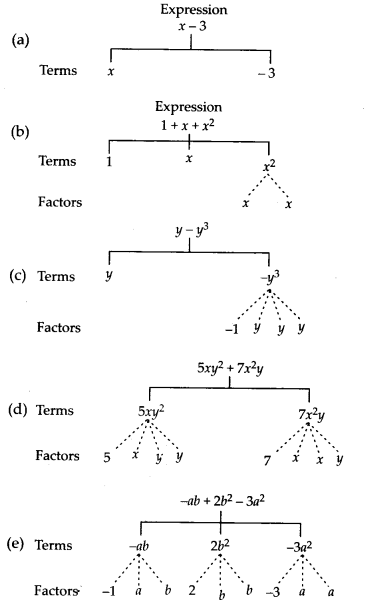
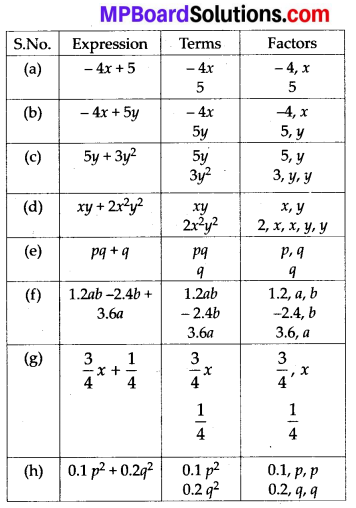
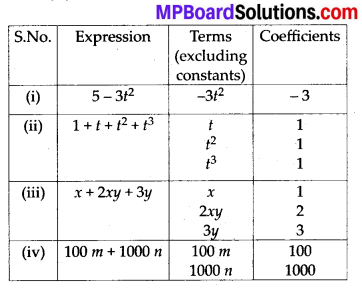
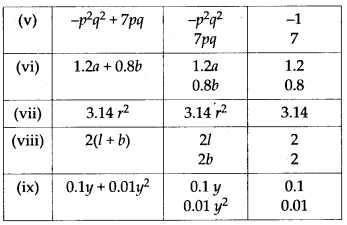
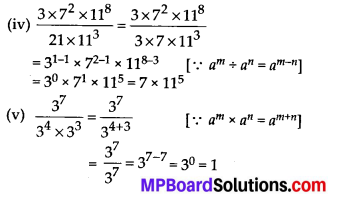
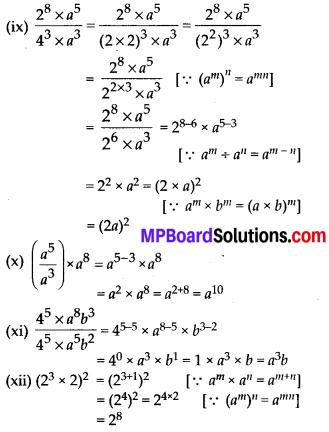
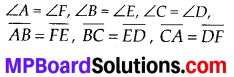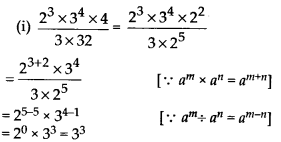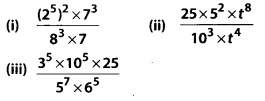MP Board Class 7th Maths Solutions Chapter 7 Congruence of Triangles Ex 7.2
Question 1.
Which congruence criterion do you use in the following?
