MP Board Class 10th Science Solutions Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compounds
MP Board Class 10th Science Chapter 4 Intext Questions
Intext Questions Page No. 61
Question 1.
What would be the electron dot structure of carbon dioxide which has the formula CO2?
Answer:
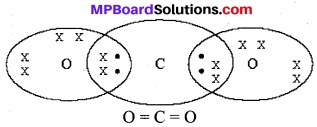
Question 2.
What would be the electron dot structure of a molecule of sulphur which is made up of eight atoms of sulphur? (Hint: The eight atoms of sulphur are joined together in the form of a ring).
Answer:

Intext Questions Page No. 68,69
Question 1.
How many structural isomers can you draw for pentane?
Answer:
Three structural isomers are possible for pentane.
Question 2.
What are the two properties of carbon which lead to the huge number of carbon compounds we see around us?
Answer:
The two features of carbon that give rise to a large number of compounds are as follows:
- Carbon has the unique ability to form bonds with other atoms of carbon, giving rise to large molecules. This property is called catenation.
- Since carbon has a valency of four, it is capable of bonding with four other atoms of carbon or atoms of some other mono-valent element.
![]()
Question 3.
What will be the formula and electron dot structure of cyclopentane?
Answer:
The formula for cyclopentane is C5H10. Its electron dot structure is given below:
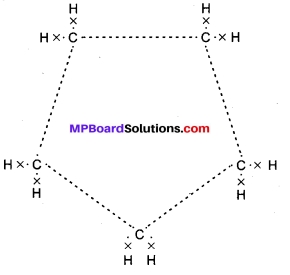
Question 4.
Draw the structures for the following compounds:
(i) Ethanoic acid
(ii) Bromopentane
(iii) Butanone
(iv) Hexanal
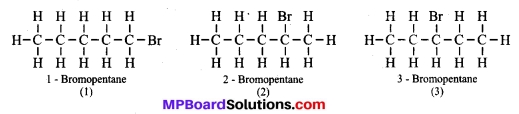
Are structural isomers possible for bromo-pentane?
Answer:
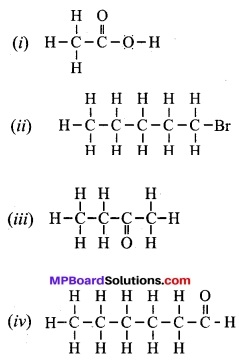
Yes, there are many structural isomers possible for bromo-pentane. Among them, the structures of the three isomers are given.
Question 5.
How would you name the following compounds?
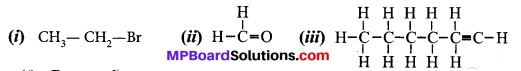
Answer:
(i) Bromoethane
(ii) Methanal (formaldehyde)
(iii) Hexyne.
Intext Questions Page No. 71
Question 1.
Why is the conversion of ethanol to ethanoic acid an oxidation reaction?
Answer:
Addition reaction means adding oxygen. Adding ethanol to potassium permanganate, we get ethanoic acid. Hence this reaction is called oxidation reaction.
![]()
Since in this reaction one oxygen is added to ethanol, hence it is an oxidation reaction.
Question 2.
A mixture of oxygen and ethyne is burnt for welding. Can you tell why a mixture of ethyne and air is not used?
Answer:
If a mixture of oxygen and ethyne is burnt, then ethyne burns completely producing a blue flame. The oxygen ethyne flame is extremely hot and produces a very high temperature which is used for welding metals. A mixture of ethyne and air is not used for welding because the burning of ethyne in air produces a sooty flame due to incomplete combination which is not enough to melt metals for welding.
Intext Questions Page No. 74
Question 1.
How would you distinguish experimentally between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid?
Answer:
- We can distinguish between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid on the basis of their reaction with carbonates and hydrogen carbonates. The acid reacts with carbonate and hydrogen carbonate to evolve CO2 gas that turns lime-water milky.
- Metal carbonate/Metal hydrogen carbonate + Carboxylic acid → Salt + Water + Carbon dioxide.
- In the litmus test, alcohol shows no change in colour whereas carboxylic acid turns blue litmus red.
