MP Board Class 8th Sanskrit व्याकरण-खण्डः
1. संज्ञा-शब्द-रूपाणि
किसी वस्तु अथवा व्यक्ति के नाम को संज्ञा कहते हैं। जैसे-राम, सीता, पुस्तक, कलम इत्यादि। संज्ञा शब्दों के रूपों में तीनों लिंग (पुल्लिंग, स्त्रीलिंग, नपुंसकलिंग) सभी विभक्तियाँ (प्रथमा से सम्बोधन तक) एवं तीनों वचन (एकवचन, द्विवचन, बहुवचन) होते हैं। जिन संज्ञा शब्दों के अन्त में स्वर हो उन्हें स्वरान्त (अजन्त) कहते हैं; जैसे-राम, रमा, पितृ, मधु इत्यादि और जिन संज्ञा शब्दों के अन्त में व्यंजन हो उन्हें व्यञ्जनान्त (हलन्त) कहते हैं; जैसे-चन्द्रमस, मरुत, राजन, महत् इत्यादि। नीचे पाठ्यक्रम में निर्धारित एवं अन्य महत्वपूर्ण शब्द रूप दिये जा रहे हैं-
I. अजन्त पुल्लिङ्ग
अकारान्तः पुल्लिङ्ग ‘राम’ शब्दः
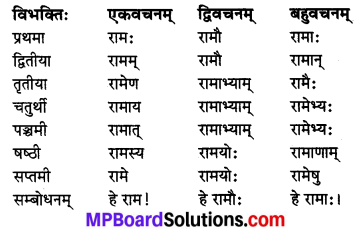
विशेषः :
‘राम’ के समान ही बालक, नर, गज, वानर, नृप, छात्र, मनुष्य, सिंह, पुत्र इत्यादि अकरान्त पुल्लिग। शब्दों के रूप चलेंगे।
![]()
इकारान्तः पुल्लिङ्ग हरि’ (विष्णु) शब्दः

विशेषः :
‘हरि’ के समान ही कपि, मुनि, रवि, नृपति, अग्नि, ऋषि इत्यादि इकारान्त पुल्लिग शब्द के रूप चलेंगे।
उकारान्तः पुल्लिङ्ग ‘भानु’ (सूर्य) शब्दः

विशेषः :
‘भानु’ शब्द के समान ही गुरु, शिशु, तरु, पशु, साधु, विष्णु इत्यादि उकारान्त पुल्लिग शब्दों के रूप चलेंगे।
ऋकारान्तः पुल्लिङ्ग ‘पितृ’ (पिता) शब्दः
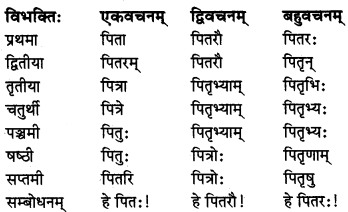
विशेष: :
‘पितृ’ शब्द के समान ही भ्रातृ, जामातृ, इत्यादि ऋकारान्त पुल्लिग शब्दों के रूप चलेंगे।
ऋकारान्तः पुल्लिङ्ग कर्तृ’ (करने वाला, कर्ता) शब्दः

विशेषः :
कर्तृ’ शब्द के समान ही धातृ, दातृ, सवितृ, नेतृ इत्यादि शब्दों के रूप चलेंगे।
![]()
II. अजन्त स्त्रीलिंग
आकारान्तः स्त्रीलिङ्ग ‘रमा’ (लक्ष्मी) शब्दः
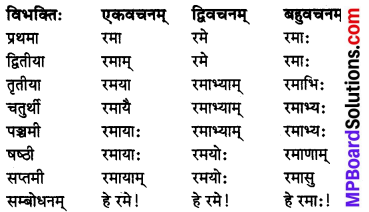
विशेषः :
‘रमा’ शब्द के समान ही सीता, लता, कन्या, बालिका, माला, विद्या, पाठशाला इत्यादि आकारान्त स्त्रीलिंग शब्दों के रूप चलेंगे।
इकारान्त स्त्रीलिङ्ग ‘मति’ ( बुद्धि) शब्दः

विशेष :
‘मंति’ शब्द के समान ही भूमि, शान्ति, बुद्धि, भक्ति, मूर्ति, कीर्ति इत्यादि इकारान्त स्त्रीलिंग शब्दों के रूप चलेंगे।
इकारान्त स्त्रीलिङ्ग ‘नदी’ (नदी) शब्दः
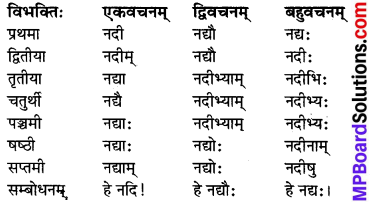
विशेषः :
‘नदी’ शब्द के समान ही पृथ्वी, जननी, कुमारी, भगिनी, सखी, स्त्री, पत्नी, नारी इत्यादि इकारान्त स्त्रीलिंग शब्दों के रूप चलेंगे।
ऋकारान्तः स्त्रीलिङ्गः ‘मातृ’ (माता) शब्दः

विशेषः :
‘मातृ’ शब्द के रूप ‘पितृ’ के समान ही चलते हैं। अन्तर केवल इतना है कि द्वितीया के बहुवचन में ‘पितृन्’ होता है, किन्तु ‘मातृ’ में ‘मातृः’।
III. अजन्त नपुंसकलिंग
अकारान्तः नपुंसकलिङ्गः ‘फल’ (फल) शब्दः
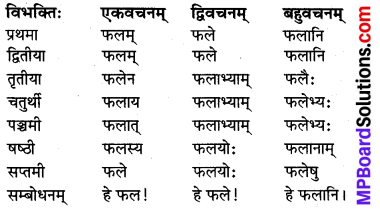
विशेषः :
‘फल’ शब्द के समान ही मित्र, पुस्तक, गृह, उद्यान, वस्त्र, पुष्प, नेत्र, नगर, जल, पत्र इत्यादि अकारान्त नपुंसकलिंग शब्दों के रूप चलेंगे।
इकारान्तः नपुंसकलिंग ‘वारि’ (जल) शब्दः

