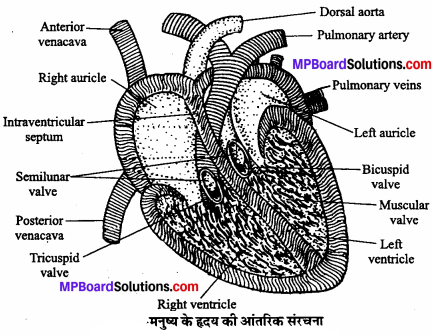
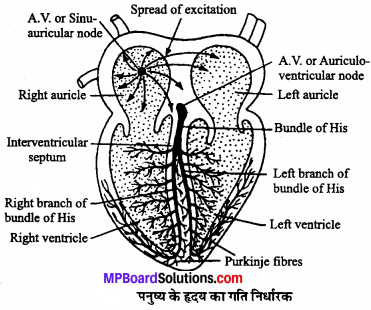
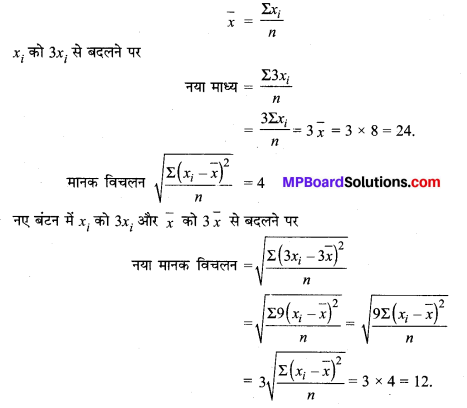
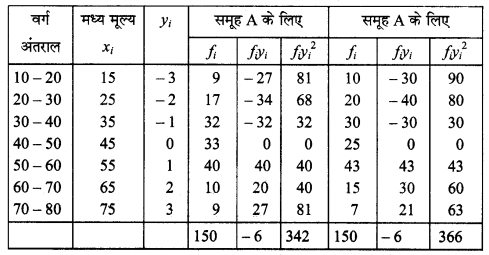
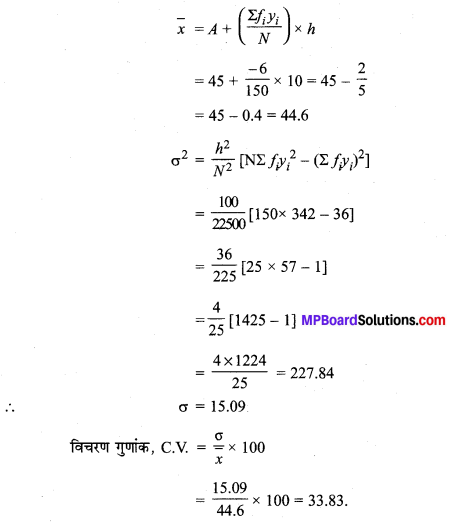
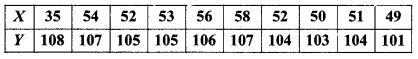
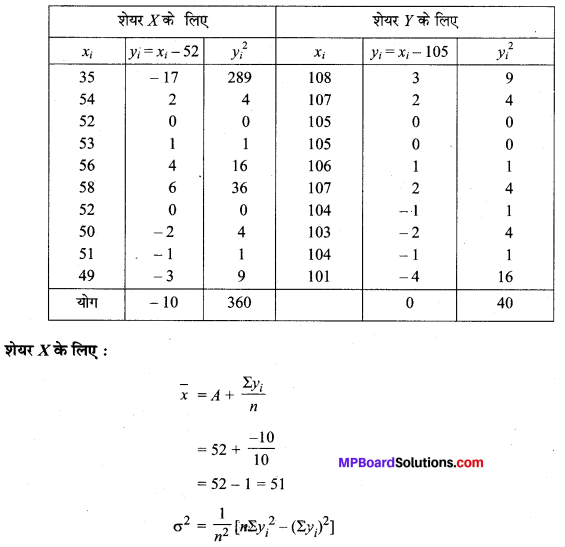
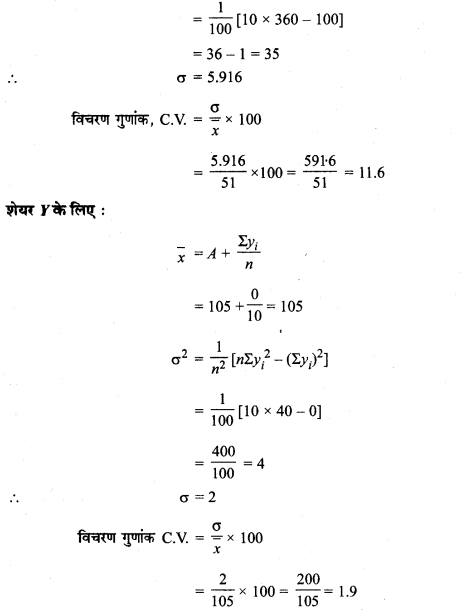
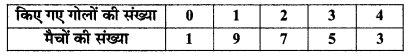