With sodium metal, alcohol gives effervescence but carboxylic acid does not give it. Alcohols, on the other hand, do not react with carbonates and hydrogen carbonates.
![]()
Question 2.
What are oxidising agents?
Answer:
some substances are capable of adding oxygen to others. These substances are known as oxidising agents.
Intext Questions Page No. 76
Question 1.
Would you be able to check if the water is hard by using a detergent?
Answer:
Margents are remaining effective in hardwater. Because of this reason, we can check if water is hard by using a detergent.
Question 2.
People use a variety of methods to wash clothes. Usually after adding the soap, they ‘beat’ the clothes on a stone, or beat it with a paddle, scrub with a brush or the mixture is agitated in a washing machine. Why is agitation necessary to get clean clothes?
Answer:
The soap molecules form structures called micelles in water, where one end of the molecules is towards the oil droplet while the ionic end-faces outside. This forms emulsion in water and we can wash our clothes clean.
MP Board Class 10th Science Chapter 4 Ncert Textbook Exercises
Question 1.
Ethane, with the molecular formula C2H6 has –
(a) 6 covalent bonds
(b) 7 covalent bonds
(c) 8 covalent bonds
(d) 9 covalent bonds
Answer:
(b) 7 covalent bonds.
Question 2.
Butanone is a four-carbon compound with the functional group.
(a) Carboxylic acid
(b) Aldehyde
(c) Ketone
(d) Alcohol
Answer:
(c) Ketone.
Question 3.
While cooking, if the bottom of the vessel is getting blackened on the outside, it means that.
(a) The food is not cooked completely.
(b) The fuel is not burning completely.
(c) The fuel is wet.
(d) The fuel is burning.
Answer:
(b) the fuel is not burning completely
Question 4.
Explain the nature of the covalent bond using the bond formation in CH3Cl.
Answer:
The structure of CH3Cl is given below:
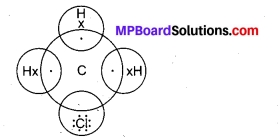
Carbon has four valence electrons. It shares one electron each with three hydrogen atoms and one electron with chlorine. The bond between C and Cl atoms is covalent but due to higher value of electro-negativity of Cl, the C-Cl bond is polar in nature.
Question 5.
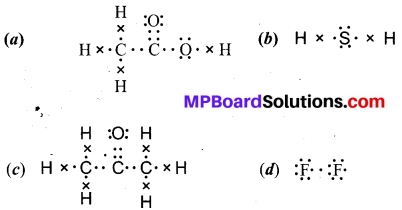
Draw the electron dot structures for:
(a) Ethanoic acid
(b) H2S
(c) Propanone
(d) F2
Question 6.
What is a homologous series? Explain with an example?
Answer:
A series of compounds in which the same functional group substitutes for hydrogen in a carbon chain is called a homologous series.
Eg: CH4 and C2H6 – These differ by a CH2 unit.
C2H6 and C3H8 – these differ by a CH2 unit.
Question 7.
How can ethanol and ethanoic acid be differentiated on the basis of their physical and chemical properties?
Answer:
Ethanol and Ethanoic acid can be differentiated on the basis of their following properties by:
- Ethanol is a liquid at room temperature with a pleasant smell. Ethanoic acid has a melting point of 17°C. Since it is below the room temperature so, it freezes during winter. Moreover, ethanoic acid has a smell like vinegar.
- Ethanol does not react with metal carbonates while, ethanoic acid reacts with metal carbonates to form a salt, water and carbon dioxide.
For example:
2CH3COOH + Na2CO3 → 2CH3COONa + CO2 +H2O - Ethanol does not react with NaOH while ethanoic acid reacts with NaOH to form sodium ethanoate and water.
For example,
CH3COOH + NaOH → CH3COONa + H2O - Ethanol is oxidized to give ethanoic acid in the presence of acidified KMnO4 while no reaction takes place with ethanoic acid in the presence of acidified KMnO4.
Difference in physical properties:
| Ethanol | Ethanoic acid |
| This is in liquid form at room temperature. Its melting point is 156° K. | Its melting point is 290K and hence it often freezes during winter in cold climates. |
| Difference in chemical properties | |
| Ethanol will not react with metallic carbonates. | Ethanoic acid reacts with carbonates and Hydrogen carbonate and forms salts, carbon dioxide and water. |
Question 8.
