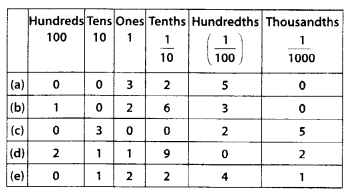
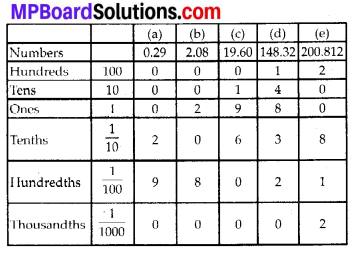
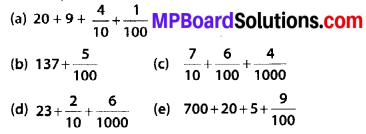
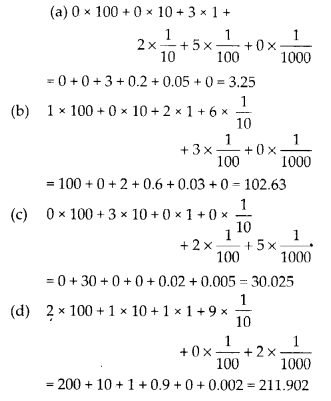MP Board Class 6th Hindi Bhasha Bharti Solutions Chapter 13 बसन्त
MP Board Class 6th Hindi Bhasha Bharti Chapter 13 पाठ का अभ्यास
प्रश्न 1.
सही विकल्प चुनकर लिखिए
(क) बसन्त का घर उजाड़ दिया
(i) वृक्ष काटकर
(ii) वृक्ष लगाकर,
(iii) सड़क बनाकर
(iv) पहाड़ काटकर।
उत्तर
(i) वृक्ष काटकर
(ख) बसन्त में झूले डाले जाते हैं
(i) गेंदा पर
(ii) अमुआ पर,
(iii) बेरी पर
(iv) चम्पा पर।
उत्तर
(ii) अमुआ पर
(ग) बसन्त के स्वागत में गीत गाती है
(i) कोयल
(ii) मोरनी,
(iii) चिड़िया
(iv) गौरेया।
उत्तर
(i) कोयल
(घ) हरे-भरे पेड़ कटने से अब पहले की तरह नहीं आता
(i) शिशिर
(ii) हेमन्त
(iii) ग्रीष्म,
(iv) बसन्त।
उत्तर
(iv) बसन्त
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति कीजिए
(क) बसन्त आने पर …………… आती थी।
(ख) कवि ने जंगल को ………. कहा है।
(ग) पत्तों के झुरमुट से …….. धुन आती थी।
(घ) बसन्त के ……….. में कोयल गीत गाती थी।
उत्तर
(क) हरियाली
(ख) जीवन
(ग) कुहू कुहू
(घ) स्वागत।
प्रश्न 3.
निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों के उत्तर दीजिए
(क) हरियाली कौन-सी ऋतु लाती है?
उत्तर
हरियाली बसन्त ऋतु लाती है।
(ख) बसन्त में कौन-कौन से फूल खिलते हैं?
उत्तर
बसन्त में चम्पा, चमेली और गेंदा के फूल खिलते हैं।
(ग) अब पहले की तरह बसन्त क्यों नहीं आता ?
उत्तर
अब पहले की तरह बसन्त इसलिए नहीं आता है क्योंकि लोगों ने हरे-भरे वृक्षों से परिपूर्ण जंगल काट दिए हैं।
![]()
(घ) पूर्व की तरह बसन्त कब आएगा?
उत्तर
पूर्व की तरह बसन्त अब तभी आएगा जब बंजर बनी हुई धरती पर हरियाली भरे पेड़-पौधे लगेंगे। वनों की हरियाली ही जीवन देती है।
(ङ) बसन्त में क्या-क्या परिवर्तन दिखाई देने लगते हैं ?
उत्तर
बसन्त में चारों ओर का वातावरण खुशहाली का होता है, हरियाली छा जाती है, तरह-तरह के फूल खिल उठते हैं। आम पर बौर आ जाता है। उनकी डालियों में झूले पड़ जाते हैं। मोर-मोरनी नाचने लगते हैं। कोयल पत्तों के झुरमुट में कुहू कुहू की धुन में गीत गाती है। सुगन्ध युक्त हवा बहने लगती है।
प्रश्न 4.
