MP Board Class 10th Sanskrit Solutions Durva Chapter 5 कुटुम्बानुरक्तिः (नाट्यांशः) (मध्यमव्यायोगात्)
MP Board Class 10th Sanskrit Chapter 5 पाठ्यपुस्तक के प्रश्न
कक्षा 10 संस्कृत पाठ 5 MP Board प्रश्न 1.
एकपदेन उत्तरं लिखत-(एक पद में उत्तर लिखिए-)।
(क) घटोत्कचः कया आज्ञप्तः? (घटोत्कच ने किससे आज्ञा ली?)
उत्तर:
जनन्या (माता से)
(ख) किमहमब्राह्मणः इति कः उक्तवान्? (‘क्या मैं ब्राह्मण नहीं यह किसने कहा?)
उत्तर:
वृद्धः (बूढ़े व्यक्ति ने)
(ग) पुरुषादः कः आसीत्? (मनुष्य को खाने वाला कौन था?)
उत्तर:
घटोत्कचः (घटोत्कच)।
(घ) कुलं का रक्षितुमिच्छति? (कुल को कौन बचाना चाहती है?)
उत्तर;
ब्राह्मणी (ब्राह्मण की पत्नी)
(ङ) ज्येष्ठः पितृसमः इति कैः उक्तम्? (बड़ा भाई पिता के समान है-यह किसने कहा?)
उत्तर:
ब्रह्मवादिभिः (ब्रह्मज्ञों द्वारा)
You can download MP Board 10th sanskrit solution to help you to revise complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Mp Board Class 10 Sanskrit Chapter 5 प्रश्न 2.
एकवाक्येन उत्तरं लिखत- (एक वाक्य में उत्तर लिखिए-)
(क) ब्राह्मणपरिवारः केन समासादितः? (ब्राह्मण परिवार किसके द्वारा पकड़ा गया?)
उत्तर:
ब्राह्मणपरिवारः घटोत्कचेन समासादितः। (ब्राह्मण परिवार घटोत्कच के द्वारा पकड़ा गया।)
(ख) सुतापेक्षी कः आसीत्? (पुत्र की अपेक्षा वाला कौन था?)
उत्तर:
सुतापेक्षी वृद्धः आसीत्। (पुत्र की अपेक्षा वाला बूढ़ा व्यक्ति था।)
(ग) पितॄणां सुसम्प्रियः कः भवति? (पिता को सबसे प्यारा कौन होता है?)
उत्तर:
पितृणां सुसम्प्रियः ज्येष्ठः श्रेष्ठः भवति।। (पिता को सबसे प्यारा बड़ा तथा श्रेष्ठ बेटा होता है।)
(घ) घटोत्कचः कति पुत्रान् विसर्जयितुं कथयति? (घटोत्कच कितने पुत्रों को छोड़ने के लिए कहता है?)
उत्तर:
घटोत्कचः एकं पुत्रं विसर्जयितुं कथयति। (घटोत्कच एक पुत्र को छोड़ने के लिए कहता है।)
(ङ) घटोत्कचः अन्ते किं कथयति? (घटोत्कच अन्त में क्या कहता है?)
उत्तर:
घटोत्कचः अन्ते कथयति-‘अहो स्वजनवात्सल्यम्। (घटोत्कच ने अन्त में कहा-‘वाह, अपने लोगों के प्रति कितना स्नेह ।’)
Chapter 5 Sanskrit Class 10 Mp Board प्रश्न 3.
अधोलिखितप्रश्नानाम् उत्तराणि लिखत-(नीचे लिखे प्रश्नों के उत्तर लिखिए)
(क) ब्राह्मणी वृद्धं किं कथयति? (ब्राह्मणी वृद्ध से क्या कहती है?)
उत्तर:
ब्राह्मणी वृद्धं कथयति-“पतिमात्रधर्मिणी पतिव्रतेति नाम गृहीतफलेनैतेन शरीरेणार्यं कलं च रक्षितमिच्छामि।”
(ब्राह्मणी ने बूढ़े व्यक्ति को कहा-पति के धर्म का पालन करने वाली मैं पतिव्रता हूँ। गृहीत फल वाले इस शरीर से आर्य, स्वामी तथा कुल की रक्षा करना चाहती हूँ।)
(ख) द्वितीयः पुत्र स्वभ्रातरं किं कथयति? (दूसरे पुत्र ने अपने भाई से क्या कहा?)
