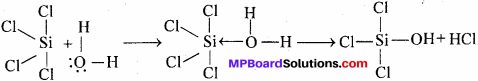
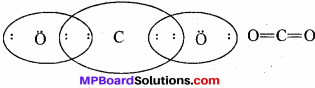
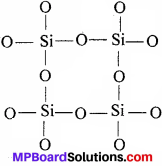
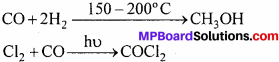MP Board Class 11th Special Hindi सहायक वाचन Solutions Chapter 4 असफलता दिखाती है नयी राह
असफलता दिखाती है नयी राह अभ्यास प्रश्न
निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों के उत्तर लिखिए
प्रश्न 1.
डॉ. कलाम बचपन में कौन-सी पौराणिक कहानी सुना करते थे? उसका उन पर क्या प्रभाव पड़ा?
उत्तर:
डॉ. कलाम को उनके पिताजी अबूबेन आदम की एक पौराणिक कथा सुनाया करते थे। एक रात अबू एक सपना देखकर जाग जाता है। सपने में वह देखता है कि एक फरिश्ता सोने की किताब में उन लोगों के नाम लिख रहा है जो ईश्वर से प्यार करते हैं। अबू उस फरिश्ते से पूछता है कि क्या खुद उसका नाम भी इस सूची में है। इस पर फरिश्ता नकारात्मक उत्तर देता है। तब निराश मगर खुशी से अबू कहता है कि मेरा नाम उनमें लिख दो, जो उसके अनुयायियों से प्रेम करते हैं। फरिश्ते ने नाम लिख दिया और गायब हो गया। अगली रात फिर फरिश्ता आया और उन लोगों के नाम दिखाए जिन्हें ईश्वर के प्रेम से आशीर्वाद मिला था। इसमें अबू का नाम सबसे ऊपर था।
इस पौराणिक कहानी का कलाम पर इतना प्रभाव पड़ा कि वे प्रत्येक जगह ईश्वर की उपस्थिति मानते थे और यह मानते थे कि सभी प्राणी ईश्वर की कृति हैं। उन्हें परस्पर सभी से प्रेम करना चाहिए। इन्हें अल्लाह में गहरी आस्था है।
प्रश्न 2.
परिवार में लगातार होने वाली मौतों के बाद, डॉ. कलाम की दिनचर्या में क्या परिवर्तन हुआ?
उत्तर:
डॉ. कलाम के परिवार में लगातार तीन वर्ष तक तीन मौतें हो जाने के बाद, उनमें अपने काम के प्रति पहले से ज्यादा प्रतिबद्धता आ गई। उन्होंने अपने लिए वह सब कुछ तलाश लिया था जिससे उन्हें आगे बढ़ना था, तरक्की करनी थी। एस. एल. वी. डॉ. कलाम के लिए एक ईश्वर द्वारा प्रदत्त मिशन था। इसके क्षेत्र में प्रगति करना उनका उद्देश्य था, ध्येय बन चुका था। इसलिए उन्होंने अपनी सभी गतिविधियों पर रोक लगा दी। यद्यपि उनकी अन्य गतिविधियाँ अधिक नहीं थीं, फिर भी जो कुछ थीं, उनको भी समाप्त कर दिया। वे शाम को बैडमिन्टन खेला करते थे, उसका खेलना भी बन्द हो गया। उन्हें साप्ताहिक अथवा अन्य अवकाश मिला करते थे, उन्हें भी लेना बन्द कर दिया। वे अपने परिवार अथवा रिश्तेदारी में यदा-कदा आया-जाया करते थे, वह भी बन्द कर दिया। प्रतिदिन मुलाकातें जिनसे हो सकती थीं, प्रायः वे उनसे मिलने जाया भी करते थे, इस श्रेणी में आने वाले दोस्तों और सहयोगियों से मिलने जाना अथवा किसी काम के सन्दर्भ में उनके यहाँ पहुँच जाना हुआ करता था, वह सब बन्द हो गया।