विशेष :
‘वारि’ शब्द के समान ही सुरभि (सुगन्धित), शुचि (स्वच्छ) इत्यादि इकारान्त नपुंसकलिंग शब्दों के रूप चलेंगे।
![]()
उकारान्तः नपुंसकलिङ्ग ‘मधु’ (शहद) शब्दः
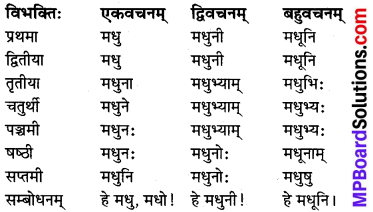
विशेष: :
‘मधु’ शब्द के समान ही वपु, वस्तु, अम्बु, अश्रु! इत्यादि उकारान्त नपुंसकलिंग शब्दों के रूप में चलेंगे।
IV. हलन्त पुल्लिंग
सकारान्तः पुल्लिङ्ग ‘चन्द्रमस्’ (चन्द्रमा) शब्दः
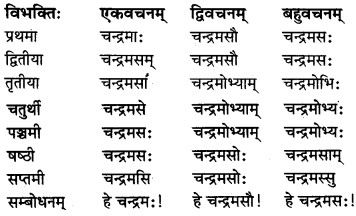
तकारान्तः पुल्लिङ्ग ‘मरुत’ (वायु) शब्दः

हलन्तः पुल्लिङ्ग ‘राजन्’ (राज) शब्दः

हलन्तः पुल्लिङ्ग ‘महत्’ (बड़ा) शब्दः
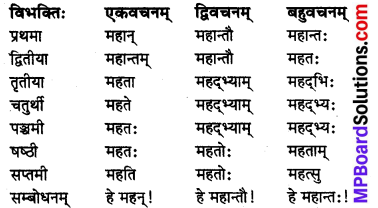
V. हलन्त स्त्रीलिंग
हलन्तः स्त्रीलिङ्गः ‘महती’ (बड़ा) शब्दः

VI. हलन्त नपुंसकलिंग
हलन्तः नपुंसकलिङ्गः ‘महत्’ (बड़ा) शब्दः

विशेषः :
‘महत्’ नपुंसकलिंग के शेष तृतीया से सप्तमी तक के रूप पुल्लिंग के समान चलते हैं। सम्बोधनम् हे महत् हे महती! हे महान्ति!
![]()
2. सर्वनाम-शब्द-रूपाणि
जिन शब्दों का प्रयोग संज्ञा के स्थान पर होता है, उन्हें सर्वनाम कहते हैं, जैसे-मैं (अहम्), तुम (त्वम्), वह (सः, सा, तत्), कौन (कः, का, किम्) इत्यादि।
सर्वनाम शब्दों में सम्बोधन नहीं होता। इनके रूप केवल सप्तमी विभक्ति तक ही चलते हैं।
पुल्लिङ्गः ‘सर्व’ (सब) शब्दः
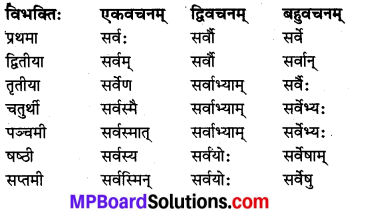
स्त्रीलिङ्गः ‘सर्व’ (सब) शब्दः

नपुंसकलिङ्गः ‘सर्व’ (सब) शब्दः

विशेषः :
‘सर्व’ नपुंसकलिंग के शेष तृतीया से सप्तमी विभक्ति तक के रूप पुल्लिग के समान ही चलते हैं।
‘कति’ (कितने) शब्दः
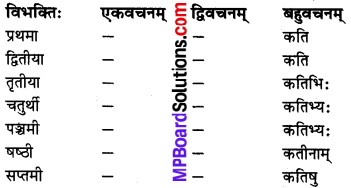
विशेष: :
‘कति’ शब्द के रूप केवल बहुवचन में चलते हैं तथा पुल्लिग, स्त्रीलिंग एवं नपुसंकलिंग में एक समान ही चलते हैं।
दकारान्तः पुल्लिङ्ग तद्’ (वह, उस, वे, उन) शब्दः

दकारान्तः स्त्रीलिङ्गः ‘तद्’ (वह, उस, वे, उन) शब्दः

दकारान्तः नपुंसकलिङ्गः ‘तद्’
(वह, उस, वे, उन) शब्दः

विशेषः :
‘तद्’ नपुंसकलिंग के शेष तृतीया विभक्ति से सप्तमी विभक्ति तक के रूप पुल्लिग के समान ही चलते हैं।
![]()
सकारान्तः पुल्लिङ्गः ‘अदस्’ (वह) शब्दः
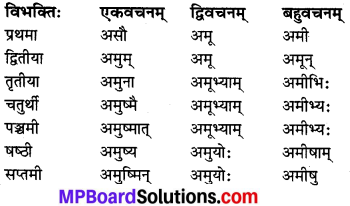
सकारान्तः स्त्रीलिङ्गः ‘अदम’ (वह) शब्दः
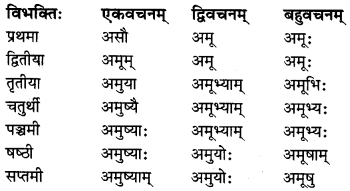
सकारान्तः नपुंसकलिङ्गः ‘अदस्’ (वह) शब्दः

विशेष: :
‘अदस्’ नपुंसकलिंग के शेष तृतीया विभक्ति से सप्तमी विभक्ति तक के रूप पुल्लिंग के समान ही चलते हैं।
मकारान्तः पुल्लिङ्गः ‘अयम्’ (यह) शब्दः
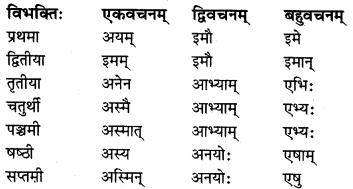
मकारान्तः स्त्रीलिङ्गः ‘इदम्’ (यह) शब्दः

मकारान्तः नपुंसकलिङ्गः ‘इदम्’ (यह) शब्दः

विशेषः :
‘इदम्’ नपुंसकलिंग के शेष तृतीया विभक्ति से सप्तमी विभक्ति तक के रूप पुल्लिंग के समान ही चलते हैं।
![]()
3. धातुरूपाणि
I. परस्मैपदम्
‘पठ्’ (पढ़ना) धातुः
लट्लकारः (वर्तमानकाले)

