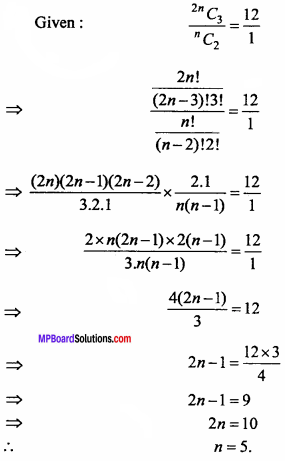
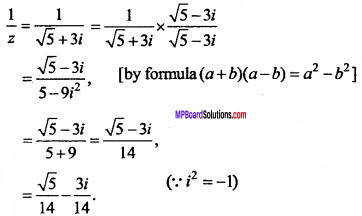
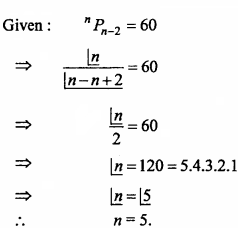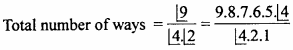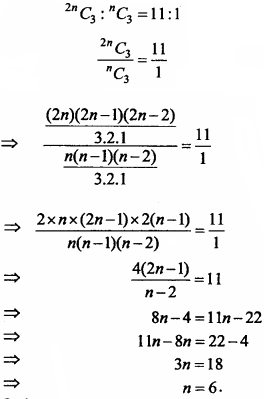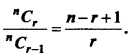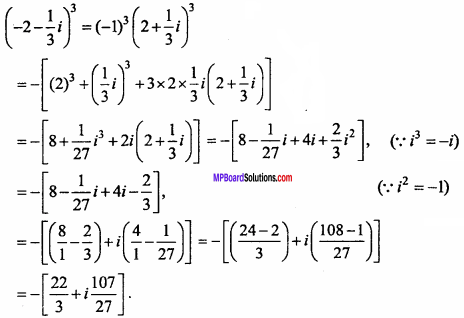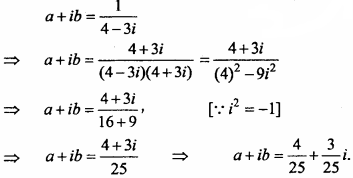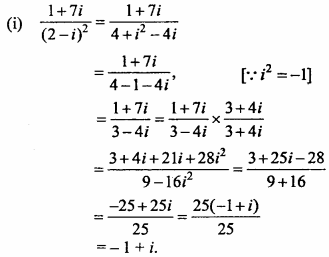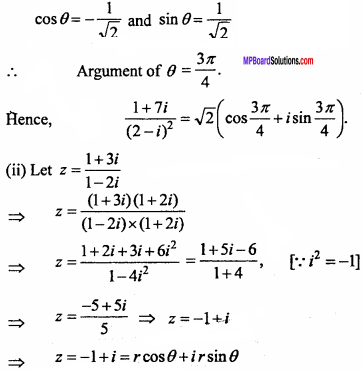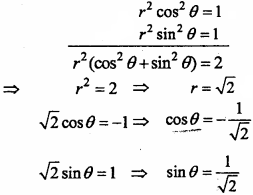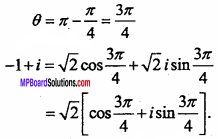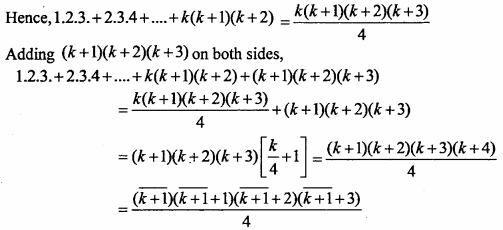MP Board Class 11th Maths Important Questions Chapter 12 Introduction to Three Dimensional Geometry
Introduction to Three Dimensional Geometry Important Questions
Introduction to Three Dimensional Geometry Objective Type Questions
(A) Choose the correct option :
Question 1.