उन्होंने अपने मिशन को सफल बनाने की इच्छा से अपने लक्ष्य के प्रति एकाग्रचित्त होकर स्वयं को समर्पित कर दिया। डॉ. कलाम सरीखे व्यक्तियों को कार्याधिकता से ग्रसित व्यक्ति कहा जाता है। उन्हें ऐसा कहे जाने के लिए विरोध करना उचित लगता था। इसका एक कारण है। कार्याधिकता से ग्रसित के रूप में पुकारा जाना एक बीमारी (रुग्णता) का प्रतीक बनता है। यह शब्द किसी बीमारी का द्योतक है। जबकि प्रतिबद्धता (वचनबद्धता), एकाग्रचित्तता अपने लक्ष्य (उद्देश्य) को प्राप्त करने का साधन हुआ करता है, किसी रोग का सूचक नहीं। डॉ. कलाम ज्यादा से ज्यादा वही करना चाहते थे, जिससे उन्हें दुनिया में सबसे ज्यादा खुशी प्राप्त हो अर्थात् अधिक से अधिक कार्य करने से उद्देश्य के निकट पहुँचा जा सकता है। सफलता प्राप्त हो सकती है। सफलता हमें प्रसन्नता देती है।
ऐसे व्यक्ति जो अपने पेशे में शीर्ष तक पहुँचना चाहते हैं, उनके अन्दर पूर्ण वचनबद्धता का मूलभूत गुण विकसित कर लेना चाहिए। जो व्यक्ति अपनी सम्पूर्ण क्षमता के साथ कार्य सम्पादन की इच्छा रखता है, उसमें शायद ही कोई अन्य इच्छा जन्म लेती हो। पुरुष हो अथवा स्त्री उन सबमें वचनबद्धता का गुण अवश्य होना चाहिए।
डॉ. कलाम के अन्दर भी इन तीन वर्षों का दुःखद घटनाओं के बाद शीर्ष पर पहुँचने के लिए दृढ़ इच्छा शक्ति का विकास होता गया।
![]()
प्रश्न 3.
रामेश्वरम् मन्दिर के पास डॉ. कलाम संध्या का समय किस प्रकार व्यतीत करते थे? (2011)
उत्तर:
डॉ. कलाम अपने बचपन की स्मृतियों को पुनः जाग्रत करके स्पष्ट रूप से बतलाते हैं कि रामेश्वरम् मन्दिर के आस-पास ही घूमा करते थे। समुद्र के आस-पास की बलुई मिट्टी चाँदनी रात में चमकती दिखाई देती थी। डॉ. कलाम को सान्ध्यकालीन वातावरण बहुत ही आकर्षित करता था। इसके अतिरिक्त समुद्र की उठती, इठलाती लहरें एक विशेष प्रकार का नृत्य प्रस्तुत करती जान पड़ती थीं। वहाँ का असीम आकाश खुला हुआ आनन्दातिरेक से डॉ. कलाम को आत्मविभोर कर देता था। अनन्त आकाश में बिखरे हुए टिमटिमाते तारे अपनी मद्धिम रोशनी विकीर्ण करते हुए धीमे से उनके कानों में कुछ रहस्यपूर्ण सन्देश देते प्रतीत होते थे। डॉ. कलाम के साथ उनके बहनोई उन्हें सान्ध्यकालीन डूबते क्षितिज को दिखाने के लिए ले जाया करते थे। उनके बहनोई का नाम जलालुद्दीन था।
डॉ. कलाम की अन्तश्चेतना पर बचपन में प्रकृति की गोद में रहने का अत्यधिक प्रभाव पड़ा। उनमें चिन्तन की गहराई परिपक्वता को प्राप्त थी।
प्रश्न 4.