लङ्लकारः (भूतकाले)

लुट्लकारः (भविष्यकाले)

लोट्लकारः (आज्ञा सूचक)

विधिलिङ्गकारः (चाहिए अर्थ में)

‘गम्’ (जाना) धातुः, विधिलिङ्गलकारः

‘वद्’ (बोलना) धातुः, विधिलिङ्गकारः

‘लिख्’ (लिखना) धातुः विधिलिङ्लकारः

विशेष: :
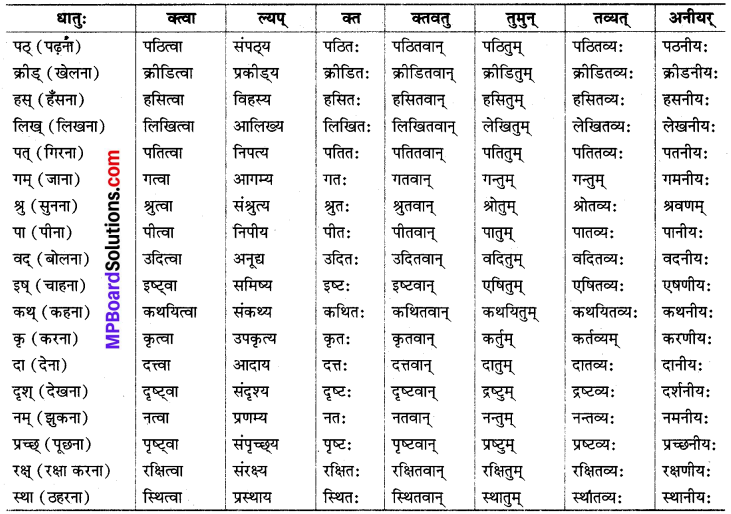
इसी प्रकार जीव, स्मृ, हस्, खाद्, क्रीड्, पत्, रक्ष्, नम्, दृश्, पा इत्यादि धातुओं के रूप चलेंगे।
![]()
II. आत्मनेपदम्
‘लभ’ (पाना) धातुः
लट्लकारः (वर्तमानकाले)

लङ्लकारः (भूतकाले)

लुट्लकारः (भविष्यकाले)

‘सेव्’ (सेवा करना) धातुः
लट्लकारः (वर्तमानकाले)

लङ्लकारः (भूतकाले)

लुट्लकारः (भविष्यकाले)

‘वृध्’ (बढ़ना) धातुः
लट्लकारः (वर्तमानकाले)

लङ्लकारः (भूतकाले)

लुट्लकारः (भविष्यकाले)