उत्तर:
द्वितीयः पुत्रः स्वभ्रातरं कथयति-“कुले, लोके पितृणां च ज्येष्ठः श्रेष्ठः सुसंप्रियः ततः गुरुवृत्तिम् अनुस्मरन् अहमेव यास्यामि।”
(दूसरे पुत्र ने अपने भाई से कहा-इस संसार में, कुल में पिता का ज्येष्ठ पुत्र से अधिक स्नेह होता है। अतः पूर्वजों के आदर्श को निभाते हुए मैं ही जाऊँगा।)
(ग) तृतीयः पुत्रः स्वभ्रातरौ किं कथयति? (तीसरे पुत्र ने अपने भाइयों को क्या कहा?)
उत्तर:
तृतीयः पुत्रः स्वभ्रातरौ कथयति-“ब्रह्मवादिभिः ज्येष्ठो भ्राता पितृसमः कथितः ततः गुरुणां प्राणरक्षणं कर्तुम् अहम् अर्हः अस्मि।
(तीसरे पुत्र ने दोनों भाइयों से कहा- “ब्राह्मणों द्वारा बड़ा भाई पिता समान कहा गया है, तो बड़ों के प्राणों की रक्षा करने के लिए मैं योग्य हूँ।”)
Class 10 Sanskrit Chapter 5 MP Board प्रश्न 4.
प्रदत्तशब्दैः रिक्तस्थानानि पूयरत-(दिए गए शब्दों से रिक्त स्थान भरिए-)
(परिणामेन, पतिव्रतेति, बलाबलं, श्रेष्ठः, पितृसमः)
(क) पतिमात्रधर्मिणी………….नाम।
(ख) ज्येष्ठः ……………कुले लोके।
(ग) कृतकृत्यं शरीरं मे…………….जर्जरम्।
(घ) ज्येष्ठो भ्राता………!
(ङ) ……….परिज्ञाय पुत्रमेकं विसर्जय।
उत्तर:
(क) पतिव्रतेति
(ख) श्रेष्ठः
(ग) परिणामेन
(घ) पितृसमः
(ङ) बलाबलं
Class 10th Sanskrit Chapter 5 MP Board प्रश्न 5.
यथायोग्यं योजयत-(उचित क्रम से जोडिए-)

उत्तर:
(क) 4
(ख) 3
(ग) 1
(घ) 5
(ङ) 2
Sanskrit Class 10 Chapter 5 Mp Board प्रश्न 6.
शुद्धवाक्यानां समक्षम् ‘आम्’ अशुद्धवाक्यानां समक्षं ‘न’ इति लिखत–
(शुद्ध वाक्यों के सामने ‘आम्’ और अशुद्ध वाक्यों के सामने ‘न’ लिखिए-)
(क) घटीत्कचः जनन्या आज्ञप्तः।।
(ख) किमहमब्राह्मणः इति प्रथमः पुत्रः कथयति।
(ग) कुले लोके च अनुजः श्रेष्ठः भवति।
(घ) ज्येष्ठो भ्राता पितृसमः इति ब्रह्मवादिभिः कथितः।
(ङ) ब्राह्मणी पतिमात्रधर्मिणी आसीत्।
उत्तर:
(क) आम्
(ख) न
(ग) न
(घ) आम्
(ङ) आम्।
Sanskrit Chapter 5 Class 10 Mp Board प्रश्न 7.
अधोलिखित शब्दानां मूलशब्दं विभक्तिं वचनं च लिखत-
(नीचे लिखे शब्दों के मूलशब्द, विभक्ति व वचन लिखिए-)

(क) गुरुणाम्
(ख) तया
(ग) पल्या
(घ) भवन्तम्
(ङ) पितृणाम्
उत्तर:

Class 10 Sanskrit Chapter 5 Question Answer प्रश्न 8.
निम्नलिखितक्रियापदानां धातुं लकारं पुरुषं वचनं च लिखत
(नीचे लिखे क्रियापदों के धातु, लकार, पुरुष और वचन लिखिए।)

उत्तर:

Chapter 5 Sanskrit Class 10 प्रश्न 9.
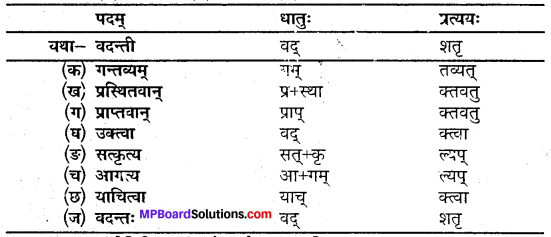
उदाहरणानुसारं धातुं प्रत्ययं च पृथक् कुरुत
(उदाहरण के अनुसार धातु और प्रत्यय अलग कीजिए-)

उत्तर:

Sanskrit Class 10th Chapter 5 प्रश्न 10.