एस. एल. वी.-3 की तैयारी में डॉ. कलाम किस तरह व्यस्त रहते थे? (2017)
उत्तर:
एस. एल. वी.-3 पर अभी काम चल रहा था। साथ ही इसकी उप-प्रणालियों को तैयार करने का काम भी पूरा होने जा रहा था। जून 1974 ई. में कुछ जटिल प्रणालियों के परीक्षण के लिए सैंटोर साउण्डिग रॉकेट छोड़ा। इन उपप्रणालियों में जो सम्मिश्र पदार्थ, कन्ट्रोल इन्जीनियरिंग और सॉफ्टवेयर प्रयोग में लाए गये थे, उनका देश में पहले कभी इस्तेमाल नहीं किया गया था, परीक्षण पूरी तरह सफल रहा, तब तक भारतीय अन्तरिक्ष कार्यक्रम साउण्डिग रॉकेटों से आगे नहीं बढ़ा था और यहाँ तक कि जानकार लोग भी इसकी कोशिशों को देखने-समझने और स्वीकार करने को राजी नहीं थे, पहली बार इन्हें राष्ट्र के विश्वास से प्रेरणा मिली थी। एस. एल. वी.-3, ए. पी. जी. रॉकेट के ऊपरी हिस्से का विकास डायामाण्ट की तरह ही तैयार किया गया। इसका उड़ान परीक्षण फ्रांस में होना था। इसमें कई समस्याएँ आ गई थीं। इन समस्याओं को दूर करने के लिए डॉ. कलाम को तत्काल फ्रांस जाना था।
एस. एल. वी.-3, ए. पी. जी. रॉकेट के सफल परीक्षण के बाद फ्रांस से लौटने पर एक दिन ब्रह्म प्रकाश ने वनहर फॉन ब्रॉन के पहुँचने के बारे में सूचना दी। रॉकेट विज्ञान के क्षेत्र में काम करने वाला हर व्यक्ति फॉन ब्रॉन के बारे में जानता है। फॉन ब्रॉन को मद्रास से थुम्बा लाने को कहा तो डॉ. कलाम बहुत ही रोमांचित हो उठे, चेन्नई से त्रिवेन्द्रम तक डॉ. कलाम व अन्य एयरक्राफ्ट से गये। इस यात्रा में नब्बे मिनट का समय लगा। फॉन-ब्रॉन ने काम के विषय में पूछा। उन्होंने इस सन्दर्भ में एक छात्र की तरह जानकारी ली। डॉ. कलाम को यह पता नहीं था कि रॉकेट विज्ञान के जन्मदाता इतने विनम्र, ग्रहणशील एवं प्रेरणा देने वाले होंगे। पूरी उड़ान के दौरान बहुत अच्छा महसूस किया। डॉ. कलाम को मिसाइलों के इतने बड़े ज्ञाता से बात करके पता चला कि वे अपनी प्रशंसा के इच्छुक नहीं हैं।
फॉन ब्रॉन ने टिप्पणी करते हुए कहा कि एस. एल. वी.-3 एक विशुद्ध भारतीय डिजाइन है। आपके सामने समस्याएँ भी आ सकती हैं। इसके लिए तुम्हें ध्यान रखना है कि व्यक्ति का सफलताओं से ही नहीं, असफलताओं से भी निर्माण होता है। उन्होंने आगे कहा कि रॉकेट विज्ञान में कठोर परिश्रम और प्रतिबद्धता की जरूरत होती है। साथ ही उस परिश्रम के द्वारा बड़ा सम्मान प्राप्त कर सकते हैं। इस विज्ञान को पेशा न बनाकर अपना धर्म समझो।
सन् 1979 ई. में छः सदस्यों की टीम नियन्त्रण प्रणाली का रूपान्तर तैयार करने में लगी थी। इस प्रणाली के बारह बाल्वों में से एक को ठीक करते समय नाइट्रिक एसिड का टैंक फट गया। एसिड टीम सदस्यों पर गिरा। वे सभी गम्भीर रूप से घायल हो गये। उन सभी को डॉ. कलाम ने त्रिवेन्द्रम् मेडिकल कॉलेज ले जाकर इलाज के लिए भर्ती कराया। घायल टीम के सदस्य दर्द से कराह रहे थे, लेकिन उपचार उचित होने से उन्हें राहत मिली। डॉ. कलाम इस दौरान बड़े चिन्तित और व्यथित रहे। परीक्षण काम रुक गया और विलम्ब हो गया। इस दुर्घटना से असफलता होने से हमें साहस अधिक मिला और सोचा कि हमारी टीम चट्टान की तरह साथ रहने में मजबूत है। अब एस. एल. वी.-3 का ठोस आकार आने लगा और उसकी परियोजना अब सफल हो रही थी।