Distance of a point (3,4, 5) from origin:
(a) 3
(b) 4
(c) 5
(d) 5\(\sqrt {2}\)
Answer:
(d) 5\(\sqrt {2}\)
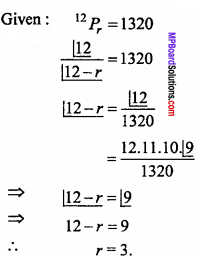
Question 2.
The perpendicular distance of the point P (x, y, z) from X – axis is:
(a) \(\sqrt { { x }^{ 2 } + { z }^{ 2 } }\)
(b) \(\sqrt { { y }^{ 2 } + { z }^{ 2 } }\)
(c) \(\sqrt { { x }^{ 2 } + { y }^{ 2 } }\)
(d) \(\sqrt { { x }^{ 2 } + { y }^{ 2 } + { z }^{ 2 } }\)
Answer:
(b) \(\sqrt { { y }^{ 2 } + { z }^{ 2 } }\)
Question 3.
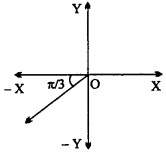
Distance of a point (3, 2, 5) from X – axis is:
(a) \(\sqrt {28}\)
(b)\(\sqrt {30}\)
(c) \(\sqrt {29}\)
(d) 3
Answer:
(c) \(\sqrt {29}\)
![]()
Question 4.
The YZ – plane divides the line segment joining the points (2, 3, 4) and (3, 5, – 4) in the ratio:
(a) 2 : 3 internally
(b) 1 : 2
(c) 2 : 3 externally
(d) 1 : 3
Answer:
(c) 2 : 3 externally
Question 5.
Distance between the points (1, 2,3) and (1,3, -2) is :
(a) \(\sqrt {- 26}\)
(b) \(\sqrt {26}\)
(c) 26
(d) ± \(\sqrt {24}\)
Answer:
(b) \(\sqrt {26}\)
Question 6.
Coordinate of a point on Z – axis, equidistant from the points (1, 5, 7) and (5, 1, – 4) is :
(a) (0, 0, \(\frac { 3 }{ 2 }\)
(b) (o, \(\frac { 3 }{ 2 }\), 0)
(c) (\(\frac { 3 }{ 2 }\), 0, 0)
(d) (4, – 4, – 11)
Answer:
(a) (0, 0, \(\frac { 3 }{ 2 }\)
Question 7.
Distance of a point (2, 1, 4) from Y – axis is:
(a) \(\sqrt {20}\)
(b) 1
(c) \(\sqrt {12}\)
(d) \(\sqrt {10}\)
Answer:
(a) \(\sqrt {20}\)
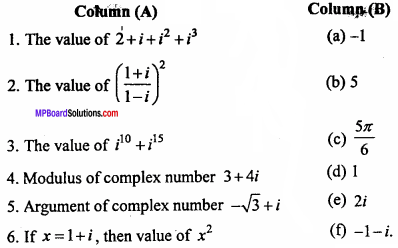
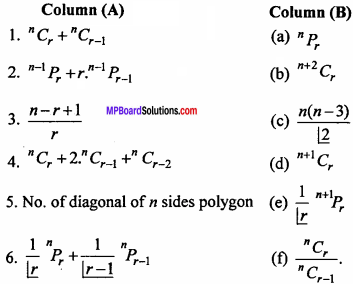
(B) Match the following :

Answer:
- (e)
- (d)
- (b)
- (a)
- (c)
(C) Fill in the blanks :
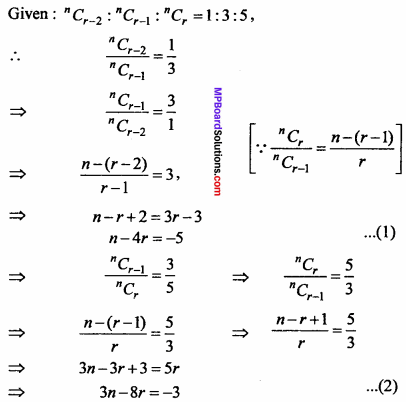
- If the points (- 1, 3, 2), (- 4, 2, – 2) and (5, 5, λ ) are collinear, then value of λ is …………….
