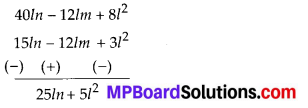
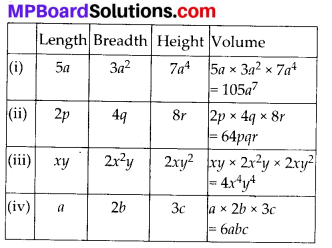
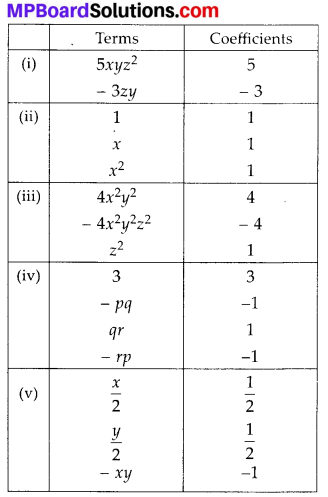
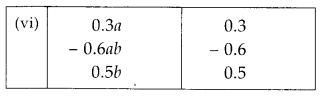
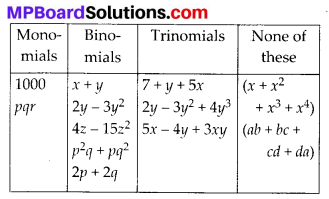
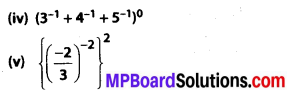
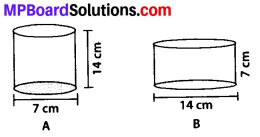
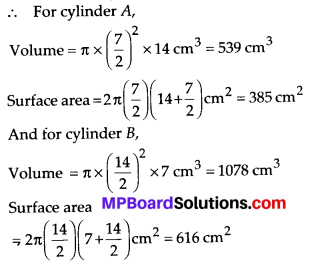
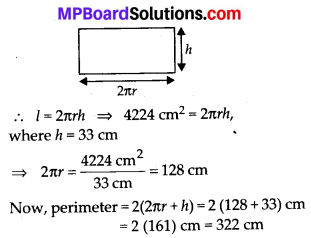
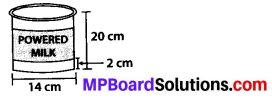
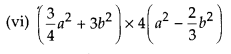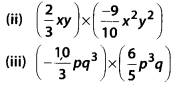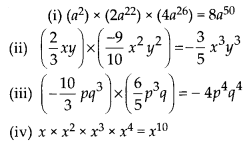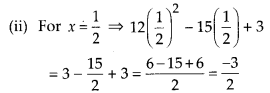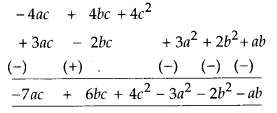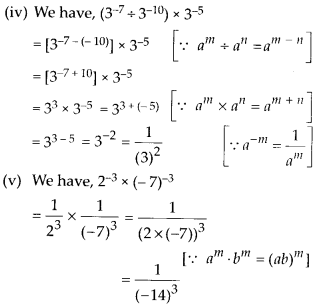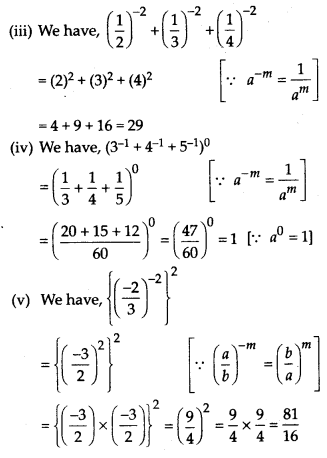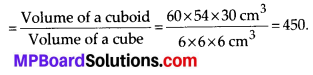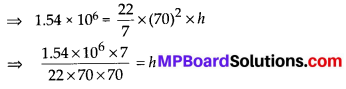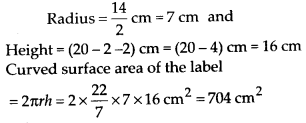MP Board Class 8th Maths Solutions Chapter 16 संख्याओं के साथ खेलना Ex 16.1
प्रश्न 1.
निम्नलिखित में से प्रत्येक में अक्षरों के मान ज्ञात कीजिए तथा सम्बद्ध चरणों के लिए कारण भी दीजिए –