एस. एल. वी.-3 का प्रायोगिक उड़ान परीक्षण 10 अगस्त, 1979 को निर्धारित किया गया। श्रीहरिकोटा प्रक्षेपण केन्द्र से समेकित प्रक्षेपण यान विकसित करना था। उड़ान प्रणालियों में-स्टेज मोटर्स, निर्देशन व नियन्त्रण प्रणाली और इलेक्ट्रॉनिक प्रणाली को जाँचना था। चैक आउट, टैकिंग, टेलीमीटरी एवं आँकड़ों से सम्बन्धित सुविधाएँ भी इस केन्द्र में विकसित करनी थीं। इस प्रकार तेईस मीटर लम्बा, चार चरणों वाला एस. एल. वी.-3 रॉकेट सुबह सात बजकर अट्ठावन मिनट पर छोड़ा गया। इसका वजन सत्रह टन था। प्रक्षेपण के तुरन्त बाद ही इसकी प्रणालियों ने अपने काम शुरू कर दिये।
इसकी उड़ान निश्चित हो जाने पर, इसमें अचानक कोई गड़बड़ी आ गई। उम्मीदों पर पानी फिर गया। रॉकेट का दूसरा चरण नियन्त्रण से बाहर हो गया। 317 सेकण्ड के बाद ही उड़ान बन्द हो गई और पूरा यान श्रीहरिकोटा से पाँच सौ साठ किमी दूर समुद्र में जा गिरा।
इस घटना से इनकी टीम को गहरा सदमा लगा। डॉ. कलाम स्वयं अपने पर नाराज हुए और निराशा हाथ लगी। उन्हें लगा कि उनके पैर थक गये हैं। उनमें पीड़ा थी। इस समस्या का असर शरीर की अपेक्षा मस्तिष्क में बहुत अधिक था।
प्रश्न 5.
जो व्यक्ति शीर्ष पर पहुँचना चाहते हैं, उनमें कौन-कौन से गुण होने चाहिए ? इसे डॉ. कलाम के जीवन के आधार पर समझाइए। (2008, 09)
उत्तर:
जो लोग अपने पेशे में शीर्ष पर पहुँचना चाहते हैं। उनमें पूर्ण वचनबद्धता का मूलभूत गुण होना चाहिए। हम अपनी सफलता चाहते हैं तो हमें यह भरोसा करना पड़ेगा कि हम जो भी काम करना चाहते हैं, तो हमें अपनी क्षमताओं पर भरोसा व दृढ़ आस्था होनी चाहिए।
अपनी क्षमताओं को जागृत कर, अपने निर्धारित उद्देश्य को प्राप्त करने के लिए जो इच्छा उठती है, तो बाद में फिर कोई भी इच्छा जन्म नहीं लेती है। डॉ. कलाम के साथ काम करने वाले व्यक्तियों को प्रत्येक सप्ताह में चालीस घण्टे काम करना पड़ता था। इस प्रकार उन्हें चालीस घण्टे तक काम करने का पैसा दिया जाता था। डॉ. कलाम बताते हैं कि वे ऐसे व्यक्तियों से भी परिचित हैं, जो सप्ताह में कम से कम साठ, अस्सी और यहाँ तक है कि वे सौ घण्टे प्रति सप्ताह काम करते थे। इसके अनुसार उन्हें पैसा दिया जाता था। वे जानते थे और समझते भी थे कि उनका काम रोमांच पैदा करने वाला है, साथ ही साथ चुनौतियों से भरा है। इसलिए इस काम से उन्हें सबसे अच्छा प्रतिफल प्राप्त होगा। इस तरह के वे पुरुष या स्त्री जो भी हों वे चुनौती भरे कामों को हाथ में लेते हैं। उन्हें अपने इन कामों में पूर्ण सफलता मिलती है क्योंकि उनमें पूर्ण-रूपेण वचनबद्धता पाई जाती है।
जिन व्यक्तियों में अपने कार्य के पूर्ण करने की वचनबद्धता होती है तो उनमें ऊर्जा अधिक होती है। उनका काम जब चुनौतीपूर्ण होता है, तो उन्हें अपने आप को पूर्ण स्वस्थ बनाए रखना पड़ेगा। पूर्ण स्वस्थ रहने के लिए विशेष ऊर्जा की जरूरत होती है।
शीर्ष पर पहुँचने के लिए दृढ़ इच्छाशक्ति की परम आवश्यकता है। यह काम माउण्ट एवरेस्ट पर चढ़ने का अथवा अपने कार्य क्षेत्र का शीर्ष हो सकता है। परन्तु हर व्यक्ति में ऊर्जा अलग-अलग मात्रा में होती है, जो जन्म के साथ ही मिलती है। अत: जो व्यक्ति सबसे पहले प्रयास करेगा और अपनी ऊर्जा का इस्तेमाल करेगा, वही सबसे पहले और शीघ्रता से अपने जीवन को सुव्यवस्थित कर पायेगा।
प्रश्न 6.