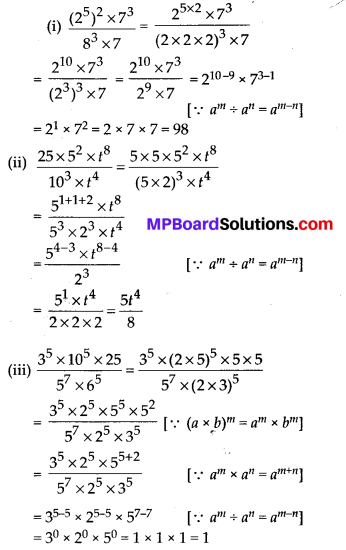
(a) Given: AC = DF
AB = DE
BC = EF
So, ∆ABC ≅ ∆DEF
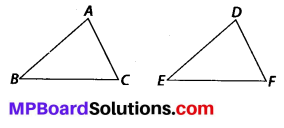
(b) Given: ZX = RP
RQ = ZY
∠PRQ = ∠XZY
So, ∆PQR ≅ ∆XYZ
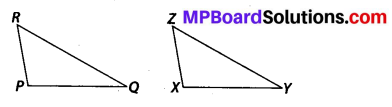
(c) Given: ∠MLN = ∠FGH
∠NML = ∠HFG
ML = FG
So, ∆LMN ≅ ∆GFH
(d) Given EB = BD
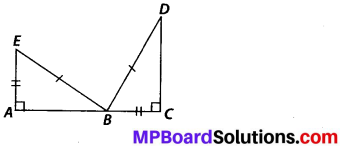
AE = CB
∠A = ∠C = 90°
So, ∆ABE ≅ ∆CDB
Solution:
(a) SSS, as all three sides of AABC are equal to the corresponding sides of ∆DEF.
(b) SAS, as two sides and the angle included between these sides of ∆PQR are equal to the corresponding sides and included angle of ∆XYZ.
(c) ASA, as two angles and the side included between these angles of ∆LMN are equal to the corresponding angles and included side of ∆GFH.
(d) RHS, as in the given two right-angled triangles, one side and the hypotenuse are respectively equal.
Question 2.
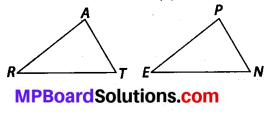
You want to show that ∆ART ≅ ∆PEN,
(a) If you have to use SSS criterion, then you need to show
(i) AR =
(ii) RT =
(iii) AT =
(b) If it is given that ∠T = ∠N and you are to use SAS criterion, you need to have
(i) RT = and
(ii) PN =
(c) If it is given that AT = PN and you are to use ASA criterion, you need to have
Solution:
(a) (i) AR = PE
(ii) RT = EN
(iii) AT = PN
(b) (i) RT = EN
(ii) PN = AT
(c) (i) ∠ATR = ∠PNE
(ii) ∠RAT = ∠EPN
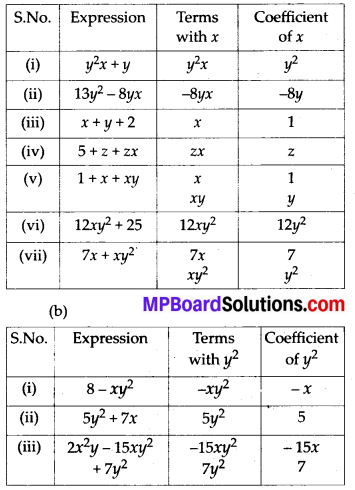
Question 3.
You have to show that ∆AMP ≅ ∆AMQ
In the following proof, supply the missing reasons.
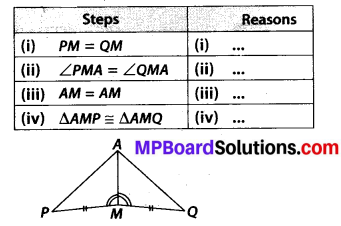
Solution:
(i) Given
(ii) Given
(iii) Common
(iv) SAS congruence criterion, as the two sides and the angle included between these sides of ∆AMP are equal to corresponding sides and included angle of ∆AMQ.
Question 4.
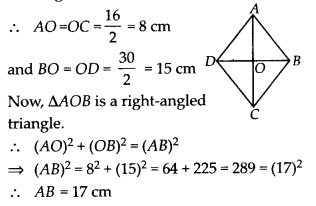
In ∆ABC, ∠A = 30°, ∠B = 40° and ∠C = 110°
In ∆PQR, ∠P = 30°, ∠Q = 40° and ∠R = 110°
A student says that ∆ABC ≅ ∆PQR by AAA congruence criterion. Is he justified? Why or why not?
Solution:
No. This property represents that these triangles have their respective angles of equal measure. However, this does not give any information about their sides. The sides of these triangles may have a ratio different from 1 : 1. Therefore, AAA property does not prove that two triangles are congruent.