Why does micelle formation take place when soap is added to water? Will a micelle be formed in other solvents such as ethanol also?
Answer:
Soaps are molecules in which the two ends have differing properties, one is hydrophilic that is, it interacts with water, while the other end is hydrophobic, that is it interacts with hydrocarbons. When soap is at the surface of water, the hydrophobic tail of soap will not be soluble in water and the soap will align along the surface of water with the ionic end in water and the hydrocarbon tail protruding out of water. Thus, clusters of molecules in which the hydrophobic tails are in the interior of the cluster and the ionic ends are on the surface of the cluster. This formation is called a micelle. Soap in the form of a micelle is able to clean. A micelle will not be formed in other solvents such as ethanol.
Question 9.
Why are carbon and its compounds used as fuels for most applications?
Answer:
Carbon and its compounds give large amount of heat on combustion due to the high percentage of carbon and hydrogen. Carbon compounds used as fuel have optimum ignition temperature with high calorific values and are easy to handle. Their combustion can be controlled. Therefore, carbon and its compounds are used as fuels.
![]()
Question 10.
Explain the formation of scum when hard water is treated with soap.
Answer:
When soap reacts with water, calcium and magnesium salts are formed which causes hardness for water. Ionic ends of soap interacts with water while the carbon chain interacts with oil. The soap molecules, thus form structures called micelles where one end of the molecules is towards the oil droplet while the ionic-end faces outside. This forms an emulsion in water.
Question 11.
What change will you observe if you test soap with litmus paper (red and blue)?
Answer:
Since soap is basic in nature, it will turn red litmus blue. However, the colour of the blue litmus will remain blue.
Question 12.
What is hydrogenation? What is its industrial application?
Answer:
Unsaturated Hydrocarbons react with Hydrogen, in presence of catalysts such as palledium or Nickel and forms saturated Hydrocarbons. This is called Hydrogenation of oils.
This process is useful in hydrogenation of oils derived from plants.
![]()
Question 13.
Which of the following hydrocarbons undergo addition reactions:
C2H6, C3H8, C3H6, C2H2 and CH4.
Answer:
Unsaturated hydrocarbons undergo addition reactions. Being unsaturated hydrocarbons, C3H6 and C2H2 undergo addition reactions.
Question 14.
Give a test that can be used to differentiate between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Answer:
Saturated Hydrocarbons will not react with Bromine, but unsaturated hydrocarbons change the colour of Bromine.
Question 15.
Explain the mechanism of the cleaning action of soaps.
Answer:
The dirt present on clothes is organic in nature and insoluble in water. Therefore, it cannot be removed by washing with water only. When soap is dissolved in water, its hydrophobic ends attach themselves to the dirt and remove it from the cloth. Then, the molecules of soap arrange themselves in micelle formation and trap the dirt at the centre of the cluster. These micelles remain suspended in the water. Hence, the dust particles are easily rinsed away by water.
MP Board Class 10th Science Chapter 4 Additional Questions
MP Board Class 10th Science Chapter 4 Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Which of the following is a three-carbon compound?
(a) Ethene
(b) Ethane
(c) Propane
(d) Acetylene
Answer:
(c) Propane
Question 2.
Which one of the following is an unsaturated hydrocarbon?
(a) Acetylene
(b) Butane
(c) Propane
(d) Decane
Answer:
(a) Acetylene
Question 3.
Two neighbours of homologous series differ by:
(a) -CH
(b) -CH2
(c) -CH3
(d) -CH4
Answer:
(b) -CH2
Question 4.
General formula of alkanes is –
(a) CnH2n+2
(b) CnH2n
(c) CnH2n-2
(d) CnHn
Answer:
(a) CnH2n+2
![]()
Question 5.
Which of the following represents alkynes?
(a) -C – C-
(b) -C = C-
(c) -C ≡ C-
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) -C ≡ C-
Question 6.
Which of the following represents ketones?
(a) -C = O
(b) -OH
(c) -CHO
(d) COOH
Answer:
(a) -C = O
Question 7.