- The perpendicular distance of point P(x, y, z) from YZ – plane is …………….
- XY – plane divides the line segment joining the points (- 3, 4, 8) and (5, – 6, 4) in the ratio …………….
- Distance between the points (1, – 3, 4) and (3, 11, – 6) is …………….
- Perpendicular distance of a point P (3,4, 5) from YZ – plane is …………….
Answer:
- 10
- x
- 2 : 1
- 10\(\sqrt {3}\)
- 3
(D) Write true / false :
- Distance of a point (4, 3, 5) from Y – axis is \(\sqrt {40}\).
- Distance of a point (5, 12, 13) from YZ – axis is \(\sqrt {313}\).
- The coordinate of a point where YZ – plane divides the join of the points (3, 5, – 7) and (- 2, 1, 8) are (0, \(\frac { 13 }{ 5 }\), 2).
- Coordinate of mid point of the line segment joining the points (- 3, 4, – 8) and (5, – 6, 4) are (1, – 1, 2).
- Points A(1, 2, 3), B(4, 0, 4) and C (- 2, 4, 2) are collinear.
Answer:
- False
- True
- True
- False
- True
(E) Write answer in one word / sentence :
- A point R lies on the line segment joining the points P (2, – 3, 4) and Q(8, 0, 10) whose x coordinate is 4, then the coordinate of R will be.
- In what ratio does the plane 2x + y – z = 3 divide the line segment joining the points A (2, 1, 3) and 5(4, – 2, 5)?
- If the origin is the centroid of the triangle ABC with vertices A (a, 1, 3), B (- 2, b, – 5), C (4, 7, c) then write the value of a, b and c.
- Find the locus of the point, which is equidistant to the points (3, 4, – 5) and (- 2, 1, 4).
- In which ratio the XY – plane divides the line joining the points (2, 4, 2) and (2, 5, – 4)?
Answer:
- (4, – 2, 6)
- 1 : 2 externally
- – 2, – 8, – 2
- 10x + 6y – 18z – 29 = 0
- 1 : 2 internally.
Introduction to Three Dimensional Geometry Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
A point is on X – axis. What are its y – co – ordinate and z – co – ordinate?
Answer:
y – co – ordinate and z – co – ordinate of point on X – axis is 0, 0 is (x, 0, 0).
Question 2.
A point is in the xz – plane. What can you say about is y – co – ordinate?
Answer:
On xz – plane the y – co – ordinate will be zero.
Question 3.
The X – axis and Y – axis taken together to form a plane, name of the plane is.
Answer:
The plane is known as xy – plane.
Question 4.
Co – ordinate of any point on xy – plane is.
Answer:
The co – ordinate of any point on xy – plane is (x, y, 0).
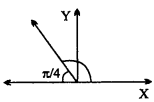
Question 5.
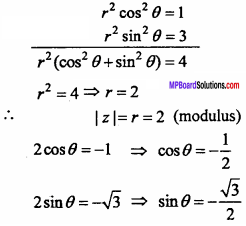
Length of perpendicular of point P(x, y, z) from X – axis is.
Answer:
Length of perpendicular = \(\sqrt { { y }^{ 2 } + { z }^{ 2 } }\)
![]()
Question 6.
Length of perpendicular of point P(x, y, z) from yz – plane is.
Answer:
Length of perpendicular of point P(x, y, z) from yz – plane is x.
Question 7.
Find the distance of point (3, 4, 5) from xz – plane.
Answer:
Distance of point (3, 4, 5) from xz – plane M(3, 0, 5) = \(\sqrt {0 + 16 + 0}\) = 4.
Question 8.
What is the centroid of ∆ABC whose vertices A(x1, y1, z1), B(x2, y2, Z2) and C(x3, y3, z3)?
Answer:
Centroid of ∆ABC is
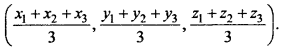
Question 9.
Find distance between points (2,3, 5) and (4,3,1).
Solution:
Distance between two points A(x1, y1, z1) and B(x2, y2, Z2):
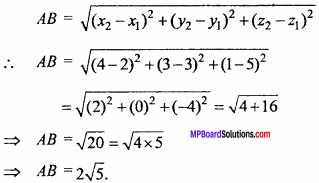
Question 10.
Find the distance between points (- 3, 7, 2) and (2, 4, – 1).
Solution:
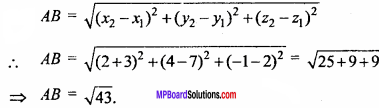
Question 11.
Find the distance of the point (3, 2, 5) from X – axis.
Solution:
Point on X – axis (3, 0, 0)
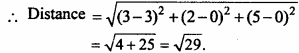
Question 12.
Find the distance of the point (2, 1, 4) from Y – axis.
Solution:
Point on Y – axis (0, 1, 0)
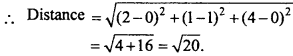
Question 13.
The three dimensional planes divides the space in how many octants?
Answer:
Three dimensional plane divides the space in eight octants.
Introduction to Three Dimensional Geometry Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
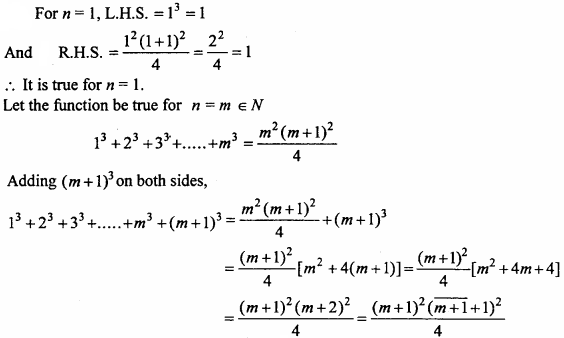
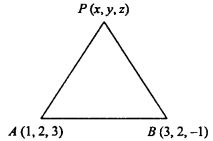
Prove that the points (- 2, 3, 5) (1, 2, 3) and (7, 0, – 1) are collinear. (NCERT)
Solution:
Given point are A (- 2, 3, 5), B(1, 2, 3) and C (7, 0, – 1).
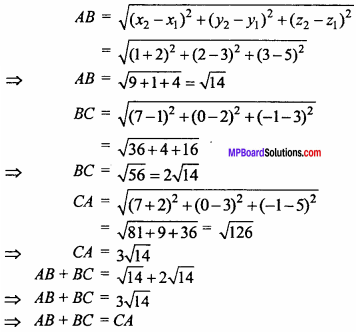
Hence points A, B, Care collinear.
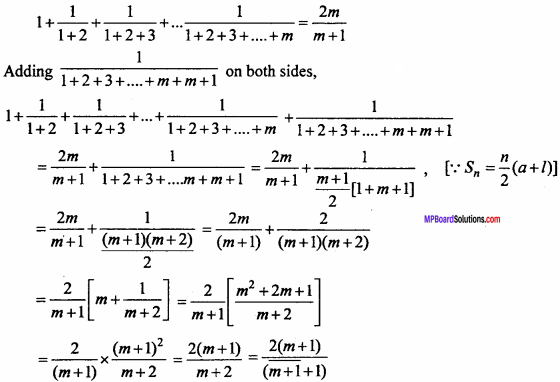
Question 2.
Find the co – ordinates of the point which divides the line segment joining the points (- 2, 3, 5) and (1, – 4, 6) in the ratio 2 : 3 internally. (NCERT)
Solution:
Required co – ordinates are :
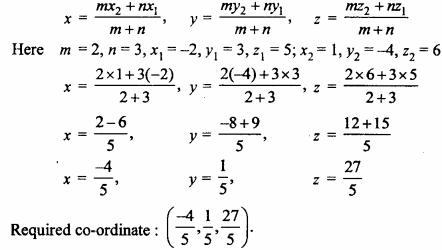
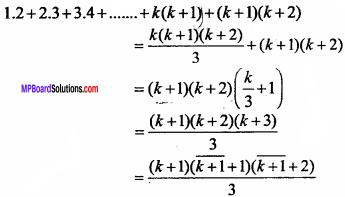
Question 3.