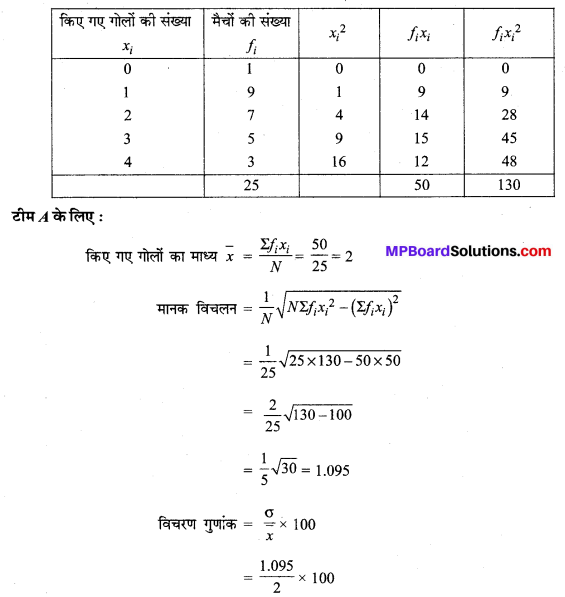
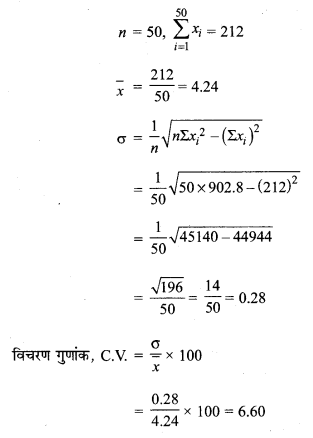
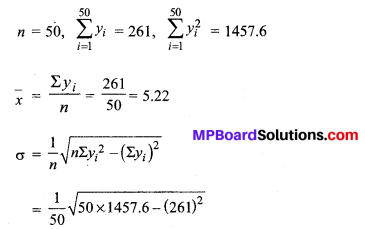
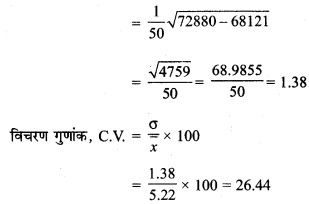
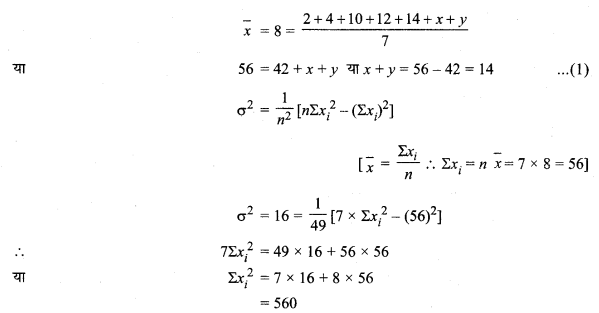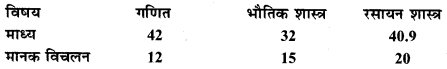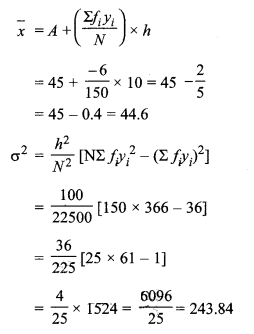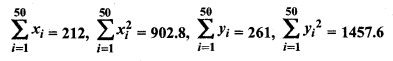MP Board Class 11th Maths Solutions Chapter 16 प्रायिकता Ex 16.2
प्रश्न 1.
