – तेजी से। cheered – उत्साहित किया।
The Cow
The cow is a domestic animal. She has four legs, two ears and two horns. She has a long tail. She keeps off flies with her tail. Her body is big. Cows are of different colours. Some cows are white, some are black and some are brown.
The cow” eat grass, straw and gram. She eats the oil cakes. She drinks water.
The cow is found every where in the world. American cows give more milk than Indian cows. In India the Hindus call her ‘Gau mata’.
The cow is a gentle animal She does not hurt anybody. Small children play with her. She is very intelligent.
She does not forget her master’s house.
The cow is a very useful animal. She gives us milk. Her milk is very useful for the children and the sick persons. We make sweets, ghee and curd from her milk. She giyes us calves which become bullocks. They plough our fields and draw carts.
Vocabulary :
Domestic – पालतू। Horns – सींग। Brown – कत्यई रंग की। Oil cakes – खल। Curd – दहि।
We believe the information shared regarding MP Board Solutions for Class 7 English Chapter 21 Tansen Questions and Answers as far as our knowledge is concerned is true and reliable. In case of any queries or suggestions do leave us your feedback and our team will guide you at soonest possibility. Bookmark our site to avail latest updates on several state board Solutions at your fingertips.