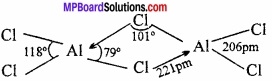
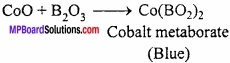
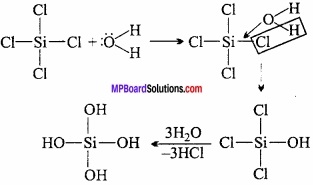
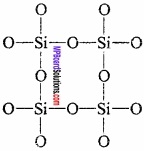
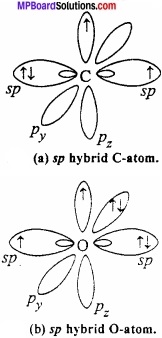
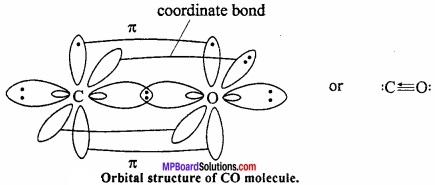
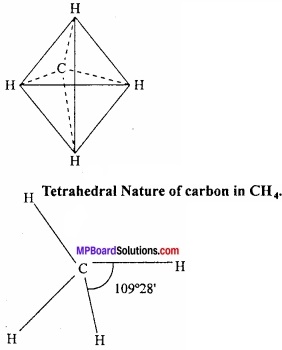
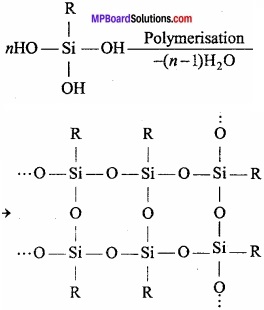
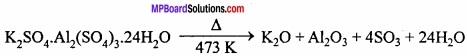
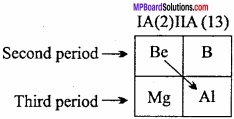
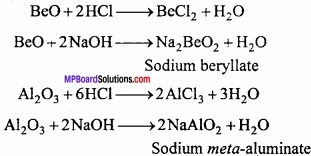
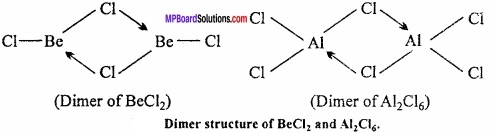
MP Board Class 11th Hindi Swati Solutions पद्य Chapter 1 भक्ति
भक्ति अभ्यास
भक्ति अति लघु उत्तरीय प्रश्न
प्रश्न 1.
सही विकल्प चुनिए
(क) तुलसीदास के पद संकलित हैं (2009)
(अ) कवितावली में
(ब) गीतावली में
(स) विनय पत्रिका में
(द) रामचरितमानस में।
उत्तर:
(स) विनय पत्रिका में।
(ख) तुलसीदास के पदों में रस प्रधान है
(अ) शान्त
(ब) श्रृंगार
(स) वीर
(द) वात्सल्य।
उत्तर:
(अ) शान्त रस।
(ग) मीराबाई भक्त थीं (2009)
(अ) राम की
(ब) कृष्ण की
(स) शिव की
(द) विष्णु की।
उत्तर:
(ब) कृष्ण की।
प्रश्न 2.
तुलसीदास किसके चरण छोड़कर नहीं जाना चाहते? (2015, 17)
उत्तर:
तुलसीदास श्रीराम के चरण छोड़कर नहीं जाना चाहते।
प्रश्न 3.
तुलसीदास प्रण करके कहाँ बसना चाहते हैं?
उत्तर:
तुलसीदास प्रण करके श्रीराम के चरण कमलों में बसना चाहते हैं।
प्रश्न 4.
कृष्ण ने किसका घमण्ड चूर करने के लिये गोवर्धन पर्वत धारण किया था? (2016)
उत्तर:
कृष्ण ने इन्द्र का घमण्ड चूर करने के लिए गोवर्धन पर्वत को धारण किया था।
प्रश्न 5.
किसी रोगी की पीड़ा को सबसे अधिक कौन अनुभव कर सकता है?
उत्तर:
किसी रोगी की पीड़ा को सबसे अधिक श्रीराम ही अनुभव कर सकते हैं।
![]()
भक्ति लघु उत्तरीय प्रश्न
प्रश्न 1.
कवि के अनुसार राम के चरणों से किन-किनका उद्धार हुआ है?
उत्तर:
कवि के अनुसार राम के चरणों द्वारा पत्थर (अहिल्या), जटायु (पक्षी), मारीच (हिरण) आदि का उद्धार हुआ है।
प्रश्न 2.
‘करहलाज निजपन’ पंक्ति में निजपन’ से कवि का क्या आशय है?(2014)
उत्तर:
‘करहु लाज निजपन’ पंक्ति से कवि का अभिप्राय है कि मैं अपने इस मन के दोषपूर्ण एवं तुच्छ कार्यों का कहाँ तक वर्णन करूँ। आप तो अन्तर्यामी हैं अतः सेवक के मन की प्रत्येक अच्छी-बुरी बात को जानते हैं। मैं अपनी दोषयुक्त बातों को कहाँ तक बताऊँ?
प्रश्न 3.
मीरा ने अपने प्रियतम से मिलने में क्या कठिनाई बताई है? (2008)
उत्तर:
मीरा के प्रियतम श्रीकृष्ण की सेज गगन मण्डल में है, उस स्थान पर पहुँचना कठिन है। इसी कारण मीरा प्रियतम कृष्ण से मिलने में कठिनाई का अनुभव करती हैं।
प्रश्न 4.
मीरा के हृदय की पीड़ा को कौन-सा वैद्य दूर कर सकेगा? (2015)
उत्तर:
मीरा के हृदय की पीड़ा को दूर करने वाला एकमात्र वैद्य साँवला सलोना कृष्ण है।
भक्ति दीर्घ उत्तरीय प्रश्न
प्रश्न 1.
तुलसीदास के अनुसार मानव मन की मूढ़ता क्या है? (2008, 13)
उत्तर:
तुलसीदास जी के अनुसार मानव मूर्ख है। वह प्रभु राम की भक्ति रूपी गंगा को त्यागकर विषय-वासना रूपी ओस के कणों से प्यास बुझाने की अभिलाषा रखता है। जिस प्रकार से धुएँ के समूह को देखकर प्यासा चातक उसे बादल समझकर अपनी प्यास बुझाना चाहता है, लेकिन उसको वहाँ से न तो शीतलता प्राप्त होती है और न ही उसकी प्यास बुझती है, लेकिन उसके नेत्रों को हानि अवश्य पहुँचती है। इसी प्रकार मनुष्य विषय-वासना में मग्न होकर आनन्द की प्राप्ति करना चाहता है, लेकिन उसको आनन्द के स्थान पर अशान्ति की प्राप्ति होती है। जिस प्रकार से मुर्ख बाज दर्पण में अपनी परछाईं को देखकर अन्य बाज समझकर उस पर झपटता है, लेकिन उसको आहार तो नहीं प्राप्त होता है परन्तु उसका मुख अवश्य क्षतिग्रस्त हो जाता है। इसी प्रकार मनुष्य भी मूर्खतावश सांसारिक विषय-वासनाओं में लिप्त रहना चाहता है। यदि मानव ईश्वर के प्रति सच्ची भक्ति करे तो निश्चय ही उसे सांसारिक कष्टों से मुक्ति मिल सकती है, क्योंकि प्रभु राम ही सब के कष्टों को दूर करके तारने वाले हैं।
प्रश्न 2.
तुलसीदास अपना भावी जीवन किस प्रकार बिताने का संकल्प लेते हैं? (2009, 10)
उत्तर:
तुलसीदास जी ने अपने भावी जीवन को श्रीराम की भक्ति में लगाने का संकल्प लिया है, क्योंकि उनका अनुभव है कि मानव जीवन की सार्थकता व मुक्ति का मार्ग राम भक्ति द्वारा ही सम्भव है। तुलसीदास जी का कथन है कि यह संसार मिथ्या है तथा संसार में अनुरक्त व्यक्ति कभी सफलता प्राप्त नहीं कर सकता है। अतः भगवान श्रीराम के चरणों में अपने मन को पूर्ण रूप से समर्पित करके ही जीवन को सफल बनाया जा सकता है।
जिस प्रकार मीरा ने कृष्ण को अपना आराध्य भाग था, उसी प्रकार तुलसीदास जी ने अपना भावी जीवन श्रीराम के चरणों में बिताने का संकल्प ले लिया।.
![]()
प्रश्न 3.
मीरा ने हरि के चरणों की कौन-कौन सी विशेषताएँ बताई हैं? (2009)
उत्तर:
मीरा ने हरि के चरणों की विशेषताओं का उल्लेख करते हुए बताया है कि जिन हरि के चरणों ने राजा बलि की दान स्वरूप प्रदान की हुई धरती को तीन पग में नाप लिया था, जिन चरणों का स्पर्श करके गौतम की पत्नी अहिल्या का उद्धार हो गया।
गोपलीला करने के लिये भगवान श्रीकृष्ण ने कालिया नाग का नाश कर भय मुक्त किया था। इन्द्र के अभिमान को नष्ट करने के लिए गोवर्धन पर्वत को अपनी कनिष्ठा उँगली पर धारण कर लिया था। ऐसे भगवान के चरण कमल ही मीरा दासी का उद्धार करने में सक्षम हैं।
प्रश्न 4.
निम्नलिखित पद्यांशों की सप्रसंग व्याख्या कीजिए
(क) ऐसी मूढ़ता या …………..आपने तन की।
(ख) अबलौं नसानी ………… कंचनहिं कसैहों।
(ग) बढ़त पल-पल …………पुनि डार।
(घ) गगन मंडल पै ………..की जिन लाई होय।
उत्तर:
(क) सन्दर्भ :
पूर्ववत्।
प्रसंग :
इस पद में भक्त तुलसीदास अपने अवगुणों को प्रभु के समक्ष प्रदर्शित करते हुए अवगुणों एवं अज्ञान से मुक्त होने की कामना व्यक्त करते हैं।