एक पासा फेंका जाता है। मान लीजिए घटना E ‘पासे पर संख्या 4’ दर्शाता है और घटना F ‘पासे पर सम संख्या’ दर्शाता है। क्या E और F परस्पर अपवर्जी हैं?
हल:
पासा फेंकने पर प्रतिदर्श समष्टि
= {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
E (संख्या 4 दर्शाता है) = {4}
F (सम संख्या ) = {2, 4, 6}
E ∩ F = {4} {2, 4, 6} = {4} ≠ ϕ
अत: E और F परस्पर अपवर्जी नहीं हैं।
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
एक पासा फेंका जाता है। निम्नलिखित घटनाओं का वर्णन कीजिए :
(i) A : संख्या 7 से कम है।
(ii) B : संख्या 7 से बड़ी है।
(iii) C : संख्या 3 का गुणज है।
(iv) D : संख्या 4 से कम है।
(v) E : 4 से बड़ी सम संख्या है।
(vi) F : संख्या 3 से कम नहीं है।
A ∪ B, A ∩ B, B ∪ C, E ∪ F, D ∩ E, A – C, D – E, F’, E ∩ F’ भी ज्ञात कीजिए।
हल:
S = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
(i) A : संख्या 7 से कम है = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
(ii) B : संख्या 7 से बड़ी है = पासे में कोई संख्या 7 से बड़ी नहीं है
= ϕ
(iii) C : संख्या 3 का गुणज है = {3, 6}
(iv) D : संख्या 4 से कम है = {1, 2, 3}
(v) E : 4 से बड़ी सम संख्या है = {6}
(vi) F = संख्या 3 से कम नहीं है
= {3, 4, 5, 6}
अब A ∪ B = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6} ∪ϕ
= {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}.
A ∩ B= {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6} ∩ ϕ
= ϕ
B ∪ C = ϕ ∪ {3, 6} = {3, 6}.
E ∪ F = {6} ∪ {3, 4, 5, 6} = {3, 4, 5, 6}.
D ∩ E = {1, 2, 3} ∩ {6}
A – C= {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6} – {3, 6}
= {1, 2, 4, 5}.
F’ = {3, 4, 5, 6}’ = S – {3, 4, 5, 6}
= {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6} – {3, 4, 5, 6}
= {1, 2}.
E ∩ F’ = {6} ∩ {3, 4, 5, 6}’
= {6} ∩ {1, 2} = ϕ.
प्रश्न 3.
एक परीक्षण में पासे के एक जोड़े को फेंकते हैं और उन पर प्रकट संख्याओं को लिखते हैं। निम्नलिखित संख्याओं का वर्णन कीजिए।
A : प्राप्त संख्याओं का योग 8 से अधिक है।
B : दोनों पासों पर संख्या 2 प्रकट होती है।
C : प्रकट संख्याओं का योग कम से कम 7 है और 3 का गुणज है।
इन घटनाओं के कौन-कौन से युग्म परस्पर अपवर्जी हैं ?
हल:
जब दो पासे फेंके जाते हैं, तो कुल संभावित परिणामों की संख्या
= 6 × 6 = 36
A= प्राप्त संख्याओं का योग 8 से अधिक है।
= {(3, 6), (4, 5), (5, 4), (6, 3), (4, 6), (5, 5), (6, 4), (5, 6), (6, 5), (6, 6)}
B = कम से कम एक पासे पर संख्या 2 प्रकट होती है
= {(1, 2), (2, 2), (3, 2), (4, 2), (5, 2), (6, 2), (2, 1), (2, 3), (2, 4), (2, 5), (2, 6)}
C = प्रकट संख्याओं का योग कम से कम 7 है और 3 का गुणज है।
= प्रकट संख्याओं का योग 9 और 12 है जो कि 3 का गुणज है।
= {(3, 6), (6, 3), (4, 5), (5, 4), (6, 6)}
A ∩ C = {(3, 6), (4, 5), (5, 4), (6, 3), (4, 6), (5, 5), (6, 4), (5, 6), (6, 5), (6, 6)} ∩ {(3, 6), (6, 3), (5, 4), (6, 6)}
= {(3, 6), (6, 3), (4, 5), (5, 4), (6, 6)}
A ∩ B = {(3, 6), (6, 3), (4, 5), (5, 4), (4, 6), (6, 4), (5, 5), (5, 6), (6, 5), (6, 6) ∩ {(1, 2), (3, 2), (2, 1), (2, 3), (4, 2), (2, 4), (5, 2), (2, 5), (2, 6), (6, 2)}
= ϕ
B ∩ C = {(1, 2), (2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 3), (3, 2), (2, 4), (4, 2), (2, 5), (5, 2), (2, 6), (6, 2)} ∩ {(3, 6), (6, 3), (4,5), (5, 4), (6, 6)}
= ϕ
A ∩ B = ϕ , B ∩ C = ϕ अर्थात् A और B, B और C परस्पर अपवर्जी हैं।
परन्तु A ∩ C ≠ ϕ, अत: A और C परस्पर अपवर्जी नहीं हैं।
प्रश्न 4.