डॉ. कलाम का जीवन संघर्षों के मध्य उभरती प्रतिभा की कहानी है, उदाहरण देते हुए समझाइए। (2008, 16)
उत्तर:
डॉ. कलाम का सारा जीवन संघर्षों से भरा हुआ था। उनके मध्य भी उन्होंने निराशा या हार नहीं मानी। अनेक बाधाओं के मध्य अपनी प्रतिभा की ऊर्चस्वलता का प्रदर्शन करते ही रहे। वे अपने जीवन के शुरूआती पक्ष में वायु सेना में भर्ती होकर पायलट बनना चाहते थे। विमान उड़ाने की उनकी चाहत पूर्ण नहीं हो सकी। इसका एक कारण यह था कि चयन बोर्ड ने उन्हें उपयुक्त नहीं समझा। लेकिन देखिये, जो व्यक्ति अपनी युवावस्था में विमान चालक की क्षमताओं से रहित माना गया, वही अपनी वृद्ध अवस्था में ऐसे विमान में उड़ने लगा जो आवाज से भी तेज गति वाला था। इस प्रकार व्यक्ति अपने अन्तःस्थल की गहराई में इच्छा की पूर्ति किसी भी तरह और किसी भी अवस्था में पूर्ण करने की क्षमता विकसित कर लेता है। प्रश्न है केवल अपनी सद् इच्छाओं के प्रति सद्प्रयास करने एवं कथनी की प्रतिबद्धता का होना। इन्हीं बातों को, गुणों को डॉ. कलाम में हम देखते हैं और उन्हें वचनबद्धता और प्रतिबद्धता से शीर्ष तक पहुँचने में सफलता मिली।
प्रतिभा के विकास और उभार में पारिवारिक स्थिति और पैतृक योग कोई खास भूमिका नहीं निभाते। डॉ. कलाम पारिवारिक रूप से बहुत साधारण माता-पिता की सन्तान थे। बस, महत्त्वपूर्ण बात थी तो केवल महान विचारों को जीवन में स्थान देने की और उनके अनुसार कर्म करने की।
डॉ. कलाम के परिवार की आर्थिक स्थिति भी ऐसी नहीं थी जो उन्हें उत्तम साधन उपलब्ध करा पाती। उन्हें सही मार्गदर्शन देने वाला भी उनके परिवार में कोई नहीं था। एक महानुभाव जलालुद्दीन महोदय थे भी, लेकिन अल्लाह ने उन्हें असमय ही अपने पास बुला लिया। जलालुद्दीन डॉ. कलाम के बहनोई थे। वे ही इनके लिए पुस्तकों का खर्च जुटाते थे। व्यय करने के लिए रुपये-पैसे भी वही जुटाते थे। यहाँ तक है कि सांताक्रूज हवाई अड्डे पर इनको विदा करने के लिए वे ही आया करते थे।
श्री जलालुद्दीन ही इन्हें रामेश्वरम् के आस-पास घुमाते थे। चाँदनी रात में चमकती मिट्टी, नाचती हुई समुद्री लहरें, आकाश में टिमटिमाते सितारे उन्हें ऊँचा उठने और ऊँची उड़ान भरने के सपने उनमें पैदा करते थे। चमकती मिट्टी उन्हें प्रेरित करती कि अपनी मातृभूमि की सेवा करने से तुम्हें भी वही चमक प्राप्त होगी। अब उन्हें लगने लगा कि वे काल के भंवर में फंस गये हैं।
