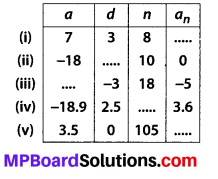
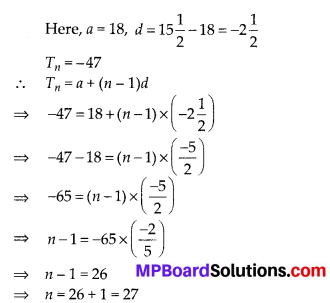
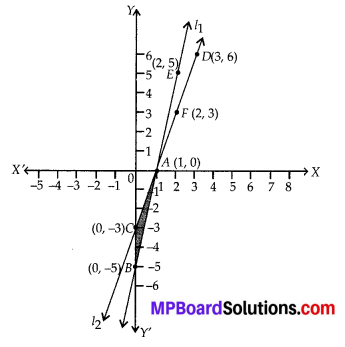
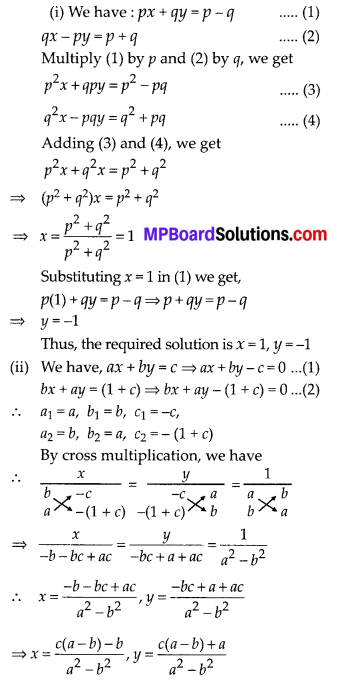
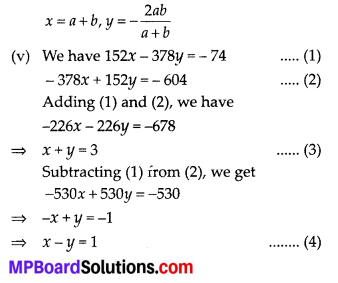
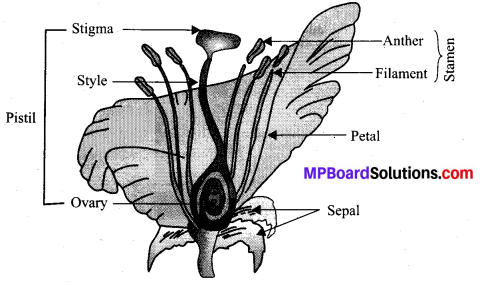
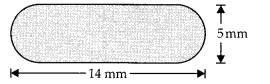
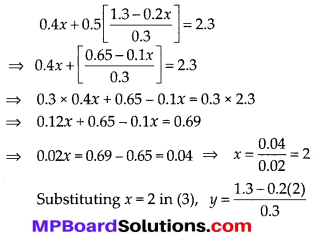
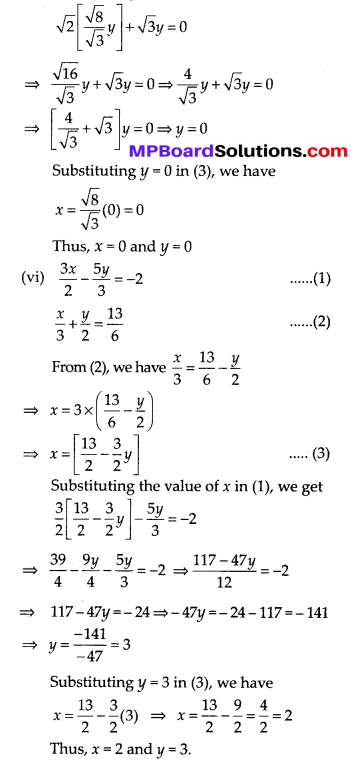
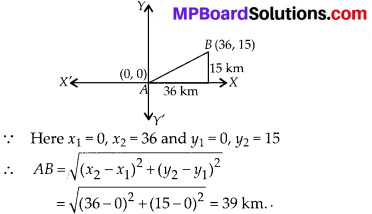
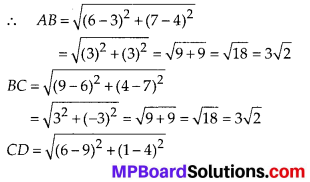
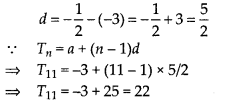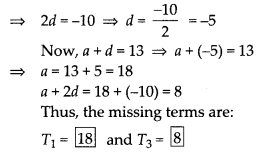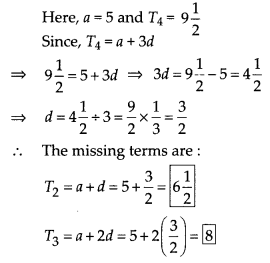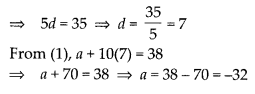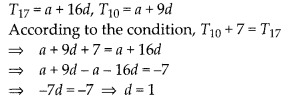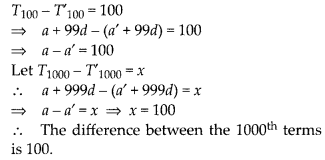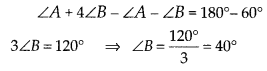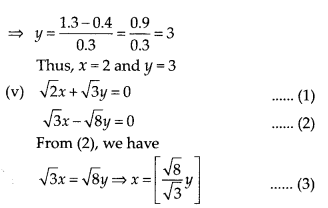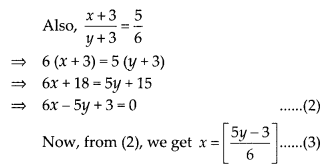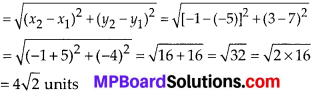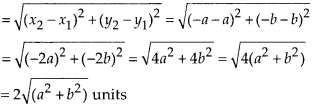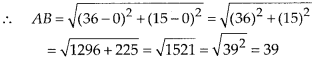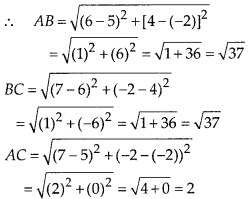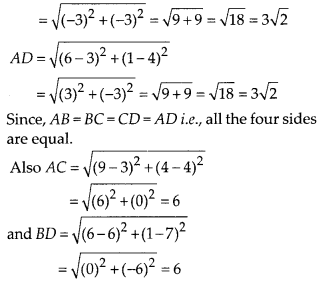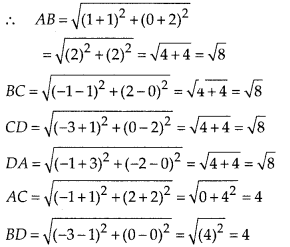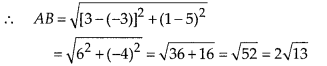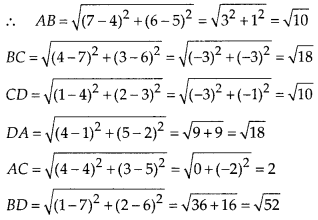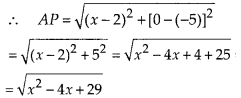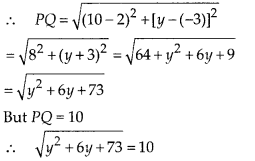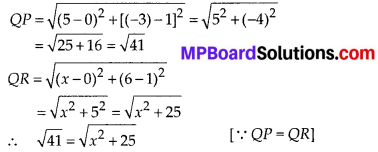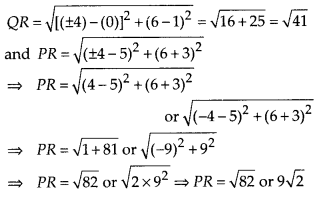In this article, we will share MP Board Class 10th Maths Book Solutions Chapter 6 Triangles Ex 6.1 Pdf, These solutions are solved subject experts from the latest edition books.
MP Board Class 10th Maths Solutions Chapter 6 Triangles Ex 6.1
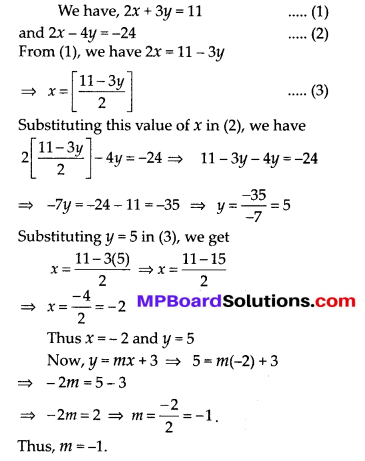
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks using the correct word given in brackets:
(i) All circles are ……….. (congruent, similar)
(ii) All squares are ………….. (similar, congruent)
(iii) All ………….. triangles are similar (isosceles, equilateral)
(iv) Two polygons of the same number of sides are similar, if
(a) their corresponding angles are ………… and
(b) their corresponding sides are …………. (equal, proportional).
Solution:
(i) All circles are similar.
(ii) All squares are similar.
(iii) All equilateral triangles are similar.
(iv) Two polygons of the same number of sides are similar.
(a) Their corresponding angles are equal and
(b) Their corresponding sides are proportional.
![]()
Question 2.
Give two different examples of pair of
i) similar figures
Solution:
coin, wheel of a cart.
ii) non-similar figures.
Solution:
A square Rhombus
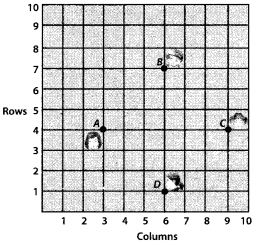
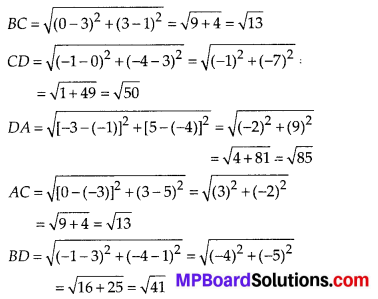
Question 3.
State whether the following quadrilaterals are similar or not:
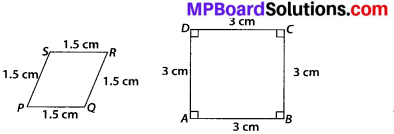
Solution:
On observing the given figures, we find that
Their corresponding sides are proportional but their corresponding angles are not equal.
∴ The given figures are not similar.