व्याख्या :
तुलसीदास जी कहते हैं कि मेरे इस मन की ऐसी मूर्खता है कि यह राम की भक्ति रूपी पवित्र गंगा को त्यागकर सांसारिक सुख रूपी ओस की इच्छा करता है। कहने का आशय है कि जिस भाँति कोई प्यासा चातक पक्षी धुएँ के समूह को देखकर उसे बादल समझ ले और जल पीने के लिए दौड़े परन्तु न उसमें शीतलता होती है न जल, अपितु नेत्रों की हानि होती है। इसी भाँति मेरा मन राम की भक्ति को त्यागकर सांसारिक विषयों में सुख समझकर उनकी ओर आकर्षित होता है।
तुलसीदास का कथन है कि मेरे मन की ऐसी स्थिति है कि जैसे फर्श में जड़े हुए काँच में कोई बाज पक्षी अपने शरीर की परछाईं को निहारे और उसे अन्य पक्षी अर्थात् अपना शिकार समझकर उस पक्षी पर भोजन के लिए झपटे। उसे यह ज्ञान नहीं है कि इस प्रकार फर्श पर टकराने से उसके मुँह की ही हानि होगी।
हे कृपालु प्रभु राम ! मैं अपने मन की कुचाल (वाचालता) का कहाँ तक वर्णन करूँ? आप तो मेरी गति को भली-भाँति समझते हैं। हे प्रभु! आप पतित पावन हैं। पतितों एवं दीन-दुःखियों की रक्षा करना आपका प्रण अथवा स्वभाव है, इसीलिए आप इस तुलसीदास के असहनीय कष्टों को हरकर अपने प्राण की लज्जा रखो।
उपर्युक्त पद्यांशों की सप्रसंग व्याख्या ‘सन्दर्भ-प्रसंग सहित पद्यांशों की व्याख्या’ भाग में देखिये।
(ख) सन्दर्भ :
पूर्ववत्।
प्रसंग :
प्रस्तुत पंक्तियों में तुलसीदास ने विगत जीवन के प्रति पश्चाताप का भाव व्यक्त किया है। अब उन्हें विवेक की प्राप्ति हो गई; अत: उन्होंने सुपथ पर चलने का दृढ़ निश्चय किया है।
व्याख्या :
हे नाथ! मेरी अब तक की आयु व्यर्थ में ही नष्ट हो गई, मैं उसका कोई भी सदुपयोग नहीं कर सका। लेकिन अब जो आयु शेष है, उसे मैं व्यर्थ में नष्ट न होने दूंगा, उसका सदुपयोग करूँगा। राम की कृपा से संसार रूपी रात्रि नष्ट हो गयी है, अब में जाग गया हूँ अर्थात् अब मैं इतना मूर्ख नहीं कि जागने के बाद पुनः सोने के लिये बिस्तर बिछा लूँ। मुझे अज्ञान और मोह के बन्धन का बोध हो गया है। अत: मैं इसकी वास्तविकता से परिचित हो गया हूँ। अब पुनः मैं सांसारिक माया में नहीं फसँगा।
मुझे तो राम नाम रूपी सुन्दर चिन्तामणि प्राप्त हो गई है जिसे मैं हृदयरूपी हाथ से खिसकने नहीं दूंगा और राम के सुन्दर श्याम रूप को कसौटी बनाकर उस पर अपने चित्त रूपी कंचन को करूँगा अर्थात् परीक्षा करूँगा कि मेरा मन राम के स्वरूप में लगता है अथवा नहीं। यदि लगता है तो वह शुद्ध स्वर्ण है और यदि नहीं लगता तो उसमें खोट निहित है।
अभी तक मेरा मन इन्द्रियों के वश में था। अतः इन्द्रियों ने मेरा खूब उपहास किया, लेकिन अब मैंने अपने मन को वश में कर लिया है, इसलिए इन्द्रियों को हँसने का अवसर अब नहीं दूंगा। मैं दृढ़ निश्चय करके अपने इस मन रूपी भ्रमर को राम के चरण कमलों में बसाऊँगा। मुझे पूर्ण विश्वास है कि मेरा मन अपनी चंचलता को त्यागकर राम के चरणों में लग जायेगा।
(ग) सन्दर्भ :
पूर्ववत्।
प्रसंग :
इस पद में मीराबाई ने मानव शरीर को पुण्य स्वरूप ठहराकर ईश्वर के प्रति समर्पित होने की प्रेरणा दी है।
व्याख्या :
मीराबाई कहती हैं कि मानव जीवन बार-बार नहीं मिलता है। जीव को पुण्य कर्मों के कारण ही मानव शरीर प्राप्त होता है। यह शरीर पल-पल एवं प्रतिक्षण क्षीण होता जा रहा है, अर्थात् मृत्यु की ओर बढ़ रहा है। जीवन का अन्त होने में तनिक भी विलम्ब नहीं होगा। जिस प्रकार वृक्ष से झड़े हुए पत्ते पुनः डाल पर नहीं लग सकते; तद्नुकूल मानव का अन्त होने पर यह निश्चय नहीं है कि उसे पुनः मानव शरीर प्राप्त होगा। संसार रूपी सागर में विषय-वासनाओं की अत्यन्त तीक्ष्ण धारा है। यदि मनुष्य सुरत अथवा प्रभु में अपना ध्यान लगाये तो शीघ्र ही संसार रूपी सागर से पार हो जायेगा अर्थात् सांसारिक विषय-वासनाओं से उसे छुटकारा मिल जायेगा।
साधु सन्त एवं महन्तों की मण्डली पुकार-पुकार कर कह रही है कि मानव जीवन चार दिनों का मेला है। अत: हे मानव! तू श्रीकृष्ण का आश्रय ग्रहण कर ले, इसी में तेरा हित है।
(घ) सन्दर्भ :
प्रस्तुत पद्यांश हमारी पाठ्य पुस्तक के पाठ ‘मीराबाई’ द्वारा रचित ‘पदावली’ शीर्षक से अवतरित है।
प्रसंग :
प्रस्तुत पद्यांश में मीराबाई की विरह जनित पीड़ा को बड़ा ही मार्मिक वर्णन है। मीराबाई का श्रीकृष्ण से मिलन नहीं हो पा रहा है। अतः उनको असहनीय पीड़ा हो रही है।
व्याख्या :
मीराबाई कहती हैं कि हे सखि! मैं तो श्रीकृष्ण के प्रेम में दीवानी हूँ। उनके प्रति मेरे प्रेम की पीड़ा को मेरे अतिरिक्त दूसरा नहीं जान सकता है। मेरी सेज (सूली) (शय्या) ऐसे दुर्गम स्थान (प्राण दण्ड देने के स्थल) पर है जहाँ मेरे समान सांसारिक प्राणी पहुँच ही नहीं सकता है। श्रीकृष्ण की शैया तो आकाश में है। अत: उनसे मिलना असम्भव है। व्यथा से व्यथित मानव ही व्यथा की पीड़ा का मूल्यांकन कर सकता है। घायल व्यक्ति की पीड़ा को घायल ही जान सकता है। मेरी वियोग की पीड़ा को केवल वही व्यक्ति जान सकता है जिसने वियोग जनित पीड़ा को भी कभी सहन किया हो।
जौहर की पीड़ा को जौहरी (स्वयं को अग्नि की गोद में समर्पित करने वाला) ही जान सकता है। वियोग की पीड़ा से मैं इतनी दुःखी हूँ कि वन-वन भटकती फिर रही हूँ। लेकिन मेरी इस पीड़ा को दूर करने वाला कोई वैद्य आज तक नहीं मिला। मेरे विरह की पीड़ा तो तभी समाप्त होगी, जब श्रीकृष्ण वैद्य के रूप में प्रस्तुत होकर इसका उपचार करें अर्थात् उनके दर्शन से ही मेरा दुःख दूर हो सकता है।
![]()
भक्ति काव्य सौन्दर्य
प्रश्न 1.
निम्नलिखित शब्दों के तत्सम रूप लिखिएनिसा, आस, पषान, चरन, सुचि, पुन्य, गरव, भौसागर।
उत्तर:
तत्सम रूप-निशा, आशा, पाषाण, चरण, शुचि, पुण्य, गर्व, भवसागर।
प्रश्न 2.
निम्नलिखित काव्य-पंक्तियों में अलंकार पहचान कर लिखिए
(अ) मन मधुकर पन कै तुलसी रघुपति पद कमल बसैहौं।
(ब) ज्यों गज काँच बिलोकि सेन जड़ छाँह आपने तन की।
(स) बढ़त पल पल घटत छिन छिन चलत न लागे बार।
(द) जौहरी की गति जौहरी जाने, की जिन जौहर होय।
(इ) स्याम रूप सुचि रूचिर कसौटी, चित कंचनहिं कसैहों।
उत्तर:
(अ) रूपक अलंकार
(ब) दृष्टान्त अलंकार
(स) पुनरुक्ति, अनुप्रास अलंकार
(द) पुनरुक्ति अलंकार
(इ) रूपक अलंकार।
प्रश्न 3.
मीरा के पदों में किन-किन बोली अथवा भाषाओं के शब्दों का प्रयोग हुआ है? संकलित अंश से छाँटकर लिखिए।
उत्तर:
मीरा के पदों में ब्रजभाषा के अतिरिक्त राजस्थानी, गुजराती एवं पंजाबी शब्दों का प्रयोग हुआ है।
उदाहरण के लिए राजस्थानी भाषा के शब्द देखें-दीवाणी, जाणे, सोणा, मिलणा, मिल्या।
ब्रजभाषा के उदाहरण- नहिं ऐसो जनम बारम्बार……….
मन रे परसि हरि के चरन……….
जिन चरन प्रभु परसि लीने तरी गौतम धरन………..
प्रश्न 4.
माधुर्य गुण में कोमलकान्त पदावली का प्रयोग किया जाता है। यह गुण प्रायः श्रृंगार, वात्सल्य और शान्त रस में होता है। संकलित अंश से उदाहरण देकर समझाइए।
उत्तर:
संकलित अंश के आधार पर रस के उदाहरण इस प्रकार हैं-श्रृंगार रस-शृंगार रस के दो भेद होते हैं-
(1) संयोग शृंगार,
(2) वियोग शृंगार। स्थायी भाव रति होता है।
वियोग श्रृंगार का उदाहरण :
हे री मैं तो प्रेम दिवाणी मेरा दरद न जाने कोय। उपर्युक्त पंक्ति में वियोग शृंगार है।
अन्य उदाहरण :
दरद की मारी वन-वन डोलूँ, वैद मिल्या नहिं कोय।
मीरा की प्रभु पीर मिटैगी, जब वैद सँवलिया होय।।
वात्सल्य रस :
सोभित कर नवनीत लिए।
मैया मैं तो चंद खिलौना लैहौं।
शान्त रस का स्थायी भाव निर्वेद है।.
उदाहरण देखें :
ऐसी मूढ़ता या मन की …………
…………. करहु लाज निज पन की।
अबलौं नसानी ………… पद कमल बसैहौं।
प्रश्न 5.
निम्नलिखित काव्य पंक्तियों में कौन-सा रस है? उसका स्थायी भाव लिखिए।
(अ) अबलौं नसानी, अब न नसैहों।
(ब) हेरी मैं तो प्रेम दिवाणी, मेरा दरद न जाने कोय।
उत्तर:
(अ) शान्त रस-स्थायी भाव निर्वेद।
(ब) वियोग शृंगार-स्थायी भाव रति।
प्रश्न 6.
“गगन मंडल पै सेज पिया की किस विध मिलणा होय।” पंक्ति में कौन-सी शब्द शक्ति है ?
उत्तर:
शब्द शक्ति लक्षणा है।
प्रश्न 7.
“ऐसी मूढ़ता या मन की परिहरि राम भक्ति सुर सरिता,
आस करत ओसकन की।”
में प्रयुक्त रस और उसका स्थायी भाव लिखिए।
उत्तर:
उपर्युक्त पंक्ति में शान्त रस है तथा स्थायी भाव निर्वेद है।
![]()
विनय के पद भाव सारांश
तुलसीदास अपने इष्टदेव श्रीराम से कहते हैं कि आपके चरणों का आश्रय छोड़कर अन्यत्र कहाँ जाऊँ? आप पतितों का उद्धार करने वाले तथा दीनों से अनुराग करने वाले हैं। देवता, राक्षस, मुनि, नाग तथा मनुष्य सभी माया के वशीभूत हैं। अग्रिम पद में अपने को मूर्ख ठहराया है जो राम भक्ति रूपी गंगाजी को त्यागकर ओस कणों से अपनी प्यास बुझाना चाहता है।
अब तुलसी संसार के माया जनित सम्बन्धों को मिथ्या ठहराकर उनके बन्धनों से मुक्त होकर, अपने जीवन को नष्ट नहीं करना चाहते हैं। वे अपने मन रूपी भौरे को श्रीराम के चरण कमलों में अर्पित करना चाहते हैं।
विनय के पद संदर्भ-प्रसंग सहित व्याख्या
[1] जाऊँ कहाँ तजि चरन तुम्हारे।
काको नाम पतित पावन जग, केहि अति दीन पियारे ।।1।।
कौने देव बराइ बिरद-हित, हठिहठि अधम उधारे।
खग, मृग, ब्याध, पषान, विटप जड़, जवन कवन सुर तारे ।।2।।
देव, दनुज, मुनि, नाग, मनुज, सब माया बिबस विचारे।
तिनके हाथ दास तुलसी प्रभु, कहा अपनपौ हारे ।।3।।
शब्दार्थ :
तजि = त्यागकर, छोड़कर; काको = किसका; पावन = पवित्र; जग = संसार; केहि = किसको; बराइ = चुन-चुन कर; बिरद = भक्ति; हठिहठि = हठपूर्वक; अधम = नीच, पापी; उधारे = उद्धार किया; खग = जटायु पक्षी; मृग = हिरण, मारीचि; ब्याध = बहेलिया; पषान = पत्थर, अहिल्या; विटप = वृक्ष; सुर = देवता; दनुज = राक्षस; मनुज = मनुष्य; बिबस = विवश, लाचार; तिनके = उनके।
सन्दर्भ :
प्रस्तुत पद्यांश हमारी पाठ्य पुस्तक के पाठ भक्ति’ के शीर्षक विनय के पद’ से अवतरित है। इसके रचयिता तुलसीदास हैं।
प्रसंग :
प्रस्तुत पद्य में तुलसीदास ने भगवान् राम के चरणों के प्रति अपनी अनन्य भक्ति का उल्लेख किया है।
व्याख्या :
तुलसीदास जी कहते हैं कि हे प्रभु ! मैं आपके चरणों को त्यागकर अन्यत्र कहाँ जाऊँ ? कहीं भी मुझे आश्रय दृष्टिगोचर नहीं होता। आपके समान पापियों को पवित्र करने वाला संसार में अन्य कोई नहीं है, निर्धनों से स्नेह करने वाला कोई दूसरा नहीं है। ऐसा कौन-सा देवता है जिसने हठपूर्वक अपने पतित भक्तों का उद्धार किया है। पक्षी, हिरन, बहेलिया, पत्थर, वृक्ष, जड़, देवता, राक्षस, ऋषि, नाग, मनुष्य सब माया के वशीभूत हैं। तुलसीदास जी कहते हैं कि ऐसे प्रभु राम के सामने मैं अपना सर्वस्व समर्पण करता हूँ।
काव्य सौन्दर्य :
- हित, हठिहठि, पतित-पावन में अनुप्रास अलंकार है।
- भाषा में तद्भव शब्दों का प्रयोग है, जैसे-पषान, बिबस, मनुज।
- ब्रजभाषा का प्रयोग है।
![]()
[2] ऐसी मूढ़ता या मन की।
परिहरि राम भक्ति सुर सरिता आस करत ओसकन की।।1।।
धूम समूह निरखि जातक ज्यों, तृषित जानि मति घन की।
नहि तहँ शीतलता न बारि, पुनि हानि होत लोचन की ।।2।। (2012)
ज्यों गच काँच बिलोकि सेन जड़ छाँह आपने तन की।
टूटत अति आतुर अहार बस, छति बिसारि आनन की ।।3।।
कहँ लौ कहाँ कुचाल कृपानिधि, जानत हौं गति जन की।
तुलसीदास प्रभु हरहु दुसह दुखः, करहु लाज निज पन की ।।4।।
शब्दार्थ :
मूढ़ता = मूर्खता; परिहरि = त्यागकर, छोड़कर; ओसकन = ओस की बूंदें; धूम = धुआँ; निरखि = देखकर; सुर-सरिता = गंगा हो; तृषित = प्यास से व्याकुल; गच= भूमि, दीवार; वारि = जल; लोचन = नेत्र; काँच = दर्पण; बिलोकि = देखकर; सेन = बाज, श्येन; जड़ = मूर्ख; तन = शरीर; छति = क्षति, हानि; आनन = मुँह, चोंच; टूटत = झपटकर गिरता है; आतुर = दुःखी; कुचाल = कुचक्र; लाज = लज्जा; निज = अपना; पन = प्रण, प्रतिज्ञा।
सन्दर्भ :
पूर्ववत्।
प्रसंग :
इस पद में भक्त तुलसीदास अपने अवगुणों को प्रभु के समक्ष प्रदर्शित करते हुए अवगुणों एवं अज्ञान से मुक्त होने की कामना व्यक्त करते हैं।
व्याख्या :
तुलसीदास जी कहते हैं कि मेरे इस मन की ऐसी मूर्खता है कि यह राम की भक्ति रूपी पवित्र गंगा को त्यागकर सांसारिक सुख रूपी ओस की इच्छा करता है। कहने का आशय है कि जिस भाँति कोई प्यासा चातक पक्षी धुएँ के समूह को देखकर उसे बादल समझ ले और जल पीने के लिए दौड़े परन्तु न उसमें शीतलता होती है न जल, अपितु नेत्रों की हानि होती है। इसी भाँति मेरा मन राम की भक्ति को त्यागकर सांसारिक विषयों में सुख समझकर उनकी ओर आकर्षित होता है।
तुलसीदास का कथन है कि मेरे मन की ऐसी स्थिति है कि जैसे फर्श में जड़े हुए काँच में कोई बाज पक्षी अपने शरीर की परछाईं को निहारे और उसे अन्य पक्षी अर्थात् अपना शिकार समझकर उस पक्षी पर भोजन के लिए झपटे। उसे यह ज्ञान नहीं है कि इस प्रकार फर्श पर टकराने से उसके मुँह की ही हानि होगी।
हे कृपालु प्रभु राम ! मैं अपने मन की कुचाल (वाचालता) का कहाँ तक वर्णन करूँ? आप तो मेरी गति को भली-भाँति समझते हैं। हे प्रभु! आप पतित पावन हैं। पतितों एवं दीन-दुःखियों की रक्षा करना आपका प्रण अथवा स्वभाव है, इसीलिए आप इस तुलसीदास के असहनीय कष्टों को हरकर अपने प्राण की लज्जा रखो।
काव्य सौन्दर्य :
- शान्त रस।
- भक्त अपने अवगुणों को प्रभु के समक्ष व्यक्त कर अपनी दीनता का प्रदर्शन कर रहा है।
- ब्रजभाषा तथा गेय मुक्तक शैली का प्रयोग है।
- भ्रान्तिमान रूपक एवं उपमा अलंकार की छटा दर्शनीय है।
[3] अबलौं नसानी, अब न नसैहों।
राम कृपा भक निसा सिरानी, जागे पुनि न डसैहौं।।1।।
पायो नाम चारु चिन्तामनि, उर कर ते न खसैहौं।
स्यामरूप सुचि रुचिर कसौटी, चित कंचनहिं कसैहों।।2।।
परबस जानि हँस्यो इन इन्द्रिन, निज बसहै न हँसैहों।
मन मधुकर पन कै तुलसी रघुपति पद कमल बसैहौं।।3।। (2008, 09)
शब्दार्थ :
अबलौं = अब तक; नसानी = नष्ट की, बिगाड़ी; भव = संसार; निसा = रात्रि; सिरानी = शान्त हो गई, बीत गई; डसैहों = स्वयं को डसाऊँगा; उर = हृदय; चारु = सुन्दर; खसैहौं = गिराऊँगा; सुचि = पवित्र; चित = मन; कंचनहिं = सोने को; परबस = दूसरे के अधीन; पन कै= प्रण करके, प्रतिज्ञा करके बसैहौं = निवास करूँगा, बसाऊँगा; मन-मधुकर = मन रूपी भौंरा।
सन्दर्भ :
पूर्ववत्।
प्रसंग :
प्रस्तुत पंक्तियों में तुलसीदास ने विगत जीवन के प्रति पश्चाताप का भाव व्यक्त किया है। अब उन्हें विवेक की प्राप्ति हो गई; अत: उन्होंने सुपथ पर चलने का दृढ़ निश्चय किया है।
व्याख्या :
हे नाथ! मेरी अब तक की आयु व्यर्थ में ही नष्ट हो गई, मैं उसका कोई भी सदुपयोग नहीं कर सका। लेकिन अब जो आयु शेष है, उसे मैं व्यर्थ में नष्ट न होने दूंगा, उसका सदुपयोग करूँगा। राम की कृपा से संसार रूपी रात्रि नष्ट हो गयी है, अब में जाग गया हूँ अर्थात् अब मैं इतना मूर्ख नहीं कि जागने के बाद पुनः सोने के लिये बिस्तर बिछा लूँ। मुझे अज्ञान और मोह के बन्धन का बोध हो गया है। अत: मैं इसकी वास्तविकता से परिचित हो गया हूँ। अब पुनः मैं सांसारिक माया में नहीं फसँगा।
मुझे तो राम नाम रूपी सुन्दर चिन्तामणि प्राप्त हो गई है जिसे मैं हृदयरूपी हाथ से खिसकने नहीं दूंगा और राम के सुन्दर श्याम रूप को कसौटी बनाकर उस पर अपने चित्त रूपी कंचन को करूँगा अर्थात् परीक्षा करूँगा कि मेरा मन राम के स्वरूप में लगता है अथवा नहीं। यदि लगता है तो वह शुद्ध स्वर्ण है और यदि नहीं लगता तो उसमें खोट निहित है।
अभी तक मेरा मन इन्द्रियों के वश में था। अतः इन्द्रियों ने मेरा खूब उपहास किया, लेकिन अब मैंने अपने मन को वश में कर लिया है, इसलिए इन्द्रियों को हँसने का अवसर अब नहीं दूंगा। मैं दृढ़ निश्चय करके अपने इस मन रूपी भ्रमर को राम के चरण कमलों में बसाऊँगा। मुझे पूर्ण विश्वास है कि मेरा मन अपनी चंचलता को त्यागकर राम के चरणों में लग जायेगा।
काव्य सौन्दर्य :
- यहाँ तुलसीदास जी ने मानव को अज्ञानता छोड़कर सुपथ पर चलने की प्रेरणा दी है।
- शान्त रस का परिपाक है।
- भाषा अलंकारिक गुणों से युक्त है। रूपक अलंकार है।
- ब्रजभाषा का प्रयोग है।
- पद्यांशों में प्रसाद गुण है।
पदावली भाव सारांश
मीरा ने अपनी पदावली में अपनी विरह जनित पीड़ा को व्यक्त किया है। उनका कथन है कि वह श्रीकृष्ण के विरह में अत्यन्त व्याकुल हैं। उनके प्रियतम की सेज आकाश मण्डल में शूली ऊपर है जहाँ पहुँचना अत्यन्त दुर्लभ है। वे यत्र-तत्र भटक रही हैं लेकिन उनकी विरह पीड़ा का शमन करने वाला कोई भी नहीं दिखाई देता। उनकी पीड़ा को तो श्रीकृष्ण ही मिटा सकते हैं।
मीरा मानव जीवन को अमूल्य ठहराती हुई कहती हैं कि संसार से पार होने के लिये प्रभु के चरणों का सहारा ही एकमात्र आश्रय है। इन्हीं चरणों ने अनेक पतितों तथा भक्तों का उद्धार किया है।
![]()
पदावली संदर्भ-प्रसंग सहित व्याख्या
[1] हेरी मैं तो प्रेम दिवाणी, मेरा दरद न जाणे कोय।
सूली ऊपर सेज हमारी, किस विधि सोणा होय।।
गगन मण्डल पै सेज पिया की, किस विध मिलणा होय।
घायल की गति घायल जानै, की जिन लाई होय।।
जौहरी की गति जौहरी जानै, की किन जौहर होय।
दरद की मारी वन वन डोलूँ, वैद मिल्या नहिं कोय।।
मीरा की प्रभु पीर मिटैगी, जब वैद सँवलिया होय।
शब्दार्थ :
दरद = पीड़ा; सेज = शैया; गगन = आकाश; पिया = प्रियतम; विध = विधि; जौहरी = जौहर करने वाला; वैद = वैद्य; वन-वन = जंगल-जंगल; डोलूँ = विचरण करूँ; प्रभु = ईश्वर; पीर = पीड़ा; मिटैगी = समाप्त होगी; सँवलिया = श्रीकृष्ण का उपनाम।
सन्दर्भ :
प्रस्तुत पद्यांश हमारी पाठ्य पुस्तक के पाठ ‘मीराबाई’ द्वारा रचित ‘पदावली’ शीर्षक से अवतरित है।
प्रसंग :
प्रस्तुत पद्यांश में मीराबाई की विरह जनित पीड़ा को बड़ा ही मार्मिक वर्णन है। मीराबाई का श्रीकृष्ण से मिलन नहीं हो पा रहा है। अतः उनको असहनीय पीड़ा हो रही है।
व्याख्या :
मीराबाई कहती हैं कि हे सखि! मैं तो श्रीकृष्ण के प्रेम में दीवानी हूँ। उनके प्रति मेरे प्रेम की पीड़ा को मेरे अतिरिक्त दूसरा नहीं जान सकता है। मेरी सेज (सूली) (शय्या) ऐसे दुर्गम स्थान (प्राण दण्ड देने के स्थल) पर है जहाँ मेरे समान सांसारिक प्राणी पहुँच ही नहीं सकता है। श्रीकृष्ण की शैया तो आकाश में है। अत: उनसे मिलना असम्भव है। व्यथा से व्यथित मानव ही व्यथा की पीड़ा का मूल्यांकन कर सकता है। घायल व्यक्ति की पीड़ा को घायल ही जान सकता है। मेरी वियोग की पीड़ा को केवल वही व्यक्ति जान सकता है जिसने वियोग जनित पीड़ा को भी कभी सहन किया हो।
जौहर की पीड़ा को जौहरी (स्वयं को अग्नि की गोद में समर्पित करने वाला) ही जान सकता है। वियोग की पीड़ा से मैं इतनी दुःखी हूँ कि वन-वन भटकती फिर रही हूँ। लेकिन मेरी इस पीड़ा को दूर करने वाला कोई वैद्य आज तक नहीं मिला। मेरे विरह की पीड़ा तो तभी समाप्त होगी, जब श्रीकृष्ण वैद्य के रूप में प्रस्तुत होकर इसका उपचार करें अर्थात् उनके दर्शन से ही मेरा दुःख दूर हो सकता है।
काव्य सौन्दर्य :
- विरह की वेदना का मार्मिक चित्रण मुहावरों द्वारा किया गया है।
- भाषा-राजस्थानी एवं ब्रजभाषा है।
- रस-वियोग शृंगार।
- अनुप्रास-दृष्टान्त, पुनरुक्तिप्रकाश है।
- गुण-माधुर्य।
- शब्द-शक्ति-लक्षणा एवं अभिधा है।’
[2] नहिं ऐसो जन्म बारम्बार।
क्या जानूँ कछु पुन्य प्रकटे, मानुसा अवतार।।
बढ़त पल पल घटत छिन छिन, चलत न लागे बार।
बिरछ के ज्यों पाँत टूटे, लागे नहिं पुनि डार।।
भौ सागर अति जोर कहिये, विषय ओखी धार।
सुरत का नर बाँधे बेंडा, बेगि उतरे पार।।
साधु सन्ता ते महन्ता, चलत करत पुकार।
‘दास मीरा’ लाल गिरिधर, जीवना दिन चार।। (2008)
शब्दार्थ :
बारम्बार = बार-बार; पुन्य = पुण्य; पल-पल = हर क्षण; घटत = कम होना, क्षीण होना; बिरछ = वृक्ष; पात = पत्ते; बार = देरी; पुनि = पुनः; डार = डाल; भौ सागर = भवसागर, संसार रूपी समुद्र; ओखी कठिन; सुरत = ध्यान लगाना, भगवान प्रेम; नर = मनुष्य; बेगि = शीघ्रता; बेंडा = आड़ा-तिरछा, कठिन; महन्ता – साधु मण्डली।
सन्दर्भ :
पूर्ववत्।
प्रसंग :
इस पद में मीराबाई ने मानव शरीर को पुण्य स्वरूप ठहराकर ईश्वर के प्रति समर्पित होने की प्रेरणा दी है।
व्याख्या :
मीराबाई कहती हैं कि मानव जीवन बार-बार नहीं मिलता है। जीव को पुण्य कर्मों के कारण ही मानव शरीर प्राप्त होता है। यह शरीर पल-पल एवं प्रतिक्षण क्षीण होता जा रहा है, अर्थात् मृत्यु की ओर बढ़ रहा है। जीवन का अन्त होने में तनिक भी विलम्ब नहीं होगा। जिस प्रकार वृक्ष से झड़े हुए पत्ते पुनः डाल पर नहीं लग सकते; तद्नुकूल मानव का अन्त होने पर यह निश्चय नहीं है कि उसे पुनः मानव शरीर प्राप्त होगा। संसार रूपी सागर में विषय-वासनाओं की अत्यन्त तीक्ष्ण धारा है। यदि मनुष्य सुरत अथवा प्रभु में अपना ध्यान लगाये तो शीघ्र ही संसार रूपी सागर से पार हो जायेगा अर्थात् सांसारिक विषय-वासनाओं से उसे छुटकारा मिल जायेगा।
साधु सन्त एवं महन्तों की मण्डली पुकार-पुकार कर कह रही है कि मानव जीवन चार दिनों का मेला है। अत: हे मानव! तू श्रीकृष्ण का आश्रय ग्रहण कर ले, इसी में तेरा हित है।
काव्य सौन्दर्य :
- राजस्थानी एवं ब्रजभाषा का प्रयोग है।
- उपमा, रूपक एवं पुनरुक्ति अलंकार हैं।
- शब्द गुण माधुर्य से परिपूर्ण है।
- शान्त-रस का प्रयोग है।
- कवयित्री ने जीवन को क्षण-भंगुर बताया है।
![]()
[3] मन रे परसि हरि के चरन।
सुभग शीतल कमल कोमल, त्रिविध ज्वाला हरन।।
जे चरन प्रह्वाद परसे, इन्द्र पदवी धरन।
जिन चरन ध्रुव अटल कीन्हों, राखि अपने सरन।।
जिन चरन ब्रह्माण्ड भेट्यो, नख सिखौ श्री भरन।
जिन चरन प्रभु परसि लीने, तरी गौतम धरन।।
जिन चरन कालीहि नाश्यो, गोप लीला करन।
जिन चरन धारयो गोवर्धन, गरब मघवा हरन।।
‘दास मीरा’ लाल गिरधर, अगम तारन तरन।
शब्दार्थ :
परसि = स्पर्श, छूना; हरि = भगवान; चरण = चरन, पग; सुभग = सुन्दर; शीतल = ठण्डा; त्रिविध ज्वाला = तीन प्रकार के ताप दैहिक, दैविक, भौतिक; हरन = नष्ट करना; ध्रुव = एक तारा; सरन = शरण; भेट्यो = भेंट करना; नख सिखौ = सिर से पाँव तक; तरी = तारना, मुक्त करना; धरन = स्त्री, पत्नी; कालीहि = कालिया नाग का; नाश्यो = नष्ट करना; गोप = ग्वाल; धारयो = धारण करना; गरब : गर्व, घमण्ड, अभिमान; मघवा = इन्द्र; हरन = हर लेना, छीन लेना; अगम = कठिन, जहाँ पहुँचा न जा सके।
सन्दर्भ :
पूर्ववत्।
प्रसंग :
प्रस्तुत पद में मीरा उद्धार करने वाले प्रभु के चरणों में आश्रय लेने के लिए अपने मन को सम्बोधित करती हुई कह रही हैं।
व्याख्या :
मीराबाई कहती हैं, हे मन! तू भगवान श्रीकृष्ण के कमल के समान कोमल, सुन्दर एवं शीतल चरणों का स्पर्श कर। ईश्वर के चरणों का स्पर्श तीनों प्रकार के तापों की अग्नि को शान्त करने वाला है (तीन प्रकार के ताप दैहिक, दैविक एवं भौतिक)। जिन भगवान के चरण कमलों के द्वारा प्रह्लाद का उद्धार हुआ, इन्द्र के पद को धारण किया।
जिन चरणों ने अपना आश्रय लेने वाले ध्रुव को अटल एवं अमर पद प्रदान किया। भगवान के चरणों ने समस्त भू-मण्डल को माप लिया तथा सिर से लेकर पाँव तक जिन चरणों का स्पर्श करके गौतम की पत्नी अहिल्या का उद्धार हो गया। ग्वाल लीला करते समय जिन चरणों ने विषधर काली नाग का नाश किया, जिन चरणों ने इन्द्र का गर्व नष्ट करने के लिए गोवर्धन पर्वत को अपनी कनिष्ठा उँगली पर धारण किया। मीराबाई कहती हैं कि मैं तो श्रीकृष्ण की दासी हूँ जो कि कठिन से कठिन कार्य अथवा घोर पापों का भी उद्धार करने वाले हैं।
काव्य सौन्दर्य :
- ब्रजभाषा है, पद गेय एवं लालित्यपूर्ण हैं।
- अनुप्रास तथा उपमा अलंकार हैं।
- गुण-माधुर्य।
- शान्त रस है।
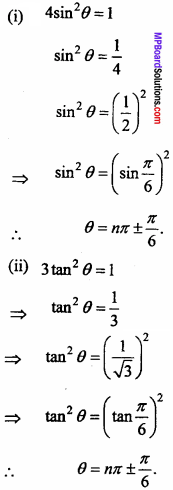
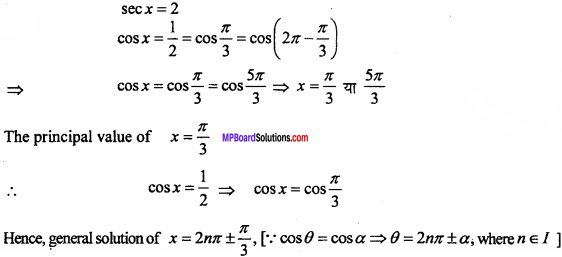
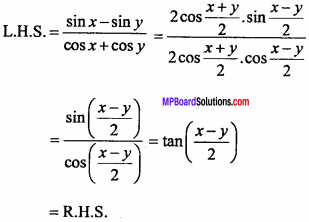
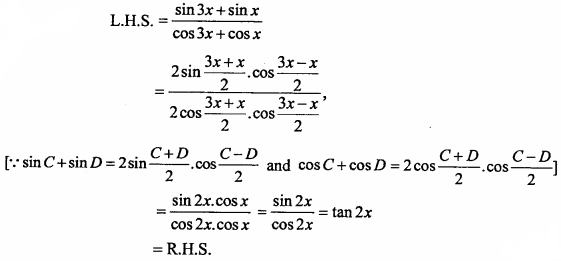
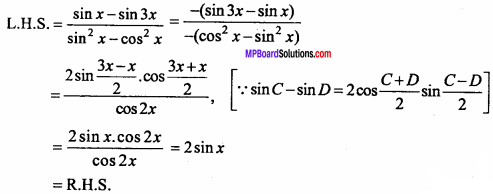
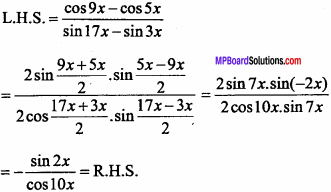
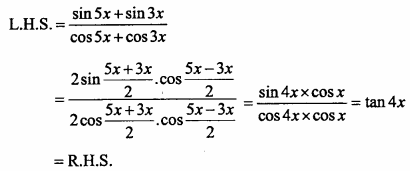
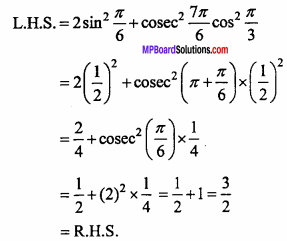
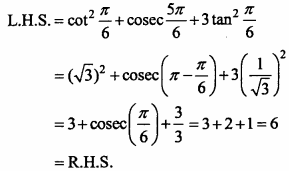