Which of the following is not an aliphatic hydrocarbon?
(a) ethene
(b) ethane
(c) propyne
(d) benzene
Answer:
(d) benzene
Question 8.
Complete combustion of a hydrocarbon gives:
(a) CO + H2O
(b) CO2 + H2O
(c) CO + H2
(d) CO2 + H2
Answer:
(b) CO2 + H2O
Question 9.
Which is NOT correct for isomers of a compound?
(a) They differ in physical properties.
(b) They differ in chemical properties.
(c) They have the same molecular formula.
(d) They have the same structural formula.
Answer:
(d) They have the same structural formula.
Question 10.
Buckminsterfullerene is an example of ………….. of carbon.
(a) an isomer
(b) an isotope
(c) an allotrope
(d) a functional group
Answer:
(c) an allotrope
Question 11.
Who prepared urea for the first time by heating ammonium cyanate?
(a) Wohler
(b) Lavoisier
(c) Fuller
(d) Haber
Answer:
(a) Wohler
Question 12.
Hexanone is a four-carbon compound with the functional group:
(a) Carboxylic acid
(b) Aldehyde
(c) Ketone
(d) Alcohol
Answer:
(c) Ketone
Question 13.
Major constituent of LPG is ………….
(a) Ethene
(b) Butane
(c) Propane
(d) Pentane
Answer:
(b) Butane
Question 14.
The gas used in welding and cutting metals is:
(a) Ethyne
(b) Ethene
(c) Ethane
(d) Propane
Answer:
(a) Ethyne
![]()
Question 15.
How is carbon atoms arranged in Buckminster fullerenes?
(a) Triangle shape
(b) Hexagonal array
(c) Football shape
(d) None
Answer:
(c) Football shape
Question 16.
Vinegar is a solution of –
(a) 40%-45% acetic acid.
(b) 90%-95% acetic acid.
(c) 5-20% acetic acid and water.
(d) 35-40% acetic acid and water.
Answer:
(c) 5-20% acetic acid and water.
Question 17.
How many covalent bonds are there in Bromoethane?
(a) 4
(b) 6
(c) 10
(d) 7
Answer:
(d) 7
Question 18.
Which functional group is present in propane?
(a) Aldehyde
(b) No group
(c) Ketone
(d) Alcohol
Answer:
(b) No group
Question 19.
Which compound/molecule is being presented by the following formula: H: C:: C: H
(a) Ethane
(b) Ethene
(c) Ethyne
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Ethene
Question 20.
Next homologous to C2H5OH will be:
(a) CH4
(b) C2H6
(c) C3H5
(d) C3H7OH
Answer:
(d) C3H7OH
Question 21.
When we burn naphthalene it produces:
(a) Smoky flame
(b) Non-sooty flame
(c) Colourless flame
(d) No flame
Answer:
(a) Smoky flame
Question 22.
Bunsen burner is used for:
(a) making food.
(b) study flames type.
(c) low heating work.
(d) all the above.
Answer:
(c) low heating work.
Question 23.
See the figure carefully.
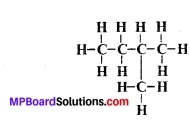
Choose the suitable name of isomer:
(a) Neo-pentane
(b) n-pentane
(c) Iso-pentane
(d) All
Answer:
(c) Iso-pentane
Question 24.
Which of the following is a structure of ethanoic acid?
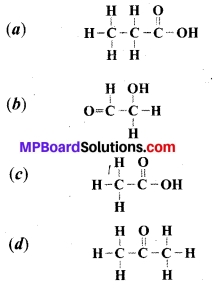
Answer:
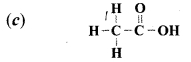
Question 25.
What is the name of CH3-CH2-Br? Choose from the following:
(a) Hex-1-one
(b) Hexanal
(c) Ethanoic acid
(d) None
Answer:
(d) None
Question 26.
What happens on the litmus test of soap?
(a) No change
(b) Red litmus turns blue
(c) Red litmus turn purple
(d) Red litmus turn green
Answer:
(b) Red litmus turns blue
MP Board Class 10th Science Chapter 4 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name two groups which can have the same general formula.
Answer:
Both alkenes and cyclo-alkanes can be represented by the same general formula.
Question 2.
Which group of compounds have general formula C2H2n?
Answer:
The general formula CnH2n represents alkenes group of compounds.
Question 3.
What is the common name and IUPAC name for CH3COCH3?
Answer:
Acetone is the common name and propanone is the IUPAC name for CH3COCH3.
Question 4.
Do isomers always show same chemical properties?
Answer:
No, isomers always do not show the same chemical properties.
Question 5.
What is the common name and formula for ethanol?
Answer:
Alcohol, CH3CH2OH.
Question 6.
What are the products of complete combustion of a hydrocarbon?
Answer:
Carbon dioxide and water.
Question 7.
What is next homologue of C3H7OH is called?
Answer:
The next homologue of C3H7OH is called butanol C4H9OH.
Question 8.
What are isomers?
Answer:
The compounds which have the same molecular formula but different structures and chemical properties are called isomers.
Question 9.
Which one are more reactive unsaturated hydrocarbons or saturated hydrocarbons? Give reason.
Answer:
Unsaturated hydrocarbons: The Presence of double and triple covalent bonds make them more reactive.
Question 10.
Discuss the general nature of covalent compounds in water.
Answer:
Generally, they are insoluble in water.
Question 11.
What type of hydrocarbons takes part in an addition reaction?
Answer:
Unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Question 12.
Which carboxylic acid freezes during winter or under cold climate conditions?
Answer:
Acetic acid and hence, known as glacial acetic acid.
Question 13.
What is the difference in molecular masses of any two successive homologous alkanes?
Answer:
14 units.
Question 14.
What is the molecular formula of the alcohol which can be derived from propane?
Answer:
Alcohol obtained from propane is propanol -1 and the molecular formula is C3H7OH.
Question 15.
Give the names of the functional groups: (CBSE 2007)
- -CHO
- -COOH
Answer:
- Aldehydic group.
- Carboxylic acid group.
Question 16.
Give the names of the following functional groups: (CBSE 2007)
- -OH
- -CO
Answer:
- Alcoholic.
- Ketonic.
MP Board Class 10th Science Chapter 4 Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is meant by the term functional group?
Answer:
An atom or a group of atoms, which makes a carbon compound reactive and decides its properties, is called a functional group.
For example aldehyde, ketone etc.
Question 2.
Which R functional groups always occur at the terminal position of a carbon chain?
Answer:
Aldehydic Group, R-CHO (R is the alkyl group),
Carboxyl Group, R-COOH (R is the alkyl group)
![]()
Question 3.
Why a candle flame burns yellow, while a highly-oxygenated gas fuel flame burns blue?
Answer:
The most important factor determining the colour of the flame is oxygen supply and the extent of fuel-oxygen, which determines the rate of combustion and thus, the temperature and reaction paths, thereby producing different colour hues. In case of a candle, it is incomplete combustion and the flame temperature is not high. This gives a yellow flame, while a highly-oxygenated gas (e.g., ethyne) flame burns blue because of complete combustion raising a very high temperature.
Question 4.
Why is the reaction between methane and chlorine considered a substitution reaction? (CBSE 2008)
Answer:
Methane reacts with chlorine in the presence of sunlight to form chloromethane and hydrogen chloride. Since chlorine substitutes or replaces hydrogen of methane to form chloromethane, it is considered as substitution reaction.
CH4 + Cl2 → CH3Cl + HCl
With the excess of chlorine, four hydrogen atoms of methane are replaced by chlorine atoms to form carbon tetrachloride (CCl4).
Question 5.
Why does carbon form compounds mainly by covalent bonding?
Answer:
Being tetravalent carbon atom, it is neither capable of losing all of its four valence electrons nor it can easily accept four electrons to complete its octet. Both of these are requirements of ionic bond formation and are energetically less favourable. Carbon completes its octet by sharing electrons and hence, covalent bonding is preferred.
Question 6.
What do you mean by Octane rating?
Answer:
Gasoline is rated on a scale known as octane rating, which is based on the way they burn in an engine. The higher the octane rating, the greater the percentage of complex-structured hydrocarbons that are present in the mixture, the more uniformly the gasoline burns, and the less knocking there is in the automobile engine. Thus, a gasoline rated 92 octane will burn more smoothly than one rated 87 octanes.