अधोलिखितसमासानां विग्रहं कृत्वा समासनाम लिखत
(नीचे लिखे समासों के विग्रह कर समास का नाम लिखिए।)
उत्तर:

योग्यताविस्तार –
संस्कृतभाषायां रूपकाणां दश भेदाः भवन्ति। ते च, नाटकम्, प्रकरणम्, भाणः, प्रहसनम्, डिमः, व्यायोगः, समवकारः, वीथी, अङ्कः, ईहामृगः। संस्कृत भाषा में रूपक के दस भेद होते हैं। वे हैं-नाटक, प्रकरण, भाण, प्रहसन, डिम, व्यायोगह, समवकार, वीथी, अङ्क, ईहामृग।
नाट्यांशस्य सामूहिकम् अभिनयं कुरुत। (नाट्यांश का सामूहिक अभिनय कीजिए।)
कुटुम्बानुरक्तिः पाठ का सार
प्रस्तुत पाठ महाकवि भास द्वारा रचित ‘मध्ययव्यायोगः’ नामक ग्रन्थ का एक अंश है। इस पाठ में घटोत्कच जब बलि के लिए एक ब्राह्मण परिवार को पकड़ता है, तब उस परिवार के सभी सदस्य अपने परिवार वालों के अन्य सदस्यों को छुड़ाने के लिए अपने प्राण देने के लिए आगे बढ़ते हैं। इस प्रकार अपने परिवार के प्रति समर्पण व प्रेम भाव इस पाठ में दर्शाया गया है।
कुटुम्बानुरक्तिः पाठ का अनुवाद
1. वृद्धः-हन्त निराशाः स्मः। भवतु पुत्र व्यपाश्रयिष्ये तावदेनम्।
प्रथमः (पुत्रः)-अलमलं परिश्रमेण।
वृद्धः-पुत्र! निर्वेदप्रत्यर्थिनी खलु प्रार्थना। भवतु पश्यामस्तावत्। भो भोः पुरुष! अस्त्वस्माकं मोक्षः?
घटोत्कचः-मोक्षोऽस्ति समयतः।
वृद्धः-कः समयः।
घटोत्कच :
अस्ति मे तत्रभवती जननी। तयाऽहमाज्ञप्तः। पुत्र! ममोपवासनिसर्गार्थमस्मिन्वनप्रदेशे कश्चिन्मानुषः प्रतिगृह्यानेतव्य इति। ततो मयाऽऽसादितो भवान्।।
शब्दार्था :
व्यपाश्रयिष्ये-निवेदन करते हैं-appeal, submit; निर्वेदप्रत्यर्थिनी-मुक्ति की याचना-appeal for freedom, मोक्षः-मुक्ति-freedom, समयतः-शर्त पर/से–on one condition, निसर्गार्थम्-पूर्ति के लिए-for the perfection, प्रतिगृह्यानेतव्य-पकड़कर लाओ-catch and bring, आसादितः-पकड़ा है-have caught.
अनुवाद :
वृद्ध पुरुष-हाय! हम निराश हो गये हैं। अच्छा पुत्र, तब निवेदन करते हैं। प्रथम पुरुष-अधिक परिश्रम मत करो।
वृद्ध-पुत्र, मुक्ति के लिए प्रार्थना करनी पड़ेगी। ठीक है, तब देखते हैं। हे पुरुष! हमें छोड़ दो।
घटोत्कच-एक शर्त पर छोड़ सकता हूँ।
वृद्ध-कैसी शर्त?
घटोत्कच :
मेरी आदरणीय माता है। उनके द्वारा मुझे आज्ञा दी गई है। पुत्र! मेरे उपवास की पूर्ति के लिए इस वन प्रदेश से कोई मनुष्य पकड़कर लाओ। इसलिए मेरे द्वारा आपको पकड़ा गया है।
English :
The old man asked Ghatotkach to leave him and his sons. Ghatotk. ch told them that he has been ordered by his mother to bring some man for perfection of her fast.
2. घटोत्कचः- पत्न्या चारित्रशालिन्या द्विपुत्रो मोक्षमिच्छसि।
बलाबलं परिज्ञाय पुत्रमेकं विसर्जय।।1॥
अन्वय :
(हे वृद्धः!) चारित्रशालिन्या पत्न्या (सह) द्विपुत्रः मोक्षम् इच्छसि (तर्हि) बलावलं परिज्ञाय एकं पुत्रं विसर्जय।
शब्दार्था :
बलाबलम्-प्रिय और अप्रिय-dear or not dear, परिज्ञाय-जानकरconsidering
अनुवाद :
हे वृद्ध ! चरित्रशाली पत्नी के साथ दो पुत्रों की मुक्ति चाहते हो, तो प्रिय और अप्रिय जानकर एक पुत्र को छोड़ दो।
English :
Consider the merits and demerits-leave one of the sons.
3. वृद्धः-हे भो राक्षसापसद! किमहमब्राह्मणः।
ब्राह्मणः श्रुतवान्वृद्धः पुत्रं शीलगुणान्वितम्।
पुरुषादस्य दत्त्वाहं कथं निवृत्तिमाप्नुयाम्॥2॥
अन्वय :
(अहम्) वृद्धः ब्राह्मणः श्रुतवान् शीलगुणान्वितं पुत्रं पुरुषादस्य दत्वा क्थं निर्वृत्तिम् आप्नुयाम्।
शब्दार्था :
राक्षसापसद-नीच राक्षस-Mean demon; श्रुतवान्-शास्त्रज्ञ-having knowledge of scriptures, पुरुषादस्य-मनुष्य को खाने के लिए-to be eaten by man, निर्वृत्तिम्-शान्ति को-peace.
अनुवाद :
(वृद्धः-अरे, नीच राक्षस! क्या मैं ब्राह्मण नहीं हूँ (अर्थात् नीच हूँ।) मैं बूढ़ा ब्राह्मण अपने शास्त्रज्ञ, शील व गुणों से युक्त पुत्र को मनुष्य को खाने के लिए देकर कैसे शान्ति प्राप्त करूँगा।
English :
I am not so mean. How can I seek peace by leaving my learned and virtuous son to be eaten.
4. घटोत्कच :
यद्यर्थितो द्विजश्रेष्ठ! पुत्रमेकं न मुञ्चसि।
सकुटुम्बः क्षणेनैव विनाशमुपयास्यसि॥3॥
अन्वय :
द्विजश्रेष्ठः ! यदि अर्थितः एकं पुत्रं न मुञ्चसि (तर्हि) सकुटुम्बः क्षणेनैव विनाशम् उपयास्यसि।
शब्दार्था :
अर्थितः-धन के लिए/प्रार्थना किए जाने पर-for money, on our words, मुञ्चसि-छोड़ते हो-leave, उपयास्यसि-प्राप्त हो जाओगे-will attain.
अनुवाद :
घटोत्कच कहता है-हे ब्राह्मण श्रेष्ठ! यदि धन के कारण (हमारे कहने से) एक पुत्र को नहीं छोड़ते हो, तो कुटुम्ब सहित क्षण भर में ही विनाश को प्राप्त हो जाओगे।
English :
If you fail to leave one of the sons, you will soon be destroyed along with your family.
5. वृद्धः-एष एव मे निश्चयः
कृतकृत्यं शरीरं मे परिणामेन जर्जरम्।
राक्षसाम्नौ सुतापेक्षी होष्यामि विधिसंस्कृतम्॥4॥
अन्वय :
सुतापेक्षी (अहम्) परिणामेन जर्जरं विधिसंस्कृतं कृतकृत्यं मे वृद्धस्य शरीरं राक्षसाम्नौ होष्यामि।
शब्दार्था :
सुतापेक्षी-पुत्र की अपेक्षा वाला- expectation of boy, विधिसंस्कृतम्अनुष्ठानों द्वारा पवित्र-purified by observance of sacraments, कृतकृत्यम्-जिसके द्वारा समस्त कार्य पूर्ण कर लिए गए हों-who has finished all the activities.
अनुवाद :
वृद्धः-यह ही मेरा निश्चय है। पुत्र की अपेक्षा वाले, वृद्धावस्था के कारण थके हुए, अनुष्ठानों के कारण पवित्र, सभी कार्यों को पूर्ण करने वाले अपने बूढ़े शरीर की मैं राक्षस की अग्नि में आहुति दे दूंगा।
English :
The old man said, “My old and exhausted body will be burnt in the fire of the demon” for the sake of my son.
6. ब्राह्मणी-आर्य, वा मैवम्। पतिमात्रधर्मिणी पतिव्रतेति नाम। गृहीतफलेनैतेन शरीरेणार्यं कुलं च रक्षितुमिच्छामि।
घटोत्कचः-भवति! न खलु स्त्रीजनोऽभिमतस्तत्रभवत्या।
वृद्धः-अनुगमिष्यामि भवन्तम्।
घटोत्कचः-आः वृद्धस्त्वमपसर।
प्रथमः (पुत्र)-भोस्तात-ब्रवीमि खलु तावत्किञ्चित्।
वृद्धः-ब्रूहि, ब्रूहि शीघ्रम्।
शब्दार्थाः-अपसर-दूर हटो-keepaside, ब्रूहि-कहो-say, अभिमतः-उचित-proper.