तीन सिक्कों को एक बार उछाला जाता है। मान लीजिए कि घटना “तीन चिल दिखना” को A से, घटना 2 चित्त और 1 पट दिखना’ को B से, घटना “3 पट लिखना’ को C से और घटना ‘पहले सिक्के पर चित्त दिखना’ को D से निरूपित किया गया है। बताइए कि इनमें से कौन-सी घटनाएँ
(i) परस्पर अपवर्जी हैं ?
(ii) सरल हैं
(iii) मिश्र हैं ?
हल:
जब तीन सिक्के उछाले जाते हैं तो प्रतिदर्श समष्टि
S = {HHH, HHT, HTH, THH, TTH, THT, HTT, TIT}
A : तीन चित्त दिखना = {HHH}
B : दो चित्त और एक पट दिखना
= {HHT, HTH, THH}
C : तीन पट दिखना = {TTT}
D : पहले सिक्के पर चित्त दिखना
= {HHH, HHT, HTH, HTT}
(i)A ∩ B = {HHH} ∩ {HHT, HTH, THH}
= ϕ
A ∩ C = {HHH} ∩ {TIT} = ϕ
A ∩ D = {HHH} {HHH, HHT, HTH, HTT}
= {HHH} ≠ ϕ
B ∩ C = {HHT, HTH, THH} ∩ {TTT}
= ϕ
B ∩ D = {HHT, HTH, THH) ∩ {HHH, HHT, HTH, HTT}
= (HHT, HTH} ≠ ϕ
C ∩ D = {TTT} {HHH, HHT, HTH, HTT}
= ϕ
A ∩ B ∩ C = {HHH} ∩ {HHT, HTH, THH} ∩ {TTT)
= ϕ
अतः परस्पर अपवर्जी घटनाएँ
A और B, A और C, B और C, C और D, A, B और C.
(ii) सरल घटनाएँ : A और C
(iii) मिश्र घटनाएँ : B और D.
![]()
प्रश्न 5.
तीन सिक्के एक बार उछाले जाते हैं। वर्णन कीजिए
(i) दो घटनाएँ जो परस्पर अपवर्जी हैं।
(ii) तीन घटनाएँ जो परस्पर अपवर्जी और निःशेष हैं।
(iii) दो घटनाएँ जो परस्पर अपवर्जी नहीं हैं।
(iv) दो घटनाएँ जो परस्पर अपवर्जी हैं किन्तु निःशेष नहीं हैं।
(v) तीन घटनाएँ जो परस्पर अपवर्जी हैं किन्तु निःशेष नहीं हैं।
हल:
(i) दो घटनाएँ जो परस्पर अपवर्जी हैं
A = कम से कम दो चित्त प्राप्त करना
= {HHH, HHT, HTH, THH}
B = कम से कम दो पेर्ट प्राप्त करना
= {TTT, TTH, THT, HTT}
(ii) तीन घटनाएँ A, B, C जो परस्पर अपवर्जी और निःशेष हैं।
A = अधिक से अधिक एक चित्त प्राप्त करना
= {TIT, TTH, THT, HTT}
B = तथ्यत, 2 चित्त प्राप्त करना
= {HHT, HTH, THH}
C = तथ्यतः, 3 चित्त प्राप्त करना = {HHH}
(iii) दो घटनाएँ A और B जो परस्पर अपवर्जी नहीं हैं।
A : अधिकतम 2 पट प्राप्त करना
= {HHH, HHT, HTH, THH, TTH, THT, HTT}
B : तथ्यतः 2 चित्त प्राप्त करना
= {HHT, HTH, THH}
A ∩ B = {HHT, HTH, THH} ≠ ϕ
(iv) दो घटनाएँ A और B जो परस्पर अपवर्जी हैं किन्तु निःशेष नहीं हैं।
A : तथ्यतः एक चित्त प्राप्त करना
= {TTH, THT, HTT}
B : तथ्यतः 2 चित्त प्राप्त करना
{HHT, HTH, THH)
(v) तीन घटनाएँ A, B, C जो परस्पर उपवर्जी हैं किन्तु निःशेष नहीं हैं।
A : तथ्यतः एक पट प्राप्त करना
= {HHT, THT, THH}
B : तथ्यतः 2 पट प्राप्त करना
= {TTH, THT, HTT}
C : तथ्यतः 3 पट प्राप्त करना = {TTT}
[नोट : घटनाएँ भिन्न-भिन्न भी हो सकती हैं।
प्रश्न 6.