विशेषः :
इसी प्रकार रुच्, रम्, भाष्, सह, शिक्ष, वृत्, शुभ, यत् इत्यादि धातुओं के रूप चलते हैं।
![]()
4. संस्कृतसंख्या
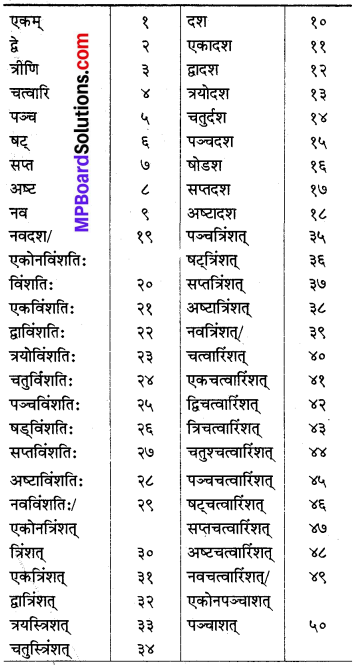
5. सन्धि -परिचय
सन्धि का अर्थ है-‘मिलाना’। दो या दो से अधिक वर्णों का मेल सन्धि है। दो वर्णों या बहुत से वर्गों के संयोग से जो रूप परिवर्तन होता है, वह सन्धि है।
सन्धि के भेद :
सन्धि तीन प्रकार की होती है-
(क) स्वर-सन्धिः या अच्-सन्धिः
(ख) व्यंजन-सन्धिः या हल-सन्धिः
(ग) विसर्ग-सन्धिः।
विशेष :
छठी और सातवीं कक्षा में छात्र ने स्वर एवं व्यंजन सन्धि को विस्तृत रूप से पढ़ा है। अतः आठवीं कक्षा में स्वर और व्यंजन सन्धि संक्षेप में और विसर्ग सन्धि विस्तार से पाठ्यक्रम में है।
(क) स्वर-सन्धिः
दीर्घ-सन्धिः
विद्या + आलय = विद्यालयः (आ + आ = आ)
देव + आश्रमः = देवाश्रमः (अ + आ = आ)
मुनि + इन्द्रः = मुनीन्द्रः (इ + इ = ई)
नदी + ईशः = नदीशः (ई + ई = ई)
साधु + उक्तिः = साधूक्तिः (उ+ उ = ऊ)
पितृ + ऋणम् = पितृणम् (ऋ + ऋ = ऋ)
![]()
गुण-सन्धिः
गज + इन्द्रः = गजेन्द्रः (अ + इ = ए)
महा + ईशः = महेशः (आ + ई = ए)
महा + उत्सवः = महोत्सवः (आ + उ = ओ)
सूर्य + उदयः = सूर्योदयः (अ + उ = ओ)
देव + ऋषिः = देवर्षिः (अ+ ऋ = अर्)
तव + लृकारः = तवल्कारः (अ + लृ = अल्)
वृद्धि-सन्धिः
एक + एकम् = एकैकम् (अ + ए = ऐ)
राज + ऐश्वर्यम् = राजैश्वर्यम् (अ + ऐ = ऐ)
तथा + एव = तथैव (आ + ए = ऐ)
जल + ओघः = जलौघः (अ+ ओ = औ)
तव + औषधम् = तवौषधम् (अ+ औ = औ)
सुख + ऋतः = सुखार्तः (अ + ऋ = आर्)
यण-सन्धिः
यदि + अपि = यद्यपि (इ को य्)
सु + आगतम् = स्वागतम् (उ को व्)
पितृ + आज्ञा = पित्राज्ञा (ऋ को र्)
अयादि-सन्धिः
चे + अनमू = चयनम् (ए को अय्)
नै + अकः = नायकः (ऐ को आय्)
भो + अनम् = भवनम् (ओ को अव्)
भौ + उकः = भावुकः (औ को आव्)
पूर्वरूप-सन्धिः
वने + अपि = वनेऽपि (ए के बाद अ को ऽ)
रामो + अपि = रामोऽपि (ओ के बाद अकोऽ)
(स्व) व्यजन-सन्धिः
श्चुत्व-सन्धिः
(हरिः) हरिस् + शेते = हरिश्शेते (स् को श्)
सत् + चरित्रम् = सच्चरित्रम् (त् को च्)
सत् + जनः = सज्जनः (त् को ज्)
![]()
ष्टुत्व-सन्धिः
(रामः) रामस् + षष्ठः = रामष्षष्ठः (स् को ए)
(दुः) दुष् + तः = दुष्टः (त् को ट्)
उत् + डीनः = उड्डीनः (त् को ड्)
जशत्व-सन्धिः
सत् + आचारः = सदाचारः (त् को द्)
अच् + अन्तः = अजन्तः (च को ज्)
दिक् + गजः = दिग्गजः (क् को ग्)
षट् + दर्शनम् = षड्दर्शनम् (ट् को ड्)
चव-सन्धिः
सद् + कारः = सत्कारः (द् को त्)
तद् + परः = तत्परः (द् को त्)
अनुस्वार-सन्धिः
धर्मम् + चर = धर्मंचर (म् को)
पुस्तकम् + पठति = पुस्तकं पठति (म् को)
अनुनासिक-सन्धिः
जगत् + नाथः = जगन्नाथः (त् को न्)
एतत् + मुरारिः = एतन्मुरारिः (त् को न्)
लत्व-सन्धिः
तत् + लयः = तल्लयः (त् को ल्)
उत् + लेखः = उल्लेखः (त् को ल्)
(ग) विसर्ग-सन्धि
परिभाषा :
विसर्ग के साथ स्वर या व्यंजन का मेल होने से जो विकार (परिवर्तन) होता है, वह विसर्ग सन्धि है, जैसे
मनः + रथः = मनोरथः।
मनः + हरः = मनोहरः।
विसर्ग-सन्धि के नियम :
नियम 1.
विसर्ग के बाद ‘च’ या ‘छ्’ हो तो विसर्ग के स्थान पर ‘श्’ होता है।
उदाहरण :
रामः + चलति = रामश्चलति
बालकः + चलति = बालकश्चलति
![]()
नियम 2.
यदि विसर्ग के बाद ‘त्’ अथवा ‘थ्’ हो तो विसर्ग के स्थान पर ‘स्’ हो जाता है।
उदाहरण :
रामः + तिष्ठति = रामस्तिष्ठति
नमः + ते = नमस्ते नियम
नियम 3.
यदि विसर्ग से पहले और बाद में ‘अ’ हो तो विसर्ग और ‘अ’ के स्थान पर ‘ओ’ हो जाता है तथा ‘अ’ के स्थान पर अवग्रह (ऽ) हो जाता है।
उदाहरण :
कः + अयम् = कोऽयम्
कः + अपि = कोऽपि
नियम 4.
यदि विसर्ग के पहले ‘अ’ हो तथा बाद में ह्रस्व ‘अ’ को छोड़कर अन्य कोई भी स्वर वर्ण हो तो विसर्ग का लोप हो जाता है।
उदाहरण :
कः + आगच्छति = क आगच्छति
देवः + इति = देव इति
नियम 5.
यदि विसर्ग के पहले ‘अ’ हो और बाद में कोई मृदु व्यजन वर्ण हो अर्थात् किसी भी वर्ग का तृतीय, चतुर्थ, पंचम वर्ण तथा य, र, ल, व्, छ हो तो पूर्व ‘अ’ के स्थान पर ‘ओ’ हो जाता है।
उदाहरण :
शिवः + वन्द्यः = शिवो वन्द्यः
रामः + गच्छति = रामो गच्छति
नियम 6.
यदि विसर्ग से पहले ‘आ’ हो और बाद में कोई स्वर अथवा कोई मृदु व्यंजन हो अर्थात् किसी भी वर्ग का तृतीय, चतुर्थ, पंचम वर्ण य, र, ल, व्, ह होता है तो विसर्ग का लोप हो जाता है।
उदाहरण :
देवाः + आगताः = देवा आगताः
नराः + यान्ति = नरा यान्ति
नियम 7.
विसर्ग से पहले ‘अ’,’आ’ वर्गों को छोड़कर कोई स्वर होता है तथा विसर्ग के बाद कोई स्वर या मृदु व्यञ्जन वर्ण अर्थात् किसी भी वर्ग का तृतीय, चतुर्थ, पंचम वर्ण य, र, ल, व्, ह होता है तो विसर्ग के स्थान पर ‘र’ होता है। यदि बाद में स्वर होता है तो ‘र’ स्वर के साथ मिलता है तथा बाद में व्यंजन वर्ण होता है तो ‘र’ वर्ण का ऊर्ध्वगमनं (रेफा) होता है।
उदाहरण :
भानुः + उदेति = भानुरुदेति
कवेः + गमनम् = कवेर्गमनम्
नियम 8.
‘स:’ और ‘एषः’ इन दोनों विसर्ग के बाद व्यंजन वर्ण होता है तो विसर्ग का लोप होता है।
उदाहरण :
सः + पठति = स पठति
सः + लिखित = स लिखति
![]()
6. समास-परिचय
दो या दो से अधिक शब्दों की विभक्ति हटाकर और उन्हें एक साथ जोड़कर एक शब्द बनाने की प्रक्रिया को समास कहते हैं। इस प्रकार मिला हुआ पद ‘समस्त पद’ कहलाता है।
समास का अर्थ है’संक्षेप’ करना, अर्थात् दो या दो से अधिक शब्दों को इस प्रकार रख देना, जिससे उनके आकार में कुछ कमी हो जाय और अर्थ पूरा-पूरा निकले। जैसे-
राज्ञः पुरुषः = राजपुरुषः
(राजा का पुरुष) = (राजपुरुष)
समास के भेद-समास के छ: भेद होते हैं-
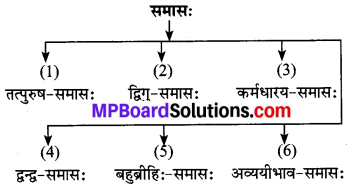
संस्कृत के एक याचक की उक्ति में इन सभी समासों का नाम आ गया है। यह उक्ति बहुत प्रसिद्ध है-
द्वन्द्वो द्विगुरपि चाहं मद्गेहे नित्यमव्ययीभावः।
तत्पुरुष कर्मधारय येनाहं स्याम् बहुव्रीहिः॥
1. तत्पुरुषः-समासः
परिभाषा :
प्रायेण उत्तरपदार्थप्रधानस्तत्पुरुषः।
जहाँ पूर्व पद (पहला शब्द) द्वितीया विभक्ति से सप्तमी विभक्ति तक होता है उत्तर पद (दूसरा शब्द) प्रथम विभक्ति में होता है वहाँ (व्यधिकरण) तत्पुरुष समास होता है। पूर्व पद की विभक्ति के अनुसार ही समास का नामकरण होता है। जैसे-
(क) द्वितीया तत्पुरुषः-इसमें पहला पद द्वितीया विभक्ति का होता है तथा समासावस्था में उसका लोप हो जाता है।
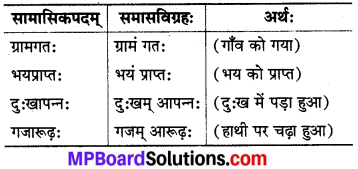
(ख) तृतीया तत्पुरुषः :
इसमें पहला पद तृतीया विभक्ति का होता है तथा समासावस्था में उसका लोप हो जाता है।
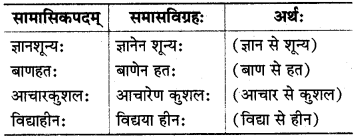
![]()
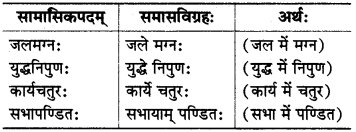
(ग) चतुर्थी तत्पुरुषः :
इसमें पहला पद चतुर्थी विभक्ति का होता है तथा समासावस्था में उसका लोप होता है।

