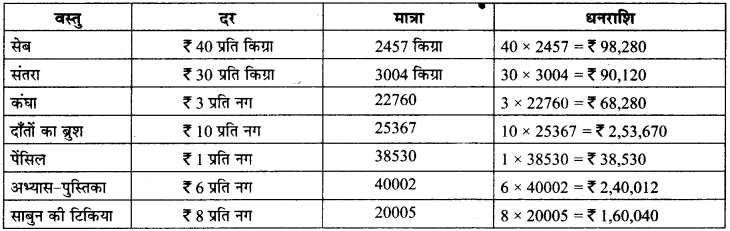
MP Board Class 6th Maths Solutions Chapter 2 पूर्ण संख्याएँ Intext Questions
पाठ्य-पुस्तक पृष्ठ संख्या # 29
प्रयास कीजिए
प्रश्न 1.
19; 1997%; 12000; 49; 100000; 2440701; 100199; और 208090 के पूर्ववर्ती और परवर्ती लिखिए।
हल :
पूर्ववर्ती : 19 – 1 = 18; 1997 – 1 = 1996; 12000 – 1 = 11999; 49 – 1 = 48; 100000 – 1 = 99999; 2440701 – 1 = 2440700; 100199 – 1 = 100198; 208090 – 1 = 208089;
परवर्ती : 19 + 1 = 20; 1997 + 1 = 1998; 12000 + 1 = 12001; 49 + 1 = 50; 100000 + 1 = 100001; 2440701 + 1 = 2440702; 100199 + 1 = 100200; 208090 + 1 = 208091
प्रश्न 2.
क्या कोई ऐसी प्राकृत संख्या है जिसका कोई पूर्ववर्ती नहीं है ?
उत्तर-
हाँ, 1 ऐसी प्राकृत संख्या है जिसका कोई पूर्ववर्ती नहीं है।
प्रश्न 3.
क्या कोई ऐसी प्राकृत संख्या है जिसका कोई परवर्ती नहीं है ? क्या कोई अंतिम प्राकृत संख्या है ?
उत्तर-
नहीं, ऐसी प्राकृत संख्या नहीं है जिसका कोई परवर्ती नहीं।
नहीं, कोई संख्या अंतिम प्राकृत संख्या नहीं है।
पाठ्य-पुस्तक पृष्ठ संख्या # 30
प्रयास कीजिए
प्रश्न 1.
क्या सभी प्राकृत संख्याएँ पूर्ण संख्याएँ भी हैं ?
उत्तर-
हाँ, सभी प्रांकृत संख्याएँ पूर्ण संख्याएँ भी हैं।
प्रश्न 2.
क्या सभी पूर्ण संख्याएँ प्राकृत संख्याएँ भी हैं ?
उत्तर-
नहीं, सभी पूर्ण संख्याएँ प्राकृत संख्याएँ नहीं हैं। क्योंकि शून्य (0) पूर्ण संख्या है लेकिन यह प्राकृत संख्या नहीं है।
प्रश्न 3.
सबसे छोटी पूर्ण संख्या कौन-सी है ?
उत्तर-
सबसे छोटी पूर्ण संख्या शून्य (0) है।
प्रश्न 4.
सबसे बड़ी पूर्ण संख्या कौन-सी है ?
उत्तर-
कोई भी सबसे बड़ी पूर्ण संख्या नहीं है।
![]()
पाठ्य-पुस्तक पृष्ठ संख्या # 31
प्रश्न 1.
संख्या रेखा का प्रयोग करके, 4 + 5; 2 + 6; 3 + 5; और 1 + 6 को ज्ञात कीजिए।
हल :
(i) 4 + 5
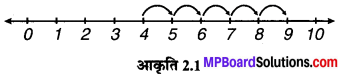
∴ 4 + 5 = 9
(ii) 2 + 6
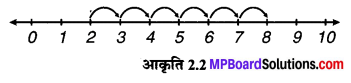
∴ 2 + 6 = 8
(iii) 3 + 5
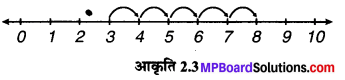
∴ 3 + 5 = 8
(iv) 1 + 6
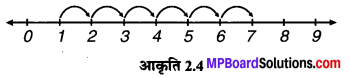
∴ 1 + 6 = 7
पाठ्य-पुस्तक पृष्ठ संख्या # 32
प्रयास कीजिए
प्रश्न 1.
संख्या रेखा का प्रयोग करके, 8 – 3; 6 – 2; और 9 – 6 ज्ञात कीजिए।
हल :
(i) 8 – 3
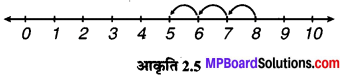
∴ 8 – 3 = 5
(ii) 6 – 2
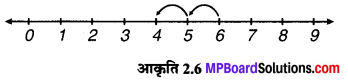
∴ 6 – 2 = 4
(iii) 9 – 6
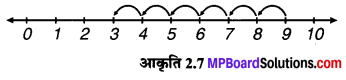
∴ 9 – 6 = 3
![]()
प्रयास कीजिए
प्रश्न 1.
संख्या रेखा का प्रयोग करके, 2 x 6; 3 x 3; और 4 x 2 ज्ञात कीजिए।
हल :
(i) 2 x 6
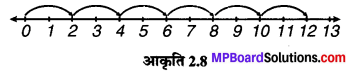
∴ 2 x 6 = 12
(ii) 3 x 3
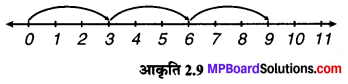
∴ 3 x 3 = 9
(iii)4 x 2
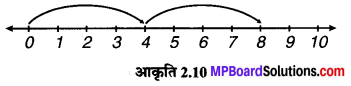
∴ 4 x 2 = 8