डॉ. कलाम ने हिम्मत नहीं हारी। वे अपने अन्दर ऊर्जावान बने रहे। उस ऊर्जा ने इनकी प्रतिभा को शक्ति प्रदान की जिसके कारण सांसारिक आपदाओं से, बाधाओं से लड़ने की हिम्मत और हौंसला बना रहा। जो व्यक्ति हौंसला पस्त नहीं होता वह उन्नति के शिखर पर विराजमान होकर ही रहता है। इस सन्दर्भ में कुछ उदाहरण प्रस्तुत हैं, “एस. एल. वी.-3 को तैयार करना कष्ट साध्य प्रक्रिया थी।” …..” इसी बीच उनके बहनोई और उन्हें रास्ता दिखाने वाले जनाब अहमद जलालुद्दीन जब इस दुनिया से चले गये थे, तो वे एकदम थम से गये, कुछ भी सोच नहीं पाये, काम करने में ध्यान लगाने की कोशिश की, लेकिन अपने आप में बहकी-बहकी बातें कर रहे हैं। तब उन्हें इस बात की अनुभूति हुई कि “अहमद जलालुद्दीन के साथ मेरा भी एक हिस्सा चला गया है।”
अहमद जलालुद्दीन की मौत के बाद उनके पिता का देहावसान होना और फिर उनकी माँ का भी चला जाना, इस तरह तीन वर्ष में लगातार तीन मौतों के दौर से गुजरना और एस. एल. वी. -3 का निर्माण व परीक्षण व्यवस्था का कार्य सभी विपरीत स्थितियाँ थीं; जिनमें से डॉ. कलाम धैर्य, उद्देश्य के प्रति आस्था और वचनबद्धता तथा ध्येय प्राप्ति की प्रतिबद्धता के गुणों के कारण आगे निकल सकें।
उपर्युक्त वर्णन से सिद्ध है कि डॉ. कलाम का जीवन संघर्षों के मध्य उभरती प्रतिभा की कहानी है।
असफलता दिखाती है नयी राह अति लघु उत्तरीय प्रश्न
प्रश्न 1.
डॉ. ए. पी. जे. अब्दुल कलाम क्या बनना चाहते थे?
उत्तर:
डॉ. कलाम वायुसेना में भर्ती होना चाहते थे तथा विमान उड़ाना चाहते थे, यद्यपि चयन बोर्ड ने उन्हें इसके उपयुक्त नहीं पाया था।
प्रश्न 2.
डॉ. ए. पी. जे. अब्दुल कलाम के पिताजी का नाम क्या था ? वह कितने वर्ष तक जीवित रहे?
उत्तर:
डॉ. ए. पी. जे. अब्दुल कलाम के पिताजी का नाम जैनुल आबदीन था। सन् 1976 में रामेश्वरम् में एक सौ दो वर्ष तक रहने के पश्चात् उनका निधन हो गया।
![]()
असफलता दिखाती है नयी राह पाठ का सारांश
प्रस्तावना :
डॉ. ए. पी. जे. अब्दुल कलाम का नाम कौन नहीं जानता ? वे भारतीय गणराज्य के राष्ट्रपति रहे हैं। वे प्रारम्भ में वायुसेना में भर्ती होना चाहते थे। लेकिन चयन बोर्ड ने उन्हें उपयुक्त नहीं पाया। उस युवक का सपना टूट गया। वह वायु सेना में भर्ती होकर विमान उड़ाना चाहता था। लेकिन उसी युवक ने, जब वह कुछ बूढ़ा हो रहा था, तब आवाज से भी तेज गति वाले विमान उड़ाकर अपने सपने को पूरा किया। डॉ. कलाम का जन्म एक कस्बे के साध पारण से परिवार में हुआ था। कलाम अपने जीवन में बड़े सपने देखते थे। साथ ही, उन्हें पूरा करने की भी जिद करते और सफलता प्राप्त करते थे। ‘अग्नि की उड़ान’ उनकी आत्मकथा है। यहाँ इस उड़ान के कुछ रोमांचक अंश प्रस्तुत हैं-
एस. एल. वी-3 पर अभी काम चल रहा था। इसकी उप-प्रणालियों को तैयार करने का काम भी पूरा होने जा रहा था। सन् 1974 के जून महीने में कुछ जटिल प्रणालियों के परीक्षण के लिए “सैंटोर साउण्डिंग रॉकेट” छोड़ा गया। इन उप-प्रणालियों में जो सम्मिश्र पदार्थ, कन्ट्रोल इन्जीनियरिंग और सॉफ्टवेयर प्रयोग में लाये गये, उनका देश में पहली बार प्रयोग किया गया। परीक्षण सफल रहा। राष्ट्र के विश्वास से प्रेरणा मिली।
