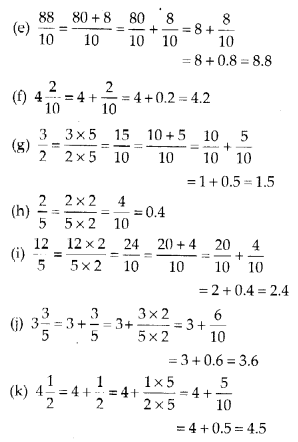MP Board Class 6th Social Science Solutions Chapter 9 The Harappan Civilization
MP Board Class 6th Social Science Chapter 9 Text Book Exercise
Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
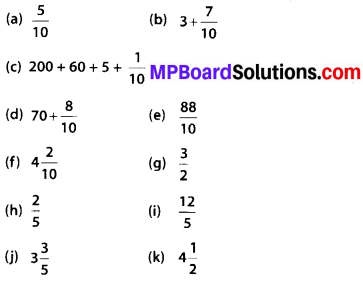
Question (a)
Why is the Indus Valley Civilization, called the Harrappan civilization?
Answer:
The Indus Valley civilization is also called as the Harrappan civilization because:
- Most of the artifacts of this civiliation are discovered from this side.
- It extended over a bigger area than any of other side of this civilization.
Question (b)
What are the main features of the Indus Valley Civilization?
Answer:
The main features of the Indus Valley Civilization are:
- It’s expanse shows that it was the largest civilization in area.
- It’s area was twenty times the area of the Egyptian civilization.
- It developed in the northern and western parts of India and Pakistan in the valley of the river Indus.
- It is expanded to Pakistan Southern Afghanistan and in Rajasthan, Gujarat, Jammu and Kashmir, Punjab, Haryana, Western Uttar Pradesh and Maharashtra in India.
![]()
Question (c)
Which tree was worshipped in the Indus Valley Civilization?
Answer:
Peepal tree was worshipped in the Indus Valley Civilization.
Question (d)
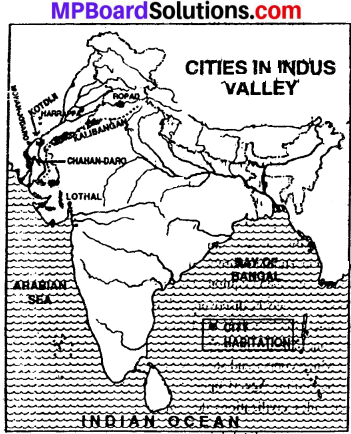
Name the four main sites of the Harrappan civilization?
Answer:
The four main sides of the Harrappan civilization are:
- Mohan – jo – dero and Chan -hu – daro (Pakistan)
- Ropad (Punjab)
- Rangpur (Sourashtra)
- Rakhigarhi (Haryana)
Answer the following questions in brief:
Question 2.
Question (a)
Why did the river valley civilization develop on the banks of rivers?
Answer:
The river valley civilization develop on the banks of rivers because:
- The soil on the banks of rivers was fertile.
- Water was also easily available.
- Transport was possible on boats and rafts.
- Grass and water for the animals was also easily available.
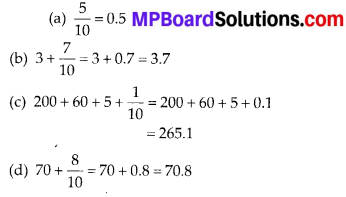
Question (b)
Write about the technology and technical knowledge in the Harrappan civilization?
Answer:
Harrappan civilization belong to the Bronze Age. Bronze is made by mixing zinc or tin with copper. Bronze is stronger than copper. The things found in excavations. prove that the people of this civilization had well developed the art of melting, moulding Their doors and windows were made of and mixing metals.
The artisans were proficient in making earthern untensils, rasp and toys. They also made ornaments of silver, gold and precious stones. The statue of a dancer in bronze is the best example of the Harappans Sculpture.
![]()
Question (c)
Which crops were grown in the Harrappan civilization?
Answer:
The Crop grown in the Harappan civilization were wheat, barley, mustard, cotton, pea and sesamum.
Question (d)
What tools were used by the Harappan people for weight and measurement?
Answer:
The Harrappan people used “weights” and “measuring rods” for weighing and measuring.
Give detailed answers to the following questions:
Question 3.
Question (a)
Explain the planning of cities in Harrappan?
Answer:
Harappan cities and their town planning:
The cities of Mohan – jo – daro and Harrappa were well – planned. They were divided in two parts. The upper part built on raised platforms is known as citadel. The lower part where majority of population lived had to take refuse sometimes in the citadel. The roads in the cities were straight and intersected each other perpendicularly.
