MP Board Class 6th Maths Solutions Chapter 6 Integers Ex 6.2
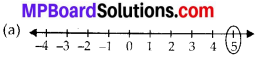
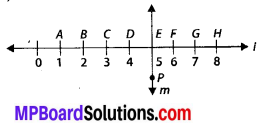
Question 1.
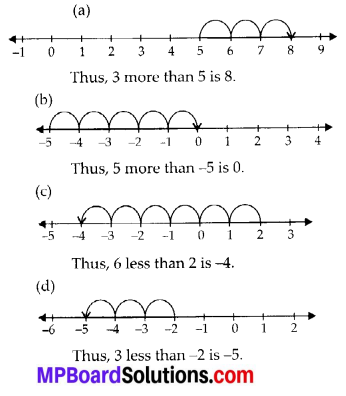
Using the number line write the integer which is:
(a) 3 more than 5
(b) 5 more than -5
(c) 6 less than 2
(d) 3 less than -2
Solution:
![]()
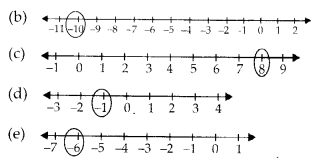
Question 2.
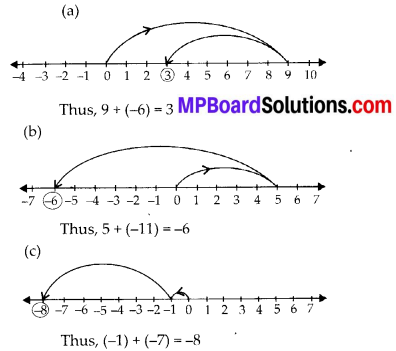
Use number line and add the following integers:
(a) 9 +(-6)
(b) 5+ (-11)
(c) (- 1) + (- 7)
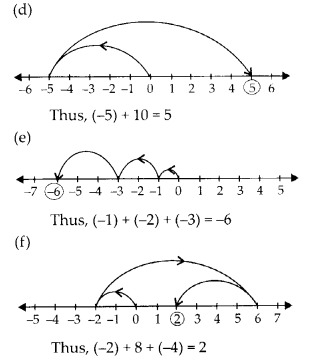
(d) (-5) +10
(e) (-1) + (- 2) + (- 3)
(f) (- 2) + 8 + (- 4)
Solution:
![]()
Question 3.
Add without using number line:
(a) 11 + (-7)
(b) (-13) + (+18)
(c) (- 10) + (+ 19)
(d) (- 250) + (+ 150)
(e) (-380) + (-270)
(f) (-217) + (-100)
Solution:
(a) 11 + (-7) = 11 – 7 = 4
(b) (-13) + (+18) = -13 + 18 = 5
(c) (-10) + (+19) = -10 + 19 = 9
(d) (-250) + (+150) = -250 + 150 = -100
(e) (-380) + (-270) = -380 – 270 = -650
(f) (-217) + (-100) = -217 – 100 = -317
![]()
Question 4.
Find the sum of:
(a) 137 and -354
(b) – 52 and 52
(c) – 312, 39 and 192
(d) – 50, – 200 and 300 .
Solution:
(a) 137 + (-354) = 137 – 354 = -217
(b) -52 + 52 = 0
(c) -312 + 39 + 192 = – 312 + 231 = -81
(d) -50 + (-200) + 300 = – 50 – 200 + 300
= – 250 + 300 = 50
![]()
Question 5.
Find the sum :
(a) (-7) + (-9) + 4 + 16
(b) (37) + (- 2) + (- 65) + (- 8)
Solution:
(a) (-7) + (-9) + 4 + 16 = -7 – 9 + 4 + 16
= -16 + 20 = 4
(b) (37) + (-2) + (-65) + (-8)
= 37 – 2 – 65 – 8
= 37 – 75 = – 38