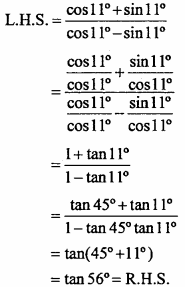
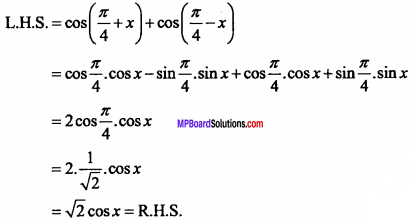
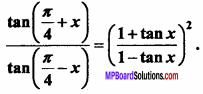
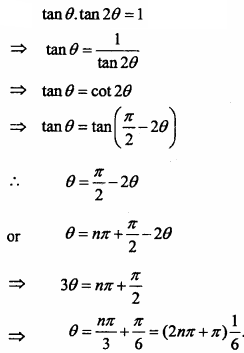
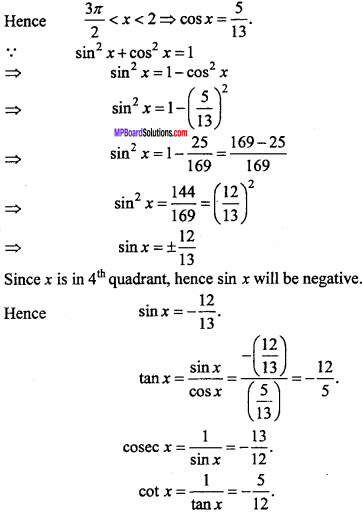
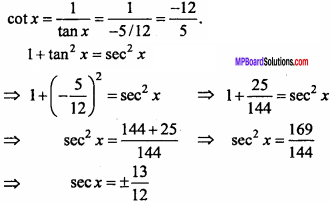
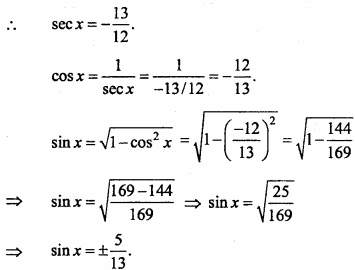