Question 7.
What is covalent bonding?
Answer:
The chemical bonding that takes place due to the mutual sharing of electron pairs of two or more atoms of different elements is called covalent bonding. By mutual sharing of electron pairs, atom attains noble gas configuration, e.g., hydrogen molecule (H2), the two H-atoms combine by covalent bonding (H-H).
Question 8.
What are hydrocarbons? Give examples.
Answer:
Compounds of carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbons. Methane, ethane, butane, ethyne, propane, benzene, petroleum products – all are examples of hydrocarbons.
Question 9.
What are saturated hydrocarbons? (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
The hydrocarbons in which valency of carbon is satisfied by a single covalent bond are called saturated hydrocarbons. Alkanes like methane (CH4), ethane(C2H6), propane (C3H8) etc. are examples of saturated hydrocarbons. Saturated hydrocarbons will generally give a clean flame.
Question 10.
Why do ionic compounds have high melting points? (HOTS)
Answer:
Ions have strong electrostatic forces of attraction among them forming ionic compounds. It requires a lot of energy to break these ionic bonds or forces. That’s why ionic bonds have high melting points.
Question 11.
What are homologous series? (HOTS)
Answer:
Homologous series are:
- Compounds with the same formula.
- Belong to the same functional group.
- Have general methods of separation.
- Have similar chemical properties.
Show similar gradation of physical properties, e.g., boiling points of alcohol increase with an increase in their molecular weights. Similarly, solubility decreases with increase in molecular weights.
Question 12.
What is a heteroatom? What is the heteroatom in the alcohol functional group? (HOTS)
Answer:
In a hydrocarbon chain, one or more hydrogen atoms can be replaced by other atoms according to their valencies. The element wh replaces hydrogen in the chain is called a heteroatom, e.g., in alcohol (-OH) functional group, oxygen is the heteroatom.
MP Board Class 10th Science Chapter 4 Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Distinguish between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons by the way of their burning in air and bromine test inferences.
Answer:
1. Saturated compounds are burnt in air, to give a clear (blue) flame but the burning of unsaturated compounds (alkenes and alkynes) give a sooty (yellowish) flame because saturated compounds contain comparatively less percentage of carbon which is completely oxidized by the oxygen present in the air.
On the other hand, the percentage of carbon in unsaturated compounds is more and it requires more oxygen to get completely oxidized that is not fulfilled by air. So, due to incomplete oxidation, they burn with a sooty flame.
2. Bromine-water test: Br2 water is a brown coloured liquid:
- Unsaturated hydrocarbons give addition reaction with Br2. So, the colour of Br2 water gets decolourised.

- Saturated hydrocarbons do not react with Br2 water, so the colour of B2-water does not get decolourised.
Question 2.
Two compounds A and B react with each other in the presence of a dehydrating agent to produce an ester. Both react with Na to evolve hydrogen gas. On reaction with Na2CO3, only A evolves CO2. Identify the functional groups present in A and B giving the reason for your answer.
Answer:
Compound A contains -COOH group while compound B contains -OH group. Since, carboxylic acids and alcohols react with each other to form an ester, out of A and B, one is an alcohol and the other is a carboxylic acid. This is further strengthened by the reaction of both with Na to evolve hydrogen gas. Only carboxylic acids react with Na2CO3 to evolve CO2, A contains -COOH group while B contains -OH group.
![]()
Question 3.
An organic compound ‘X’ is widely used as a preservative in pickles and has a molecular formula C2H2O2. This compound reacts with ethanol to form a sweet-smelling compound ‘Y’.
- Identify the compound ‘X’.
- Write the chemical equation for its reaction with ethanol to form compound ‘Y’.
- How can we get compound ‘X’ back from ‘Y’?
- Name the process and write a corresponding chemical equation.
- Which gas is produced when compound ‘X’ reacts with washing soda? Write the chemical equation.
- Answer:
- Compound X is ethanoic acid which gives and ester (Y) when reacts with ethanol.
- CH3COOH + CH3CH2OH → CH3COOC2H5.
- Esters give back alcohol and carboxylic acid in the presence of acid or base.