(घ) पञ्चमी तत्पुरुषः :
इसमें पहला पद पंचमी विभक्ति का होता है तथा समासावस्था में उसका लोप होता है।
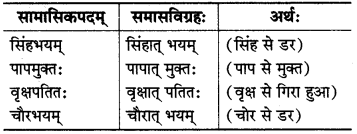
(ङ) षष्ठी तत्पुरुषः :
इसमें पहला पद षष्ठी विभक्ति का होता है तथा समासावस्था में उसका लोप होता है।
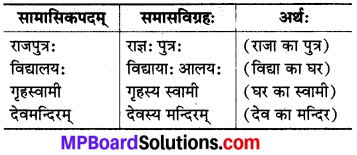
(च) सप्तमी तत्पुरुषः :
इसमें पहला पद सप्तमी विभक्ति का होता है और समासावस्था में उसका लोप हो जाता है।
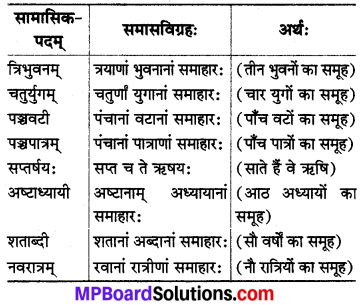
2. द्विगु-समासः
परिभाषा :
सङ्ख्यापूर्वो द्विगुः।
जहाँ पहला पद संख्यावाची होता है तथा दूसरे पद की विशेषता बताता है वहाँ द्विगु समास होता है। द्विगु समास में समूहवाचक अर्थ होता है।
3. कर्मधारयसमासः
परिभाषा :
स चासौ कर्मधारयः।
जहाँ प्रथम पद विशेषण या उपमान तथा द्वितीय पद विशेष्य या उपमेय होता है वहाँ कर्मधारय समास होता है।
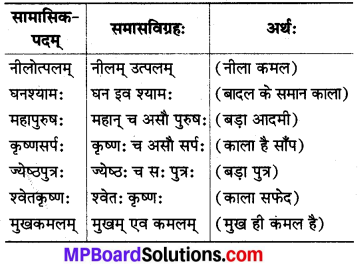
4. द्वन्द्वसमासः
परिभाषा :
प्रायेणोभयपदार्थप्रधानो द्वन्द्वः।
जहाँ सभी पदों की प्रधानता होती है वहाँ द्वन्द्व समास होता है। ‘चार्थे द्वन्द्वः’ अर्थात् ‘च’ (और) अर्थ में द्वन्द्व समास होता है।’
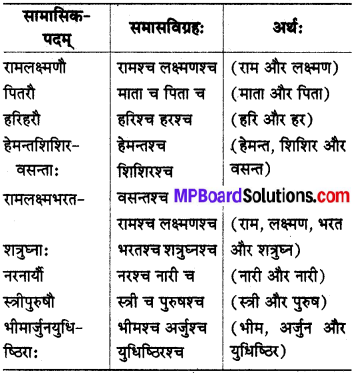
5. बहुब्रीहिसमासः
परिभाषा :
प्रायेण अन्यपदार्थप्रधानो बहुब्रीहि।-
जहाँ सामासिक पदों से अन्य का बोध होता है, वह बहुब्रीहि समास होता है। बहुब्रीहि समास के अन्त में ‘यस्य सः’ (जिसका वह) अथवा ‘येन’ (जिसके द्वारा) शब्द होता है।
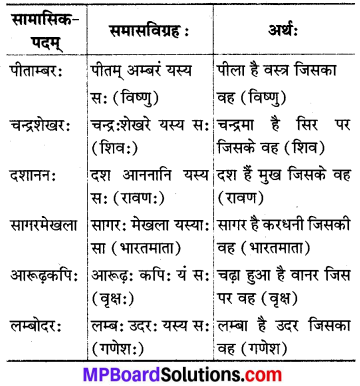
6. अव्ययीभावसमासः
परिभाषा :
प्रायेण पूर्वपदार्थप्रधानोऽव्ययीभावः।
जहाँ प्रथम पद प्रधान होता है तथा प्रथम पद अव्यय होता है और द्वितीय पद संज्ञावाचक होता है, वह अव्ययीभाव समास होता है।
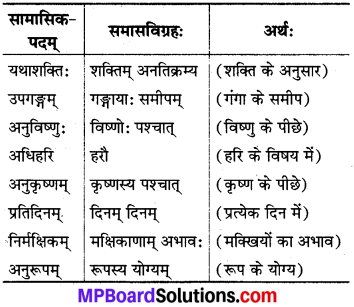
![]()
7. कारक-परिचयः
परिभाषा :
क्रियान्वयित्वं कारकम् –
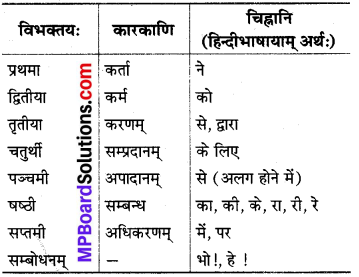
अर्थात् जिस पद का सम्बन्ध साक्षात् क्रिया से होता है, वह ‘कारक’ कहलाता है। कारक छह होते हैं ‘सम्बन्ध’ कारक नहीं है, किन्तु विभक्तियाँ सात होती हैं। कारकों के विषय में कहा गया है कि-
कर्ता कर्म च कारणं न सम्प्रदानं तथैव च।
अपादानाधिकरणमिव्याहुः कारकाणि घट्॥
विशेष :
सम्बोधन में प्रथमा विभक्ति होती है।
कर्ताकारकम् (प्रथमाविभक्तिः) :
क्रिया के करने वाले को कर्ता कहते हैं। कर्ता कारक में प्रथमा विभक्ति होती है। जैसे-
- बालकः गच्छति। (बालक जाता है।)
- राम पठति। (राम पढ़ता है।)
कर्मकारकम् (द्वितीया विभक्तिः) :
- कर्ता जिसको सबसे अधिक चाहता है, वह कर्म कारक’ कहा जाता है। कर्म कारक में द्वितीया विभक्ति होती है। जैसे-
- रामः पत्रम् लिखति। (राम पत्र लिखता है।)
- बालक पुस्तकम् पठति। (बालक पुस्तक पढ़ता है।) कर्मकारक में यह विशिष्ट नियम है’
- अभितः, परितः, समया, निकषा, प्रति, अनु, विना इत्यादि के योग में भी ‘द्वितीया विभक्ति’ होती है। जैसे-
- ग्रामम् अभितः वृक्षाः सन्ति। (गाँव के दोनों ओर वृक्ष हैं।)
- ज्ञानम् विना मुक्तिः नास्ति। (ज्ञान के बिना मुक्ति नहीं है।)
- ‘गति’ अर्थ वाली धातुओं के योग में ‘द्वितीया विभक्ति’ होती है। जैसे-
- सः विद्यालयं गच्छति। (वह विद्यालय जाता है।)
- वानरः वृक्षम् आरोहति। (वानर वृक्ष पर चढ़ता है।)
![]()
करणकारकम् (तृतीया विभक्तिः) :
- जिस साधन से कर्ता अपना कार्य पूर्ण करता है, उस साधन को करण कारक कहते हैं। करण कारक में तृतीया विभक्ति होती है। जैसे-