Grainaries were the most impressive buildings in the citadel of Harrappa. They were neatly laid out in rectangles and lay close to the river. These granaries used to be full to meet out the demands of city dwellers. Some palace-like buildings have also been found. A building having a big hall has also been found. The best known of the building is citadel is called Great Bath.
The Great Bath resembled a large swimming pool. Houses in the Mohen – jo – daro were carefully planned. They were built of brick and had thick, strong walls, which were plastered and coloured. The roofs were flat. Their doors and windows were made of wood. The kitchen had a fireplace and large jar of pottery.
The main points of Harrappan’s cities:
- The use of fired bricks in building was the speciality of the Harrappan Civilization. These were not used in the contemporary Egyptian and Mesopotamian civilizations.
- The Harrappan people were the first to develop planned cities with a network of streets and drainage system.
![]()
Question (b)
What do you know about the religious beliefs of the Harrappan people?
Answer:
Religious Beliefs of Harrappa People:
The Historians have made some guess work about the Harrappa people. Clay figures of mother goddess have been found, so they probably worshipped these. A seated figure of a male god, carved on a small stone seal was also found. This Pasupati seal was found at Mohen – jo – daro. Some of the Harrappan people buried their dead in graves, other practised urn burial. They believed that there was life somewhere even after death because often contained household pottery, ornaments and mirrors.
Question (c)
Write the reasons for the decline of the Harrappan people?
Answer:
The following reasons have been attributed to the probable decline of the Harrappan civilization on the basis of the evidences found so far:
- The river Indus have changed its route due to earthquake causing great landslides which buried the cities underearth.
- Some historians believe that the civilization was destroyed by Aryan invasion.
- The scarcity of rain in this area and the increase in the desert land adversely affected agriculture and animal rearing which caused the decline of the civilization.
- Some people presume that the civilization declined due the flood in the river Indus.
Question 4.
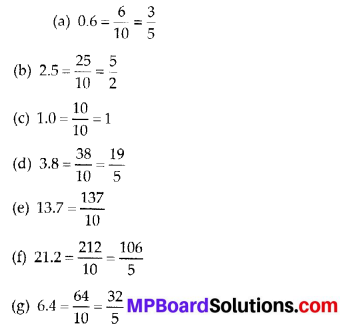
Fill in the blanks:
- The most important public place plastered and coloured in Mohan -jo- daro was the great ………………….. (godown/bath)
- The Harrappan Civilization was …………………… civilization (Urban/rural)
- The dancer in bronze found in the Harappan. Civilization is the best example of ……………….
(sculpture/architecture) - The picture of an ox with a hump is found on ……………. (building/seals)
- The Harrapan script was ……………… (Devanagari/pictorial)
- Attention was paid in the Harrappan Civilization on ……………… and pollution free environment, (cleanliness/fifth)
Answer:
- bath
- urban
- sculpture
- seals
- pictorial
- cleanliness
![]()
Question 5.
Match the civilizations with the river valleys in which they developed.
- Valley of the river Nile – Mohan – jo – daro and Harrappa Civilization
- Valley of the rivers – Egyptian Civilization Euphrates and Tigris
- Valley of the river Indus – Chinese Civilization
- Valley of the river Hwang – Ho Chinese Civilization.
Answer:
- Valley of the river Nile – Egyptian Civilization
- Valley of the rivers – Euphrates and Tigris Mesopotamian Civilization
- Valley of the river Indus – Mohan – jo – daro and Harrappa Civilization
- Valley of the river Hwang – Ho Chinese Civilization –
Choose the correct alternative :
Question 6.
Question (a)
Which among the following is not a characteristic of the Harrappan Civilization?
(a) Planned cities
(b) The art of melting and moulding metals
(c) Shelter on trees and in caves
(d) Animal rearing and agriculture.
Answer:
(c) Shelter on trees and in caves
Question (b)
Which among the following metals was mostly used by the Harrappans?
(a) iron
(b) copper
(c) gold
(d) silver
Answer:
(b) copper
Question (c)
Which among the following was one of the causes for the decline of the Harappan Civilization?
(a) Fire
(b) Aryan invasion
(c) Maghal in vasion
(d) Heavy rainfall
Answer:
(b) Aryan invasion
![]()
Project Work
Question 1.
Write the achievements of the Harrappan Civilization in a sequence?
Answer:
Please do with the help of your teacher.
Question 2.
Show the following cities on a map?
Harrappa, Mohan – jo – daro, Kalibangan, Lothal, Ropad.
Answer: