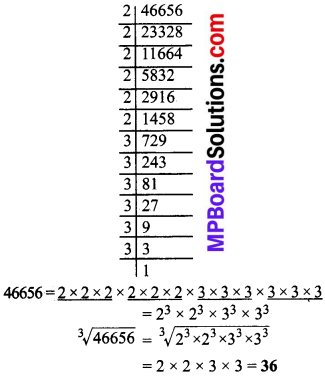
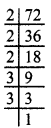
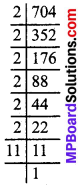
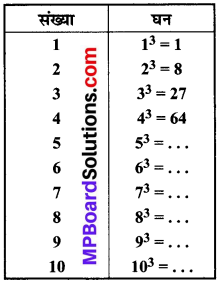
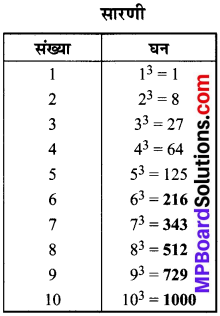
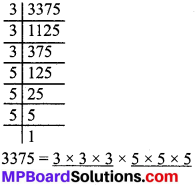
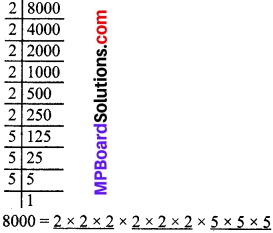
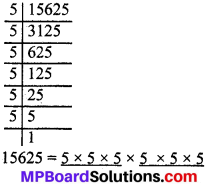
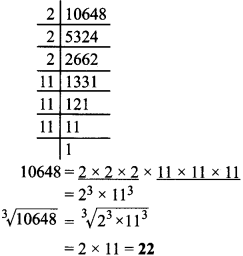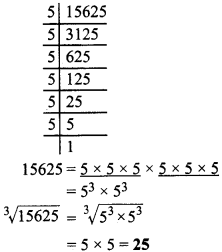MP Board Class 8th Social Science Solutions Chapter 26 Study of Local Map
MP Board Class 8th Social Science Chapter 26 Text Book Exercise
MP Board Class 8th Social Science Chapter 26 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Which are the three main landforms of surface?
Answer:
Mountains, Plains and Plateaus are the major landforms.
Question 2.
Which are the two methods to show the landform?
Answer:
There are two methods to show the landforms:
- Colour method
- Contours method.
![]()
Question 3.
What are contour lines?
Answer:
Contour:
A contour is an imaginary line drawn on a map which joins the points of the same height above sea-level. Contrours are the most accurate and common form of showing the landforms.
Question 4.
In what colours plain, platform and mountain are shown in a map?
Answer:
Plains are shown in green colour, Dark green colour shows the high plains. The high rising places are shown in yellow colour, while the colour of high plateau is grey. The low height mountains is of dark grey or light brown colours and the high mountains are shown with the darkbrown colour.
Question 5.
Show the conical hill and plateau through contour lines?
Answer:
Conical hills:
The contour lines are also of equal distance and equal round. If you see such contour lines in the map you will easily know that this is conical hill.
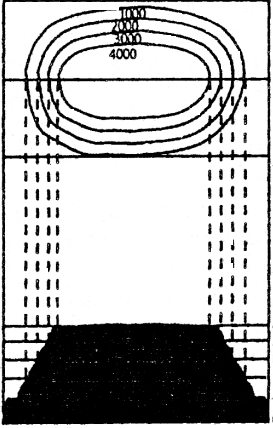
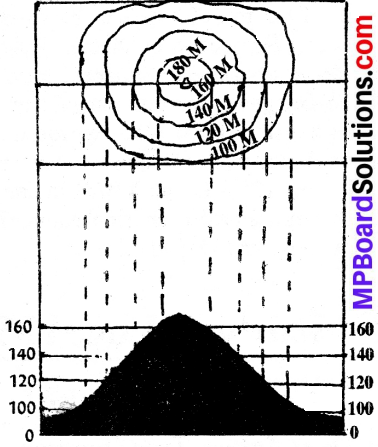
Plateau:
The top of plateau is more or less flat is represented by very few contours but its sides are steep and they are shown by closely spaced contours on a map.
Question 6.
What do the light blue and dark blue colours indicate?
Answer:
Depth of sea is shown by various shades. The sea is shown in map by blue colour, sea nearby land surface is shown by light blue colour. As the depth of sea increases the blue colour becomes darker. The deep and trenches of sea is indicated by the very dark blue colour.
![]()
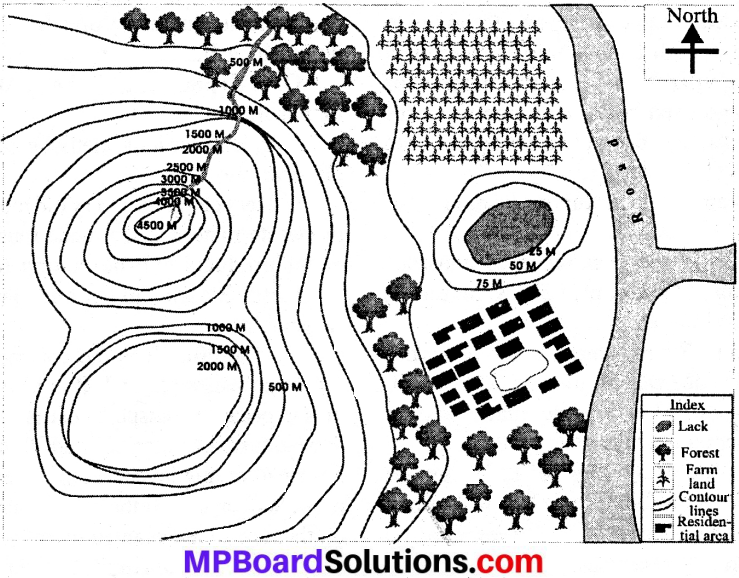
Project Work
Make a local map of your village or city and then discuss with colleagues in class.
The local map contains following conventional signs.
- Contour lines
- Road
- Forest
- Field
- Pond
- River
- Residential areas.
With the help of local map, write in your exercise book.
Question 1.
Which landforms are being shown by the contour lines?
Question 2.
In which direction river is flowing?
Question 3.
Which landform is near forest?
Question 4.
Which is the landform between field and residential area?