- छात्रः कन्दुकेन क्रीडति। (छात्र गेंद से खेलता है।)
- कृष्णः यानेन गच्छति। (कृष्ण विमान से जाता है।) करण कारक में यह विशेष नियम है
- ‘सह, साकम्, समम्, सार्धम्, अलम् इत्यादि के योग में भी तृतीया विभक्ति होती है। जैसे-
- बालकः जनकेन सह गच्छति। (बालक पिता के साथ जाता है।)
- अलम् अति रुदितेन। (बहुत ज्यादा मत रोओ।)
- शरीर के जिस अंग में विकार हो उसमें तृतीया विभक्ति होती है। जैसे-
- भिक्षुकः पादेन खञ्जः अस्ति। (भिक्षुक पैर से लँगड़ा है।)
- सत्र नेत्रेणः काणः अस्ति।(वह आँख से काना है।)
- करणबोधक (साधन) शब्दों में तृतीया विभक्ति होती है। जैसे-
- श्रमेण सफलता मिलति। (परिश्रम से सफलता मिलती है।)
- विद्यया यशः प्राप्यते। (विद्या से यश मिलता है।)
सम्प्रदानकारकम् (चतुर्थी विभक्तिः) :
- जिसके लिए कोई वस्तु दी जाए अथवा जिसके लिए कोई कार्य किया जाए, वह सम्प्रदान कारक कहलाता है। सम्प्रदान कारक में चतुर्थी विभक्ति होती है। जैसे-
- गीता पुत्राय दुग्धं ददाति।। (गीता पुत्र को दूध देती है।)
- बालकः पठनाय विद्यालयं गच्छति।। (बालक पढ़ने के लिए विद्यालय जाता है।)
सम्प्रदान कारक में यह विशेष नियम है।
- नमः, स्वस्ति, स्वाहा, स्वधा, अलम्, वषट् के योग में चतुर्थी विभक्ति होती है। जैसे-
- श्री गणेशाय नमः। (श्री गणेश को प्रणाम)
- विप्रेभ्यः स्वस्ति। (विप्रों का कल्याण हो)
- ‘रुचि’ अर्थ वाली धातुओं के योग में चतुर्थी विभक्ति होती है। जैसे-
- बालकाय मोदकं रोचते। (बालक को लड्डू अच्छा लगता है।)
अपादानकारकम् (पञ्चमी विभक्तिः) :
- जिस वस्तु से किसी का अलग होना पाया जाता है, उस वस्तु की अपादान संज्ञा होती है। अपादान कारक में पंचमी विभक्ति होती है। जैसे-
- वृक्षात् पत्रं पतति। (पेड़ से पत्ता गिरता है।)
- युवकः अश्वात् पतति। (युवक घोड़े से गिरता है।)
अपादान कारक के ये विशेष नियम हैं।
- भय, रक्ष्, अर्थ वाली धातुओं के योग में भी पंचमी विभक्ति होती है। जैसे-
- बालकः सिंहात् विभेति। (बालक शेर से डरता है।)
- जुगुप्सा, विरम, प्रमाद अर्थ वाली धातुओं के योग में पंचमी विभक्ति होती है। जैसे-
- गुरुः पापात् विरमति। (गुरु पाप से रोकता है।)
- अन्य, आरात्, इतर, ऋते इत्यादि के योग में पंचमी विभक्ति होती है। जैसे-
ज्ञानात् ऋते मुक्तिः नास्ति। (ज्ञान के बिना मुक्ति नहीं है।) - दूरम्, अन्तिकम् (पास) अर्थ में पंचमी या षष्ठी विभक्ति होती है। जैसे-
- ग्रामस्य ग्रामात् वा अन्तिकम्। (गाँव के पास)
![]()
सम्बन्धः (घष्टी विभाजन) :
हेतु शब्द के प्रयोग में षष्ठी विभक्ति होती है। जैसे-
भिक्षुकः अन्नस्य हेतोः वसति। (भिक्षुक अन्न के लिए रहता है।)
अधिकरणकारकम् (नामी विभक्तिः)
- आधार को अधिकरण कारक कहते हैं। अधिकरण कारक में सप्तमी विभक्ति होती है। जैसे-
- सिंहः वने वसति। (शेर वन में रहता है।)
- साधुः, असाधुः शब्द के प्रयोग में भी सप्तमी विभक्ति होती है। जैसे-
- अहं मित्रेषु साधुः शत्रुषु च असाधुः अस्मि। (मैं, मित्रों के लिए अच्छा और शत्रुओं के लिए बुरा हूँ।)
8. प्रत्ययपरिचयः
परिभाषा :
‘प्रतीयते विधीतते अनेन इति प्रत्ययः।’
धातु अथवा प्रातिपदिक शब्द के अन्त में जुड़कर विशेष अर्थ का जो बोध कराता है वह ‘प्रत्यय’ है।
अथवा
प्रातिपदिक शब्दों या धातुओं के अन्त में जो प्रयुक्त होते – हैं, वे प्रत्यय हैं।
यथा-
कृ + क्तवतु = कृतवान् (किया)
लघु + तरप् = लघुतरः (अधिक छोटा)
प्रत्यय के भेद-प्रत्यय दो प्रकार के होते हैं-
I. कृत् प्रत्यय :