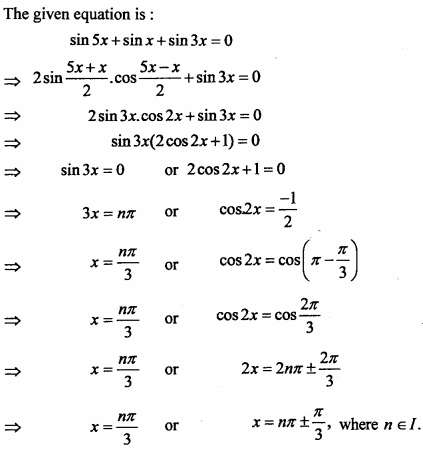

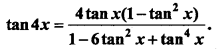
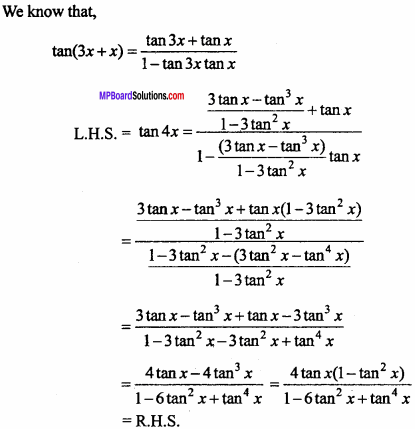
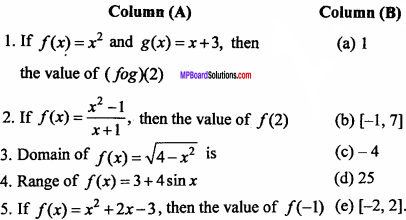
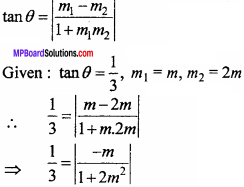
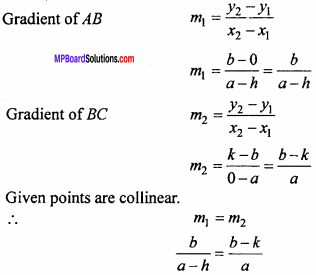
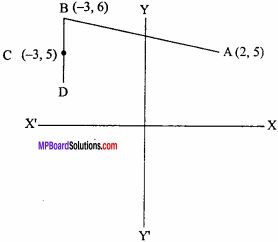
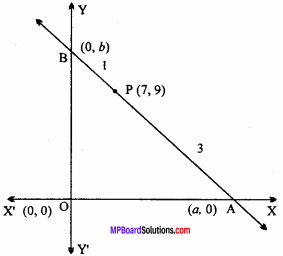