Given that P (3, 2, – 4), Q (5, 4, – 6) and R (9, 8, – 10) are collinear. Find the ratio in which Q divides PR. (NCERT)
Solution:

⇒ 5k + 5 = 9k + 3
⇒ 4k = 2
⇒ k = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
Hence, point Q divides PR internally in ratio 1 : 2.
Question 4.
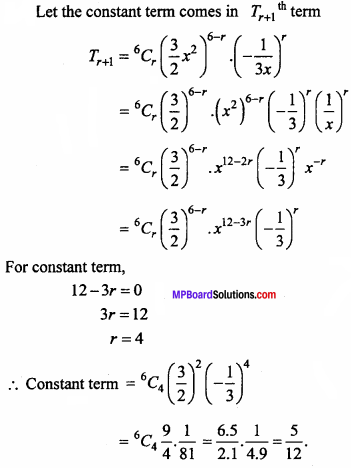
Find the ratio in which the YZ – plane divides the line segment formed by joining the points (- 2, 4, 7) and (3, – 5, 8).
Solution:
Let the point R (0, y, z) on YZ – plane divides the points P (- 2, 4, 7) and Q (3, – 5, 8) in the ratio m : n.
x = \(\frac{m x_{2}+n x_{1}}{m+n}\)
⇒ 0 = \(\frac { m × 3 + n( – 2) }{ m + n }\)
⇒ 3m – 2n = 0
⇒ 3m = 2n
⇒ \(\frac { m }{ n }\) = \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\)
⇒ m : n = 2 : 3
YZ – plane divides the line PQ internally in ratio 2:3.
![]()
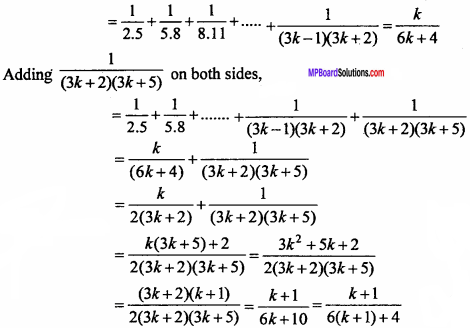
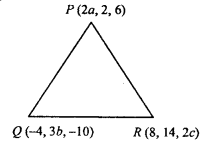
Question 5.
If the origin is the centroid of the ∆PQR with vertices P(2a, 2, 6), Q(- 4, 3b, – 10) and R (8, 14, 2c) then find the value of a, b and c. (NCERT)
Solution:
Centroid of APQR is :
x = \(\frac{x_{1} + x_{2} + x_{3}}{3}\), y = \(\frac{y_{1} + y_{2} + y_{3}}{3}\), z = \(\frac{z_{1} + z_{2} + z_{3}}{3}\)
Co – ordinate of centroid are (0, 0, 0),
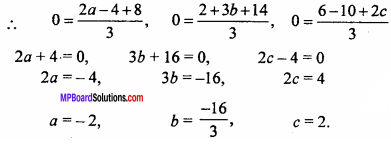
Question 6.
Find the co – ordinates of a point on Y – axis which are at a distance of 5\(\sqrt {2}\) from the point P(3, – 2, 5).
Solution:
Let A (0, y, 0) be any point on Y – axis.