जो धातुओं के अन्त में जोड़े जाते हैं, वे ‘कृत्-प्रत्यय’ कहलाते हैं। जैसे-क्त्वा, ल्यप्, क्तवतु, तुमुन्, क्त, तव्यत्, अनीयर् इत्यादि।
II. तद्धित प्रत्यय :
जो प्रत्यय प्रातिपदिक शब्दों के अन्त में जोड़े जाते हैं, वे ‘तद्धित प्रत्यय’ कहलाते हैं। जैसे-तरप्, तमप् अण् इत्यादि।
I. कृत्प्रत्ययः :
क्त्वा प्रत्यय :
जब एक क्रिया को समाप्त करके दूसरी क्रिया की जाती है, तब समाप्त होने वाली क्रियार्थक धातु से क्त्वा प्रत्यय होता है। इसका हिन्दी अर्थ ‘करके’ या ‘कर’ है।
उदाहरण :
रामः जलं पीत्वा लिखति ।(राम जल पीकर लिखता है।)
ल्यप् प्रत्यय :
जब धातु से पूर्व कोई उपसर्ग या उपसर्ग-स्थानीय पद प्रयुक्त होता है, तो क्त्वा के स्थान पर ‘ल्यप्’ प्रत्यय का प्रयोग होता है।
उदाहरण :
कृष्णः आगत्य पठति। (कृष्ण आकर पढ़ता है।)
क्त, क्तवतु प्रत्यय :
ये दोनों भूतकाल में प्रयुक्त होते हैं। क्त प्रत्यय का प्रयोग कर्मवाच्य या भाववाच्य में होता है तथा क्तवतु प्रत्यय का प्रयोग कर्तृवाच्य में होता है।
उदाहरण :
मयाः ग्रन्थः लिखितः (मेरे द्वारा ग्रन्थ लिखा गया।)
बालकः लेखं लिखितवान्। (बालक ने लेख लिखा।)
![]()
तुमुन् प्रत्यय :
जाना, जाने को, जाने के लिए, जाने का, जाने में आदि निमित्त अथवा प्रयोजन को प्रकट करने के लिए ‘तुमुन्’ प्रत्यय का प्रयोग होता है। यह चतुर्थी विभक्ति के अर्थ में भी प्रयुक्त होता है।
उदाहरण :
रामः पठितुम् विद्यालयं गच्छति। (राम पढ़ने के लिए विद्यालय जाता है।)
तव्यत्, अनीयर् प्रत्यय :
इन दोनों प्रत्ययों का प्रयोग विधिलिंग लकार का अर्थ प्रकट करने के लिए एवं ‘योग्य’ अर्थ में होता है।
उदाहरण :
रामेण ग्रन्थः ‘पठितव्यः (या) पठनीयः।’ (राम के द्वारा ग्रन्थ पढ़ा जाना चाहिए।)
मध्यप्रदेशः दर्शनीयः अस्ति। (मध्य प्रदेश देखने योग्य है।)
II. तद्धित-प्रत्ययः
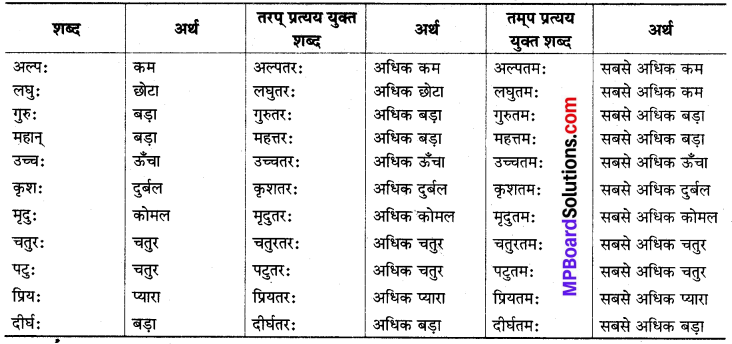
तरप्, तमप् प्रत्यय :
विशेषण शब्दों के भाववर्धन के लिए तरप् (तर) और प्रत्ययों का प्रयोग होता है। विशेषण शब्दों की तीन अवस्थाएँ होती हैं-
(क) सामान्य अवस्था-सुन्दरः रामः सुन्दरः बालकः अस्ति।
(ख) उत्तर-अवस्था-सुन्दरतरः रामः मोहनात् सुन्दरतरः अस्ति।
(ग) उत्तम-अवस्था-सुन्दरतमः रामः सर्वेषु बालकेषु सुन्दरतमः अस्ति।
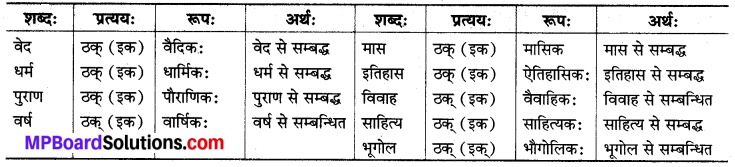
ठक् (इक्) प्रत्यथ इस प्रत्यय का प्रयोग भवावचक संज्ञा बनाने के लिए होता हैं।
![]()
9. अव्ययपरिचयः
सदृशं त्रिषु लिङ्गेषु सर्वासु च विभक्तिषु।
वचनेषु च सर्वेषु यन्नव्येति तदव्ययम्॥
अर्थात् जिन शब्दों में लिंग, कारक और वचन के कारण किसी प्रकार का विकार (परिवर्तन) नहीं होता और जो प्रत्येक दशा में एक समान रहते हैं, उन्हें अव्यय शब्द कहते हैं।
अव्ययों के भेद-
अव्ययों के पाँच भेद हैं-
(I) उपसर्गः
(II) क्रियाविशेषणम्
(III) चादिः
(IV) समुच्चयबोधकः
(V) विस्मयादिबोधकः
I. उपसर्गः
धातु अथवा धातु से बने अन्य शब्दों (संज्ञा, विशेषण) आदि के पूर्व लगने वाले निम्नलिखित 22 शब्दांशों को उपसर्ग कहते हैं
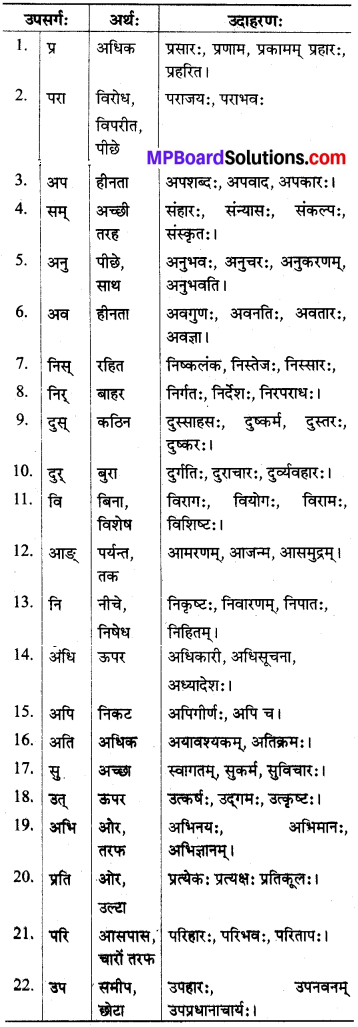
II. क्रियाविशेषणम्
जिन शब्दों से क्रिया के काल, स्थान आदि विशेषताओं का बोध होता है, उन्हें क्रिया-विशेषण कहते हैं। ये अव्यय हैं, इनके रूप नहीं बनते हैं।
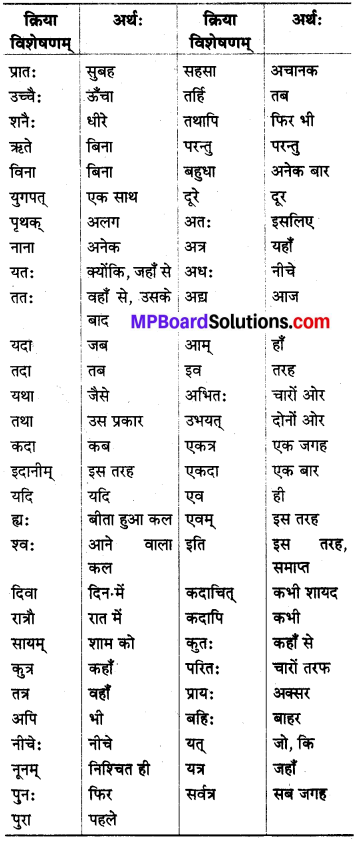
इत्यादि
![]()
III. चादिः
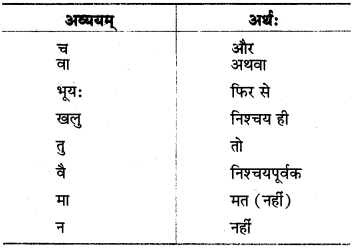
इत्यादि
IV. समुच्चयबोधका:
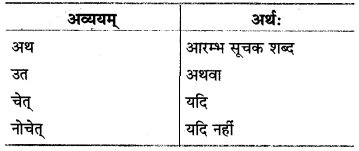
इत्यादि
V. विस्मयादिबोधकाः