हल:
1. इकाई स्तम्भ को जोड़ने पर अर्थात् A + 5 को जोड़ने पर हम इकाई का अंक 2 प्राप्त करते हैं।
अत: A = 7, (∴ A + 5 = 7 + 5 = 12)
अब दहाई स्तम्भ को जोड़ने पर
1 + 3 + 2 = B या B = 6
अतः अब पहेली इस प्रकार होगी –

∴ A = 7, B = 6
2. इकाई स्तम्भ से, A + 8 = 3
अर्थात् इकाई का अंक = 3 होना चाहिए।
अतः A = 5, (∴ A + 8 = 5 + 8 = 13)
अब दहाई स्तम्भ से, 1 + 4 + 9 = B या B = 14
∴ स्पष्ट है, B = 4 और C = 1 अब पहेली इस प्रकार होगी –

∴ A = 5, B = 4 तथा C = 1
3. क्योंकि इकाई का अंक A x A = A है।
∴ A = 1, A = 5 या A = 6
जबकि A = 1, तब,

अत: A ≠ 1
जबकि A = 5, तब,
![]()
अत: A ≠ 5
जबकि A = 6, तब,
![]()
अतः A = 6
4. दी हुई पहेली से,
B + 7 = A तथा A + 3 = 6
अतः सम्भावित मान
0 + 7 = 7 अर्थात् A = 7 परन्तु 7 + 3 ≠ 6
1 + 7 = 8 अर्थात् A = 8 परन्तु 8 + 3 ≠ 6
2 + 7 = 9 अर्थात् A = 9 परन्तु 9 + 3 ≠ 6
3 + 7 = 10 अर्थात् A = 0 परन्तु 1 + 0 + 3 ≠ 6
4 + 7 = 11 अर्थात् A = 1 परन्तु 1 + 1 + 3 ≠ 6
5 + 7 = 12 अर्थात् A = 2 और 1 + 2 + 3 = 6
B = 5 तथा A = 2
अब पहेली इस प्रकार है –

A = 2 और B = 5
5. ∴ इकाई स्तम्भ 3 x B = B, ∴ B = 0
अब पहेली इस प्रकार है –

अब, 3 x A = A, ∴ A = 5
अब, पहेली इस प्रकार है –

∴ A = 5, B = 0 और C = 16
6. ∴ इकाई स्तम्भ 5 x B = B अर्थात् B = 0 या 5
यदि B = 0, तब

अब, 5 x A = A या A = 0 या 5
परन्तु A0, A = 5 के लिए
![]()
∴ A = 5, B = 0 और C = 2
यदि B = 5, तब

अब, 5 x A + 2 = A ⇒ A = 2, ∴ 5 x 2 + 2 = 12
∴ इकाई का अंक = 2 = A
∴ B = 5 के लिए,

∴ A = 2, B = 5 और C = 1
7.

BBB के सम्भव मान: 111, 222, 333, आदि
∴ 111 ÷ 6 = 18 और शेषफल = 3 ∴ B ≠ 3
222 ÷ 6 = 37, शेषफल = 0, अतः भागफल 37 ≠ A2
333 ÷ 6 = 55, शेषफल = 3, अतः भागफल 55 ≠ A3
444 + 6 = 74, शेषफल = 4, अतः भागफल 74 ≠ A4
अतः A = 7 और B = 4
8. इकाई स्तम्भ से 1 + B = 0, इकाई स्तम्भ का अंक 0 है।
∴ B = 9 अब

परन्तु 90 – 19 = 71 अत: A1 = 71 या A = 7
अतः A = 7, B = 9
9. इकाई स्तम्भ से,
B + 1 = 8 अतः इकाई अंक 8 है।
B = 8 – 1 = 7
∴ B स्वयं एक अंक है, ∴ B = 7
अब

दहाई स्तम्भ से, A + 7 = 1
अतः A का इकाई अंक 1 होना चाहिए।
∴ A स्वयं एक अंक है। अत: A = 4
अब, पहेली

अतः A = 4, B = 7
10. दहाई के स्तम्भ से,
2 + A = 0
∴ संख्या का इकाई अंक 0 होना चाहिए।
∴ A = 8, तब

अब, 8 + B = 9, ∴ B = 9 – 8 = 1
अब,

∴ A = 8 और B = 1
पाठ्य-पुस्तक पृष्ठ संख्या # 268
प्रयास कीजिए (क्रमांक 16.6)
![]()
(पहला प्रश्न आपकी सहायता के लिए किया हुआ है।)
प्रश्न 1.
यदि विभाजन N ÷ 5 से शेषफल, 3 प्राप्त होता है, तो N की इकाई अंक क्या हो सकता है?
हल:
इकाई के अंक को 5 से भाग देने पर शेषफल 3 आना चाहिए। अतः इकाई का अंक 3 या 8 होगा।
प्रश्न 2.
यदि विभाजन N ÷ 5 से शेषफल 1 प्राप्त होता है, तो N का इकाई अंक क्या हो सकता है?
हल:
इकाई के अंक को 5 से भाग देने पर शेषफल 1 आना चाहिए।
अतः इकाई का अंक 1 या 6 होगा।
प्रश्न 3.
यदि विभाजन N 5 से शेषफल 4 प्राप्त होता है, तो N की इकाई का अंक क्या हो सकता है?
हल:
इकाई के अंक को 5 से भाग देने पर शेषफल 4 आना चाहिए।
अतः इकाई का अंक 4 या 9 होगा।
प्रयास कीजिए (क्रमांक 16.7)
(पहला प्रश्न आपकी सहायता के लिए किया हुआ है।)
प्रश्न 1.
यदि विभाजन N ÷ 2 से शेषफल 1 प्राप्त होता है, तो N की इकाई का अंक क्या हो सकता है?
हल:
N विषम है। इसलिए इसकी इकाई का अंक विषम होगा। अतः N की इकाई का अंक 1, 3, 5, 7 या 9 होगा।
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
यदि विभाजन N ÷ 2 से कोई शेष प्राप्त नहीं होता (अर्थात् शेषफल 0 है), तो N की इकाई का अंक क्या हो सकता है?
हल:
N सम होना चाहिए। इसलिए इसकी इकाई का अंक सम होगा। – अंत: N की इकाई का अंक 0, 2, 4, 6 या 8 होगा।
प्रश्न 3.
मान लीजिए कि विभाजन N ÷ 5 से शेषफल 4 और विभाजन N ÷ 2 से 1 प्राप्त होता है। N की इकाई का अंक क्या होना चाहिए?
हल:
क्योंकि N ÷ 5 से शेषफल 4 प्राप्त होता है। अत: N की इकाई का अंक 4 या 9 होगा।
N ÷ 2 से शेषफल 1 प्राप्त होता है। इसलिए इकाई का अंक विषम होना चाहिए।
अतः N की इकाई का अंक 1, 3, 5, 7 या 9 होगा। परन्तु यहाँ 9 दोनों स्थितियों को सन्तुष्ट करेगा।
अतः N की इकाई का अंक 9 होगा।
पाठ्य-पुस्तक पृष्ठ संख्या # 270
प्रयास कीजिए (क्रमांक 16.8)
प्रश्न 1.
निम्नलिखित संख्याओं की 9 से विभाज्यता की जाँच कीजिए –
1. 108
2. 616
3. 294
4. 432
5. 927
हल:
हम जानते हैं कि कोई संख्या 9 से विभाज्य होती है, यदि इसके अंकों का योग 9 से विभाज्य हो।
1. संख्या = 108
संख्या के अंकों का योग = 1 + 0 + 8 = 9, यह 9 से विभाज्य है।
इसलिए 108, 9 से विभाज्य है।
2. संख्या = 616
संख्या के अंकों का योग = 6 + 1 + 6 = 13, यह 9 से विभाज्य नहीं है।
इसलिए 616, 9 से विभाज्य नहीं है।
3. संख्या = 294
संख्या के अंकों का योग = 2 + 9 + 4 = 15, यह 9 से विभाज्य नहीं है।
इसलिए 294, 9 से विभाज्य नहीं है।
4. संख्या = 432
संख्या के अंकों का योग = 4 + 3 + 2 = 9, यह 9 से विभाज्य है।
इसलिए 432, 9 से विभाज्य है।
5. संख्या = 927
संख्या के अंकों का योग = 9 + 2 + 7 = 18, यह 9 से विभाज्य है।
इसलिए 927, 9 से विभाज्य है।
सोचिए, चचों कोजिए और लिखिए।
![]()
प्रश्न 1.
आप देख चुके हैं कि 450, 10 से विभाज्य है। यह 2 और 5 से भी विभाज्य है, जो 10 के गुणनखण्ड हैं। इसी प्रकार संख्या 135, 9 से विभाज्य है। यह 3 से भी विभाज्य है, जो 9 का एक गुणनखण्ड है।
क्या आप कह सकते हैं कि यदि कोई संख्या किसी संख्या m से विभाज्य हो, तो वह m के प्रत्येक गुणनखण्ड से भी विभाज्य होगी?
हल:
हाँ, यदि कोई संख्या m से विभाज्य हो, तो वह m के प्रत्येक गुणनखण्ड से भी विभाज्य होगी।
प्रश्न 2.
1. एक तीन अंकों की संख्या abc की 100 a + 10b + c के रूप में लिखिए। अब 100a + 10b + c = 99a + 11b + (a – b + c)
= 11 (9a + b) + (a – b + c)
यदि संख्या abc, 11 से विभाज्य है, तो आप (a-b+ c) के बारे में क्या कह सकते हैं ? क्या यह आवश्यक है कि (a+c-b), 11 से विभाज्य हो?
2. एक चार अंकों की संख्या abcd को इस प्रकार लिखिए –
1000a + 100b + 10c + d = (1001 a + 99b + 11c) -(a – b + c – d)
= 11 (91a + 9b + c) + [(b + d) – (a + c)]
यदि संख्या abcd, 11 से विभाज्य है, तो (b + d) – (a + c) के बारे में आप क्या कह सकते हैं?
3. उपर्युक्त (i) और (ii) से, क्या आप कह सकते हैं कि कोई संख्या 11 से विभाज्य होगी, यदि इसके विषम स्थानों के अंकों का योग और समस्थानों के अंकों के योग का अन्तर 11 से विभाज्य होगा?
हल:
1. हाँ, यह आवश्यक है कि (a + c – d), 11 से विभाज्य होगी।
2. यदि संख्या abcd, 11 से विभाज्य है, तब (b + d) – (a + c), 11 से विभाज्य होगी।
3. हाँ, हम कह सकते हैं कि यदि कोई संख्या 11 से विभाज्य होगी यदि इसके विषम स्थानों के अंकों का योग और समस्थानों के अंकों का योग का अन्तर 11 से विभाज्य हो।
पाठ्य-पुस्तक पृष्ठ संख्या # 271
![]()
प्रयास कीजिए (क्रमांक 16.9)
प्रश्न 1.
निम्नलिखित संख्याओं की 3 से विभाज्यता की जाँच कीजिए –
1. 108
2. 616
3. 294
4. 432
5. 927.
हल:
हम जानते हैं कि कोई संख्या 3 से विभाज्य होती है, यदि इसके अंकों का योग 3 से विभाज्य हो।
1. संख्या = 108
अंकों का योग = 1 + 0 + 8 = 9, यह 3 से विभाज्य है।
इसलिए 108,3 से विभाज्य है।
2. संख्या = 616
अंकों का योग = 6 + 1 + 6 = 13, यह 3 से विभाज्य नहीं है।
इसलिए 616, 3 से विभाज्य नहीं है।
3. संख्या = 294
अंकों का योग = 2 + 9 + 4 = 15, यह 3 से विभाज्य है।
इसलिए 294, 3 से विभाज्य है।
4. संख्या = 432
अंकों का योग = 4 + 3 + 2 = 9, यह 3 से विभाज्य है।
इसलिए 432, 3 से विभाज्य है।
5. संख्या = 927
अंकों का योग = 9 + 2 + 7 = 18, यह 3 से विभाज्य है।
इसलिए 927, 3 से विभाज्य है।