In this article, we will share MP Board Class 8 Hindi Book Solutions Sugam Bharti विविध प्रश्नावली 2 Pdf, These solutions are solved subject experts from the latest edition books.
MP Board Class 8th Hindi Sugam Bharti Solutions विविध प्रश्नावली 2
लघुउत्तरीय प्रश्नोत्तर
प्रश्न 1.
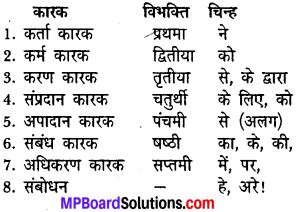
सही जोड़ी बनाइए


उत्तर
(अ) 4, (ब) 1, (स) 2, (द) 3
प्रश्न 2.
सही विकल्प चुनकर रिक्त स्थान की पूर्ति कीजिए
(1) हम पंछी उन्मुक्त ……………….के पिंजरबद्ध न ___गा पाएँगे।(चमन, गगन)
(2) अमीर खुसरो ने मन को छू लेने वाले …. लिखे। (गीत, लेख)
(3) दीनानाथ को विचारों में खोया देख उनकी पत्नी .. …………….. बोली। (मधुमती, मधुमिता)
(4) जो लोग समय तय करके भी घर नहीं मिलते हैं, वे मुझे भगवान के……. मालूम होते
(प्रेजेंट, एजेंट)
(5) ऐसा न कहिए जेलर साहब! मैं ………….. तरह अटल हूँ। (चटूटान, फौलाद)
उत्तर
(1) गगन
(2) गीत
(3) मधुमती
(4) एजेंट
(5) चट्टान।
![]()
अति लघु उत्तरीय प्रश्न तर
प्रश्न 3.
1. बिस्मिल की माँ को किस बात का अफसोस था?
2. साँची में हर्षित कहाँ रुका था?
3. गाँव में सब्जियों की बेलें किस पर छाई हुई हैं?
4. बड़े सवाल का छोटा-सा जवाब पाने पर लेखक को कैसा लगता है?
5. छगन अचानक एक दिन किस समाचार को सुनकर उदास हो गया?
6. अपने गुरु के प्रतति खुसरो के मन में कौन-सा प्रेरक __ भाव था?
7. कवि किस प्रकार के पंखों के टूटने की बात कह रहा है?
उत्तर-
1. बिस्मिल की माँ को इस बात का अफ़सोस था कि उसका दूसरा बेटा अभी छोटा क्यों है?
2. साँची में हर्षित मध्य-प्रदेश पर्यटन विभाग के पर्यटक आवास गृह में रुका था।
3. गाँव में सब्जियों की बेलें खपरैलों पर छाई हुई हैं।
4. बड़े सवाल का छोटा-सा जवाब पाने पर लेखक को लगता है कि वह बच्चा है और किसी बुजुर्ग के सामने बक-बक कर रहा है।
5. छगन अचानक एक दिन यह समाचार सुनकर उदास हो गया कि शर्मा जी का स्थानांतर अन्य शहर में हो गया है।
6. अपने गुरु के प्रति खुसरो के मन में समर्पण का प्रेरक भाव था।
7. कवि पुलकित पंखों के टूटने की बात कह रहा है।
लघु उत्तरीय प्रश्नोत्तर
प्रश्न 4.
(क) ‘हम बहता जल पीने वाले मर जाएँगे भूखे-प्यासे’ कवि ने ऐसा क्यों कहा है?
(ख) ईश्वर प्राप्ति के संबंध में खुसरों के गुरु के क्या विचार थे?
(ग) नर्सिंग होम के उद्घाटन के समय किस प्रकार का वातावरण था?
(घ) हरिशंकर परसाई के अनुसार किस प्रकार के लोगों की चर्चा करना व्यर्थ है?
(ङ) ‘ग्राम्य जीवन’ कविता के आधार पर लिखिए कि “गाँव के लोग परिश्रमी होते हैं।”
(त) अपने साथियों को बढ़ने के लिए स्कूल जाते देखकर लिंकन क्या सोचते थे?
(य) बिस्मिल की माँ अन्य साधारण स्त्रियों से किस प्रकार भिन्न थी?
(द) हर्षित ने साँची के संग्रहालय में क्या-क्या देखा?
उत्तर
(क) ‘हम बहता जल पीने वाले मर जायेंगे भूखे-प्यासे’ कवि ने ऐसा इसलिए कहा है कि स्वतंत्रता परतंत्रता के बंधन से समाप्त हो जाती है। उसके सारे अरमान और शक्तिक्षमता एक-एक करके व्यर्थ हो जाती हैं।
(ख) ईश्वर-प्राप्ति के संबंध में खुसरो के गुरु के विचार बहुत उत्तम थे। उनके अनुसार ईश्वर को अलौकिक प्रेम से ही प्राप्त किया जा सकता है।
(ग) नर्सिंग होम के पास पंडाल लगा था। अतिथियों का आगमन शुरू हो चुका था। चारों ओर हँसी-खुशी का वातावरण दिखाई दे रहा था।
(घ) हरि शंकर परसाई के अनुसार ऐसे लोगों की चर्चा करना व्यर्थ है जो समय पर घर मिलते हैं और समय पर दूसरे के घर भी जाते हैं। ये घर में रहेंगे तो टाइमपीस देखते रहेंगे और बाहर होंगे तो हाथ घड़ी देखते रहेंगे।
(ङ) गाँव के लोग घोर परिश्रम करते हैं। इसलिए वे आलसी नहीं होते हैं। वे दिन-भर खेतों में काम करते रहते हैं। इस प्रकार वे आत्मनिर्भर होते हैं।
(त) अपने अमीर साथियों को पढ़ने के लिए स्कूल जाते लिंकन देखता तो सोचता ये पढ़ने जाते हैं। इनके पास सुख के अनेक साधन हैं। ये बड़े होकर कुर्सी पर बैठेंगे।
(थ) बिस्मिल की माँ अन्य साधारण स्त्रियों की तरह रोने-चीखने वाली नहीं थीं। उसने अपने बेटे बिस्मिल को बचपन से त्याग, वीरता और देश-प्रेम का पाठ पढ़ाया था।
(द) हर्षित ने संग्रहालय में अनेक पुरातत्त्व महत्त्व की वस्तुएँ देखीं। उसने अनेक मूर्तियों और मंदिरों के भग्नावशेषों व कलाकृतियों को देखा। उसने अशोक स्तंभ का सिंह-चिह्न और बौद्ध-भिक्षुओं द्वारा उपयोग किए जाने वाले पात्रों को भी देखा।
![]()
प्रश्न 5.