इत्यादि
10. विलोमशब्दपरिचयः
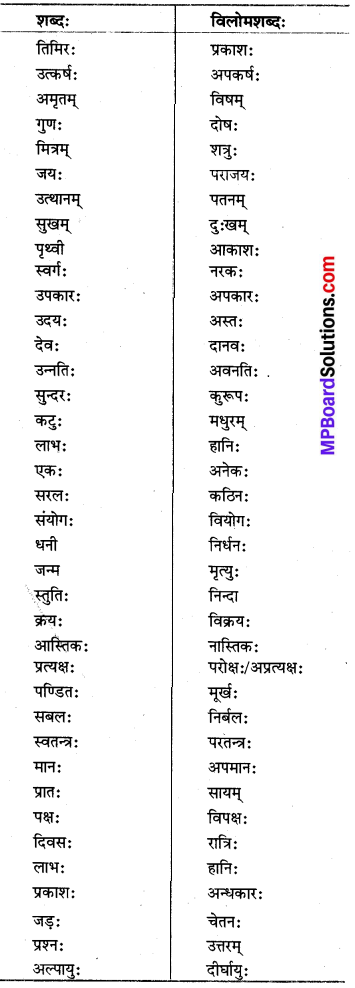
![]()
11. पर्यायवाचीशब्दपरिचयः