Given : PA = 5\(\sqrt {2}\)
PA2 = 50
⇒ (3 – 0)2 + (- 2 – y)2 + (5 – 0)2 = 50
⇒ 9 + 4 + y2 + 4y + 25 = 50
⇒ y2 + 4y + 38 – 50 = 0
⇒ y2 + 4y – 12 = 0
⇒ y2 + 6y – 2y – 12 = 0
⇒ y(y + 6) – 2(y + 6) = 0
⇒ (y – 2)(y + 6) = 0
⇒ y = 2, – 6
The co – ordinate on Y – axis is (0, 2, 0) or (0, – 6, 0).
Question 7.
A point R with x co – ordinate 4 lies on the line segment joining the points P (2, – 3, 4) and Q (8, 0, 10). Find the co – ordinate of the point R.
Solution:
Let the point R (x, y, z) divides PQ in ratio m : n.
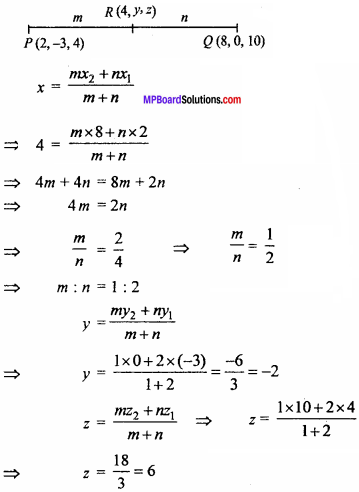
Co – ordinate of R (4, – 2, 6).
Question 8.
Find the equation of set of points which are equidistant from the points (1, 2, 3) and (3, 2, – 1). (NCERT)
Solution:
Let point P (x, y, z) be equidistant from points A (1, 2, 3) and B (3, 2, – 1).
∴ PA = PB
⇒ PA2 = PB2
⇒ (x – 1)2 + (y – 2)2 + (z – 3)2 = (x – 3)2 + (y – 2)2 + (z +1)2
⇒ x2 – 2x + 1 + z2 – 6z + 9
– 2x – 6z + 10 = – 6x + 2z + 10
⇒ 4x – 8z = 0