दो पासे फेंके जाते हैं। घटनाएँ A, B और C निम्नलिखित प्रकार से हैं :
A : पहले पासे पर सम संख्या प्राप्त होना।
B : पहले पासे पर विषम संख्या प्राप्त होना।
C : पासों पर प्राप्त संख्याओं का योग 55 होना।
निम्नलिखित घटनाओं का वर्णन कीजिए :
(1) A’
(ii) B – नहीं
(iii) A या B
(iv) A और B
(v) A किन्तु C नहीं
(vi) B या C
(vii) B और C
(viii) A ∩ B’ ∩ C’
हल:
दो सिक्के फेंकने पर प्रतिदर्श समष्टि
S = {(1, 1), (1, 2), …(1, 6), (2, 1), (2, 2), … (2, 6), (3, 1), (3, 2), … (3, 6), (4, 1), (4, 2), … (4, 6), (5, 1), (5, 2),… (5, 6), (6, 1), … (6, 6)}
A= पहले पासे पर सम संख्या प्राप्त होगा।
= {(2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 3), (2, 4), (2, 5), (2, 6), (4, 1), (4, 2), (4, 3), (4, 4), (4,5), (4, 6), (6, 1), (6, 2), (6, 3), (6, 4), (6, 5), (6, 6)} = A
B = पहले पासे पर विषम संख्या प्राप्त होना।
= {(1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (1, 5), (1, 6), (3, 1), (3, 2), (3, 3), (3, 4), (3, 5), (3, 6), (5, 1), (5, 2), (5, 3), (5, 4), (5, 5), (5, 6)}
C = पासों पर प्राप्त संख्याओं का योग ≤ 5 होना।
= {(1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 3), (3, 1), (3, 2), (4, 1)}
(i) A’ = S – A
= {(1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (1, 5), (1, 6), (3, 1), (3, 2), (3, 3), (3, 4), (3, 5), (3, 6), (5, 1), (5, 2), (5, 3), (5, 4), (5, 5), (5, 6)}
= B
(ii) B-नहीं = B’ = पहले पासे पर विषम संख्या का न होना
= {(2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 3), (2, 4), (2, 5), (2, 6), (4, 1), (4, 2), (4, 3), (4, 4), (4,5), (4,6), (6, 1), (6, 2), (6, 3), (6, 4), (6, 5), (6, 6)} = A
(iii) A या B= A ∪ B= {x : x पहले पासे पर सम संख्या का होना} ∪ {पहले पासे पर विषम संख्या का होना}
= S
(iv) A और B = A ∩ B
= {x : x पहले पासे पर सम संख्या का होना} ∩ {पहले पासे पर विषम संख्या का होना}
= ϕ
(v) A किन्तु C – नहीं
= {x : x पहले पासे पर सम संख्या का होना} – {पासों पर प्राप्त संख्याओं का योग ≤ 5}
A – C = {(2, 1), (2, 2), …, (2, 6), (4, 1), (4, 2), … (4, 2), … (4, 6), (6, 1), (6, 2), …. (6,6)} – {(1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (1,4), (2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 3), (3, 1), (3, 2), (4, 1)}
= {(2, 4), (2, 5), (2, 6), (4, 2), (4, 3),…(4, 6), (6, 1), (6, 2), … (6, 6)}
(vi) B या C = B ∪ C = {x : x, पहले पासे पर विषम संख्या होगा} ∪ {पासों पर प्राप्त संख्याओं का योग ≤ 5}
= {(1, 1), (1, 2), …, (1, 6), (3, 1), (3, 2), …, (3, 6), (5, 1), (5, 2), … (5, 6)} ∪ (1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 3), (3, 2), (4, 1)}
= {(1, 1), (1, 2), … (1, 6), (2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 3), (3, 1), (3, 2), … (3, 6), (4, 1), (5, 1), (5, 2), (5, 3), … (5, 6).