कष्टसाध्य प्रक्रिया :
एस. एल. वी.-3 को तैयार करना एक कष्टसाध्य प्रक्रिया थी। एक दिन डॉ. कलाम और उनकी टीम पहले चरण की मोटर परीक्षण के काम में पूरी तरह तल्लीन थी। तभी डॉ. कलाम को सूचना मिली कि उनके बहनोई अहमद जलालुद्दीन अब इस दुनिया में नहीं रहे। इस खबर से कलाम महोदय कुछ समय तक अस्त-व्यस्त रहे। काम में उनका मन नहीं लगा क्योंकि मुः जलालुद्दीन डॉ. कलाम के जीवन का अहम् हिस्सा थे।
बचपन की यादें :
डॉ. कलाम को अपने बचपन की स्मृतियाँ उभर कर आने लगीं। मुहम्मद जलालुद्दीन उन्हें संध्याकाल में रामेश्वर मन्दिर के आस-पास घुमाने ले जाते थे। चाँदनी रात में चमकती समुद्र की रेत और नृत्य करती समुद्री लहरें, अनन्त आकाश से टिमटिमाते तारों का प्रकाश तथा डूबते सूरज के क्षितिज को दिखाने ले जाते थे। वे ही कलाम साहब के लिए पुस्तकों का बन्दोबस्त करते थे। सांताक्रूज हवाई अड्डे पर इन्हें विदा करने के लिए जलालुद्दीन (डॉ. कलाम के बहनोई) ही जाया करते थे।
डॉ. कलाम का अधीर होना :
मुहम्मद जलालुद्दीन का इस दुनिया से चला जाना कलाम को ऐसा लगा मानो समय और काल के भंवर में उन्हें फेंक दिया हो। उनके पिता की उम्र सौ साल से अधिक रही होगी। उनके दामाद का जनाजा उठाना था जो उनकी उम्र से आधी उम्र के थे। कलाम की बहन जोहरा की आत्मा कलप रही थी। उसका चार साल का बेटा भी चल बसा था, उसके चले जाने के घाव अभी भरे भी नहीं थे। ये सभी दृश्य कलाम की धुंधलाई सी आँखों के सामने तैर रहे थे। कलाम ने स्वयं को सम्भाला और परियोजना के उप निदेशक डॉ. एस. श्रीनिवास को अपनी गैरहाजिरी में काम को देख लेने के बारे में निर्देश दिये।
अल्लाह में गहरी आस्था :
बसें बदलते हुए रामेश्वर का सफर तय किया। डॉ. कलाम के पिता इनका हाथ थामे थे। उनकी आँखों में कोई भी आँसू नहीं था। पिता बोले देखो ईश्वर किस प्रकार अन्धेरा कर देता है। जलालुद्दीन तुम्हें रास्ता दिखाने वाला सूरज था, वही गहरी नींद में सो गया। वह पूरी तरह शान्त और अचेतन है। अल्लाह की नियति के आगे कुछ नहीं कर सकते। बेटे कलाम! अल्लाह पर भरोसा रखो।
वैराग्यभाव की जागृति :
डॉ. कलाम थुम्बा लौट आये। उन्हें हर काम निरर्थक लगा। एक वैराग्य जैसा अनुभव हुआ।
पिता की मृत्यु :
सन् 1976 ई. में डॉ. कलाम के पिता का इन्तकाल हो गया। वे रामेश्वरम् की भूमि पर एक सौ दो वर्ष तक रहे। उनका नाम जैनुल आबदीन था।
प्राणिमात्र से प्रेम :
डॉ. कलाम के पिता सभी प्राणियों से प्रेम करते थे। इस दुनिया के प्राणी ईश्वर की प्रतिकृति हैं। इनसे प्रेम करना ईश्वर से प्रेम करना है। ऐसा डॉ.कलाम के पिता का जीवन दर्शन था।
एस. एल.वी.-3, ए. पी. जी. रॉकेट का निर्माण व परीक्षण :