⇒ x – 2z = 0.
This is the required equation.
![]()
Question 9.
In which ratio the point (1, 1, 1) divides the line joining the points (3, – 2, 4) and (- 1, 4, 2)?
Solution:
Let point R (1,1,1), divides the line joining the points P (3, – 2, 4) and Q(- 1, 4, 2) in ratio λ : 1.
By formula:
x = \(\frac{m x_{2}+n x_{1}}{m+n}\)
Here x1 = 3, x2 = – 1, x = 1, m = λ and n = 1.
∴ 1 = \(\frac { λ(- 1) + 1 × 3 }{ λ + 1}\)
⇒ λ + 1 = – λ + 3
⇒ 2λ = 2
∴ λ = 1
Hence, required ratio is 1 : 1.


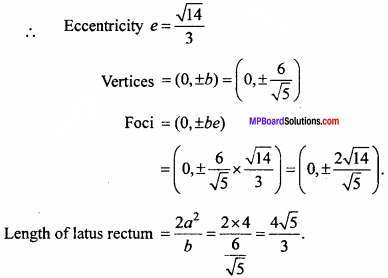
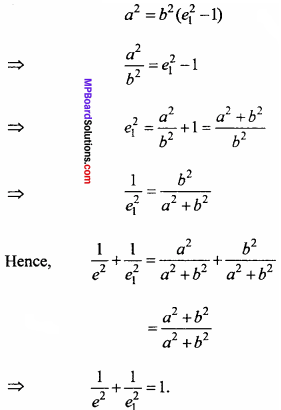
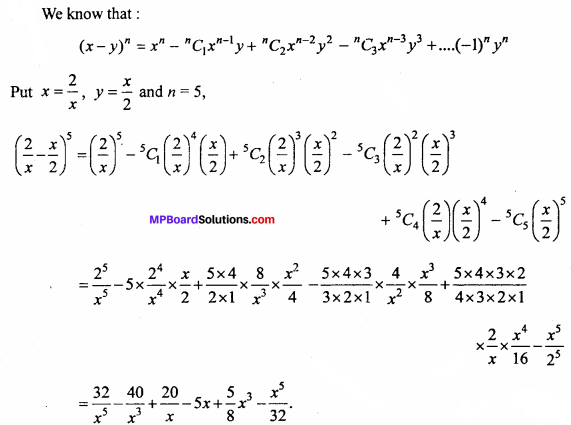

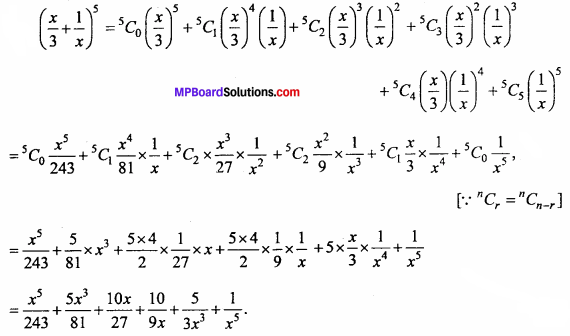

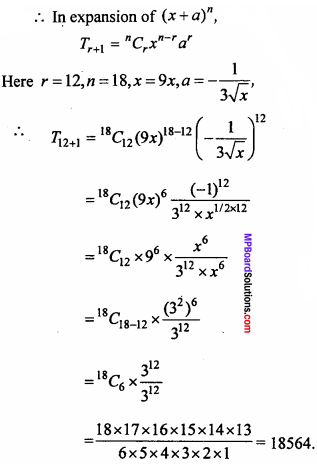
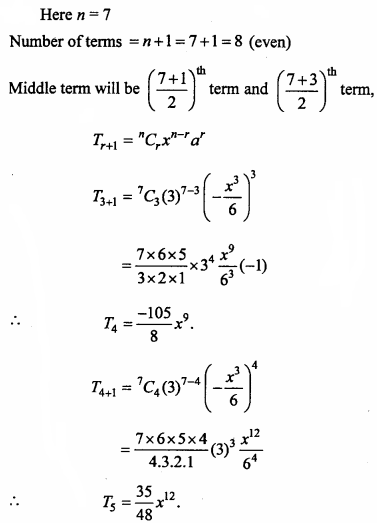
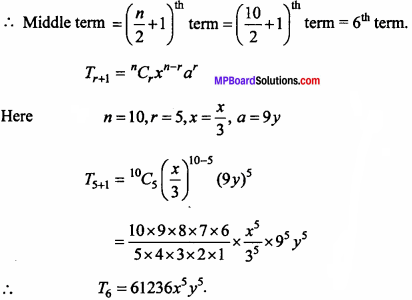
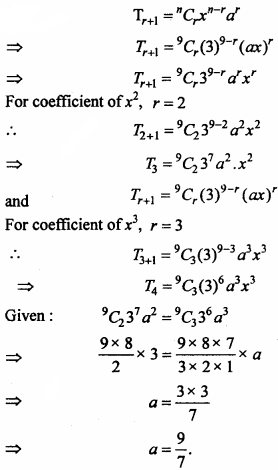

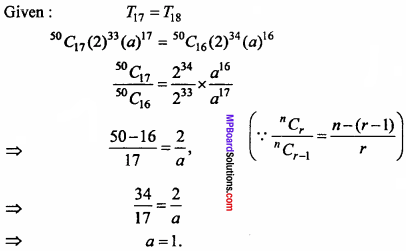
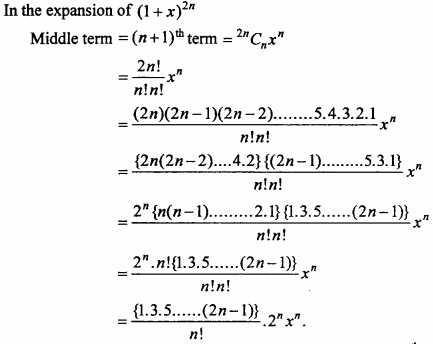
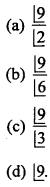
 will be?
will be?