निम्नलिखित पद्यांशों का भाव स्पष्ट कीजिए
(i) बहती थी मस्त पवन, झूम उठे पागल मन,
मोर भी नाचा था, वन में मयूर संग।
(ii) बोला बसन्त फिर, अब कहाँ आऊँ मैं ? . कट गए वृक्ष सब, कहाँ ठहर जाऊँ मैं?
उत्तर
‘सम्पूर्ण पद्यांशों की व्याख्या’ शीर्षक में पद्यांश संख्या 1 व 3 की व्याख्या देखिए।
भाषा की बात
प्रश्न 1.
निम्नलिखित शब्दों का शुद्ध उच्चारण कीजिए
उजाड़, आँगन, हरियाली, झुरमुट।
उत्तर
कक्षा में अपने अध्यापक के सहयोग से शुद्ध उच्चारण कीजिए और अभ्यास कीजिए।
प्रश्न 2.
निम्नलिखित में से सही वर्तनी वाला शब्द चुनकर लिखिए
(क) चमिली, चमैली, चमेली।
(ख) मायूर, मयूर, मयुर।
(ग) जगंल, जगलं, जंगल।
(घ) उजाढ़, उजाड़, ऊजाड।
उत्तर
(क) चमेली
(ख) मयूर
(ग) जंगल
(घ) उजाड़।
प्रश्न 3.
निम्नलिखित शब्दों के दो-दो पर्यायवाची शब्द लिखिए
(i) फूल
(ii) मयूर
(iii) जंगल
(iv) पवन
(v) वृक्ष।
उत्तर
(i) फूल = पुष्प, कुसुम
(ii) मयूर = मोर, केकी
(ii) जंगल = वन, अरण्य
(iv) पवन = हवा, वायु, समीर
(v) वृक्ष = पेड़, पादप, विटप।
![]()
प्रश्न 4.
निम्नलिखित पंक्तियों में से अनुप्रास अलंकार वाली पंक्तियाँ छाँटकर लिखिए
(i) चम्पा चमेली संग
(ii) गेंदा भी फूले थे
(iii) कुहू-कुहू धुन आती थी।
(iv) कहाँ ठहर जाऊँ में।
(v) तरनि तनूजा तट तमाल तरुवर बहु छाये।
(vi) सन सिय सत्य असीस हमारी।
उत्तर
(i) चम्पा चमेली संग
(iii) कुहू कुहू धुन आती थी
(v) तरनि तनूजा तट तमाल तरुवर बहु छाये
(vi) सुनु सिय सत्य असीस हमारी।
प्रश्न 5.
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों में से विशेषण और विशेष्य छाँटकर लिखिए
(क) आज मस्त पवन बह रही है।
(ख) बगीचे में सुन्दर फूल खिले हुए हैं।
(ग) काली कोयल कुहू कुहू कर रही है।
उत्तर
(क) विशेषण-मस्त, विशेष्य-पवन।
(ख) विशेषण-सुन्दर, विशेष्य-फूल।
(ग) विशेषण-काली, विशेष्य-कोयल।
बसन्त सम्पूर्ण पद्यांशों की व्याख्या
(1) बसन्त तुम आते थे
हरियाली लाते थे।
चम्पा चमेली संग
गेंदा भी फूले थे
अमुआ की डाली पर
डाले फिर झूले थे।
बहती थी मस्त पवन
झूम उठे पागल मन
मोर भी नाचा था
वन में मयूर संग।
शब्दार्थ-अमुआ = आम। पवन = हवा।
सन्दर्भ-प्रस्तुत पंक्तियाँ हमारी पाठ्यपुस्तक ‘भाषा-भारती’ की कविता ‘बसन्त’ से ली गई हैं। इस कविता की रचना ‘प्रमोद सोनी’ ने की है।
प्रसंग-बसन्त के आगमन पर चारों ओर सुन्दरता बिखर पड़ती है।
व्याख्या-कवि कहता है कि हे बसन्त ! जब तुम आते हो तब अपने साथ हरियाली लाते हो। बसन्त ऋतु में चम्पा, चमेली और गेंदा के फूल खिल रहे थे। आम के वृक्षों पर बौर आ गया है, भीनी गन्ध के मध्य झूले डाल दिए गए हैं। मतवाली हवा बहने लगी थी; उससे पागल हुआ मन भी झूम उठता था। वन में मोर भी मयूरी (मोरनी) के साथ नाचा करते थे।