निम्नलिखित पंक्तियों का अर्थ लिखिएनीड़ न दो, चाहे टहनी का आश्रय छिन्न-भिन्न कर डालो, लेकिन पंख दिये हैं, तो आकुल उड़ान में विघ्न न डालो।
उत्तर
पंक्षी मनुष्य से कह रहा है कि उसे टहनी का आश्रय भले न हो और उसे छिन्न-भिन्न कर डालो। लेकिन उसे विष्ट पता ने उड़ने के लिए पंख दिए हैं, तो उसे उड़ने से मत रोको। उसे स्वतंत्र उड़ान भरने दो।
प्रश्न 6.
आपके द्वारा देखे गए किसी दर्शनीय स्थल का तिथिवार वर्णन अपने शब्दों में कीजिए।
उत्तर
इस प्रश्न को छात्र/छात्रा अपने अध्यापक/अध्यापिका की सहायता से हल करें।
प्रश्न 7.
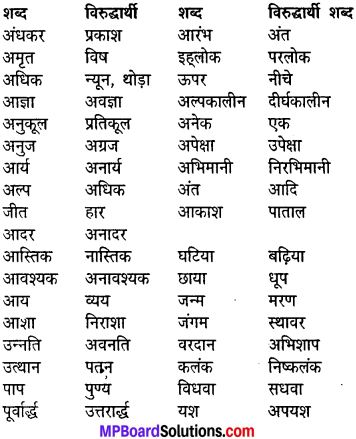
(अ) निम्नलिखित शब्दों के विलोम शब्द लिखिएसाक्षर, शिष्टता, निंदा, सुविधा अल्पायु।
उत्तर-
(अ) शब्द – विलोम शब्द
साक्षर – निरक्षर
शिष्टता – धृष्टता
निंदा – स्तुति
सुविधा – असुविधा
अल्पायु – दीर्घायु
(ब) निम्नलिखित शब्दों के दो-दो पर्यायवाची लिखिए
विश्व, शाम, घर, माँ, जमीन, देश।
उत्तर-
विश्व – संसार, जगत
शाम – संध्या, साँझ
माँ – जननी, जन्मदात्री
जमीन – भूमि, भू
देश – राष्ट्र, वतन
(स) निम्नलिखित मुहावरों का वाक्यों में प्रयोग कीजिए
जी चाहना, आँखों से परनाले बहना, कदम डगमगाना।
उत्तर-
(स) जी चाहना-पुत्र को देखने के लिए माँ का जी चाहता है। आँखों से परनाले बहना-पुत्र को जेल की कोठरी में देखकर माँ की आँखों से परनाले बहने लगे। कदम डगमगाना-अदालत में बयान देते समय अपराधी के कदम डगमगाने लगे।
(द) निम्नलिखित वाक्यों में से सरल, संयुक्त और मिश्र वाक्य पहचानकर लिखिए-
अपनी भारत माँ की अच्छी तरह सेवा करना। मेरे देश को आजादी मिले और मेरे देशवासी उस दिन आँसू बहाएँ यह मुझसे सहन नहीं हो सकेगा माँ। मेरी इच्छा है कि तू मातृभूमि की रक्षा करे।
उत्तर-
(द) अपनी भारत माँ की अच्छी तरह सेवा करना – सरल वाक्य।_मेरे देश को आजादी मिले और मेरे देशवासी उस दिन आँसू बहाएँ, यह मुझसे सहन नहीं हो सकेगा माँ-संयुक्त वाक्य। मेरी इच्छा है कि तू मातृभूमि की रक्षा करे-मिश्रित वाक्य।
![]()
प्रश्न 8.
(अ) नीचे लिखे शब्दों से विशेषण शब्द अलग करके लिखिए
(1) बूढ़ा नीम
(2) फटे जूते
(3) सूखा घास
(4) मीठी बातें
उत्तर-
(अ) शब्द – विशेषण शब्द
बूढ़ा नीम – बूढ़ा
फटे जूते – फटे
सूखा घास – सूखा
मीठी बातें – मीठी
(ब) पाठ्य पुस्तक में पढ़ी हुई किसी कविता की चार पंक्तियाँ लिखिए।
(घ) स्वर्ण-शृंखला के बंधन में
अपनी गति, उड़ान सब भूलें,
बस सपनों में देख रहे हैं,
तरु की फुनगी पर के झूले।
प्रश्न 9.
अपने प्रधान अध्यापक को फीस माफ करने विषयक प्रार्थना-पत्र लिखिए।
उत्तर
देखें पत्र-भाग।