- Saponification reaction: CH3COOC2H5 + NaOH → C2H5OH + CH3COOH + Na.
- CO2 gas is released,
CH3COOH + Na2CO3 → 2CH3COONa + H2O + CO2.
Question 4.
“Saturated hydrocarbons burn with a blue flame while unsaturated hydrocarbons burn with a sooty flame.” Why?
Answer:
Saturated hydrocarbons have only C-C and C-H single bonds and thus, contain the maximum possible number of hydrogen atoms per carbon atom. With sufficient oxygen, saturated hydrocarbons burn completely and give blue flame,
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
Unsaturated hydrocarbons contain a carbon-carbon double bond (C=C) or triple bond (C=C). Hence, they contain less number of hydrogen than carbon. Unsaturated hydrocarbons undergo incomplete combustion and give yellow flame along with black sooty carbon.
C2H4 + O2 → CO2 + 2H2O + C(s)
Question 5.
What makes some molecular formula compound different? (HOTS)
Answer:
The arrangement makes them different compounds with identical molecular formula but different structures are called structural isomers. Organic compounds show a great level of isomerism. Isomers may be structural (due to difference in the arrangement of C atoms forming chain) or stereo (due to arrangement of bonds in a chain). With the increase in the number of carbon atoms in molecular formula, it leads to an increase in the number of isomers.
For example:

MP Board Class 10th Science Chapter 4 Textbook Activities
Class 10 Science Activity 4.1 Page No. 58
- Make a list of ten things you have used or consumed since the morning.
- Compile this list with the lists made by your classmates and then sort the items into the following table.
- If there are items which are made up of more than one material, put them into both the relevant columns.
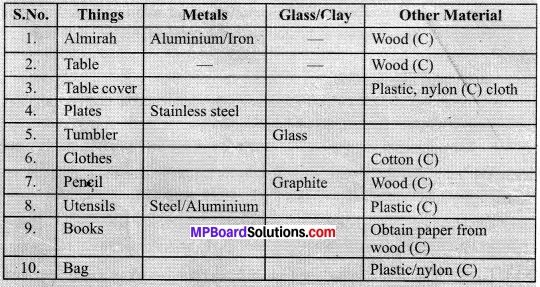
- (C) Indicates carbon. Most substances contain carbon in it.
Class 10 Science Activity 4.2 Page No. 67
- Calculate the difference in the formulae and molecular masses for
(a) CH3OH and C2H5OH.
(b) C2H5OH and C3H7OH.
(c) C3H7OH and C4H9OH. - Is there any similarity between these three?
- Arrange these alcohols in the order of increasing carbon atoms to get a family. Can we call this family a homologous series?
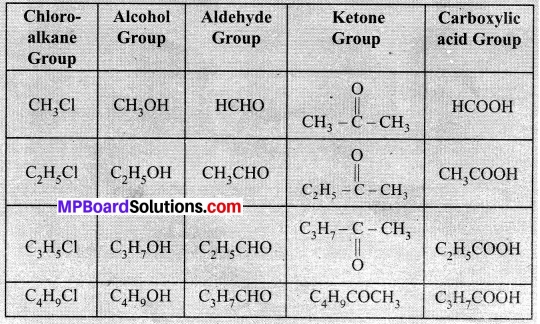
- Generate the homologous series for compounds containing up to four. carbons for the other functional groups given in the above table.
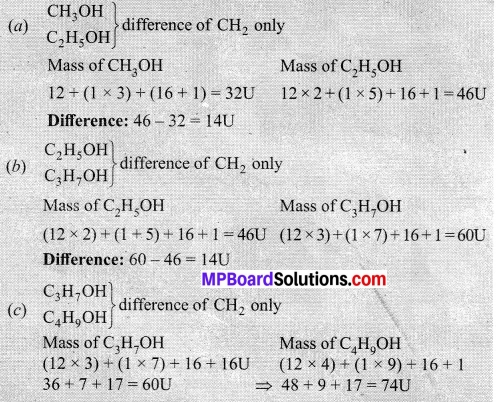
Difference: 70 – 60 = 14U
All three groups given above are homologous.