(2) स्वागत में गीत कोई
कोयल भी गाती थी
पत्तों के झुरमुट से
कुहू कुहू धुन आती थी।
क्यों नहीं लगता अब
जैसे तुम आए हो
हरियाली मस्त पवन
संग नहीं लाए हो।
शब्दार्थ-मस्त = मतवाला बनाने वाला।
सन्दर्भ-पूर्व की तरह।
प्रसंग-अब बसन्त के आगमन पर पक्षियों द्वारा कोई भी गीत आदि नहीं गाये जाते हैं।
व्याख्या-कवि कहता है कि पहले बसन्त के आने पर उसके स्वागत में कोयल अपनी कुहू कुहू की ध्वनि में गीत गाया करती थी। पेड़ों के पत्तों के झुरमुट में छिपकर कोयल जो अपनी मीठी तान छेड़ती तो सब कुछ आनन्दमय हो जाता था। लेकिन अब तुम्हारे (बसन्त के) आगमन पर वैसा नहीं लगता। हे बसन्त! तुम अब अपने साथ कोई वैसी हरियाली, मतवाला बना देने वाली हवा को भी नहीं लाते हो। इसलिए अब ऐसा क्यों नहीं लगता कि बसन्त आ गया है।
![]()
(3) बोला बसन्त फिर
अब कहाँ आऊँ मैं?
कट गए वृक्ष सब
कहाँ ठहर जाऊँ मैं ?
हरे भरे जंगल सब
तुमने तो काट दिए
घर मेरा उजाड़ कर
अपनों में बाँट दिए।
शब्दार्थ-उजाड़कर = बरबाद करके। सन्दर्भ-पूर्व की तरह।
प्रसंग-‘बसन्त’ आ गया है, ऐसा क्यों नहीं लगता ? इस प्रश्न का उत्तर बसन्त देता है।
व्याख्या-बसन्त ने उत्तर देते हुए कहा कि मैं कहाँ पर आऊँ, क्योंकि मेरे ठहरने के स्थान हरे-भरे पेड़-पौधे थे, उन सबको तुमने काट दिया है। बताओ तो मैं अब कहाँ ठहरूँ? हरियाली से परिपूर्ण जंगलों को तुमने काट दिया है। हरे-भरे वन ही मेरे निवास स्थान थे, उन्हें ही काटकर मेरा घर बरबाद कर दिया है। हे मनुष्यो। तुमने ही हरे-भरे वनों को काट कर अपनों में आपस में बाँट लिया है। मेरे लिए तो रहने का स्थान छोड़ा ही नहीं है।
(4) दुखी है मेरा मन
कुछ तो दुख बाँटो
जंगल ही जीवन है
जंगल को मत काटो।
मेरे घर आँगन को फिर से बसाओगे
बंजर इस धरती पर
हरियाली लाओगे।
अब तो मैं आऊँगा
वृक्ष जब लगाओगे।
शब्दार्थ-बंजर = ऊसर; वह भूमि जिसमें कोई भी बीज अंकुरित नहीं होता है।
सन्दर्भ-पूर्व की तरह।
प्रसंग-दुःखी मन वाला बसन्त अपने आगमन की शर्त बताता है कि इस धरती को हरे-भरे पेड़-पौधों से युक्त कीजिए, मैं अवश्य ही समय से आऊँगा।।
व्याख्या-बसन्त कहता है कि मेरे मन के अन्दर व्याप्त दु:ख को, हे मनुष्यो ! आप सभी बाँट लीजिए। यह मेरा दुःख तभी जा सकेगा, जब आप जंगलों को नहीं काटोगे। जंगलों की वृद्धि कीजिए। जंगल हैं तो जीवन सुरक्षित है। पेड़-पौधे लगाकर मेरे घर-आँगन को हरियाली से सम्पन्न कर दीजिए। यह हरियाली ही मेरा निवास है, घर है। यह धरती जिसे पेड़-पौधों को काटकर बंजर बना दिया है। उसे हरियाली से सम्पन्न बनाइए। बसन्त का आगमन तो तभी हो सकेगा जब वृक्षों का रोपण किया जाएगा।