अनुवाद :
ब्राह्मणी-ऐसा मत कहो।मैं केवल पति के धर्म का पालन करने वाली पतिव्रता हूँ। इस फल प्राप्त किए हुए शरीर के द्वारा आर्य और कुल की रक्षा करना चाहती हूँ।
घटोत्कच-देवी! उनके आदेश के अनुसार स्त्री नहीं चाहिए।
वृद्ध-तुम्हारे साथ मैं चलूँगा।
घटोत्कच-तुम वृद्ध हो, तुम दूर हटो।
प्रथम (पुत्र)-हे पिता! तो मैं कुछ कहूँ।
वृद्ध-कहो, शीघ्र कहो।
English :
The Brahmin woman and the old man offered themselves to save the family. Ghatotkach asked them to keep aside. The first son desired to say something.
7. प्रथमः (पुत्र)- मम प्राणैर्गुरुप्राणानिच्छामि परिरक्षितम्।
रक्षणार्थ कुलस्यास्य मोक्तुमर्हति मां भवान॥5॥
अन्वय :
(अहं प्रथमः पुत्रः) मम प्राणैः गुरुप्राणान् परिरक्षितुम इच्छामि (अतः) भवान् अस्य कुलस्य रक्षणार्थं मां मोक्तुम अर्हति।
शब्दार्था :
परिरक्षितुम्-रक्षा करने के लिए-toprotect, गुरु-(पूर्वजों) बड़ों के-of the elderly people.
अनुवाद :
(मैं, पहला पुत्र) अपने प्राणों के द्वारा बड़ों के प्राणों की रक्षा करना चाहता हूँ। इसलिए आप इस कुल की रक्षा के लिए मुझे छोड़ दीजिए।
English :
The first son desired that he should be left to protect the lives of the elderly people in the family.
8. द्वितीयः (पुत्रः) आर्य! मा मैवम् ।
ज्येष्ठः श्रेष्ठ कुले लोके पितृणां च सुसंप्रियः।
ततोऽहमेव यास्यामि गुरुवृत्तिमनुस्मरन॥6॥
अन्वय :
(भो जनक!) कुले, लोके पितॄणां च ज्येष्ठः श्रेष्ठः सुसंप्रियः (भवति) ततः गुरुवृत्तिम् अनुस्मरन् अहमेव यास्यामि।।
शब्दार्था :
सुसंप्रियः-अच्छा व प्यारा-mostloving,गुरुवृत्तिम्-पूर्वजों के आदर्श को-the ideals of the ancestors, अनुस्मरन्-चलाते हुए, याद करते हुए-following, recalling, यास्यामि-जाऊँगा-shall go.
अनुवाद :
दूसरा (पुत्र)-आर्य! ऐसा मत कहो।
हे पिता! इस संसार में, कुल में सबसे बड़ा व श्रेष्ठ ही माता-पिता को अच्छा व प्यारा लगता है। तब पूर्वजों के आदर्श का अनुकरण करते हुए मैं ही जाऊँगा।
English :
Second son : Being the elder, the better and the more loving son, I would go in accordance with the ancestral practice.
9. तृतीयः (पुत्रः)-आर्य! मा मैवम्।
ज्येष्ठो भ्राता पितृसमः कथितो ब्रह्मवादिभिः।
ततोऽहं कर्तुमस्म्य) गुरुणां प्राणरक्षणम्॥7॥
घटोत्कचः-अहो स्वजनवात्सल्यम्।
(इति निष्क्रान्ताः सर्वे)
अन्वयः-ज्येष्ठः भ्राता ब्रह्मवादिभिः पितृसमः कथितः ततः गुरुणां प्राणरक्षणं कर्तुम् अहम् अर्हः अस्मि।
शब्दार्था :
पितृसमः-पिता के समान-like a father, ब्रह्मवादिभिः-ब्रह्मज्ञों ने-by the brahmins, अर्हः-योग्य-capable, वात्सल्यम्-प्रेम-affection.
अनुवाद :
तृतीय (पुत्र) – आर्य! ऐता मत कहो।
ब्रह्मज्ञों के अनुसार बड़े भाई को पिता के समान कहा गया है। तो बड़ों की प्राणरक्षा करने के लिए मैं योग्य हूँ।
घटोत्कच-वाह! अपने लोगों के लिए कितना स्नेह।
(सब निकल जाते हैं)
English :
Eldest son is like a father-Hence Iam capable of saving my elderly people-filial affection praised (appreciated)