एस. एल. वी.-3, ए. पी. जी. रॉकेट का निर्माण सफलतापूर्वक किया गया और इसका परीक्षण विदेश में फ्रांस की भूमि पर किया गया। इस परीक्षण में आई हुई जटिल समस्याओं का निराकरण करने डॉ. कलाम को फ्रांस तत्काल जाना था। परन्तु उसी दिन इनकी माँ के इन्तकाल की खबर दी गई। डॉ. कलाम नागर कोइल से रामेश्वर पहुँचे। उनका अन्त समय आ गया था। डॉ. कलाम ने उसी मस्जिद में प्रार्थना की जहाँ उनके पिताजी हर शाम इन्हें ले जाया करते थे। कलाम ने ईश्वर से क्षमा माँगी। ईश्वर ने जो उन्हें जिम्मेदारी दी, उसका निर्वाह डॉ. कलाम ने ईमानदारी से किया। कलाम ने स्वयं को समझाते हुए कहा कि शोक क्यों मना रहे हो ? उस काम पर ध्यान दो जो तुम्हारे लिए पड़ा है। अपने कार्यों के करने से ही परमानन्द प्राप्त करो। मस्जिद में कलाम ने इन शब्दों को सुना। मस्जिद से बाहर आकर, अपने घर की ओर देखे बिना ही वहाँ से चल दिये।
अपने उद्देश्य के प्रति प्रतिबद्धता :
डॉ. कलाम के घर में तीन वर्ष में तीन मौतें हो गईं। फिर भी वे अपने काम में उनकी प्रतिबद्धता बनी रही। एस. एल. वी. उनके लिए ईश्वरीय मिशन है और उसकी प्रगति उनका उद्देश्य बन गया था। उन्होंने बैडमिन्टन खेलना बन्द कर दिया। साप्ताहिक छुट्टियाँ भी नहीं करते। रिश्तेदारी और मित्रों के यहाँ आना-जाना सब छूट गया। डॉ. कलाम के अनुसार वचनबद्धता, एकाग्रचित्तता लक्ष्य प्राप्त करने के साधन हैं।
नियन्त्रण प्रणाली का उड़ान रूपान्तर :
सन् 1979 ई. में छः सदस्यों की टीम दूसरे चरण की जटिल नियन्त्रण प्रणाली की उड़ान रूपान्तर तैयार करने में लगी थी। परन्तु अचानक ही लाल धुएँ वाले नाइट्रिक एसिड (आर. एफ. एन. ए.) का टैंक फट गया और नाइट्रिक एसिड टीम के सदस्यों पर जा गिरा। टीम के सदस्य गम्भीर रूप से जल गये। कलाम सभी को त्रिवेन्द्रम मेडीकल कॉलेज ले गये और उनका इलाज कराया।
इस टीम में कलाम को गहरा विश्वास हो गया कि ये सभी सफलता और असफलता में एक चट्टान की भाँति खड़े रह सकते हैं। जीवन एक प्रवाह है जिसमें काम करते-करते आराम और आनन्द की अनुभूति होती है। सन् 1979 के मध्य तक एस. एल. वी. का सपना पूरा हो गया और श्रीहरिकोटा प्रक्षेपण केन्द्र से एल. एल. वी.-3 का प्रायोगिक उड़ान परीक्षण 10 अगस्त, 1979 को निर्धारित किया गया।
उपसंहार :
पहले चरण का कार्य पूर्ण सफल हुआ परन्तु दूसरे चरण में परिवर्तित करने का कार्य एस. एल. वी.-3 को उड़ते देखना उम्मीदों से पीछे रहा। 317 सेकण्ड के बाद उड़ान बन्द हो गई और चौथे चरण सहित पूरा यान श्रीहरिकोटा से पाँच सौ साठ किमी. दूर समुद्र में आ गिरा। इस घटना से हम सभी निराश हुए। परन्तु डॉ. ब्रह्म प्रकाश के साथ डॉ. कलाम के अन्दर एक विश्वास जगा और इसी विश्वास से नई सफलताओं के क्षितिजों तक पहुँचा जा सकता है।