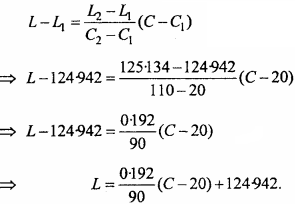





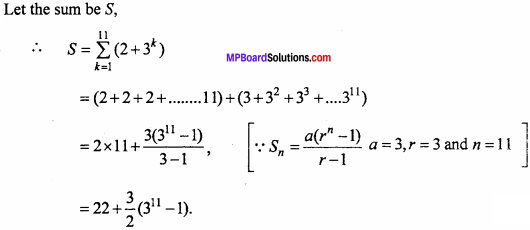
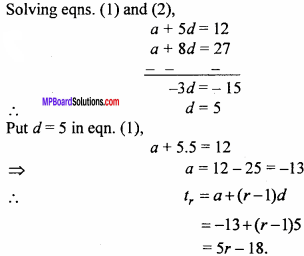
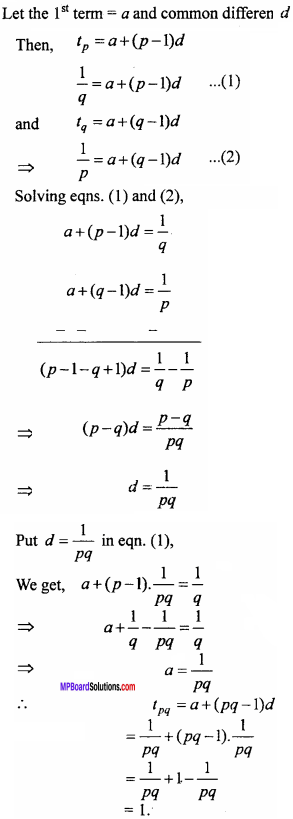




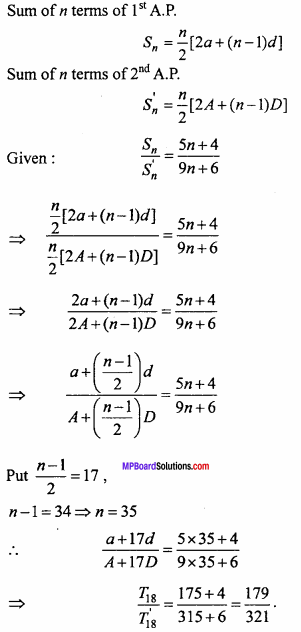
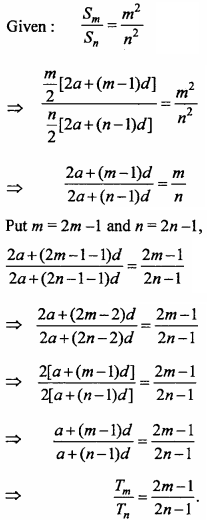

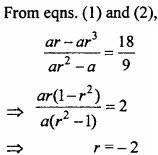
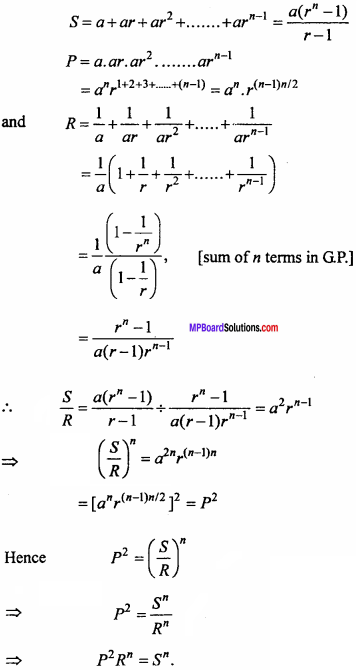
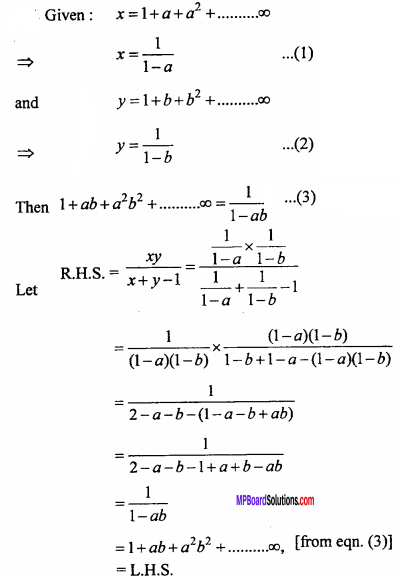
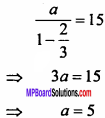
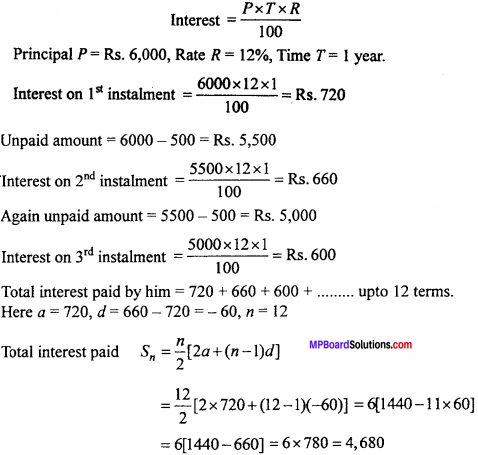
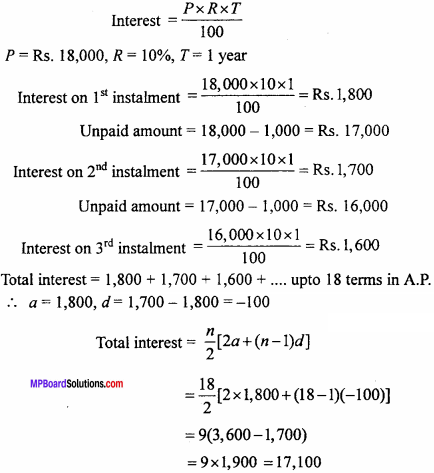




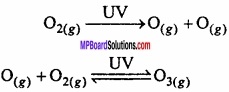

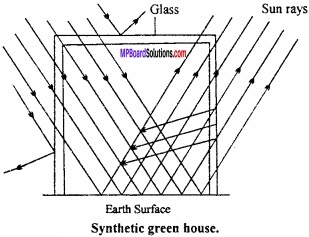







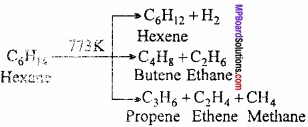

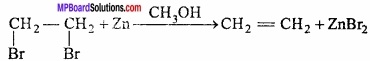






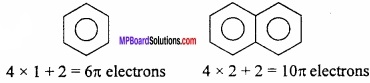


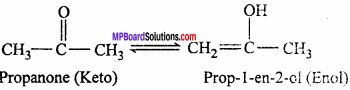








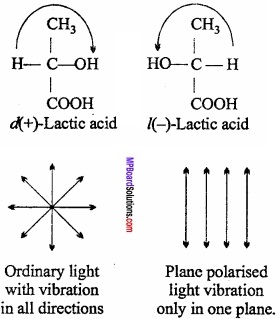

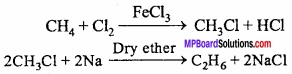










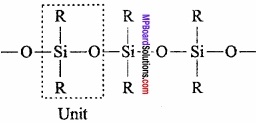
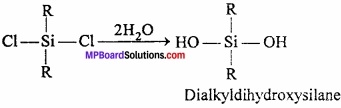
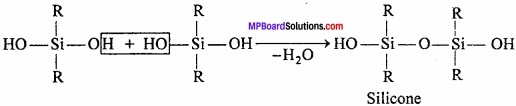
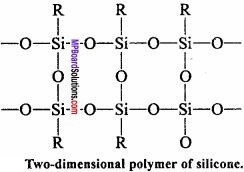
 = CH2 does not have six electrons i.e., (4n + 2) π – electrons in the ring. Therefore, it is not an aromatic compound.
= CH2 does not have six electrons i.e., (4n + 2) π – electrons in the ring. Therefore, it is not an aromatic compound.















































































 = \(\frac{60}{30}\) = 2
= \(\frac{60}{30}\) = 2