Class 10 Science Activity 4.3 Page No. 69
Caution:
- This Activity needs the teacher’s assistance.
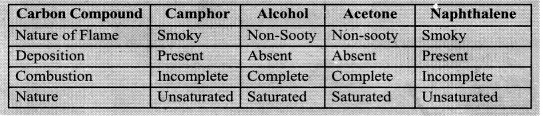
- Take some carbon compounds (naphthalene, camphor, alcohol) one by one on a spatula and burn them.
- Observe the nature of the flame and note whether smoke is produced.
- Place a metal plate above the flame. Is there a deposition on the plate in case of any of the compounds?
Observations:
Class 10 Science Activity 4.4 Page No. 69
- Light a bunsen burner and adjust the air hole at the base to get different types of flames/presence of smoke.
- When do you get a yellow, sooty flame?
- When do you get a blue flame?
Observations:
- Yellow, Sooty flame is formed – when the hole is closed.
- A blue flame is observed – when the hole is open.
Class 10 Science Activity 4.5 Page No. 70
- Take about 3 ml of ethanol in a test tube and warm it gently in a water bath.
- Add a 5% solution of alkaline potassium permanganate drop by drop to this solution.
- Does the colour of potassium permanganate persist when it is added initially?
- Why does the colour of potassium permanganate not disappear when excess is added?
Observations:
Doing the above activities we found that potassium permanganate act here as oxidising agents only and their colour do not change at,
![]()
Class 10 Science Activity 4.6 Page No. 72
Teacher’s demonstration:
- Drop a small piece of sodium, about the size of a couple of grains of rice, into ethanol (absolute alcohol).
- What do you observe?
- How will you test the gas evolved?
Observations:
Sodium is an inflammable substance hence, it should be handled very carefully. When we place it in alcohol, hydrogen gas is evolved and sodium ethoxide is formed,
2Na + 2CH3CH2OH → 2CH3CH2ONa+ + H2 ↑
Class 10 Science Activity 4.7 Page No. 73
- Compare the pH of dilute acetic acid and dilute hydrochloric acid using both litmus paper and universal indicator.
- Are both acids indicated by the litmus test?
- Does the universal indicator show them as equally strong acids?
Observations:
The litmus test and pH test show the acidity and alkalinity of substance or chemical:

Class 10 Science Activity 4.8 Page No. 73
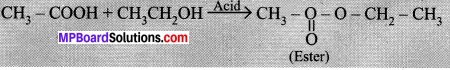
- Take 1 ml ethanol (absolute alcohol) and 1 ml glacial acetic acid along with a few drops of concentrated sulphuric acid in a test tube.
- Warm in a water-bath for at least five inutes as shown in Figure.
- Pour into a beaker containing 20-50 ml of water and smell the resulting mixture.

Observations:
When acetic acid reacts with alcohol a new compound with an ester functional group is formed. It has fruit like smell. This reaction is called esterification reaction.
Class 10 Science Activity 4.9 Page No. 74
- Take a spatula full of sodium carbonate in a test tube and add 2 ml of dilute ethanoic acid.
- What do you observe?
- Pass the gas produced through freshly prepared lime-water. What do you observe?
- Can the gas produced by the reaction between ethanoic acid and carbonate be identified by this test?
- Repeat this Activity with sodium hydrogen carbonate instead of sodium carbonate.
Observations:
Sodium acetate is produced when we add carbonate or hydrogen carbonate to acetic acid.
2CH3COOH + Na2CO3 → 2CH3COONa + H2O + CO2
CH3COOH + NaHCO3 → CH3COONa + H2O + CO2
Class 10 Science Activity 4.10 Page No. 74
- Take about 10 mL of water each in two test tubes.
- Add a drop of oil (cooking oil) 10 both the test tubes and table them as A and B.
- To test tube B add a few drops of soap solution.
- Now shake both the test tubes vigorously for the same period of time.
- Can you see the oil and water layers separately in both the test tubes immediately after you stop shaking them?
- Leave the test tubes undisturbed for some time and observe. Does the oil layer separate out? In which test tube does this happen first?
Observations:
Yes, a layer of oil separates out by reacting with the soap solution. Dirt has an oily nature. It happens first in test tube B.