(vii) B और C अर्थात् B ∩ C = {(1, 1), … (1, 6), (3, 1), (3, 2),… (3, 6), (5, 1), (5, 2), (5, 3), … (5, 6) ∩ {(1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (2, 1), (2, 2) (2, 3), (3, 1), (3, 2), (4, 1)}.
= {(1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (3, 1), (3, 2)}
(viii) यहाँ B’ = A
∴ A ∩ B’ = A ∩ A = A
∴ A ∩ B’ ∩ C’ = {(2, 1), (2, 2), … (2, 6), (4, 1), (4, 2),…,(4, 6), (6, 1), (6, 2),… (6, 6)} ∩ {(1, 5), (1, 6), (2, 4), (2, 5), (2, 6), (3, 3), (3, 4), (3, 5), (3, 6), (4, 2), (4, 3),…(4, 6), (5, 1), (5, 2),… (5, 6), (6, 1), (6, 2), … (6, 5)}
= {(2, 4), (2, 5), (2, 6), (4, 2), (4, 3), (4, 4), (4, 5), (4, 6), (6, 1), (6, 2), (6, 3), (6, 4), (6, 5), (6, 6)}.
![]()
प्रश्न 7.
उपर्युक्त प्रश्न 6 को देखिए और निम्नलिखित में सत्य या असत्य बताइए (अपने उत्तर का कारण दीजिए :
(i) A और B परस्पर अपवर्जी हैं।
(ii) A और B परस्पर अपवर्जी और निःशेष हैं।
(iii) A = B’
(iv) A और C परस्पर अपवर्जी हैं।
(v) A और B’ परस्पर अपवर्जी हैं।
(vi) A’, B’, C परस्पर अपवर्जी और निःशेष घटनाएँ हैं।
हल:
(i) सत्य A : पहले पासे पर सम संख्या का होना
B : पहले पासे पर विषम संख्या का होना
A और B में कोई भी घटना समान नहीं है।
A ∩ B = ϕ ⇒ A और B परस्पर अपवर्जी घटनाएँ हैं।
(ii) सत्य : A = पहले पासे पर सम संख्या होना
B : पहले पासे पर विषम संख्या होना
A ∪ B = पहले पासे पर सम या विषम कोई भी संख्या हो सकती है, दूसरे पासे पर 1 से 6
तक कोई भी संख्या हो सकती है।
अर्थात् A और B परस्पर अपवर्जी और निःशेष घटनाएँ हैं।
(iii) सत्य : B’ = {पहले पासे पर विषम संख्या होना। .
= पहले पासे पर विषम संख्या न होना
= पहले पासे पर सम संख्या होना
= A
(iv) असत्य A= पहले पासे पर सम संख्या होना
C = {(1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 3), (3, 1), (3, 2), (4, 1}}
A और C में (2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 3), (4, 1) समान घटनाएँ हैं।
∴ A ∩ C ≠ ϕ
अत: A और C परस्पर अपवर्जी नहीं हैं।
(v) असत्य B’= A
∴ A ∩ B’= A ∩ A = A ≠ ϕ
A तथा B’ परस्पर अपवर्जी नहीं हैं।
(vi) असत्य A’ = B, B’ =A
∴ A’ ∩ B’ = B ∩ A = ϕ
परन्तु A’ ∩ C = B ∩ C = {x : x पहले पासे पर विषम संख्या होना} {(1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 3), (3, 1), (3, 2), (4, 1)}
= {(1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (3, 1), (3, 2)} ≠ ϕ
B’ ∩ C = A ∩ C [∵ B’ = A]
= {x : x, पहले पासे पर सम संख्या का होना} ∩ {(1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 3), (3, 1), (3, 2), (4, 1)
(2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 3), (4, 1), A और C दोनों में समान घटनाएँ हैं।
B’ ∩ C ≠ ϕ
अर्थात् A’, B’, और C परस्पर अपवर्जी नहीं हैं और न ही नि:शेष हैं।