![]()
Question 5.
In the figure, the two triangles are congruent. The corresponding parts are marked. We can write ∆RAT ≅ ?
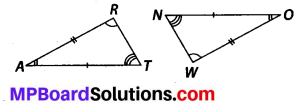
Solution:
It can be observed that,
∠RAT = ∠WON
∠ART = ∠OWN
AR = OW
Therefore, ∆RAT ≅ ∆WON, by ASA criterion.
Question 6.
Complete the congruence statement:
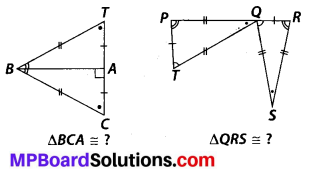
Solution:
In ∆BCA and ∆BTA,
BC = BT (given)
TA = CA (given)
BA is common.
Therefore, ∆BCA ≅ ∆BTA
(by SSS congruence criterion)
Now, in AQRS and ATPQ,
∠RQS = ∠PTQ (given)
RQ = PT (given)
∠SRQ = ∠QPT (given)
Therefore, ∆QRS = ∆TPQ
(by ASA congruence criterion)
![]()
Question 7.
In a squared sheet, draw two triangles of equal areas such that
(i) the triangles are congruent.
(ii) the triangles are not congruent. What can you say about their perimeters?
Solution:
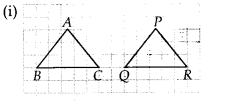
Here, ∆ABC and ∆PQR have the same area and are congruent to each other also. Also the perimeter of both the triangles will be the same.
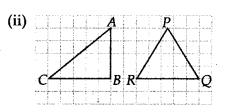
Here, ∆ABC and ∆PQR have the same height and same base. Thus, their areas are equal. However, these triangles are not congruent to each other. Also, the perimeter of both the triangles will not be the same.
Question 8.
Draw a rough sketch of two triangles such that they have five pairs of congruent parts but still the triangles are not congruent.
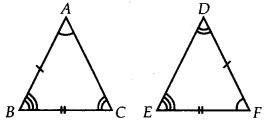
Solution:
∆ABC & ∆DEF are not congruent to each other but have five congruent parts i.e., ∠BAC = ∠EFD, ∠ABC = ∠DEF, ∠BCA = ∠EDF, AB = DF and BC = EF
![]()
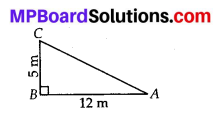
Question 9.
If ∆ABC and ∆PQR are to be congruent, name one additional pair of corresponding parts. What criterion did you use?
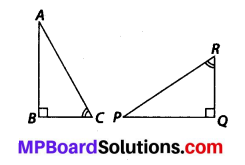
Solution:
∠ABC = ∠PQR = 90° and
∠BCA = ∠QRP (Given)
For triangles to be congruent, BC = QR
∆ABC ≅ ∆PQR (ASA congruence criterion)
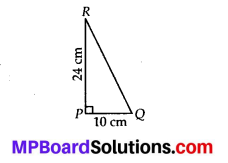
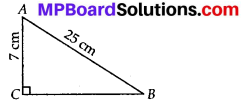
Question 10.
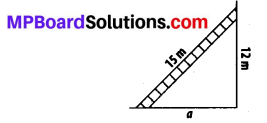
Explain, why ∆ABC ≅ ∆FED
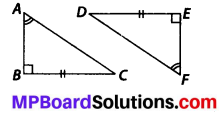
Solution:
Given that, ∠ABC = ∠FED = 90° and ∠BAC = ∠EFD
The two angles of ∆ABC are equal to the two respective angles of ∆FED. Also, the sum of all interior angles of a triangle is 180°. Therefore, third angle of both triangles will also be equal in measure.
∴ ∠BCA = ∠EDF
Now, in ∆ABC and ∆FED,
∠ABC = ∠FED, BC = ED and ∠BCA = ∠EDF
⇒ ∆ABC = ∆FED
(ASA congruence criterion)
![]()